Bio Medical Incinerator Cost Model: From Hazardous Waste to Safe Disposal
_11zon.webp)
What is Bio Medical Incinerator?
A bio medical incinerator is a high-temperature combustion system specialized for biomedical waste disposal by hospitals, clinics, laboratories, and research institutions. Biomedical waste usually consists of infectious waste, pathological waste, sharps, pharmaceuticals, and contaminated disposables that are very hazardous to human health and the environment if not treated.
Key Applications Across Industries:
The incineration process is designed by exposing the waste to temperatures of over 850–1200°C, providing for maximum oxidation and volume reduction up to 90%, resulting in inert ash that can be safely disposed of in landfills. The major features of biomedical incinerators are high thermal efficiency, strong refractory linings, emission control systems, and the capability of continuous operation. Applications are to be found in healthcare facilities, pharmaceutical manufacturing plants, and research centers where safe and compliant hazardous waste disposal is critical. Benefits are quick sterilization, dramatic reduction of waste volume, and elimination of pathogens, toxins, and harmful organics. Economically, biomedical incinerators lower the disease transmission risk, facilitate regulatory compliance, and minimize environmental pollution. With increasing healthcare infrastructure, tightened biomedical waste regulations, and the need for environmentally friendly waste-to-energy technology, the future prospects for biomedical incinerators are strong.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The India biomedical waste management market reached a value of USD 286.98 Million in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 486.09 Million by 2033, at a projected CAGR of 6.0% during 2025-2033.
The biomedical incinerator industry is fueled by a number of perennial drivers. The primary driver is the exponential rise in healthcare waste because of increasing hospital chains, diagnostics centers, and pharmaceutical activities. Second, strict government rules like the Biomedical Waste Management Rules (2016, amended 2018) in India and international guidelines under the WHO framework require safe disposal practices. Third, the COVID-19 crisis hastened the production of biomedical waste, especially from PPE and testing supplies, increasing the call for strong disposal mechanisms. Fourth, community concern and pressure from environmental organizations are compelling the need for advanced incinerators equipped with emission control systems. Foremost among major trends for the next five years are the incorporation of energy recovery systems, implementation of hybrid waste-to-energy plants, and automation in handling for labor protection. Competitive strengths are reliability, emission standards compliance, and scalability from small clinics to big hospitals. The risks are high operating expenses, possible environmental resistance, and stringent monitoring for dioxins and furans. Incinerators help infection control in a sustainability perspective while new technology with energy recovery offers double benefits. Industry response also involves investment in green burners, continuous emission monitoring systems (CEMS), and modular incinerators for decentralized waste treatment.
Case Study on Cost Model of Bio Medical Incinerator Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium to medium-scale bio medical waste treatment plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed Bio Medical Incinerator plant in India. This plant is designed to treat 4,000 kg of waste per day by incinerators, 5,440 kg of waste per day by autoclave.
Treatment Process: The process of treating biomedical waste consists of several stages for safety, disinfection, and environmental protection. Waste from health care facilities is first collected in color-coded, sealed, non-chlorinated bags and taken to the treatment facility, where incinerable and autoclavable waste are segregated. Incineration is applied to infectious and non-infectious burnable waste in two phases, primary combustion at less air supply and secondary combustion at higher temperatures (up to 1,095°C) to guarantee complete destruction. Flue gases are processed through an Air Pollution Control (APC) system with Venturi scrubbers, alkaline neutralization, and droplet separators for clean emissions through a 30-meter stack. Non-incinerable infectious waste is autoclaved, with steam sterilization at 121°C and 15 psi pressure killing pathogens. The waste is shredded after sterilization to make it unrecognizable and prevent it from being reused, with materials such as plastics, rubber, glass, and metal being sorted for safe recycling or disposal. Effluents produced in the course of treatment are treated in a biological effluent treatment plant (ETP), with the treated water recycled into the process or for non-potable purposes like plantation and sprinkling. This coupled system, segregation, incineration, autoclaving, shredding, and effluent treatment is used to make biomedical waste harmless, avoid disease transmission, and reduce environmental pollution.
_11zon.webp)
Machineries Required:
- Primary Chamber
- Secondary Chamber
- Hydraulic Waste Feeding System
- FD Fan
- Automatic Oil/Gas Burner For Primary Chamber
- Automatic Oil/Gas Burner For Secondary Chamber
- Automatic Emergency Stack
- Air Cooled Flue Gas Cooler With Cooling Fan
- Cyclon Separator
- Flue Gas Neutralizing System
- Dioxin Control System
- Filtration System with Pneumatic Control (Air Pollution Control Device)
- Damper For ID Fan
- ID Fan with Motor
- PLC Based Control Panel
- Chimney of 30 Meters Height
- Sampling Platform
- Ladder for Chimney
- Diesel Tank
- Shaft
- Electrical Motor
- Electrical Control Panel
- Screen Chamber
- Equalization Tank
- Oil & Grease Trap
- Dosing Tank
- Mixing Tank
- Clarifier
- Supernatant Tank
- Dual Media Filter
- Filter Feed PUMP
- Activated Carbon Filter
- Effluent Transfer Pump
- Air blower
- Piping & Valves
- Platform & Structure
- Electrical Panel and wiring+ water Flow Meter
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Investment (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a Treatment plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
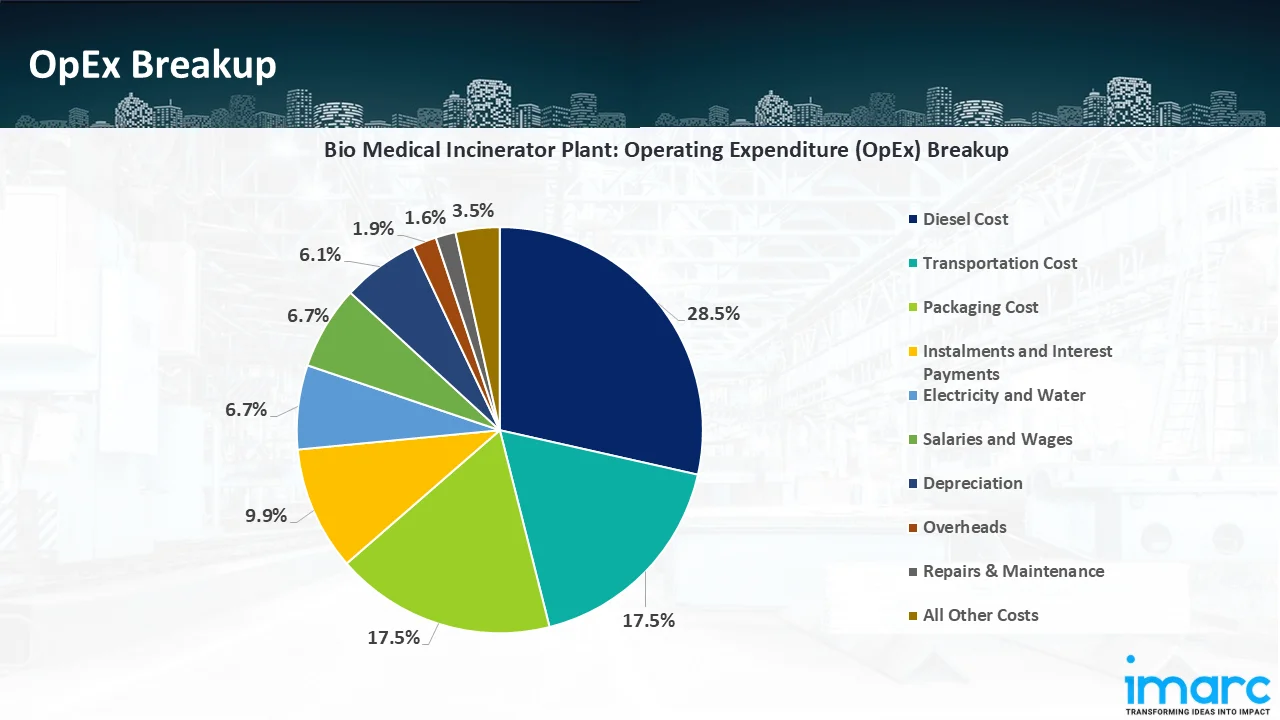
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a Treatment plant effectively. Opex in a Treatment plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a Treatment plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth.
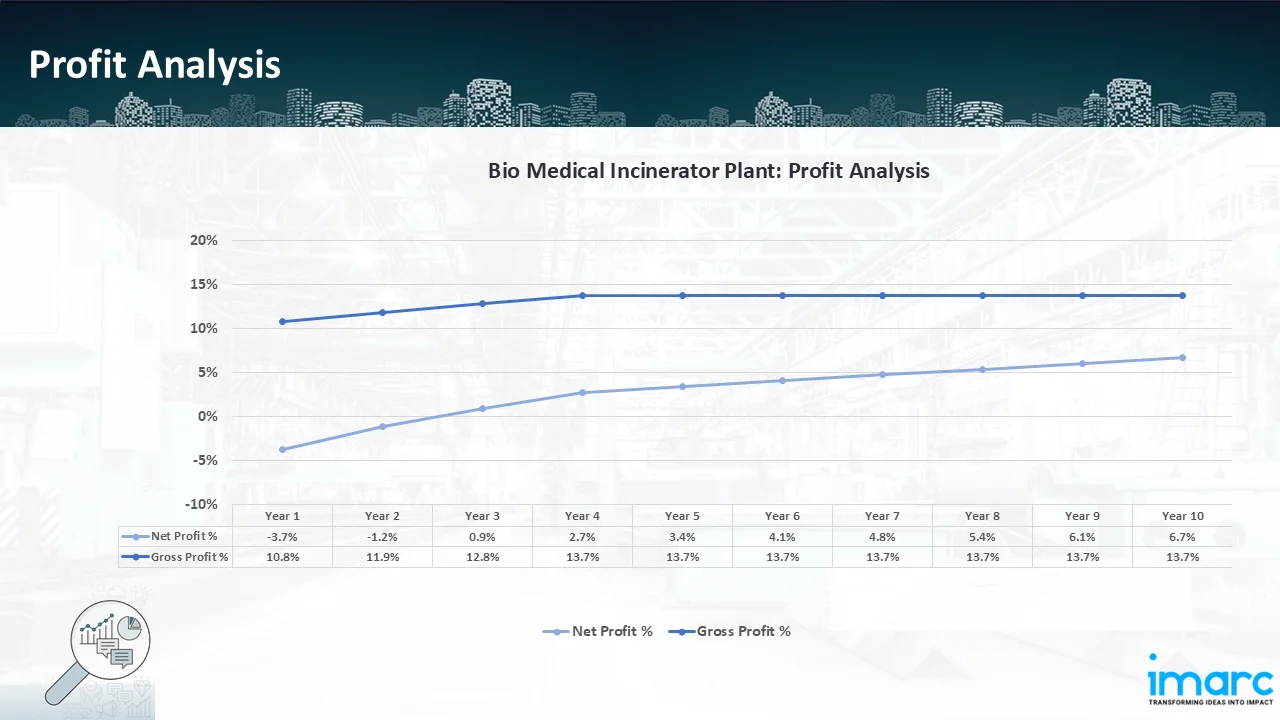
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: The proposed plant, with a capacity of treating 4,000 kg of waste per day by incinerators, 5,440 kg of waste per day by autoclave, achieved an impressive revenue of INR 71.9 million in its first year. We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins improve from 10.8% to 13.7% by year 10, and net profit rises from a negative of 3.7% to a positive of 6.7%, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the Bio Medical Incinerator plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, Treatment, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of treating 4,000 kg of waste per day by incinerators, 5,440 kg of waste per day by autoclave, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale Treatment ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In June 2025, Veolia, has announced a major expansion of its capacity to handle hazardous waste. In order to proactively address growing global demand, severe treatment capacity shortages, and the urgent need to safeguard the environment and public health, Veolia is adding 530,000 tonnes of new hazardous waste annual treatment capacity by 2030 through both organic growth and targeted acquisitions.
- In February 2025, India's first domestic Automated Biomedical Waste Treatment Plant was inaugurated at AIIMS New Delhi by Union Minister Dr. Jitendra Singh. The Minister formally dedicated the Automated Biomedical Waste Treatment Rig, known as "Srjanam," to the country during a ceremony in the AIIMS auditorium.
- In January 2025, a hazardous medical waste recycling and treatment facility is being built in Jeddah Third Industrial City by the Saudi Investment Recycling Company (SIRC), with trial operations set to commence in November 2025. The project's goal is to offer integrated solutions for hazardous medical waste management that adhere to the most recent health and environmental regulations. The facility supports environmental sustainability, maintains adherence to environmental standards, and encourages a circular economy in line with the National Transformation Program and Saudi Vision 2030 by utilising cutting-edge foreign experience in the field.
Why Choose IMARC:
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the Treatment facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish Treatment facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104










