
Japan Building Insulation Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by type, Application, End User, and Region, 2026-2034
Japan Building Insulation Market Summary:
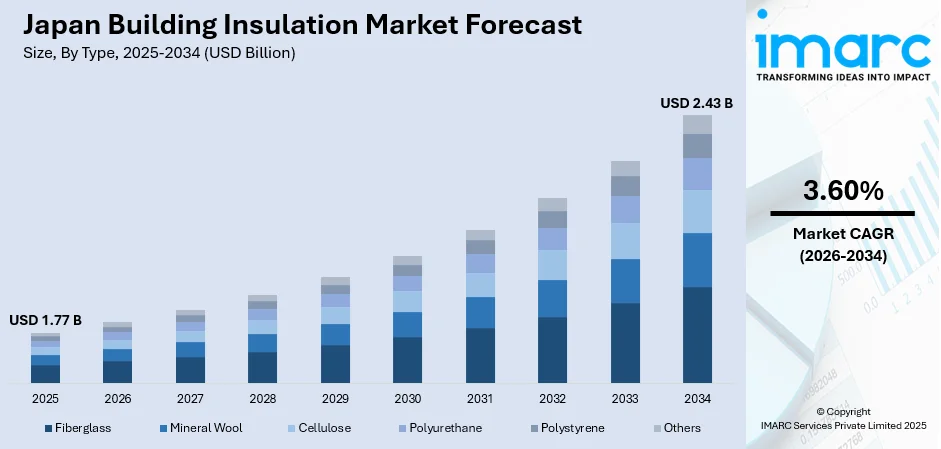
The Japan building insulation market size was valued at USD 1.77 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 2.43 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 3.60% from 2026-2034.
The market is experiencing momentum driven by mandatory energy efficiency standards requiring all new residential buildings to meet Thermal Insulation Performance Grade 4 minimum. Rising electricity costs are intensifying focus on operational expense reduction, while robust construction sector growth is creating sustained demand for insulation systems across residential, commercial, and infrastructure projects. The market is further supported by government subsidies, encouraging thermal performance upgrades that deliver both energy savings and documented health benefits for occupants, thereby expanding the Japan building insulation market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Type: Fiberglass dominates the market with a share of 35% in 2025, driven by its cost-effectiveness compared to alternative materials, ease of installation requiring minimal specialized labor, and widespread adoption in residential wall insulation.
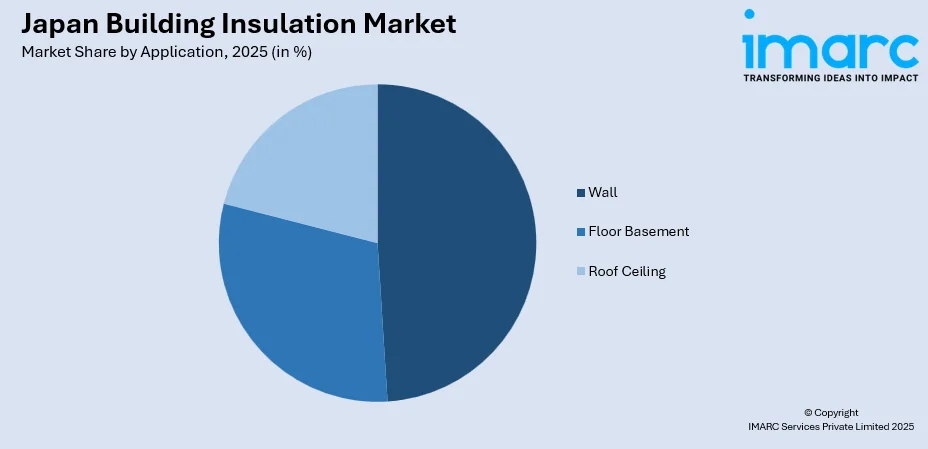
- By Application: Wall leads the market with a share of 49% in 2025, owing to regulatory focus on envelope thermal performance and compatibility with diverse construction methodologies from traditional timber framing to modern prefabricated systems.
- By End User: Residential represents the largest segment with a market share of 66% in 2025, propelled by the implementation of government subsidies, mandatory energy conservation compliance for all new housing, and awareness about long-term utility savings through improved thermal efficiency.
- By Region: Kanto region leads the market with a share of 32% in 2025, driven by the region commanding national construction activity with megaprojects including high-rise condominiums and infrastructure developments.
- Key Players: The Japan building insulation market exhibits moderate competitive intensity with established materials manufacturers competing alongside regional construction suppliers across price segments, differentiated through product innovation in thermal performance, partnerships with major developers for large-scale projects, and technical support capabilities for complex architectural applications.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The market demonstrates strong fundamentals supported by long-term regulatory drivers and infrastructure investment cycles. The country marked a watershed moment with nationwide mandatory compliance for energy conservation standards, requiring all new residential and commercial buildings to comply to government environmental policies. This regulatory enforcement represents substantial market expansion opportunity as builders transition from voluntary adoption to compulsory integration of high-performance insulation systems. The construction sector provides robust underlying demand. In 2025, Tiger Corporation in partnership with Nippon Express and Gifu Plastic Industry, will implement the newly designed Stainless Steel Vacuum Insulation Panel for the first time for cold transport during Expo 2025 in Osaka, Japan, commencing in May 2025. The Stainless Steel Vacuum Insulation Panel is an eco-friendly material that helps lower CO₂ emissions by decreasing the electric energy consumption needed for temperature maintenance, as it is used in cold storage containers for transport and in construction materials.
Japan Building Insulation Market Trends:
Mandatory Energy Efficiency Standards Driving Comprehensive Market Transformation
Japan implemented mandatory energy conservation compliance for all new buildings from April 2025, requiring Thermal Insulation Performance Grade 4 and Primary Energy Consumption Grade 4 minimum specifications. This regulatory shift eliminates voluntary guidelines that had governed construction practices since 1999, compelling builders to integrate high-performance insulation regardless of project scale or budget constraints. The mandate extends beyond residential construction to encompass commercial and institutional developments, creating universal baseline standards that fundamentally reshape material selection criteria and construction methodologies. Properties failing to meet these specifications become ineligible for housing loan tax deductions, effectively penalizing non-compliance through financial mechanisms. This regulatory enforcement accelerates market transition toward advanced thermal solutions including polyurethane foam, mineral wool, and vacuum insulation panels optimized for low thermal conductivity and extended operational lifespans.
Zero Energy House Program Expansion Accelerating Residential Adoption
The government's Zero Energy House initiative continues expanding with enhanced financial incentives targeting net-zero annual energy consumption through combined insulation improvements and renewable energy integration. Starting in April 2025, every home must comply with Thermal Insulation Performance Grade 4 and Primary Energy Consumption Grade 4 or above. As obtaining a determination of conformity with energy conservation standards will be required for building permits, construction cannot commence until adherence to those standards has been verified. The aim is to reach even greater energy efficiency (ZEH standard) by 2030, and energy conservation requirements for new homes will be progressively enhanced moving forward. This policy framework creates sustained demand for advanced insulation systems capable of supporting ultra-low energy consumption targets while maintaining construction cost feasibility.
Health-Focused Insulation Adoption Gaining Market Momentum
Research demonstrating quantifiable health benefits from improved thermal insulation is reshaping consumer decision criteria beyond traditional energy efficiency considerations. November 2024 findings from Institute of Science Tokyo established that well-insulated warm homes reduced cardiovascular disease risks while increasing quality-adjusted life years, with economic benefits justifying upgrade costs against Japan's healthcare cost-effectiveness thresholds. These findings validate insulation investments through health economics frameworks rather than purely energy savings calculations, expanding market appeal to aging demographics prioritizing wellness outcomes. Floor insulation studies correlating improved thermal comfort with reduced incidence of high blood pressure and diabetes further strengthen the medical justification narrative. This health-centric positioning enables builders and material suppliers to differentiate products through wellness benefits, particularly targeting seniors and health-conscious homeowners willing to pay premiums for demonstrated quality-of-life improvements.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Japan building insulation market is projected to demonstrate robust expansion trajectory through 2035, supported by mandatory regulatory compliance cycles, sustained construction sector growth, and progressive tightening of thermal performance standards. The market generated a revenue of USD 1.77 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 2.43 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 3.60% from 2026-2034. The 2030 escalation to Zero Energy House standards is further supporting the market growth, requiring comprehensive thermal insulation upgrades.
Japan Building Insulation Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Fiberglass | 35% |
| Application | Wall | 49% |
| End User | Residential | 66% |
| Region | Kanto Region | 32% |
Type Insights:
- Fiberglass
- Mineral Wool
- Cellulose
- Polyurethane
- Polystyrene
- Others
Fiberglass dominates with a market share of 35% of the total Japan building insulation market in 2025.
Fiberglass insulation maintains market dominance through cost-performance equilibrium addressing budget constraints prevalent in Japanese residential construction. Installation simplicity reduces labor expenses as fiberglass batts conform readily to standard cavity dimensions common in Japanese two-by-four framing systems without requiring specialized application equipment or extensive worker training. Supply chain maturity ensures consistent material availability through domestic manufacturing facilities operated by Saint-Gobain's Mag-Isover subsidiary maintaining glass wool production capacity, enabling rapid delivery schedules supporting tight project timelines characteristic of Japanese construction practices. In 2025, Saint-Gobain Isover has started manufacturing at its enhanced Forssa glass wool insulation facility in Kanta-Häme. The energy for the production comes from a 50:50 blend of biogas and hydroelectric power.
Acoustic performance characteristics complement thermal properties making fiberglass particularly suitable for multi-family residential structures where sound transmission control between dwelling units constitutes essential design consideration. Fire resistance ratings meeting Japanese building codes enable fiberglass specification in applications requiring non-combustible materials, including proximity to heating equipment and penetrations through fire-rated assemblies. These combined attributes sustain fiberglass preference among builders, architects, and property developers throughout Japanese construction sectors despite emerging competition from advanced material technologies offering superior thermal conductivity ratings within thinner installation profiles.
Application Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Floor Basement
- Wall
- Roof Ceiling
Wall leads with a share of 49% of the total Japan building insulation market in 2025.
Wall insulation specifications receive heightened regulatory scrutiny under revised energy conservation standards emphasizing building envelope thermal resistance as primary determinant of heating and cooling energy consumption. Wall assemblies typically represent largest continuous surface area in typical Japanese residential construction, offering maximum opportunity for thermal performance improvement through insulation enhancement. Installation within wall cavities during framing phase integrates seamlessly with conventional construction sequencing, avoiding workflow disruptions that complicate retrofitting other building elements.
Thermal bridge mitigation through continuous insulation layers along exterior wall surfaces addresses heat loss pathways through structural framing members that compromise cavity insulation effectiveness. Regional climate variations necessitate wall insulation specifications ranging from moderate thermal resistance in temperate southern prefectures to enhanced protection in northern regions experiencing prolonged winter heating seasons. Advanced window renovation subsidies offered through government programs specifically target wall envelope improvements recognizing synergistic benefits achieved through coordinated insulation and fenestration upgrades delivering comprehensive thermal performance enhancements reducing energy consumption while improving occupant comfort throughout seasonal temperature variations characteristic of Japanese climate zones.
End User Insights:
- Residential
- Non-Residential
Residential exhibits a clear dominance with a 66% share of the total Japan building insulation market in 2025.
Residential insulation demand accelerates through mandatory compliance requirements eliminating construction permit issuance for dwellings failing energy conservation standards from April 2025. Zero Energy House subsidy programs provide financial assistance ranging from 550,000 yen for enhanced ZEH+ specifications, materially reducing net costs for homeowners pursuing superior thermal performance exceeding baseline regulatory minimums. Housing loan tax deduction eligibility restrictions disqualify newly constructed residences lacking energy efficiency certification, creating financial penalties reinforcing insulation investment decisions. Property value premiums emerging for energy-efficient residences incentivize builders to incorporate enhanced insulation specifications differentiating offerings within competitive housing markets, particularly pronounced in metropolitan areas where buyer sophistication drives appreciation for long-term operational cost advantages achievable through superior thermal envelope performance.
Demographic trends including aging population heighten residential insulation relevance as elderly occupants demonstrate increased sensitivity to indoor temperature fluctuations requiring stable thermal environments for health maintenance. Retrofitting existing residential stock gains momentum through government support programs addressing substantial housing inventory constructed prior to modern thermal performance standards, with typical Japanese dwelling lifespan averaging thirty-five years creating continuous renovation opportunities. Construction market growth projecting expansion sustains residential segment vitality as housing construction maintains substantial share of overall building activity throughout Japanese prefectures.
Regional Insights:
- Kanto Region
- Kansai/Kinki Region
- Central/ Chubu Region
- Kyushu-Okinawa Region
- Tohoku Region
- Chugoku Region
- Hokkaido Region
- Shikoku Region
Kanto region leads with a share of 32% of the total Japan building insulation market in 2025.
Kanto Region encompasses Tokyo metropolitan area plus surrounding prefectures including Saitama, Chiba, Kanagawa, Ibaraki, Tochigi, and Gunma. Infrastructure megaprojects including Linear Chuo Shinkansen maglev railway connecting Tokyo, Nagoya, and Osaka drive substantial commercial and transportation facility construction requiring comprehensive building envelope systems. Urban redevelopment initiatives transforming districts including Shibuya Sakura Stage complex with retail stores and Yaesu 2-Chome Central District demanding sophisticated thermal management solutions supporting energy efficiency mandates while maintaining occupant comfort throughout seasonal temperature variations.
Regional regulatory leadership positions Kanto as early adopter of advanced building codes subsequently influencing national standards, with Tokyo Metropolitan Government implementing photovoltaic panel requirements and enhanced energy efficiency mandates exceeding federal minimums scheduled for enforcement from 2025. Construction workforce concentration in Kanto Region facilitates adoption of building information modeling technologies and prefabrication methods enabling precise insulation specifications in complex architectural designs. Property values commanding premium pricing in central Tokyo incentivize developers to maximize usable floor area through advanced insulation systems delivering requisite thermal performance within thinner wall assemblies.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Japan Building Insulation Market Growing?
Mandatory Energy Conservation Standards Implementation From April 2025
Regulatory architecture establishes universal thermal performance requirements across Japanese construction sectors. The revised Building Energy Conservation Act eliminates voluntary participation frameworks previously characterizing energy efficiency programs, instead mandating Thermal Insulation Performance Grade 4 compliance for all residential and non-residential buildings regardless of floor area dimensions. Construction permits become contingent upon demonstrating conformity with prescribed thermal resistance values for building envelope components including walls, roofs, floors, and window assemblies. Buildings failing conformity assessments face enforcement actions including remediation orders carrying potential fines reaching three million yen for continued non-compliance. Moreover, Japan seeks to decrease its greenhouse gas emissions by 46% by 2030 and will persist in its vigorous efforts to achieve the ambitious target of halving its emissions by 50%. The country has successfully accomplished a decrease of roughly 20% and its reduction is progressing as planned.
Construction Activity Expansion Across Metropolitan Regions
Infrastructure investment and urban development initiatives generate sustained insulation material demand. As per IMARC Group’s predictions, Japanese construction market is projected to attain USD 941.3 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 4.15% during 2026-2034 reflecting public infrastructure priorities and private real estate development activity. Kanto Region captured a significant percent of national construction revenue in 2024, driven by megaprojects including rail network extensions, high-rise residential towers, and data center facilities requiring comprehensive thermal envelope systems. Commercial construction activity responds to e-commerce logistics infrastructure requirements necessitating temperature-controlled warehouse facilities demanding superior insulation performance for operational efficiency.
Rising Energy Costs Incentivizing Thermal Efficiency Investments
Electricity expense escalation establishes compelling economic justification for insulation adoption. Electricity production in the country reached 81,442 GWh in July 2025, compared with 66,073 GWh in the previous month reflecting sustained high energy utilization across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. Utility cost increases drive property owners to evaluate lifecycle operational expenses alongside initial construction costs, revealing insulation investments generate utility savings offsetting capital expenditures within reasonable payback periods. Building operators calculate heating and cooling energy reductions achievable through thermal envelope improvements, particularly valuable in urban areas with dense populations and elevated energy consumption per capita.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the Japan Building Insulation Market is Facing?
Skilled Labor Shortages in Construction Sector
Japan's construction industry is experiencing noteworthy shortages of skilled labor, mainly because of an aging workforce and a deficiency of younger individuals entering the field. The nation's falling birth rate and a rising population of retirees have intensified this problem. Numerous skilled workers, including electricians and carpenters, are hitting retirement age without a sufficient influx of new talent to take their place. This has led to delays in projects, heightened expenses, and a rising reliance on overseas workers. To tackle the shortage, Japan is considering measures such as training programs for younger employees, enhancing work conditions, and relaxing immigration regulations to draw in skilled foreign labor.
High Upfront Compliance Costs for Enhanced Standards
Regulatory compliance necessitates material and equipment investments elevating construction costs. Thermal Insulation Performance Grade 4 requirements mandate high-performance windows, enhanced wall cavity insulation, and continuous thermal barriers addressing thermal bridges, collectively increasing residential construction expenses. Small-scale builders operating on constrained budgets encounter particular difficulty absorbing cost increases, potentially limiting market participation and competitive intensity.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities and Material Price Volatility
Material availability disruptions and pricing fluctuations introduce project execution uncertainties. Global supply chain turbulence experienced 2022-2024 generated insulation material shortages delaying building projects and driving price spikes despite volume demand slowdowns. Raw material costs including glass fiber, mineral wool precursors, and petrochemical feedstocks for foam insulation exhibit sensitivity to commodity market dynamics and geopolitical tensions affecting material procurement.
Competitive Landscape:
Market structure exhibits moderate concentration with multinational corporations maintaining substantial presence alongside specialized domestic manufacturers. Competition intensifies across product categories including fiberglass, mineral wool, and foam insulation systems, with differentiation occurring through thermal conductivity performance specifications, fire resistance ratings, acoustic properties, and installation system innovations. Manufacturers pursue capacity expansion strategies positioning production facilities proximate to major construction markets, reducing transportation costs while enabling rapid response to regional demand fluctuations. Distribution networks leverage building material wholesalers and construction supply retailers, though direct relationships with large-scale developers and general contractors secure substantial project volumes. Technology investments focus on manufacturing process efficiency improvements reducing material costs while maintaining performance specifications, alongside product development targeting enhanced thermal resistance within thinner installation profiles valuable for space-constrained urban construction environments.
Recent Developments:
-
In April 2025, LIXIL Corporation, a producer of innovative solutions for the water and housing sector, and Schueco International KG are enhancing their collaboration to collectively minimize the emissions produced during the complete life cycle of a building. This aligns with the objective of the Japanese government to attain climate neutrality by 2050. LIXIL supplies Schueco products in Japan, such as the Schueco ASE 60 high-performance aluminum window and the Schueco FWS 50.SI curtain walling system. The system solutions are appropriate for different construction applications, including residential and commercial structures, and provide outstanding thermal insulation, airtightness, and design versatility.
Japan Building Insulation Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Fiberglass, Mineral Wool, Cellulose, Polyurethane, Polystyrene, Others |
| Applications Covered | Floor Basement, Wall, Roof Ceiling |
| End Users Covered | Residential, Non-Residential |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kansai/Kinki Region, Central/Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Japan building insulation market size was valued at USD 1.77 Billion in 2025.
The Japan building insulation market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 3.60% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 2.43 Billion by 2034.
Fiberglass dominated the market with 35% revenue share, driven by cost-effectiveness, proven thermal performance, and widespread contractor familiarity enabling rapid installation across diverse building types and architectural applications throughout Japan.
Key factors driving the Japan building insulation market include mandatory energy conservation compliance implemented April 2025, expanding construction activities to create comprehensive living spaces and offices, and rising electricity costs monthly compelling property owners toward efficiency investments.
Major challenges include fluctuating raw material costs for petrochemical-based foam products driving price volatility, chronic skilled labor shortages constraining installation capacity and quality, and high initial investment requirements for advanced insulation technologies limiting adoption among cost-sensitive residential developers and renovation projects.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












