Electric Cable Manufacturing Economics: A Cost Model Analysis
_11zon.webp)
What is Electric Cable?
Electric cables or power cables are the fundamental parts employed for the transfer of electrical power or signals over short and long distances. They generally comprise one or more conductors, typically composed of copper or aluminum, covered with insulating materials and protective sheaths.
Key Applications Across Industries:
Electric cables, based on their use, differ in structure, including low-voltage, medium-voltage, and high-voltage power cables, control cables, instrumentation cables, or data transfer cables like fiber optics. These cables find application in a broad spectrum of industries like construction, energy, telecommunications, transport, and manufacturing. New generation electric cables have been produced to provide high conductivity, mechanical strength, durability against environmental conditions, and fire retardancy, thus providing safety and efficiency in the transmission of energy or signals.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global power cables market size reached USD 186.5 Billion in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 289.9 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 4.98% during 2025-2033. The global market for electric cables is being propelled by a mix of rapid urbanization, increasing electricity consumption, and continued infrastructure development. Government policies supporting smart cities, rural electrification, and renewable energy adoption are driving the demand for robust cabling systems.
The growth of data centers and deployment of 5G technology are driving the demand for sophisticated communications cables. In industrial and construction segments, demand for energy-saving and fire-resistant cables is increasing on account of tighter safety standards. In addition, the rapidly increasing trend toward electric vehicles (EVs) is propelling demand for automotive cable solutions. Advances in technology like high-performing insulation materials, halogen-free flame retardant cables, and smart cable monitoring systems are also fueling market growth. Moreover, increased investments in grid modernization and transmission line upgrades across emerging and developed economies are further driving demand. The expansion of the cable sector is also supported by energy transition trends, particularly in wind and solar power schemes, which need dedicated cabling infrastructure.
Case Study on Cost Model of Electric Cable Manufacturing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a large-scale electric cable manufacturing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed electric cable manufacturing plant in Gaborone, Botswana. This plant is designed to produce 110 km of electric cables per day.
Manufacturing Process: The production of electrical cables in Botswana starts with the sourcing of raw materials, such as copper or aluminium rod, frequently imported from neighbouring South Africa to save costs, as well as XLPE, PVC, copper tape, and galvanized steel. Wire drawing is where the production process begins, with metal rods being pushed through dies to obtain the required diameter according to SABS standards. This is then annealed to soften drawn wires by controlled heat to enhance pliability and minimize brittleness. Then, in stranding, several wires are twisted together by compacting dies to enhance electrical conductivity and mechanical strength. These stranded wires are then insulated with substances such as XLPE or PVC to avoid current leakage and external interference. Following insulation, the wires are twisted or laid up to create the cable structure and are then extruded with a protective PVC sheath. Following sheathing, the cables undergo rewinding and extensive testing such as insulation resistance, voltage, and tensile strength testing in accordance with SABS and customer specifications. Lastly, the two ends of the cables are closed with heat-shrinkable caps, wound onto wooden or metal drums, and lagged with protective wooden battens for secure transport and handling. The standard lengths of drums are preserved depending on the type of cable, in order to ensure quality and durability in transport and installation.
_11zon.webp)
Mass Balance and Raw Material Required: The primary raw materials used in the electric cable manufacturing plant include aluminium rod, XLPE, copper rod, PVC, galvanized steel and copper tape. For a plant producing 1 km of cable ABC 4 core 50mmsq, 562 kg of aluminium rod and 268 kg of XLPE is required. For a plant producing 1 km of cable ABC 4 core 95mmsq, 1,058 kg of aluminium rod and 352 kg of XLPE is required. Additionally, to produce 1 km of cable concentric service 16mmx3 core, 410 kg of copper rod, 192 kg of PVC, and 45 kg of XLPE is required. Furthermore, to produce 1 km of cable XLPE 150mm 3core 11kv, 3,920 kg of copper rod, 2,460 kg of PVC, 1,045 kg of XLPE, 3,437 kg of galvanized steel, and 236 kg of copper tape is required.
List of Machinery:
The following equipment was required for the proposed plant:
- Aluminum Wire Drawing Machine
- RBD Drawing Machine
- Intermediate Drawing Machine
- Fine Wire Drawing Machine
- 500 1+6 Machine Rigid Frame Stranding Machine
- 500 1+6+12 Rigid Frame Stranding Machine
- 500 1+6+12+18+24 Rigid Frame Stranding Machine
- PLC 1250 Cantilever Twist Machine
- PLC 1600 Bow Type Twisting Machine
- Cross Link XLPE Triple Layer Co-Extrusion
- PLC 90 Extrusion Machine
- PLC 100+90 Extrusion Machine
- PLC 120 Extrusion Machine
- JLY 500 Planetary Stranding Machine
- CTD 600 Tape Shielding Machine
- 1600 CLY Cradle Type Cable Laying Up Machine
- 1600-1000 Cable Transferring Unit
- 2500-1600 Cable Transferring Unit
- Automatic Intelligent Low Temperature Elongation and Winding Tester
- LCD Digital Display Tensile Tester (Double Columns)
- Renshaw Cable Bending Tester
- Wire and Cable Sheath Scratch Resistance Tester
- Automation Cable Twist Tester
- Low Temperature Impact Test Device
- Pressure Test Device at High Temperature
- Thermostatic Water Bath
- Wire and Cable High Voltage Withstand, Insulation Resistance, Conductor DC Resistance Tester,
- Series Bridge Fixtures
- Intelligent Auto Profile Projector
- Spark Tester
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Investment (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
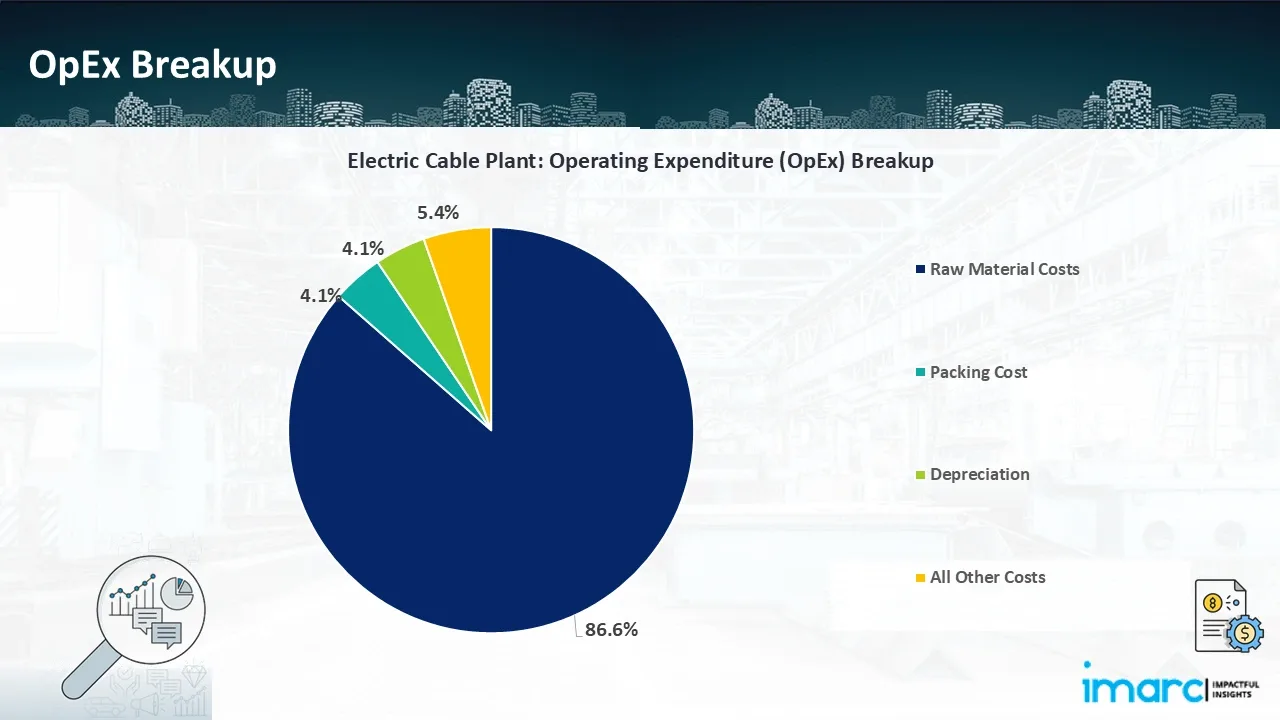
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. Opex in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth.
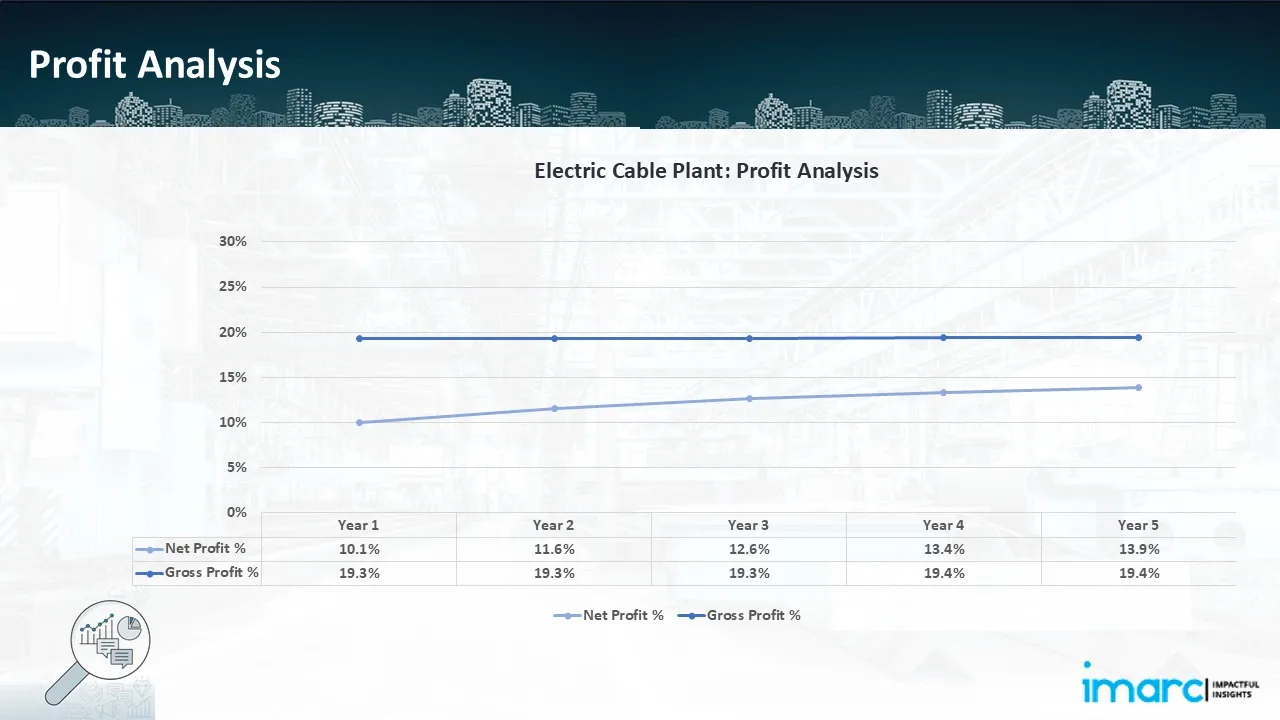
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: The proposed electric cable plant, with a capacity of approximately 110 km of electric cables per day, achieved an impressive revenue of US$ 203.6 million in its first year. We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins improve from 19.3% to 19.4% by year 5, and net profit rises from 10.1% to 13.9%, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the electric cable manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of producing 110 km of electric cable per day, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights for strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In June 2025, the Adani and Aditya Birla companies made their debut in India's wires and cables industry, raising hopes of consolidation and potential acquisitions with the goal of quickly scaling up and changing market dynamics.
- In March 2025, cable manufacturer Prysmian Group strengthened its presence in the United States by agreeing to pay up to $1.15 billion to acquire Channell Commercial Corp., extending its digital and communication cable lines for data centres and 5G infrastructure.
- In January 2025, A Capacity Reservation Agreement (CRA) covering the supply and installation of a second 525kV HVDC cable link between Shetland and the Scottish mainland has been signed by Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd., consortium partner Van Oord, and client SSEN Transmission.
Why Choose IMARC?
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104