Understanding the Economics: A Copper Wire Manufacturing Case Study

The global copper wire market reached a size of 20.5 Million Tons in 2023. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.26% during 2024-2032, reaching 33.0 Million Tons by 2032. The growth of the copper wire market is primarily driven by increased electricity demand, heightened investments in construction, expansion of electrical infrastructure, the rise of renewable energy, a shift toward electric vehicles in the automotive industry, and the growing adoption of electric appliances. The development of smart grids and investments in upgrading power transmission systems further boost global copper wire demand. Additionally, the telecom industry's use of copper in optic fiber cables and infrastructure development in emerging markets, especially in Asia Pacific and Latin America, are expected to sustain high demand for copper wire in the coming years.
Case Study on Cost Model of Copper Wire Manufacturing Plant
Objective: One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a large-scale copper wire manufacturing plant. We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of the plant in the United States. The proposed facility is designed to have a production capacity of 8.8 tons, with 2.9 tons of 0.25 mm wire, 2.9 tons of 1.38 mm wire, and 3.0 tons of 1.78 mm wire per day, covering a land area of 7,500 square meters.
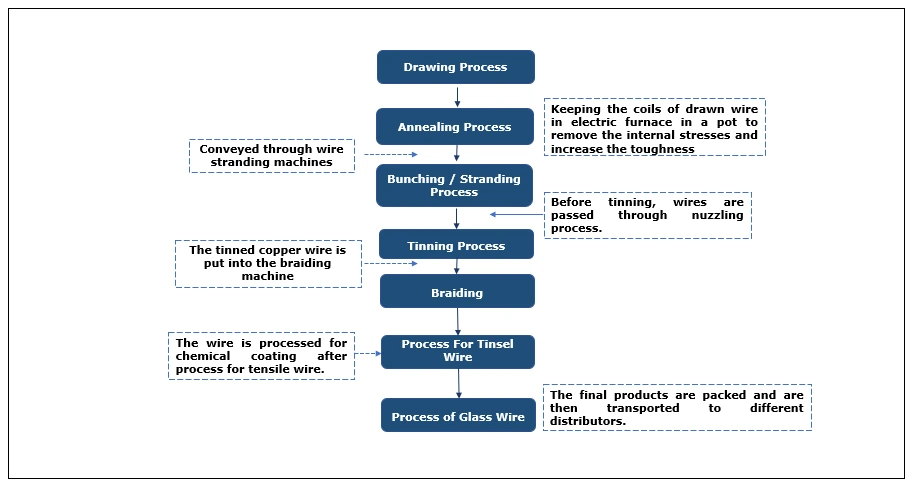
Manufacturing Process: The copper wire manufacturing process involves several steps. It begins with the drawing process, where EC-grade continuous cast copper rods (8 mm diameter) are drawn into wires of various gauges using diamond dies, lubricated, and cooled for precision. Next, the wires undergo annealing in an electric furnace to remove internal stresses and enhance toughness by heating to 1000°F while preventing oxidation. Afterward, the annealed wires are wound on reels for bunching or stranding, combining wires into twisted strands of different sizes for flexibility and strength, followed by nozzling for a smooth finish. The wires then go through the tinning process, either via hot-dip tinning, where wires are coated with molten tin, or electroplating, where the tin coating is achieved chemically with an electric current. Post-tinning, the wires are processed through braiding machines, forming flexible patterns like stranded, round, or flat layers for use in appliances and batteries. Specialized processes follow, such as tinsel wire production, where wires are flattened, lapped with nylon, braided, and chemically coated, and glass wire production, involving fiberglass braiding, polypropylene lapping, and varnish coating for enhanced durability and utility.
Figure: Copper Wire Manufacturing: Detailed Process Flow
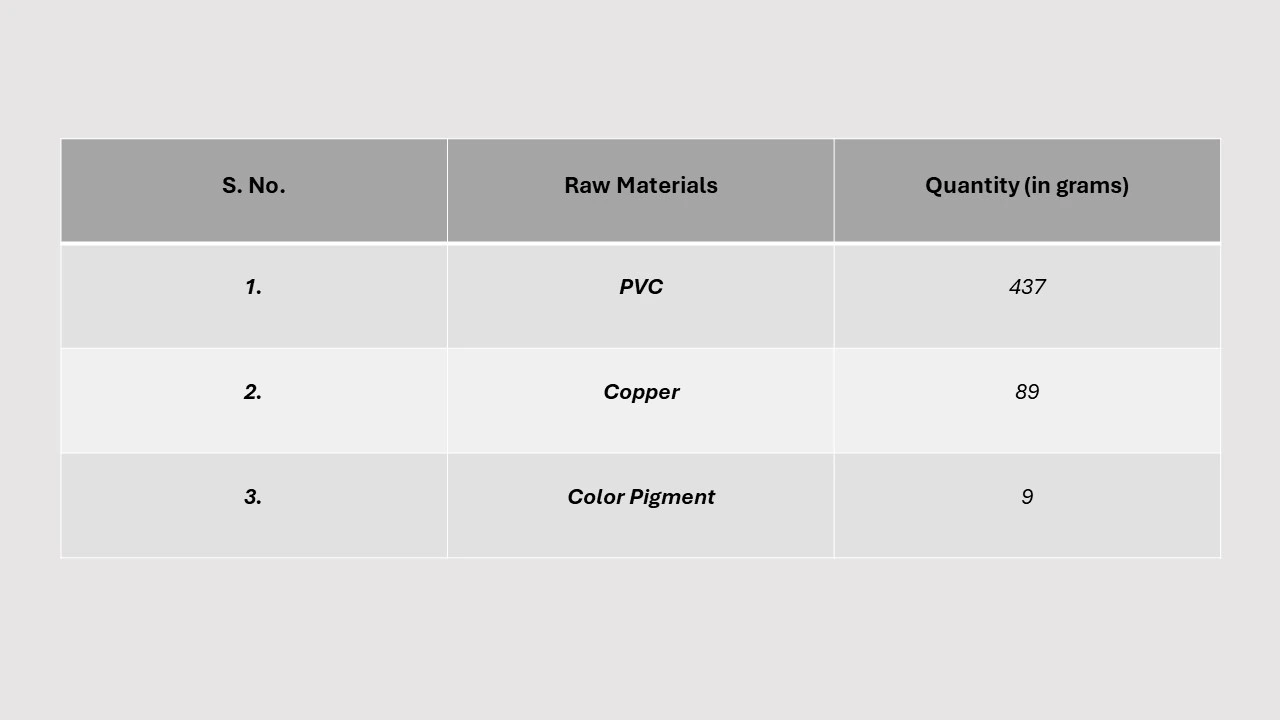
Mass Balance and Raw Material Required: The primary raw materials used in the manufacturing of copper wires include copper, PVC, and color pigments. PVC, or polyvinyl chloride, is a thermoplastic resin that softens easily with heat, making it ideal for insulation. Since PVC is an excellent insulator and does not conduct electricity, it plays a vital role in the copper wire manufacturing process. Additionally, color pigments are used to differentiate and enhance the appearance of the wires. These pigments are categorized into two types: organic and inorganic. Recently, mixed-phase metal oxides have also emerged in the market, offering innovative solutions for color pigments in copper wire production.
Table: Copper Wire Manufacturing from Copper Rod: Conversion Rate of Products for 100-meter 0.25 mm Copper Wire
List of Machinery:
The following lines were required for the proposed plant:
- Rod Breakdown Line
- High-Speed Insulation Line
- Multi-wire Drawing Line
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
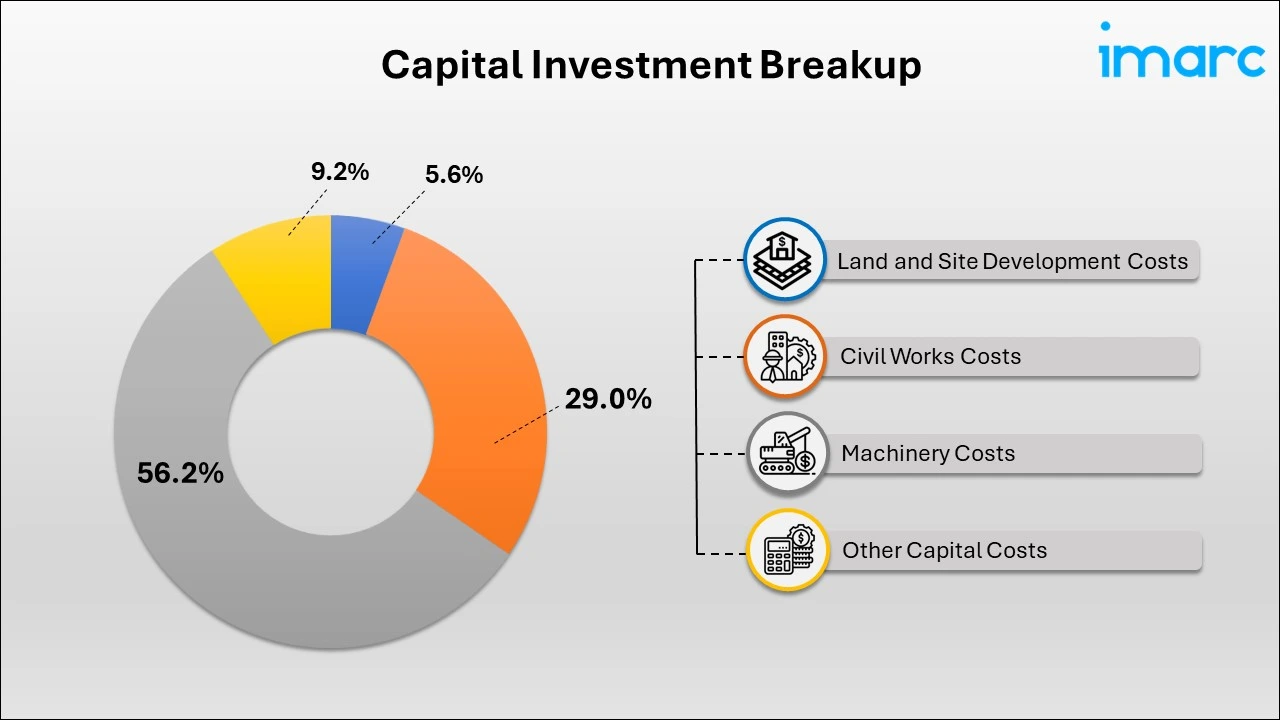
- Breakup by Capital Investment: The total capital cost for establishing the proposed plant is approximately US$ 8.37 million. Machinery costs comprise 56.2% of the total capital costs for the copper wire production plant. Civil works for the copper wire manufacturing plant include site preparation, foundation construction, building structures for production units, administrative offices, storage areas, utility setups, drainage systems, and roadways, ensuring structural integrity and efficient workflow.
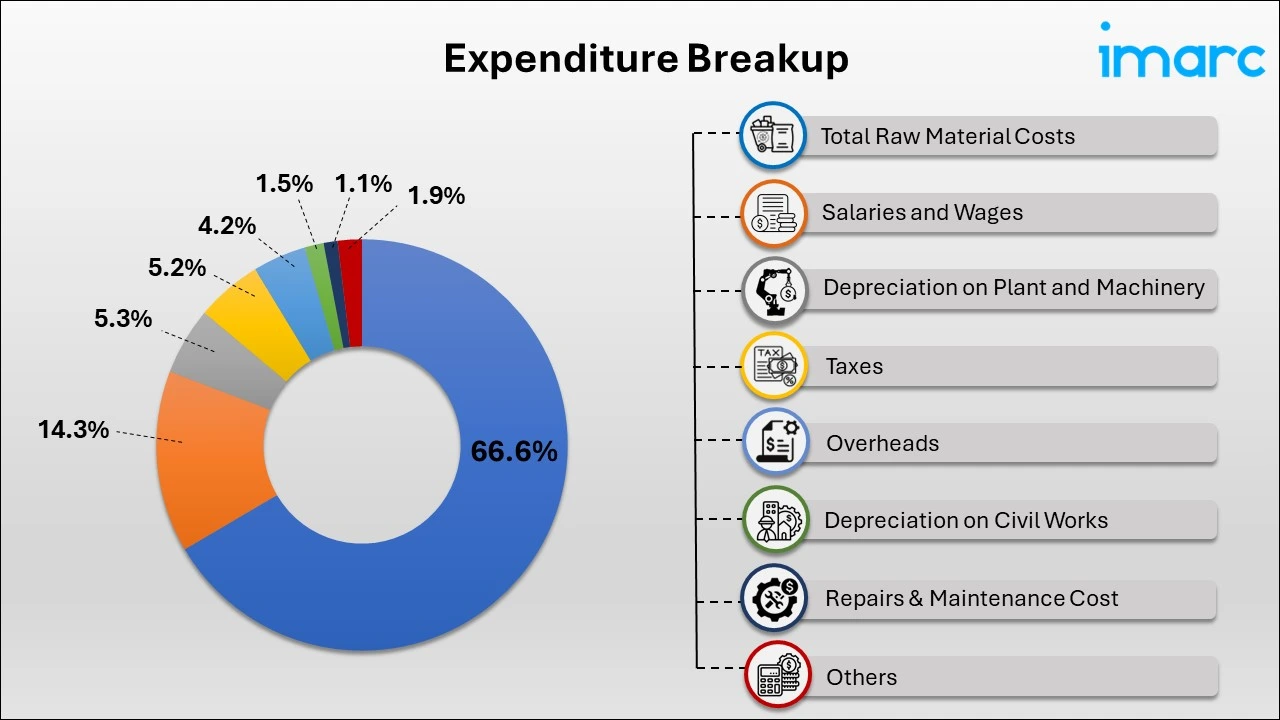
- Breakup by Expenditure: In the copper wire manufacturing plant, the expenditure cost for the first year of operations is projected at US$ 10.82 million. This estimate includes the cost of essential inputs like copper cathodes, insulating materials (PVC), and other necessary resources. By the fifth year, the raw material cost is expected to increase by 26.7%. This projected rise accounts for inflation, market fluctuations, and potential increases in the prices of key materials influenced by factors such as supply chain challenges, shifts in market demand, and global economic conditions.
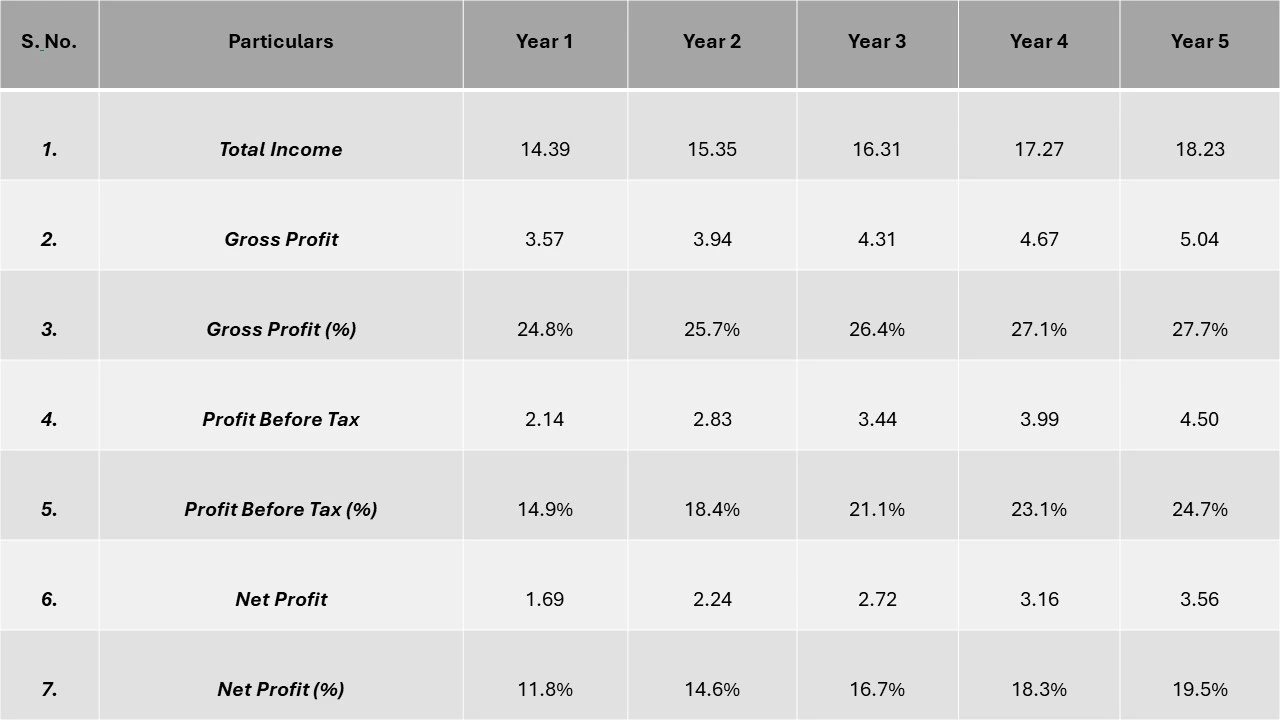
- Profitability Analysis Year-on-Year Basis
(All values are in US$ Million, except % ages)
Conclusion
Our financial model for the copper wire manufacturing plant was meticulously crafted to align with the client’s goals. It delivers an in-depth analysis of production costs, covering raw materials, manufacturing processes, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. Designed to meet the specific requirement of producing 8.8 tons daily comprising 2.9 tons of 0.25 mm wire, 2.9 tons of 1.38 mm wire, and 3.0 tons of 1.78 mm wire, the model highlights key cost drivers and projects profitability while considering market trends, inflation, and raw material price fluctuations. This comprehensive model equips the client with critical insights for strategic decisions, emphasizing our commitment to precise, client-focused solutions that foster long-term success in large-scale manufacturing projects.
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
At IMARC, we leverage extensive industry expertise and advanced financial modeling to enable clients to make informed decisions about market entry and operational strategies. By integrating competitive intelligence, regulatory analysis, and cost research, we assist clients in strategically positioning their manufacturing facilities within competitive markets. Our financial models extend beyond cost estimates, providing insights into industry trends, competitor strategies, and emerging technologies. This comprehensive approach empowers clients to plan sustainable, efficient, and profitable operations while ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations. With IMARC’s guidance, businesses can optimize plant setups, effectively manage costs, and drive long-term growth through data-driven, strategic insights.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104










