
Japan Nuclear Power Equipment Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Reactor Type, Equipment Type, and Region, 2026-2034
Japan Nuclear Power Equipment Market Summary:
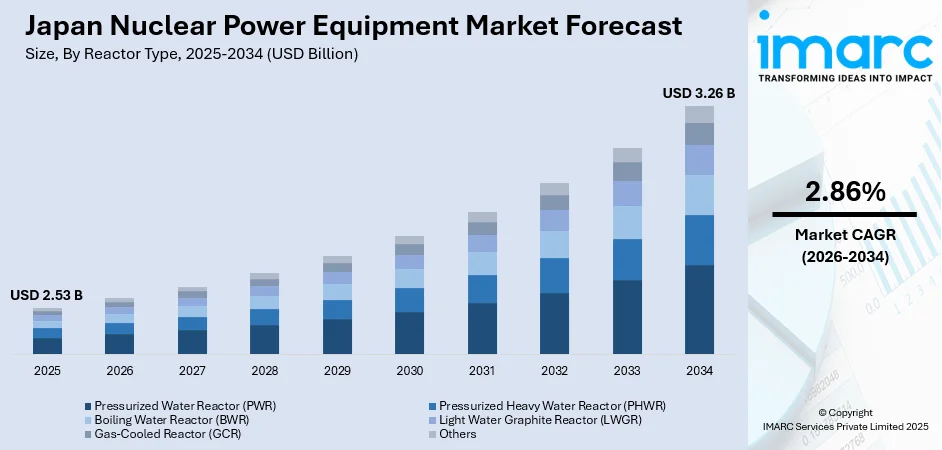
The Japan nuclear power equipment market size was valued at USD 2.53 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 3.26 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 2.86% from 2026-2034.
The Japan nuclear power equipment market is experiencing renewed momentum as the country advances its energy transition strategy following post-Fukushima recovery efforts. The market expansion is primarily driven by the government's commitment to maximizing nuclear power utilization for achieving carbon neutrality targets and enhancing energy security. Japan's strategic pivot toward reactor restarts, equipment modernization, and next-generation nuclear technologies continues to stimulate demand for advanced reactor components and safety systems.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Reactor Type: Boiling Water Reactor (BWR) dominates the market with a share of 51% in 2025, owing to its established infrastructure across major power utilities and recent strategic restarts of BWR units marking significant progress in Japan's nuclear revival efforts.
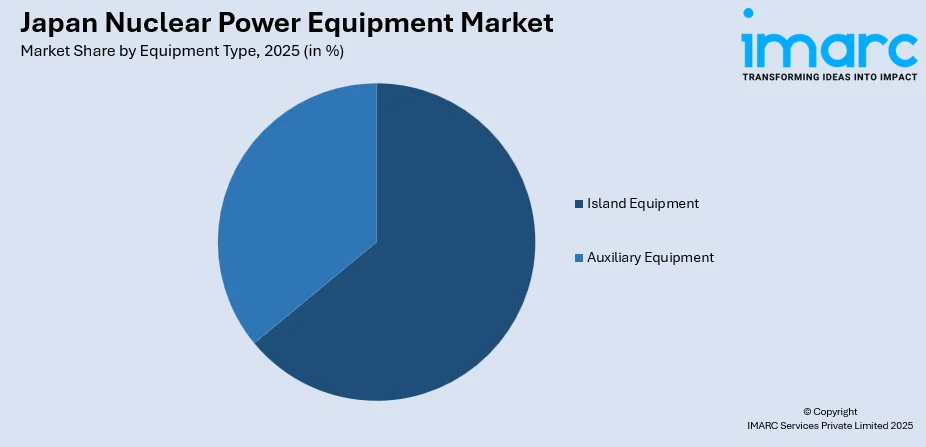
- By Equipment Type: Island equipment leads the market with a share of 64% in 2025, driven by substantial investments in reactor core components, pressure vessels, and steam generation systems essential for maintaining operational efficiency and safety compliance.
- Key Players: The Japan nuclear power equipment market features a consolidated competitive landscape dominated by established domestic manufacturers with extensive expertise in reactor technology and component fabrication, supported by strategic international partnerships for advanced reactor development.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The Japan nuclear power equipment market continues to evolve against the backdrop of the country's comprehensive energy transformation agenda. Government policies under the Seventh Strategic Energy Plan emphasize nuclear power as a cornerstone of the decarbonization strategy, targeting a nuclear share of approximately 20-22% in the energy mix by the mid-2030s. The recent restart of reactors, including the first boiling water reactors to resume operations since the Fukushima incident, demonstrates growing confidence in nuclear technology and regulatory frameworks. Equipment manufacturers are witnessing increased demand for safety retrofitting components, specialized anti-terrorism facilities, and advanced monitoring systems as utilities work to bring additional units online while meeting stringent regulatory requirements established by the Nuclear Regulation Authority.
Japan Nuclear Power Equipment Market Trends:
Accelerated Reactor Restart Programs and Equipment Modernization
Japan's nuclear industry is witnessing a significant surge in reactor restart activities following governmental policy shifts prioritizing nuclear energy for baseload power generation. Utilities are investing substantially in equipment upgrades, including enhanced cooling systems, seismic reinforcement structures, and filtered containment venting systems to meet post-Fukushima safety standards. The successful commercial operation of boiling water reactors in eastern Japan marks a watershed moment, demonstrating the technical feasibility and regulatory approval pathway for additional units awaiting restart authorization. For instance, in July 2025, Kansai Electric Power announced that it would initiate studies for building a new nuclear reactor at its Mihama plant in Fukui Prefecture, located in western Japan. The planned unit is intended to serve as a replacement for the current reactor operating at the site.
Advancement of Next-Generation Reactor Technologies
Japanese manufacturers and research institutions are actively developing innovative reactor designs to position the country at the forefront of global nuclear technology evolution. Investments in sodium-cooled fast reactors, small modular reactors, and fusion energy research are driving demand for specialized equipment, including advanced fuel handling systems, superconducting magnetic confinement components, and novel heat exchange technologies. International collaborations with European and American partners are accelerating technology transfer and knowledge sharing for next-generation nuclear systems. For instance, in October 2025, Japanese start-up Helical Fusion announced that it had completed a key performance trial of a high-temperature superconducting (HTS) coil, representing a significant step toward the development of commercially viable fusion power.
Rising Demand from Data Centers and Industrial Electrification
The proliferation of artificial intelligence applications and semiconductor manufacturing facilities is creating unprecedented electricity demand growth in Japan, reversing previous projections of declining consumption. The Japan artificial intelligence market size was valued at USD 6.6 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 35.2 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 20.4% from 2025-2033. Nuclear power equipment manufacturers are benefiting from the urgent need for reliable baseload generation capacity to support technology sector expansion. This trend is reinforcing government commitment to maximizing nuclear utilization while accelerating timelines for equipment procurement and installation across both existing and planned facilities.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Japan nuclear power equipment market outlook remains positive as the country intensifies efforts to enhance energy security and achieve decarbonization objectives through expanded nuclear utilization. Ongoing reactor restart programs, coupled with investments in equipment safety upgrades and life extension initiatives for aging plants, are expected to sustain market momentum throughout the forecast period. The development of next-generation reactor technologies and potential new construction projects at existing sites further strengthen long-term growth prospects. The market generated a revenue of USD 2.53 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 3.26 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 2.86% from 2026-2034.
Japan Nuclear Power Equipment Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Reactor Type | Boiling Water Reactor (BWR) | 51% |
| Equipment Type | Island Equipment | 64% |
Reactor Type Insights:
- Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR)
- Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR)
- Boiling Water Reactor (BWR)
- Light Water Graphite Reactor (LWGR)
- Gas-Cooled Reactor (GCR)
- Others
The Boiling Water Reactor (BWR) dominates with a market share of 51% of the total Japan nuclear power equipment market in 2025.
The dominance of boiling water reactors in Japan's nuclear equipment landscape reflects the historical development trajectory established through partnerships with international technology providers and subsequent domestic manufacturing capabilities. Japanese utilities operating BWR facilities have accumulated extensive operational expertise and maintain comprehensive supply chain relationships with domestic equipment manufacturers specializing in reactor-specific components. The recent successful restarts of BWR units following rigorous safety assessments demonstrate continued confidence in this reactor technology for future power generation needs.
Equipment demand for boiling water reactor facilities encompasses specialized components including reactor pressure vessels, steam separators, recirculation systems, and control rod drive mechanisms. The requirement for filtered containment venting systems unique to BWR technology has generated additional equipment procurement opportunities as utilities comply with enhanced safety regulations. Major power stations in regions including Kanto and Tohoku continue to drive demand for BWR-specific equipment as restart programs progress and operating life extensions are pursued for existing units.
Equipment Type Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Island Equipment
- Auxiliary Equipment
The island equipment leads with a share of 64% of the total Japan nuclear power equipment market in 2025.
Island equipment encompasses the critical nuclear and conventional island components essential for reactor operation and power generation, including reactor pressure vessels, steam generators, turbines, and associated structural systems. The substantial capital investment required for island equipment reflects its fundamental role in determining plant capacity, efficiency, and operational lifespan. Japanese manufacturers have developed sophisticated fabrication capabilities for these high-specification components, supporting both domestic requirements and export opportunities across the Asia-Pacific region.
The ongoing equipment replacement and upgrade programs at operating plants continue to sustain demand for island equipment components as utilities extend reactor operating lifespans beyond initial design specifications. Safety enhancement initiatives mandated by regulatory authorities require substantial investments in structural reinforcement, seismic isolation systems, and emergency cooling equipment classified within the island equipment category. The development of specialized safety facilities and anti-terrorism measures at nuclear sites further expands the scope of island equipment requirements across the Japanese nuclear fleet.
Regional Insights:
- Kanto Region
- Kansai/Kinki Region
- Central/ Chubu Region
- Kyushu-Okinawa Region
- Tohoku Region
- Chugoku Region
- Hokkaido Region
- Shikoku Region
The Kanto region’s market is driven by high electricity demand from dense metropolitan centers, advanced research institutions, and strong government involvement in energy security planning. Utilities across the region prioritize upgraded safety, monitoring, and cooling technologies to support reactor restarts and modernization. The presence of major engineering firms and technology suppliers further accelerates investment in next-generation nuclear equipment to stabilize grid capacity and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
Demand in the Kansai region is strengthened by the concentration of heavy industries, technology manufacturers, and utilities committed to improving nuclear plant efficiency. Modernization programs focus on enhanced seismic-resistant equipment, digital control systems, and advanced fuel-handling solutions. The region’s large corporate energy consumers encourage the adoption of reliable baseload power sources, driving upgrades across aging nuclear infrastructure and reinforcing investment in long-term operational safety.
Chubu’s nuclear equipment market is supported by its role as a core manufacturing hub, particularly for automotive, chemicals, and precision engineering sectors that require stable energy supplies. Utilities are investing in advanced reactor components, enhanced monitoring tools, and upgraded safety systems to strengthen operational resilience. Regional emphasis on industrial continuity and disaster-preparedness further promotes the adoption of high-reliability nuclear technologies and modernized plant infrastructure.
Kyushu is a key driver of nuclear activity in Japan, with operational reactors that require continual upgrades to meet evolving regulatory standards. Investments center on digital instrumentation, cooling systems, fuel-cycle equipment, and seismic-resistant technologies. The region’s rising renewable energy integration also raises the need for stable baseload power, encouraging utilities to enhance nuclear plant performance. Local engineering capabilities support equipment replacement and lifecycle extension efforts.
In Tohoku, demand is driven by ongoing reconstruction and energy-resilience initiatives following past seismic events. Utilities emphasize state-of-the-art safety systems, emergency-power equipment, and robust containment technologies to bolster plant reliability. As the region expands its industrial base and grid modernization programs, nuclear facilities are investing in advanced monitoring, digital controls, and upgraded structural components to support long-term energy stability and regulatory compliance.
The Chugoku region’s market benefits from industrial growth and the strategic importance of nuclear power in stabilizing regional electricity supply. Utilities focus on upgrading aging equipment, implementing enhanced cooling and safety systems, and integrating predictive maintenance technologies. The region’s coastal plant locations require advanced corrosion-resistant materials and flood-protection solutions, driving demand for innovative nuclear equipment that ensures reliable, resilient operations.
Hokkaido’s nuclear equipment demand is shaped by its cold climate, dispersed grid, and need for dependable power generation. Utilities pursue highly efficient reactor components, thermal-management systems, and upgraded emergency-response equipment. The region continues investing in seismic-resistant technologies and digitalized plant controls to enhance safety and operational reliability. Industrial expansion and winter-driven energy peaks further reinforce the importance of nuclear modernization projects.
Shikoku’s market is supported by utilities focused on plant maintenance, modernization, and regulatory compliance for existing nuclear facilities. Investment priorities include advanced instrumentation, upgraded fuel-handling systems, and enhanced cooling and containment technologies. The region’s smaller but industrially active economy depends on consistent electricity supply, encouraging utilities to adopt high-reliability nuclear equipment that strengthens grid stability and extends plant operational life.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Japan Nuclear Power Equipment Market Growing?
Government Policy Support for Nuclear Energy Expansion
The Japanese government's strategic energy planning framework has established nuclear power as an indispensable element of the national energy mix, providing strong policy support for equipment market growth. Recent revisions to the Strategic Energy Plan emphasize maximizing nuclear utilization while pursuing new reactor construction opportunities at existing sites. Policy mechanisms, including long-term decarbonized power source auctions and financial support measures for construction cost recovery, are designed to stimulate investment in nuclear facilities and associated equipment procurement. The extension of reactor operating lifespans beyond traditional limits creates sustained demand for maintenance, upgrade, and replacement equipment across the existing fleet.
Energy Security Imperatives and Import Dependency Reduction
Japan's heavy reliance on imported fossil fuels for electricity generation exposes the economy to significant supply disruption risks and price volatility, strengthening the strategic case for nuclear power expansion. Geopolitical tensions affecting global energy markets have reinforced governmental commitment to diversifying the domestic energy portfolio through increased nuclear utilization. Nuclear power equipment investments contribute directly to energy self-sufficiency objectives by enabling reliable baseload generation from domestic fuel sources with minimal import requirements. The compelling energy security rationale supports equipment procurement decisions across both established utilities and potential new market participants.
Decarbonization Commitments and Climate Policy Alignment
Japan's ambitious carbon neutrality targets require substantial expansion of zero-emission electricity generation capacity, positioning nuclear power as a critical contributor to climate objectives alongside renewable energy sources. Nuclear power equipment investments align with national and international climate commitments by enabling low-carbon baseload generation that complements variable renewable energy production. The green transformation policy framework explicitly encourages nuclear energy development as part of the decarbonization strategy, creating favorable conditions for equipment market expansion. Corporate sustainability requirements and growing environmental awareness among consumers further reinforce the demand trajectory for nuclear power equipment supporting clean energy generation. For instance, in October 2023, Japan’s Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), together with Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI), Mitsubishi FBR Systems (MFBR), and U.S.-based TerraPower, broadened their existing Memorandum of Understanding to advance sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR) technologies. The updated agreement now includes collaborative demonstration initiatives from both parties as Japan moves toward launching its fast reactor (FR) demonstration program in 2024.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges is the Japan Nuclear Power Equipment Market Facing?
Stringent Regulatory Requirements and Approval Timelines
The comprehensive safety assessment procedures established following the Fukushima incident create extended timelines for reactor restarts and equipment approval processes, constraining market growth momentum. Utilities face significant uncertainty regarding regulatory outcomes and schedules, complicating investment planning and equipment procurement decisions. The requirement for specialized safety facilities and anti-terrorism measures adds complexity and cost to restarting programs.
Local Community Opposition and Consent Processes
Securing consent from local governments and communities remains a significant challenge for nuclear facility operations, creating uncertainty for equipment investment decisions. Historical concerns regarding nuclear safety continue to influence public opinion in areas surrounding nuclear facilities. The necessity for extensive stakeholder engagement and dialogue processes extends project timelines and adds complexity to restart programs.
Workforce Constraints and Supply Chain Limitations
The extended period of reduced nuclear activity following the Fukushima incident has impacted workforce availability and supply chain capacity within the nuclear equipment sector. Specialized skills required for nuclear component fabrication and installation face shortage challenges as the industry rebuilds capabilities. Construction labor availability constraints are delaying completion of safety upgrade projects and extending equipment installation timelines.
Competitive Landscape:
The Japan nuclear power equipment market exhibits a concentrated competitive structure characterized by established domestic manufacturers with deep expertise in reactor technology and component fabrication. Market participants benefit from long-standing relationships with utility customers and a comprehensive understanding of regulatory requirements governing nuclear equipment specifications. Strategic international partnerships enable technology sharing and collaborative development of advanced reactor designs while strengthening export capabilities. The competitive landscape is evolving as manufacturers expand into next-generation reactor technologies, including small modular reactors and fast reactor systems, positioning themselves for emerging market opportunities in both domestic and international markets.
Recent Developments:
- In November 2025, the Governor of Niigata Prefecture approved the restart of two reactors at the Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Plant, the world's largest nuclear facility, marking a watershed moment for Japan's nuclear industry and creating significant equipment and maintenance demand for the facility.
Japan Nuclear Power Equipment Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Reactor Types Covered | Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR), Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR), Boiling Water Reactor (BWR), Light Water Graphite Reactor (LWGR), Gas-Cooled Reactor (GCR), Others |
| Equipment Types Covered | Island Equipment, Auxiliary Equipment |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kansai/Kinki Region, Central/ Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Japan nuclear power equipment market size was valued at USD 2.53 Billion in 2025.
The Japan nuclear power equipment market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 2.86% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 3.26 Billion by 2034.
Boiling Water Reactor (BWR) held the largest market share at 51% in 2025, driven by established infrastructure across major Japanese utilities and the successful restart of BWR units, demonstrating continued confidence in this reactor technology for reliable baseload power generation.
Key factors driving the Japan nuclear power equipment market include government policy support for nuclear energy expansion, energy security imperatives driving import dependency reduction, decarbonization commitments requiring low-carbon baseload generation, and rising electricity demand from data centers and industrial electrification.
Major challenges include stringent regulatory requirements and extended approval timelines, local community opposition requiring extensive consent processes, workforce constraints and specialized skill shortages, supply chain limitations following extended industry inactivity, and construction cost uncertainties affecting investment decisions.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












