
Japan Plant-based Seafood Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Product Type, Distribution Channel, and Region, 2026-2034
Japan Plant-based Seafood Market Summary:
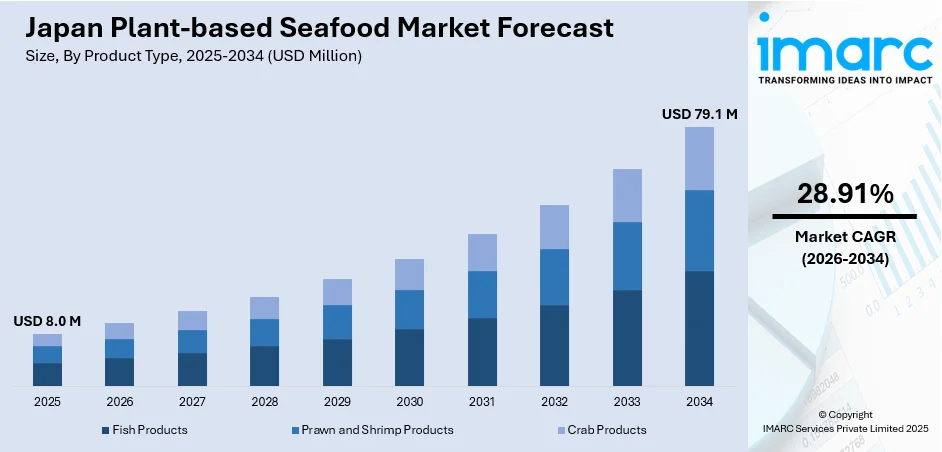
The Japan plant-based seafood market size was valued at USD 8.0 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 79.1 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 28.91% from 2026-2034.
The market expansion is driven by increasing environmental awareness concerning overfishing and marine resource depletion, rising health consciousness among consumers seeking alternatives free from mercury contamination, and growing vegan and flexitarian populations embracing sustainable dietary choices. Additionally, government initiatives supporting alternative protein development and expanding retail accessibility through supermarkets and convenience stores are enhancing the Japan plant-based seafood market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
-
By Product Type: Fish products dominate the market with a share of 50.09% in 2025, driven by strong consumer demand for plant-based alternatives to popular species like tuna and salmon, which align with traditional Japanese culinary preferences for sashimi and sushi preparations.
-
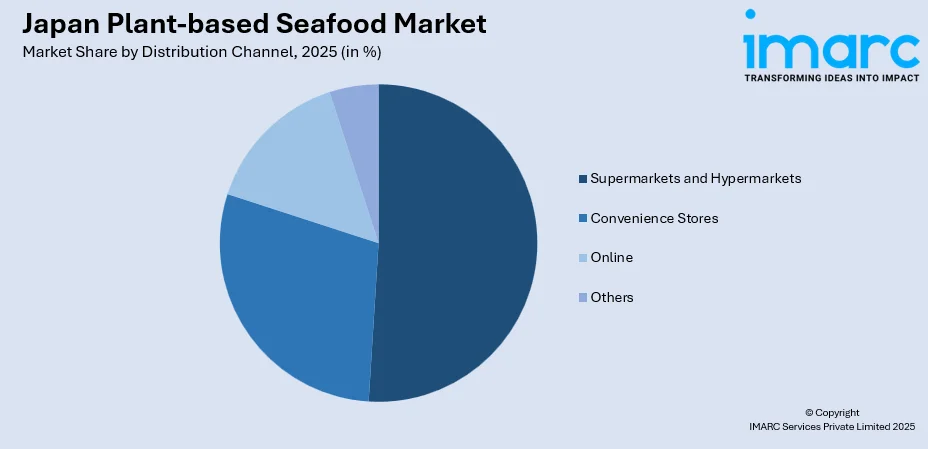
By Distribution Channel: Supermarkets and hypermarkets lead the market with a share of 50.15% in 2025, supported by expanding plant-based product aisles and strategic partnerships between retailers and food manufacturers to increase product accessibility.
-
Key Players: The Japan plant-based seafood market exhibits moderate competitive intensity, with established domestic food manufacturers leveraging their traditional seafood processing expertise to develop innovative konjac-based and plant protein alternatives alongside emerging specialized producers.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The market is witnessing significant transformation as Japanese consumers increasingly recognize the environmental impact of overfishing and seek sustainable protein sources. According to the Vegewel survey conducted in January 2023, 26.1% of Japanese respondents reported consciously minimizing their consumption of animal products, including fish and meat. This behavioral shift is particularly pronounced among younger urban demographics who prioritize sustainability and health in their food choices. Strong support from food-tech startups, advancements in plant protein formulations, and increasing availability of plant-based seafood in retail, convenience stores, and restaurant chains are strengthening the market’s momentum. Japan’s commitment to reducing environmental impact and enhancing food security aligns well with the adoption of sustainable seafood substitutes. As plant-based sushi, sashimi, tempura, and ready-to-cook options gain mainstream acceptance, the market is set for steady long-term growth and broader nationwide adoption.
Japan Plant-based Seafood Market Trends:
Rising Vegan and Flexitarian Consumer Base
Japan is experiencing notable growth in its vegan and flexitarian populations, fundamentally reshaping demand patterns for plant-based seafood alternatives. Findings from a 2023 survey indicated that 5.9% of the Japanese population identified as vegetarian or vegan. This dietary evolution is particularly evident among health-conscious urban consumers seeking sustainable alternatives to conventional seafood without sacrificing culinary traditions. Social media influence and celebrity endorsements continue to accelerate awareness and adoption of plant-based eating patterns across diverse demographic segments.
Technological Innovations in Konjac-Based Products
Manufacturers are advancing sophisticated processing technologies to create plant-based seafood products that closely replicate the texture and appearance of conventional fish. Companies are utilizing konjac flour combined with locust bean gum, dietary fiber, and specialized processing techniques to develop sashimi-grade alternatives that satisfy discerning Japanese consumers. These innovations address the unique challenge of recreating the delicate mouthfeel essential for raw fish preparations. In January 2024, NH Foods, a Japanese ham producer recognized locally as Nippon Ham, was set to launch a plant-based tuna sashimi for the food service industry. Nippon Ham’s innovative plant-based tuna sashimi was created from plant-sourced components, such as konjac flour, dietary fiber, and yeast, utilizing exclusive processing methods to mimic the tender texture of tuna.
Expanding Food Service Industry Adoption
Restaurants, hotels, and institutional food service providers are increasingly incorporating plant-based seafood into their menus to accommodate diverse dietary preferences and international tourists. This business-to-business (B2B)-focused distribution strategy enables manufacturers to gather consumer feedback and build brand recognition before broader retail expansion. Fine dining establishments and convenience store chains alike are exploring plant-based seafood applications ranging from premium kaiseki courses to ready-to-eat bento boxes. In December 2024, FamilyMart expanded its Blue Green plant-based product line across Japan.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Japan plant-based seafood market is anticipated to demonstrate robust expansion throughout the forecast period, supported by continued innovations in product formulations and expanding distribution networks. The market generated a revenue of USD 8.0 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 79.1 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 28.91% from 2026-2034. Strategic government investments in alternative protein development, combined with intensifying sustainability concerns among consumers, will catalyze market penetration across both retail and food service channels. Manufacturers focusing on authentic taste replication and price competitiveness will likely capture increasing market share as consumer acceptance accelerates.
Japan Plant-based Seafood Market Report Segmentation:
|
Segment Category |
Leading Segment |
Market Share |
|
Product Type |
Fish Products |
50.09% |
|
Distribution Channel |
Supermarkets and Hypermarkets |
50.15% |
Product Type Insights:
- Fish Products
- Prawn and Shrimp Products
- Crab Products
Fish products dominate with a market share of 50.09% of the total Japan plant-based seafood market in 2025.
Fish products represent the cornerstone of Japan's plant-based seafood market, reflecting the cultural significance of fish in traditional Japanese cuisine. Plant-based tuna, salmon, and squid alternatives have gained particular traction, as manufacturers successfully develop konjac-based formulations that replicate the appearance and texture essential for sashimi and sushi preparations. These products address growing consumer concerns about overfishing impacts on marine ecosystems while providing allergen-free and mercury-free alternatives suitable for health-conscious demographics, including pregnant women. In March 2024, Azuma Foods launched its Future Fish range under the Green Surf brand in Japan, featuring certified vegan tuna, salmon, and squid alternatives made from konjac and locust bean gum.
The fish products segment benefits from established manufacturing expertise among Japanese food companies with decades of traditional seafood processing experience. Domestic producers leverage this knowledge to achieve authentic flavor profiles compatible with wasabi and soy sauce, critical factors for consumer acceptance in the discerning Japanese market. Additionally, rising import restrictions on certain seafood species and volatile pricing in conventional fish markets are encouraging food service operators to explore plant-based alternatives that offer consistent quality and extended shelf life through frozen distribution formats.
Distribution Channel Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Supermarkets and Hypermarkets
- Convenience Stores
- Online
- Others
Supermarkets and hypermarkets lead with a share of 50.15% of the total Japan plant-based seafood market in 2025.
Supermarkets and hypermarkets serve as the primary retail gateway for plant-based seafood products, offering consumers convenient access to emerging alternatives alongside conventional seafood offerings. Major retail chains are expanding dedicated plant-based product sections, strategically positioning alternatives near traditional seafood counters to encourage trial among mainstream shoppers. Data from Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry indicated retail sales increased 2.8% year-on-year in November 2024, surpassing expectations and demonstrating continued consumer spending momentum across food categories. This retail channel strength enables manufacturers to achieve broad geographic coverage while benefiting from established cold chain infrastructure.
The supermarket and hypermarket channel facilitates consumer education through in-store tastings, clear product labeling, and promotional activities that build familiarity with plant-based seafood options. Retailers are increasingly collaborating with manufacturers on exclusive product launches and private-label offerings to differentiate their plant-based portfolios. The convenience factor of one-stop shopping combined with competitive pricing strategies positions this channel favorably for capturing both dedicated plant-based consumers and flexitarians seeking occasional sustainable alternatives to conventional seafood purchases.
Regional Insights:
- Kanto Region
- Kansai/Kinki Region
- Central/Chubu Region
- Kyushu-Okinawa Region
- Tohoku Region
- Chugoku Region
- Hokkaido Region
- Shikoku Region
The Kanto Region holds prominence in the market, driven by Tokyo's concentration of health-conscious urban consumers, innovative food startups, and international tourism generating demand for diverse dietary options, including vegan and halal-friendly alternatives.
The Kansai/Kinki Region demonstrates strong growth momentum, supported by Osaka's culinary innovation ecosystem and Osaka-Kansai Expo 2025, which is accelerating investments in sustainable and inclusive food offerings across the region.
The Central/Chubu Region exhibits expanding plant-based adoption through health-conscious consumer preferences and increasing plant-based tourism activities, with several big and small restaurants incorporating vegan seafood options to attract domestic and international visitors.
The Kyushu-Okinawa Region reflects the growing interest in plant-based alternatives, with Fukuoka's food service sector exploring innovative applications and numerous flavors and Okinawa's traditional longevity diet culture supporting sustainable protein transitions.
The Tohoku Region shows emerging demand for plant-based seafood, with local restaurants developing fish-free dipping sauces and chefs creating innovative alternatives that honor regional culinary traditions while addressing sustainability concerns.
The Chugoku Region demonstrates gradual but steady market development, with Yamaguchi's plant-based seafood market growing, as konjac-based alternatives are gaining popularity among health and wellness conscious consumers seeking sustainable and eco-friendly options.
The Hokkaido Region presents unique opportunities given its significant thriving traditional fishing industry, with Kushiro's fishing communities continuously investing in exploring alternative seafood development alongside conventional operations to diversify revenue streams.
The Shikoku Region is positioning itself as a center for innovative plant-based alternatives, with local companies developing soy-free options utilizing regionally sourced ingredients to reduce environmental impact and support local agriculture.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Japan Plant-based Seafood Market Growing?
Government Support for Alternative Protein Development
The Japanese government has demonstrated strong commitment to advancing alternative protein sectors through strategic funding initiatives and supportive policy frameworks. These investments reflect national priorities, including food security enhancement, reduced dependence on imported protein sources, and achievement of carbon neutrality targets aligned with international sustainability commitments. Regulatory bodies are actively developing safety assessment frameworks and labeling standards specifically for plant-based and cultivated protein products. In January 2024, the Japanese government granted USD 27.7 Million to two alternative protein startups: Umami United, which makes plant-based eggs, and IntegriCulture, a cultivated meat biotech firm, reflecting strategic national focus on food security and sustainable food systems development. This demonstrates governmental recognition of alternative proteins as strategically important food categories.
Marine Resource Depletion and Overfishing Concerns
Marine resource depletion and growing overfishing concerns are major forces accelerating the market growth in Japan. As traditional fish stocks decline and sustainability risks intensify, consumers and industry stakeholders are increasingly seeking responsible alternatives that lessen pressure on marine ecosystems. Japan, being a seafood-centric nation, is highly aware of the ecological impacts of overharvesting, biodiversity loss, and unstable supply chains. These issues create uncertainty around long-term seafood availability and price stability, prompting demand for substitutes that offer consistency without environmental harm. Plant-based seafood provides a solution by mimicking taste and texture while eliminating reliance on ocean resources. Food manufacturers, retailers, and restaurants are adopting these products to align with sustainability goals and meet rising consumer expectations. This shift not only supports marine conservation but also strengthens Japan’s food security, making plant-based seafood an attractive and rapidly growing category.
Health Awareness and Dietary Shift Trends
Health awareness and evolving dietary shift trends are strongly driving the Japan plant-based seafood market, as consumers increasingly prioritize cleaner eating, reduced cholesterol intake, and avoidance of contaminants such as mercury and microplastics often associated with conventional seafood. With lifestyle diseases on the rise, many Japanese consumers are adopting flexitarian and plant-forward diets that balance traditional cuisine with modern nutritional choices. Younger generations, in particular, are exploring protein alternatives that support long-term wellness without compromising taste or authenticity. Food companies are responding by creating nutrient-rich, allergen-friendly, and low-fat plant-based seafood options that align with daily dietary needs. The growing focus on label transparency and functional ingredients further fuels trust and adoption. Overall, these shifting health-conscious preferences are making plant-based seafood a preferred choice for individuals committed to long-term health and wellness. As per IMARC Group, the Japan health and wellness market is set to attain USD 291.7 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 3.47% during 2026-2034.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the Japan Plant-based Seafood Market is Facing?
Taste and Texture Replication Difficulties
Achieving authentic sensory characteristics that satisfy discerning Japanese consumers remains a significant technical challenge for plant-based seafood manufacturers. The subtle flavor profiles and delicate textures characteristic of premium sashimi and sushi preparations prove particularly difficult to replicate using plant-based ingredients. Japanese consumers' sophisticated palates and high expectations for seafood quality create substantial barriers to widespread market acceptance without continued technological advancement.
Limited Consumer Awareness and Cultural Preferences
Despite growing interest in sustainability, plant-based diets remain relatively niche in Japan compared to Western markets. Deep-rooted cultural preferences for traditional seafood preparations and skepticism toward processed food alternatives constrain mainstream adoption rates. Effective consumer education campaigns and strategic product positioning are essential to overcome perception barriers and expand market penetration beyond early adopter segments.
Price Premium Over Conventional Seafood
Plant-based seafood alternatives typically command higher retail prices compared to conventional seafood products, limiting accessibility for price-sensitive consumers. Production scale limitations, specialized ingredient sourcing requirements, and ongoing research and development (R&D) investments contribute to elevated cost structures. Achieving price parity with traditional seafood remains essential for capturing mainstream market segments and competing effectively across diverse retail and food service channels.
Competitive Landscape:
The Japan plant-based seafood market features a dynamic competitive environment comprising established domestic food manufacturers, specialized plant-based startups, and international alternative protein companies seeking market entry. Leading domestic players leverage decades of traditional seafood processing expertise to develop innovative alternatives that resonate with local taste preferences and culinary traditions. Companies are investing significantly in R&D activities to improve product formulations, enhance sensory characteristics, and expand manufacturing capabilities. Strategic partnerships between food manufacturers and retailers are accelerating product distribution and consumer awareness building. The competitive landscape emphasizes innovations in texture replication technology, clean label formulations, and sustainable sourcing practices as key differentiators for market positioning and brand development.
Recent Developments:
-
In September 2025, Mitsui DM Sugar, based in Japan, revealed plans to introduce a new vegan tuna brand in 2026. The Osakana Kakumei (or ‘Fish Revolution’) label mimics maguro, or bluefin tuna, the most valued type of the fish. The product was created by Mitsui DM Sugar's subsidiary Taisho Technos, a specialist in food additives whose technology aided in mimicking the texture and look of tuna.
Japan Plant-based Seafood Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Product Types Covered | Fish Products, Prawn and Shrimp Products, Crab Products |
| Distribution Channels Covered | Supermarkets and Hypermarkets, Convenience Stores, Online, Others |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kansai/Kinki Region, Central/Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Japan plant-based seafood market size was valued at USD 8.0 Million in 2025.
The Japan plant-based seafood market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 28.91% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 79.1 Million by 2034.
Fish products dominated the market with a share of 50.09%, driven by strong consumer demand for plant-based alternatives to popular species like tuna and salmon that align with traditional Japanese sashimi and sushi preparations.
Key factors driving the Japan plant-based seafood market include government funding initiatives for alternative protein development, growing environmental concerns about overfishing and marine resource depletion, rising health awareness among consumers, and expanding retail distribution networks.
Major challenges include difficulties in replicating authentic seafood taste and texture characteristics, limited consumer awareness and cultural preferences for traditional seafood, premium pricing compared to conventional products, and the relatively small vegan and vegetarian population base in Japan.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












