
Indonesia Vegetable Oil Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Oil Type, Application, and Region, 2025-2033
Indonesia Vegetable Oil Market Overview:
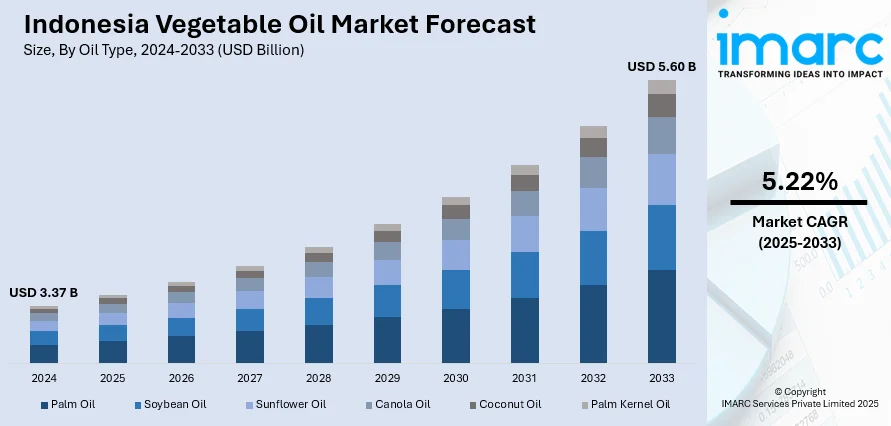
The Indonesia vegetable oil market size reached USD 3.37 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, the market is projected to reach USD 5.60 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 5.22% during 2025-2033. The market is driven by palm oil’s centrality to local cooking, packaged food manufacturing, and household affordability across income levels. Government policies encouraging refining, price controls, and fortified oil promotion are reshaping the sector’s domestic structure. Growing demand in biodiesel, cosmetics, and oleochemicals is further augmenting the Indonesia vegetable oil market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 3.37 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 5.60 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 5.22% |
Indonesia Vegetable Oil Market Trends:
Palm Oil Dominance in Domestic Consumption and Food Industry
Indonesia is the world’s largest producer of palm oil, which is deeply embedded in the nation’s food system. The oil is used extensively in household cooking, street food, packaged snacks, instant noodles, and traditional confectionery. Local demand is supported by the affordability, high smoke point, and versatility of palm oil across cuisines and food processing. Indonesia’s low-income and middle-income households rely on bulk palm oil, often subsidized or price-controlled, as a staple kitchen item. According to latest industry reports, Indonesia's weekly per capita vegetable oil consumption reached approximately 228 milliliters for frying oil, while coconut oil intake remained much lower at just 7 milliliters. The government periodically intervenes to ensure affordability through domestic market obligation (DMO) mandates, especially when global prices rise. At the same time, fast-growing food processing companies depend on refined palm oil for consistency and stability in large-scale frying and baking operations. The expansion of modern retail, convenience stores, and hypermarkets has introduced branded and fortified oil options to urban consumers, diversifying product offerings. In rural areas, unbranded and bulk palm oil continues to dominate traditional markets. As household spending on food increases and packaged products penetrate deeper into the consumer landscape, palm oil remains a vital ingredient. This wide spectrum of utilization underpins Indonesia vegetable oil market growth across socioeconomic and regional lines.
To get more information of this market, Request Sample
Government Mandates and Regulatory Support for Value Addition
Indonesia’s vegetable oil sector is shaped heavily by government regulations intended to promote domestic processing, stabilize prices, and support national food security. Policies such as the palm oil export levy and the mandatory biodiesel blending (B35) program are designed to redirect a portion of raw oil production into local value chains. Through the Ministry of Trade and Ministry of Industry, the government requires producers to allocate a percentage of crude palm oil (CPO) output for local food and biodiesel markets before export permits are granted. These measures incentivize local refining and bottling, creating jobs and encouraging downstream investment. Indonesia produces 3.74 tons of palm oil per hectare annually, far surpassing rapeseed (0.67), sunflower (0.48), and soybean (0.38), while using just 47 kg of fertilizer and 2 kg of pesticides per hectare. Certified under ISPO, ISCC, and RSPO, Indonesian palm oil ensures both high agricultural efficiency and globally recognized sustainability standards. The imposition of traceability, halal certification, and sustainability standards reinforces quality assurance, particularly for branded oils sold in supermarkets. Public campaigns promoting fortified cooking oil and healthy frying practices aim to improve consumer outcomes while driving sales of higher-margin products. These regulatory mechanisms not only protect domestic supply but also foster the evolution of a more structured and diversified oil market. Strategic policy interventions thus serve as an underlying enabler of modernization and vertical integration within the vegetable oil industry.
Indonesia Vegetable Oil Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on oil type and application.
Oil Type Insights:
- Palm Oil
- Soybean Oil
- Sunflower Oil
- Canola Oil
- Coconut Oil
- Palm Kernel Oil
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the oil type. This includes palm oil, soybean oil, sunflower oil, canola oil, coconut oil, and palm kernel oil.
Application Insights:
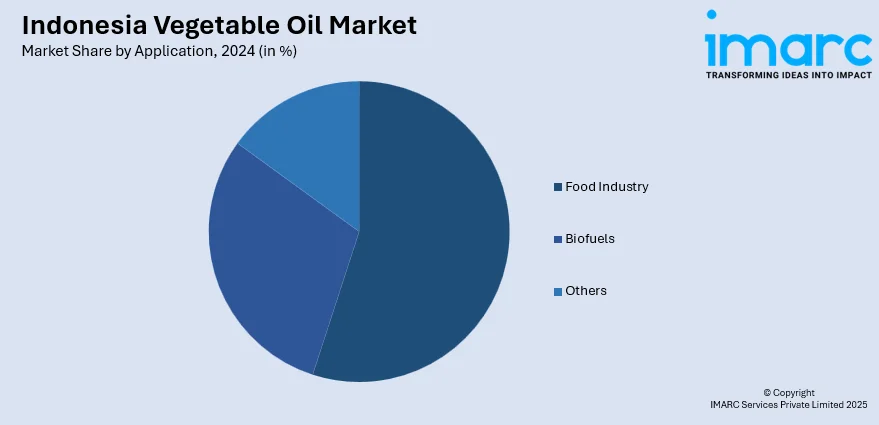
- Food Industry
- Biofuels
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the application. This includes food industry, biofuels, and others.
Regional Insights:
- Java
- Sumatra
- Kalimantan
- Sulawesi
- Others
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all major regional markets. This includes Java, Sumatra, Kalimantan, Sulawesi, and others.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Indonesia Vegetable Oil Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Oil Types Covered | Palm Oil, Soybean Oil, Sunflower Oil, Canola Oil, Coconut Oil, Palm Kernel Oil |
| Applications Covered | Food Industry, Biofuels, Others |
| Regions Covered | Java, Sumatra, Kalimantan, Sulawesi, Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the Indonesia vegetable oil market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What is the breakup of the Indonesia vegetable oil market on the basis of oil type?
- What is the breakup of the Indonesia vegetable oil market on the basis of application?
- What is the breakup of the Indonesia vegetable oil market on the basis of region?
- What are the various stages in the value chain of the Indonesia vegetable oil market?
- What are the key driving factors and challenges in the Indonesia vegetable oil market?
- What is the structure of the Indonesia vegetable oil market and who are the key players?
- What is the degree of competition in the Indonesia vegetable oil market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Indonesia vegetable oil market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Indonesia vegetable oil market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Indonesia vegetable oil industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












