
Italy Vegetable Seeds Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Crop Type, Cultivation Method, Seed Type, and Region, 2025-2033
Italy Vegetable Seeds Market Size and Share:
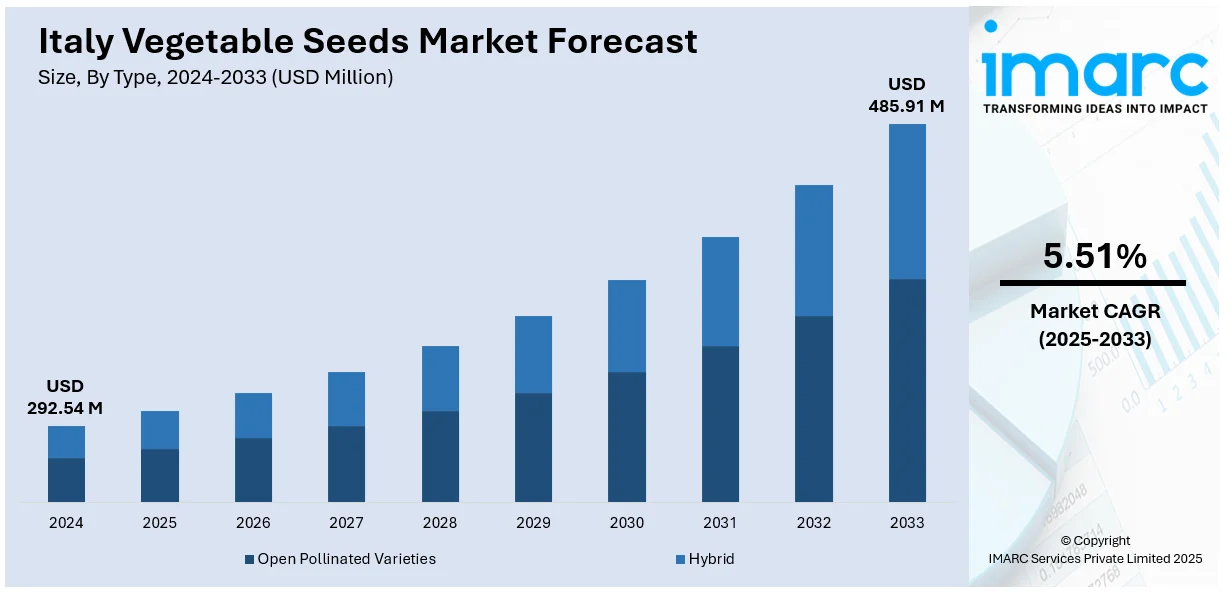
The Italy vegetable seeds market size was valued at USD 292.54 Million in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 485.91 Million by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 5.51% from 2025-2033. The market is witnessing significant growth, driven by rising demand for high-yield, disease-resistant varieties and the expansion of greenhouse and organic farming. Increased consumer preference for fresh, locally grown produce and supportive EU agricultural policies are also encouraging seed innovation and adoption. Technological advancements in seed breeding and strong export potential further contribute to market expansion, boosting the overall Italy vegetable seeds market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 292.54 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 485.91 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 5.51% |
One of the primary drivers of the Italy vegetable seeds market is the growing demand for high-yield, disease-resistant seed varieties due to increasing pressure on farmers to enhance productivity and reduce crop losses. The expansion of greenhouse cultivation and adoption of precision farming techniques are also influencing seed selection, with a preference for hybrids that perform well under controlled conditions. Rising input costs and limited arable land are prompting a shift toward genetically improved and climate-resilient seed varieties. According to the data published by CEIC, Italy, a Southern European peninsula and EU member, has a land area of 298,000 km² and a population of 59 million, resulting in a density of 196 persons/km². Forests cover 10 million hectares, while 13 million hectares are agricultural, producing grains in the north and fruits and olive oil in the south.
Another major driver is the consumer trend toward fresh, organic, and locally produced vegetables, which is pushing farmers to adopt premium-quality seeds that cater to health-conscious and sustainability-oriented markets. The rise of farm-to-fork initiatives, supported by EU and Italian government subsidies, is encouraging growers to diversify their crops using certified and traceable seed inputs. Export-oriented production also plays a role, especially in Mediterranean vegetables.
Italy Vegetable Seeds Market Trends:
Increasing demand for fresh vegetables
The increasing demand for fresh vegetables is significantly driving the vegetable seeds market in Italy. As consumers become more health-conscious, there is a growing preference for fresh, nutrient-rich vegetables over processed and packaged alternatives. This shift is fueling demand for a diverse range of vegetable seeds as farmers and gardeners seek to grow fresh produce to meet consumer needs. Furthermore, the Italian food culture places a high value on fresh ingredients, which has heightened the demand for vegetables that are both flavorful and nutritious. An industry survey showed that 45% of Italian consumers discard products containing preservatives, 66% prefer organic items, and 65% choose products of regional or local origin. Moreover, the rise in demand for fresh vegetables is driving innovation in vegetable seed varieties. Seed companies are developing and offering new, high-yielding, and disease-resistant seed varieties to meet consumer preferences and ensure a steady supply of fresh produce. Technological advancements in seed development, including the enhancement of pest resistance and yield optimization, have also played a crucial role in meeting the evolving demands of the market. Moreover, the rise of e-commerce platforms has made vegetable seeds more accessible to a broader audience, facilitating greater participation in vegetable cultivation across diverse regions of Italy. According to Italy vegetable seeds market forecast, the market is expected to witness steady growth over the coming years, driven by the convergence of consumer health trends, innovation in seed technology, and expanding access through digital retail channels.
Rising awareness regarding the benefits of consuming vegetables
Increased understanding of the benefits of vegetables, combined with growing health concerns, has resulted in an increase in demand for vegetables in both established and emerging nations. This heightened consciousness about health and nutrition has catalyzed a substantial increase in the demand for high-quality vegetable seeds, as both commercial farmers and home gardeners seek to cultivate a diverse array of nutrient-rich produce. According to the European Union, dietary risks (such as low fruit and vegetable intake and high sugar and salt consumption) were expected to account for approximately 14% of all deaths (87,000 deaths) in Italy in 2019. Consequently, farmers in Italy are concentrating on increasing vegetable production by incorporating diverse agricultural resources, such as premium vegetable seeds for planting. This, in turn, is bolstering the market. Furthermore, educational campaigns and public health initiatives are encouraging increased vegetable consumption, which is stimulating the Italy vegetable seeds market growth.
Italy Vegetable Seeds Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Italy vegetable seeds market, along with forecasts at country and regional levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on type, crop type, cultivation method, and seed type.
Analysis by Type:
- Open Pollinated Varieties
- Hybrid
Open pollinated varieties play a significant role in the Italy vegetable seeds market, particularly among smallholder and organic farmers who value seed-saving practices, affordability, and adaptability to local conditions. These seeds promote genetic diversity and are well-suited for traditional and sustainable farming systems. While hybrid seeds lead in commercial production, open pollinated varieties continue to find strong acceptance in regional and niche applications, contributing to a balanced and inclusive Italy vegetable seeds market.
Hybrid seeds are widely favored in the Italy vegetable seeds market for their superior yield potential, uniformity, and resistance to pests and diseases. They are extensively used in high-value crops such as tomatoes, peppers, and lettuce, supporting intensive and commercial farming operations. Backed by advances in seed technology and breeding, hybrid varieties offer consistent performance, shaping a dynamic and innovation-driven Italy vegetable seeds market outlook.
Analysis by Crop Type:
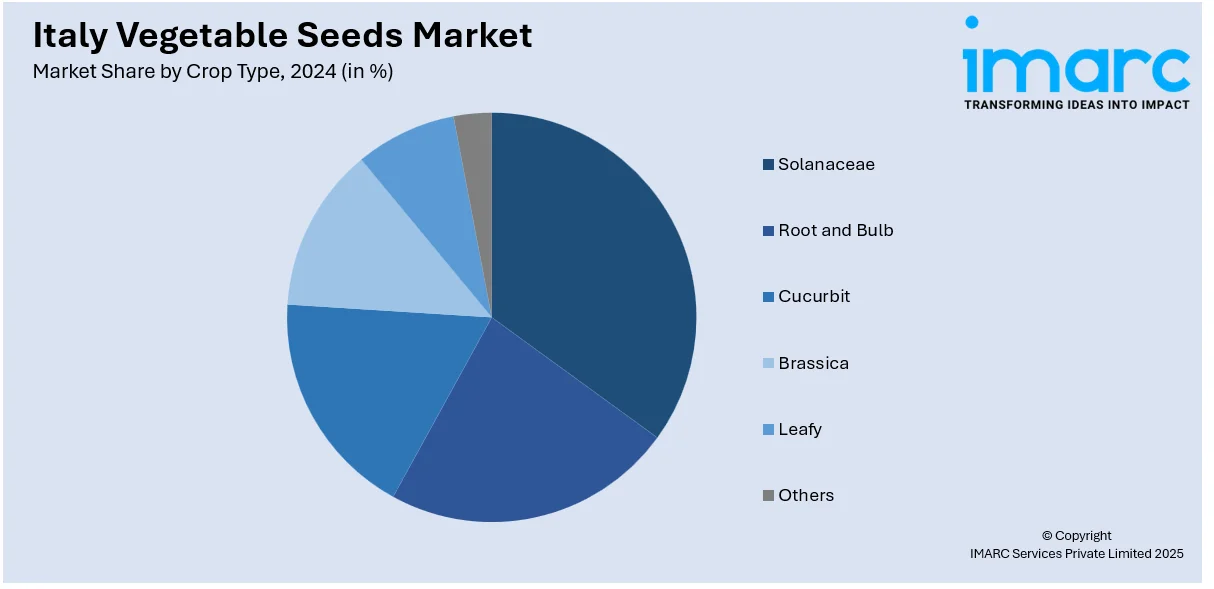
- Solanaceae
- Root and Bulb
- Cucurbit
- Brassica
- Leafy
- Others
Solanaceae crops like tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants are widely cultivated due to their culinary importance and export value. Their growth is supported by ongoing hybrid advancements and greenhouse farming. Farmers prefer these crops for their high returns and consistent demand, making them a vital part of Italy’s vegetable production landscape.
Root and bulb crops, including carrots, onions, and garlic, remain essential for both household consumption and industrial processing. Their stable demand and compatibility with various soil types make them a dependable choice for farmers. New seed varieties offering disease resistance and longer shelf life are helping expand their cultivation.
Cucurbit crops such as zucchini, cucumbers, and melons are favored for their versatility and strong local market demand. Improved seed varieties focusing on yield and disease tolerance are encouraging broader adoption. These crops are popular in open-field and protected cultivation across diverse Italian regions.
Brassica crops like cabbage, cauliflower, and broccoli are valued for their nutritional content and year-round demand. Farmers benefit from seed options that support crop resilience and consistency in yield. These vegetables are commonly grown for fresh markets and increasingly for processed food industries due to rising health-conscious consumer preferences.
Leafy vegetables, including lettuce, spinach, and arugula, are popular in fresh salads and convenience foods. Fast crop cycles and high turnover make them attractive for intensive farming. Breeding advancements focusing on disease resistance and extended shelf life are helping producers meet consumer expectations for freshness and quality.
Analysis by Cultivation Method:
- Protected
- Open Field
Protected cultivation is gaining traction in Italy due to its ability to ensure stable yields, optimize resource use, and support year-round vegetable production. Greenhouses and net houses enable better control over temperature, humidity, and pests, leading to higher-quality produce and reduced crop losses. This method is particularly beneficial for high-value crops like tomatoes, peppers, and leafy greens. With rising climate variability and land pressure, protected cultivation is becoming a preferred approach among commercial growers seeking consistent returns and efficiency.
Open field cultivation remains the most common method across Italy, particularly for large-scale production of crops like onions, carrots, cabbage, and zucchini. It offers low setup costs and is well-suited for traditional and seasonal farming cycles. Many farmers continue to rely on open field techniques due to established infrastructure and familiarity. Advances in mechanization, irrigation, and disease-resistant seed varieties are enhancing productivity and sustainability in open field vegetable farming.
Analysis by Seed Type:
- Conventional
- Genetically Modified Seeds
Conventional seeds dominate Italy’s vegetable farming landscape, favored by both smallholders and commercial growers for their reliability and alignment with EU regulations. These seeds are developed through traditional breeding methods and are widely accepted across organic and non-GMO production systems. Their compatibility with various farming practices and market preferences ensures continued adoption, especially in regions prioritizing natural and sustainable agricultural inputs.
Genetically modified (GM) seeds have limited presence in Italy due to stringent regulatory restrictions and public resistance. Italy, in line with broader EU policy, maintains a cautious stance on GM cultivation, favoring biodiversity and consumer health. Despite the scientific support for GM benefits like pest resistance and yield improvement, legal and market barriers limit their adoption. As a result, GM seeds remain largely restricted to research settings or imported products, with minimal role in mainstream vegetable seed use.
Regional Analysis:
- Northwest
- Northeast
- Central
- South
- Others
The Northwest region of Italy, including areas like Piedmont and Lombardy, is a major hub for commercial vegetable farming. Fertile plains, advanced irrigation, and strong logistics infrastructure support large-scale cultivation and seed demand. The region's focus on quality and innovation drives the uptake of hybrid and high-performance seed varieties.
In the Northeast, regions such as Veneto and Emilia-Romagna have a well-developed agricultural sector with a strong emphasis on horticulture. Farmers here actively adopt new seed technologies and efficient farming practices. The region benefits from cooperative networks and access to domestic and export markets, sustaining consistent demand for quality seeds.
Central Italy, including Tuscany and Lazio, features a mix of commercial and traditional farming. Medium-scale vegetable cultivation is prominent, with growing interest in organic practices. Demand for both conventional and open pollinated seeds is notable, supporting balanced growth across seed types.
Southern Italy, covering regions like Campania and Apulia, contributes significantly to Italy’s vegetable output, supported by favorable climate and long growing seasons. Seed usage here is diverse, with increasing interest in drought-tolerant and pest-resistant varieties due to changing environmental conditions and water availability.
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape of the Italy vegetable seeds market is characterized by the presence of both global seed giants and domestic players focused on regional crop varieties. Companies compete on traits such as yield, disease resistance, climate adaptability, and suitability for organic farming. Innovation in hybrid seed development and tailored breeding programs is central to market positioning. Strategic partnerships with agricultural cooperatives, direct engagement with growers, and investment in R&D are common approaches. As demand for traceable and high-performance seeds grows, firms offering certified, sustainable, and locally adapted varieties are gaining traction in both conventional and niche vegetable segments.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the Italy vegetable seeds market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
Latest News and Developments:
- April 2025: Source.ag partnered with Axia Vegetable Seeds to implement AI solutions in Axia’s Demo Greenhouse, enhancing trial registration and data-driven cultivation strategies. The partnership supports Axia’s breeding work, including its major tomato program in Italy, and aims to boost high-yield vegetable production through advanced simulations and precision insights.
- February 2025: BASF launched “FIELD MANAGER For Fruits & Veggies” to aid grape cultivation in France, Italy, Spain, and Türkiye. It integrates Horta’s seed-focused Decision Support System to deliver data-driven agronomic insights for sustainable, high-yield horticulture.
- February 2025: The Verisem Group acquired Blumen Vegetable Seeds to strengthen its seed sector presence. The deal includes brands, IP, genetic assets, and staff, integrating into Verisem Italia. Operations will continue across Italian research sites, enhancing global reach and focus on breeding and research for professional vegetable seed markets.
- November 2024: ISI Sementi (Italy) and Top Seeds International (Israel), both under Mitsui & Co., announced their integration into a single entity based in Fidenza, Italy. The new company will enhance global seed offerings with a broader crop portfolio and stronger breeding and research capabilities.
- July 2024: CapGen Seeds opened a new branch in Sicily, Italy, to strengthen its European presence. The site will focus on developing high-yield papaya and tomato seed varieties tailored to Italian conditions.
Italy Vegetable Seeds Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Open Pollinated Varieties, Hybrid |
| Crop Types Covered | Solanaceae, Root and Bulb, Cucurbit, Brassica, Leafy, Others |
| Cultivation Methods Covered | Protected, Open Field |
| Seed Types Covered | Conventional, Genetically Modified Seeds |
| Regions Covered | Northwest, Northeast, Central, South, Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Italy vegetable seeds market from 2019-2033.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Italy vegetable seeds market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Italy vegetable seeds industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The vegetable seeds market in the Italy was valued at USD 292.54 Million in 2024.
The Italy vegetable seeds market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 5.51% during 2025-2033, reaching a value of USD 485.91 Million by 2033.
Key factors driving the Italy vegetable seeds market include increasing demand for high-yield and disease-resistant crops, rising adoption of hybrid and organic farming practices, technological advancements in seed breeding, and growing consumer preference for fresh and healthy vegetables supported by both domestic consumption and export opportunities.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












