Bamboo Cost Model: Immense Economic Prospects

What is Bamboo?
Bamboo is a poaceous grass which regrows rapidly, has a high yield of biomass and good material properties, ranging from tiny clumping species to huge timber-grade culms over 20 meters tall; genera of economic importance are Bambusa, Phyllostachys and Dendrocalamus. Botanically, bamboo integrates the regenerative benefit of an agricultural crop (short rotation, annual or multi-annual yield) with certain mechanical characteristics of softwoods like large specific strength, good tensile performance, and natural hollow culm geometry for light-weight structural property.
Key Applications Across Industries:
These properties form the basis for its wide range of end-uses: construction (scaffolding, flooring, engineered bamboo panels), furniture, handicrafts, pulp and paper, textile feedstock (bamboo viscose/lyocell), activated carbon, charcoal, bioenergy pellets, and increasing use in composite materials and bioplastics. Processing routes differ by end-use: culms are split, treated and laminated into engineered boards; residues are pulped for fibers; and sawdust is pelletized or carbonized. Principal production areas are Asia (China, India, Indonesia, Vietnam), with growing interest in Africa and Latin America where appropriate species are being cultivated. Sustainability credentials quick carbon sequestration, soil stabilization and potential to substitute slow-growing hardwood make bamboo an appealing item in circular-economy planning. Quality results, however, are highly dependent on the choice of species, appropriate treatment against rot and insects, and scalable processing infrastructure; untreated bamboo is susceptible to biodegradation and dimensional instability. For consumers and developers, bamboo offers an attractive combination of renewability, performance and rural value-chain potential, if quality control and certification are integrated into sourcing and processing.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global bamboo market reached a value of USD 68.04 Billion in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 107.37 Billion by 2033, at a projected CAGR of 4.80% during 2025-2033. The international bamboo market is driven by converging sustainability, economic and technological forces. To begin, climate and environmental policy momentum net-zero ambitions, reforestation incentives and circular-economy directives discriminate in favor of fast-renewable feedstocks; bamboo's high sequestration rates and capacity to rehabilitate degraded land are powerful policy sell-points. Second, construction and engineered-materials demand are growing as developers and architects look for low-carbon substitutes for concrete and timber; engineered bamboo materials (glulam, laminated bamboo) compete with traditional lumber in mid-rise buildings and interior use with growing frequency.
Third, the textile and fiber market grow by virtue of consumer demand for sustainable fabrics and advances in closed-loop viscose/lyocell, fueling demand for pulpified bamboo feedstock. Fourth, applications of bioenergy and biochar including pellets, briquettes, activated carbon are scaling with plantation wood residues and bamboo residues delivering competitive feedstock economics. Fifth, rural development and income diversification schemes in producer countries (India, China, Southeast Asia, Africa) encourage bamboo plantations and processing clusters with government grants, clustering policies and public–private partnerships. Technology drivers such as advanced treatment technologies, low-capex mechanical processing, and modular pellet/pulp plants lead to lower capex and expand feasible project sizes. Trade and certification patterns (FSC-type claims, sustainability certifications) are also significant: European and Japanese importers increasingly demand chain-of-custody and lifecycle information, building premium channels for certified supply. Limitations like competition for land use, poor management of species and variable processing standards constrain growth, but overall, the intersection of decarbonization targets, material innovation and rural-economic drivers suggests steady world expansion of the bamboo market.
Case Study on Cost Model of Bamboo Processing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale bamboo processing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed bamboo pellets processing plant in China. This plant is designed to process 20,000 tons of bamboo pellets annually.
Processing Flow: The processing of bamboo pellets is a series of mechanical and thermal treatments that transform raw bamboo biomass into dense, energy-rich fuel pellets. The procedure starts with raw material gathering and preparation in which the bamboo culms, sawdust, or residues from processing are collected and chopped into pieces. The bamboo material is crushed or chipped using a hammer mill or crusher to produce fine-sized and uniform particles suitable for pelletizing. After this, the ground bamboo particles are dried to minimize their water content to approximately 8–12%, which is important in ensuring proper pellet formation and combustion efficiency. Industrial flash dryers or rotary drum dryers are generally employed to meet the required moisture content. Then, the dried process bamboo powder is charged to a pellet mill, where it undergoes high-pressure and temperature (about 200–300°C) compression through die holes to create cylindrical pellets, which are typically 6–10 mm in diameter and 20–30 mm in length. At this stage of compression, the inherent lignin within the bamboo softens and becomes a binding agent, so no extraneous adhesives are required, and the pellets achieve their smooth surface and mechanical strength. After forming, the hot pellets are then cooled with air-cooling systems to harden and stabilize them. The last step is screening and packaging, where undersize or broken pellets are separated, and product is bagged for transport and storage. This creates high-density, low-moisture bamboo pellets with greater combustion efficiency and suitable for applications in residential space heating systems, industrial boilers, and renewable power generation plants.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
Raw Material Required:
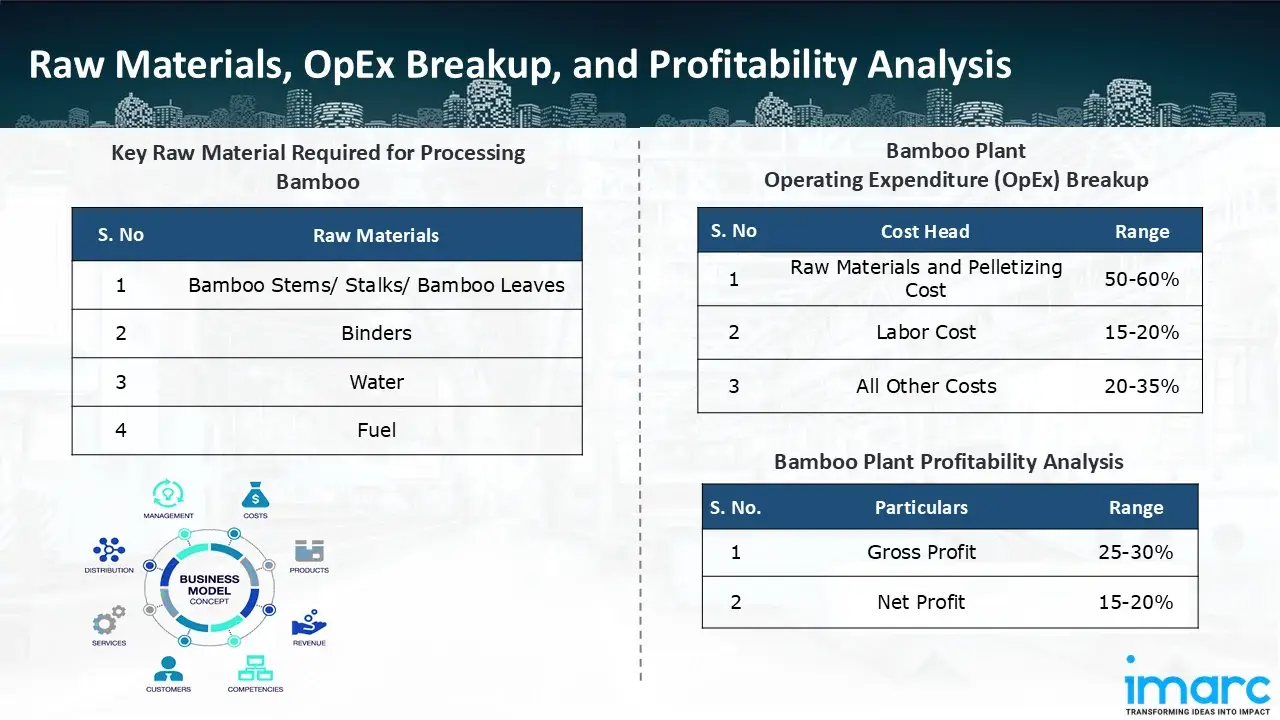
The basic raw materials required for bamboo processing include:
- Bamboo Stems/ Stalks/ Bamboo Leaves
- Binders
- Water
- Fuel
Machineries Required:
- Bamboo Chipper / Shredder
- Hammer Mill / Pulverizer
- Rotary Dryer
- Belt Dryer
- Ring Die Pellet Mill
- Counterflow Cooler
- Vibrating or Rotary Sieve
- Automatic Bagging Machine
- Bulk Storage Silos
- Dust Control Unit
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a processing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a processing plant effectively. Opex in a processing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a processing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material and pelletizing cost in a bamboo processing plant ranges between 50-60%, labor cost ranges between 15% to 20%, and all other costs ranges between 20-35% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 25-30%, and net profit lie between the range of 15-20% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the bamboo processing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, processing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of manufacturing 20,000 tons of bamboo pellets annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale processing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In August 2025, Japan made an announcement to provide up to 60 billion yen (about US$ 408 million) in public and private sector investment for an Indian biofuel project that will turn bamboo biomass into vehicle fuel.
- In May 2025, key bamboo processing facilities built at the Sairang Horticulture Centre under the National Bamboo Mission with financing of Rs. 252.826 lakh were officially opened by the Chief Minister of Mizoram. The facilities consist of an Activated Charcoal Unit (used to produce charcoal), a Bamboo Depot & Godown, and a Bamboo Treatment & Seasoning Plant.
- In January 2025, NTPC signs a contract to purchase bamboo biomass from Maharashtra farmers. A sustained supply will be ensured by the signing of initial 50-year agreements with Farmer Producer Companies (FPCs).
Why Choose IMARC?
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104