Biochar Industry Growth: Pioneering a Greener Approach to Agriculture

Introduction:
Sustainability is reshaping the future of agriculture, energy, and environmental management, with biochar emerging as a transformative force within the ecosystem. Produced from biomass through pyrolysis, biochar enriches soils, strengthens crop resilience, and reduces dependence on chemical fertilizers. According to reports, long-term application delivers measurable benefits—boosting average crop yields by 10.8% and increasing soil organic carbon by 52.5%—underscoring its role in restoring soil health while combating degradation.
Biochar transforms agricultural and forestry residues into valuable resources, cutting emissions and supporting circular economies. Innovations like mobile units and precision pyrolysis boost efficiency, while applications span farming, remediation, livestock, and construction. Viewed as both climate solution and economic opportunity, biochar embodies a systemic shift toward soil restoration and sustainable growth.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
Influence of Biochar on Soil Health and Agricultural Productivity:
Biochar, rich in stable carbon, acts as a soil regeneration catalyst, enhancing porosity, water retention, and nutrient levels. It curbs nutrient loss, reduces fertilizer use, and fosters biodiversity, strengthening crop resistance to pests and climate stress. In drought-prone regions, its water-holding capacity ensures reliable yields. Moreover, biochar’s integration into precision farming is proving transformative. Farmers are blending biochar with compost, manures, and even synthetic fertilizers to boost efficiency while lowering environmental footprints. Studies reveal that crop yields in biochar-amended soils can rise by 10–30%, depending on soil type and application practices. This evidence positions biochar not just as a soil amendment, but as a long-term investment in food security.
Role of Biochar in Carbon Sequestration and Climate Change Mitigation:
While biochar enhances soil fertility, its climate benefits are equally significant. Through pyrolysis, it locks biomass carbon into a stable form for centuries, converting agricultural residues and forestry waste into long-term carbon sinks. This dual role—enriching soils and sequestering carbon—makes biochar vital for nations pursuing net-zero goals. Each ton applied offsets multiple tons of CO2 equivalent, strengthening climate action. With the growth of carbon credit markets, biochar offers both environmental solutions and economic incentives, positioning it at the nexus of sustainable farming and climate finance.
Key Industry Trends:
Increasing Adoption in Agriculture and Forestry
The agriculture sector remains biochar’s strongest foundation, with farmers, cooperatives, and agribusinesses embracing it as a soil enhancer and productivity booster. Its role extends to forestry, where biochar restores degraded lands and improves seedling survival, reinforcing ecosystem resilience. Large-scale plantations in Asia, Latin America, and Africa are increasingly incorporating biochar into agroforestry and reforestation initiatives. In India, certain fields have seen sugarcane yields rise from 60–70 to over 100 tons per acre, driven by enhanced soil organic carbon through the combined use of biochar and compost. This synergy highlights biochar’s potential to deliver both economic benefits and environmental restoration.
Growing Interest in Biochar for Waste Management
Biochar’s role in waste management is transforming urban and industrial sustainability strategies. Biomass residues from agriculture, forestry, and food processing—once difficult to dispose of—are now being converted into biochar, reducing emissions while generating valuable soil enhancers. In co-composting scenarios, studies show that adding biochar can cut methane emissions by up to 80% compared to standard composting, offering a powerful climate benefit. Municipalities are beginning to adopt biochar facilities to process organic waste streams, turning liabilities into opportunities. This shift not only prevents harmful emissions but also establishes localized circular economies where waste is reimagined as a sustainable resource.
Advancements in Biochar Production Technologies
Production process technology advancements are enhancing efficiency and scalability in biochar production. Kilns are being displaced by advanced pyrolysis facilities with temperature, feedstock, and emissions control. Some operators have adopted mobile pyrolysis facilities to produce bio-oil and syngas in addition to biochar on-site in remote areas. Others are testing hybrid designs that co-produce bio-oil and syngas with biochar, maximizing value streams. These developments are expected to reduce costs, increase adoption, and create more consistent product quality.
Development of New Applications for Biochar
Beyond agriculture, biochar is emerging as a multi-industry innovation hub with impressive versatility. In construction, it is used as a lightweight filler, creating stronger and more sustainable building materials. In water treatment, biochar demonstrates remarkable efficiency—tea waste–derived biochar removed 98% of lead, while sesame husk, rice husk, and chaff-based variants achieved 100%, 90%, and 85% removal respectively, showcasing its potential for heavy metal remediation. In animal husbandry, it supports digestion and waste management. Meanwhile, research into biochar-based electrodes promises breakthroughs in batteries and supercapacitors. These applications highlight biochar’s adaptability as both an environmental solution and an industrial catalyst.
Supportive Government Policies and Carbon Credit Markets
Governments across Europe, North America, and the Asia-Pacific recognize the strategic significance of biochar. They are introducing subsidies, research grants, and pilot projects to encourage take-up. The EU Green Deal and U.S. American climate initiatives are increasingly referring to biochar as a carbon-farming technique. Compliance-based and voluntary carbon markets are, at the same time, providing cash. Agriculturalists and companies can generate revenue through verifying carbon sequestration by means of approved biochar ventures. This policy and financial support is also expected to be a backbone of the biochar market trend over the next decade.
Market Segmentation & Regional Insights:
Biochar Industry Segmentation:
Analysis by Feedstock Type:
Woody Biomass: Dominating with a 50% market share
- Woody Biomass: Woody biomass dominates the feedstock as it is sourced from forest residues, wood chips, and sawdust, dominates biochar feedstock with high carbon, low moisture, and stability, supporting large-scale soil enrichment and carbon sequestration projects globally.
- Agricultural Waste: Agricultural waste fuels biochar growth as farmers use pyrolysis to convert residues into soil enhancers, reducing burning and boosting sustainability, though fragmented collection limits its market share versus woody biomass.
- Animal Manure: Animal manure, a nutrient-rich biochar feedstock, boosts soil fertility and recycling in livestock-intensive regions. However, odor issues and inconsistent composition restrict broader adoption versus woody biomass and crop residues.
- Others: Nontraditional feedstocks like municipal waste, aquatic biomass, and industrial byproducts support circular economy goals, but face scalability and quality issues. Though niche, ongoing research may expand their future market role.
Analysis by Technology Type:
Slow Pyrolysis: Dominating with a 56% market share
- Slow Pyrolysis: Slow pyrolysis leads the market, accounting for more than half of total share, by producing high-quality, porous biochar. Its controlled process enhances carbon retention, reduces emissions, and promotes carbon sequestration, while providing sustainable soil improvement across a wide range of feedstocks.
- Fast Pyrolysis: Fast pyrolysis is gaining traction for producing bio-oil alongside biochar, offering multiple revenue streams. Despite lower biochar yields than slow pyrolysis, its speed and scalability make it attractive for industrial applications.
- Gasification: Gasification primarily produces syngas with biochar as a byproduct. Though yields are lower, its dual role in clean energy generation and carbon capture appeals to industries prioritizing energy efficiency and sustainability.
- Hydrothermal Carbonization (HTC): Hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) processes wet biomass without drying, lowering costs for select feedstocks. It produces “hydrochar” with unique properties for energy and environmental uses. Though nascent, research highlights strong scalability potential.
- Others: Other emerging technologies, such as microwave pyrolysis and torrefaction, remain at pilot stages with limited market share but demonstrate continued innovation in the evolving biochar production landscape.
Analysis by Product Form:
Fine Powder: Dominating with a 41% market share
- Fine Powder: Fine powder biochar dominates with over 41% share, favored for its large surface area that boosts nutrient uptake and water retention. Easily blended with compost or fertilizers, it supports precision farming and nursery crops.
- Fine and Coarse Chips: Biochar chips, though less common than powders, are favored in forestry and large-scale land restoration. Their coarse texture enhances soil aeration, structural stability, and ecosystem recovery, making them valuable for land rehabilitation.
- Pellets, Granules, and Prills: Pelletized biochar is popular in commercial farming for its easy handling, storage, and machinery compatibility. Its uniform size supports fertilizer blending, though higher production costs make it pricier than powder forms.
- Liquid Suspension: Liquid suspension biochar is gaining traction in niche applications like horticulture and soil remediation, enabling precise delivery through irrigation systems. Though currently a smaller segment, it is expected to grow with liquid agriculture advancements.
Analysis by Application:
Farming: Dominating with a 42% market share
- Farming: Biochar dominates farming applications, enhancing soil fertility, nutrient retention, and water efficiency. Farmers benefit from reduced fertilizer use, lower emissions, and higher yields, addressing global agricultural challenges and positioning farming as the leading sector for biochar adoption.
- Gardening: Gardeners increasingly use biochar for backyard soil improvement. Its eco-friendly profile and ease of use in potting media, flower beds, and lawns make it accessible to households. Though smaller in scale, gardening serves as a key entry point for domestic adoption.
- Livestock Feed: Biochar is emerging as a livestock feed supplement, improving digestion and reducing methane emissions. It offers dual benefits—enhancing animal health and lowering environmental impact. While adoption is currently limited, its role in sustainable animal husbandry is steadily growing.
- Soil, Water, and Air Purification: Biochar is applied in environmental remediation due to its high surface area, which adsorbs heavy metals, organics, and odor-causing molecules. It is used in wastewater treatment, soil remediation, and air purification, representing a niche but growing market segment.
- Other Applications: Beyond agriculture, biochar finds uses in construction materials, energy storage, and carbon capture technologies. These innovative applications highlight its versatility, indicating potential diversification across sectors and expanding biochar’s role in industrial and environmental solutions.
Analysis by Region:
North America: Dominating with a 41% market share
- North America is at the forefront of the world market with a share of more than 41%. Tight research networks, government climate programs, and carbon offset policies promote extensive use. Farmers, industries, and municipalities partner with biochar manufacturers to incorporate it in sustainable farming and carbon sequestration ventures.
- Europe is a key market region, propelled by strict environmental regulations and the EU’s Green Deal. Carbon credit incentives and circular economy initiatives are encouraging widespread biochar use in agriculture and waste management. The region’s strong focus on achieving climate neutrality continues to support consistent growth in the biochar market.
- Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, fueled by extensive agricultural land and abundant biomass resources. Rising population pressures, land degradation, and government-backed sustainability programs are driving biochar adoption, especially in China, India, and Southeast Asian countries.
- While still in its infancy, the Middle East and Africa are starting to use biochar for land rehabilitation, desertification management, and food security initiatives. Local governments are experimenting with pilot programs that might grow quickly over the next ten years.
- Latin America uses biochar in agroforestry, coffee production, and reforestation programs. Rich biomass and growing sustainability agendas make it a promising area but with infrastructure and investment issues persisting.
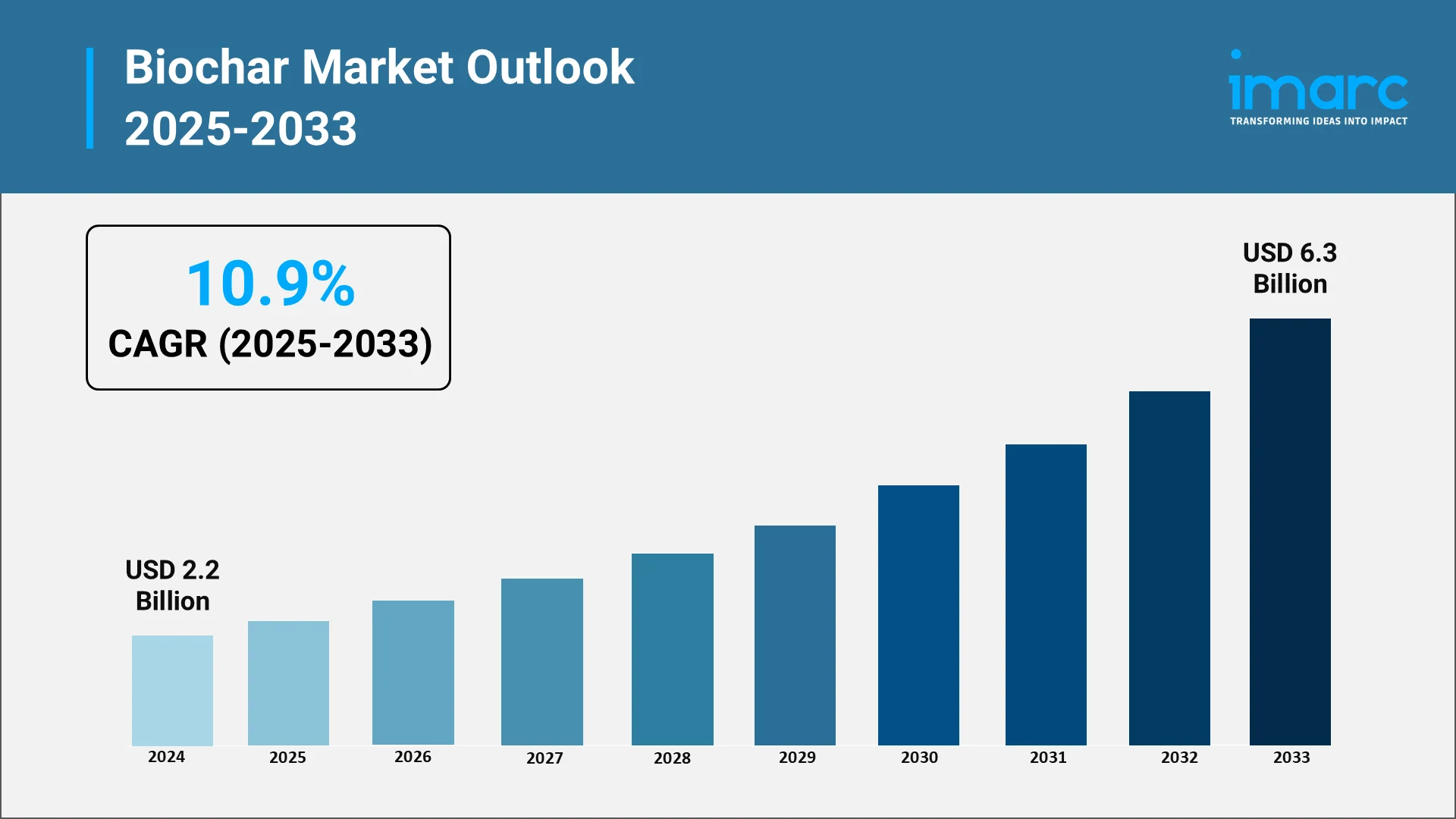
Forecast (2025-2033):
The global biochar market size in 2024 was valued at USD 2.2 Billion and is projected to reach a value of USD 6.3 Billion by 2033, driven by strong adoption in agriculture, forestry, and waste management. From 2025 to 2033, the market is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 10.9%, reaching new highs in both volume and value.
Key demand drivers include:
- Rising Demand for Sustainable Agricultural Practices: Farmers are increasingly seeking alternatives to chemical fertilizers, with biochar emerging as a cost-effective and eco-friendly solution.
- Growing Concerns Over Soil Degradation: Biochar offers a long-term soil remediation strategy, especially vital in regions affected by desertification and nutrient depletion.
- Increasing Focus on Carbon Sequestration: Corporates and governments are investing in carbon capture technologies, with biochar providing an immediate and scalable solution.
- Abundance of Biomass Feedstock: Agricultural and forestry residues provide a continuous, low-cost raw material supply for biochar production.
- Government Initiatives and Subsidies: Policy frameworks and subsidies reduce production costs, stimulate research, and create market confidence.
Conclusion:
The global biochar industry is leading the charge towards sustainable change, reconciling farm productivity and climate action. With its established capacity to improve soil quality, trap carbon, and facilitate circular economy practices, biochar is no longer a specialty solution but a mainstream choice. From biochar market trends 2025 to the distant future, demand is being driven by favorable policies, technological advancements, and diversified uses across sectors.
At this point, IMARC Group offers the skills to crack market trends, predict opportunities, and direct strategic choices. Whether you are an investor, policymaker, or farmer, our actionable intelligence helps you tap the full potential of biochar and be at the helm of the next generation of sustainable growth.
From Soil to Sustainability: IMARC’s Guide to Unlocking the Global Biochar Market
IMARC Group equips farmers, investors, and policymakers to navigate the evolving Global Biochar Market, as sustainable agriculture, climate action, and carbon credit mechanisms reshape the industry. Our expertise helps stakeholders leverage biochar for soil regeneration, carbon sequestration, and circular economy solutions, fostering innovation, environmental resilience, and long-term growth.
- Market Insights: We track emerging trends in biochar adoption across agriculture, forestry, waste management, and environmental remediation. From advances in pyrolysis technologies to applications in construction, energy storage, and water treatment, IMARC monitors innovations driving the biochar market through 2025 and beyond.
- Strategic Forecasting: Our analyses assess global biochar market size and growth opportunities across feedstocks, production technologies, and applications. Demand is projected to surge between 2025–2033, driven by sustainable farming practices, government incentives, and expanding carbon credit markets.
- Competitive Intelligence: We benchmark leading producers, startups, and research institutions pioneering biochar solutions, highlighting R&D, partnerships, and supply chain shifts.
- Policy & Regulatory Analysis: IMARC decodes global programs, subsidies, and climate policies—helping stakeholders leverage regulatory momentum in Europe, North America, and Asia-Pacific.
- Tailored Consulting: We deliver strategies to optimize feedstock use, enhance production efficiency, scale adoption, and align with climate finance and regional market opportunities.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










