
Japan Power Transmission Equipment Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Equipment Type, Voltage Level, Application, and Region, 2026-2034
Japan Power Transmission Equipment Market Summary:
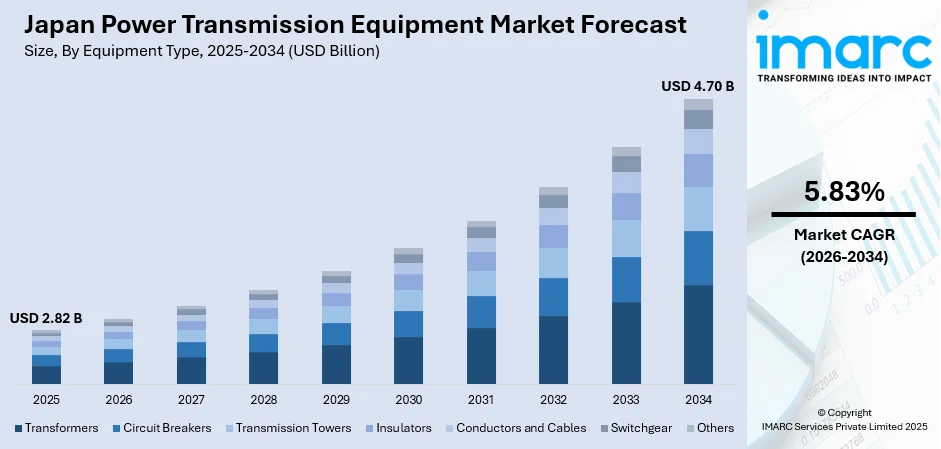
The Japan power transmission equipment market size was valued at USD 2.82 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 4.70 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 5.83% from 2026-2034.
Japan's power transmission equipment sector is experiencing robust expansion driven by the nation's aggressive clean energy transition and grid modernization initiatives. The country's commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 necessitates substantial infrastructure upgrades to accommodate growing renewable energy integration, particularly offshore wind power. Additionally, the unique dual-frequency electrical system requires specialized equipment for seamless interregional power exchange, further stimulating market demand.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Equipment Type: Transformers dominate the market with a share of 26% in 2025, driven by escalating demand for efficient voltage conversion equipment to support renewable energy integration and grid modernization across industrial and utility applications.
- By Voltage Level: High Voltage (HV) leads the market with a share of 48% in 2025, owing to extensive deployment in transmission networks connecting power generation facilities with distribution systems across Japan's regional electricity grids.
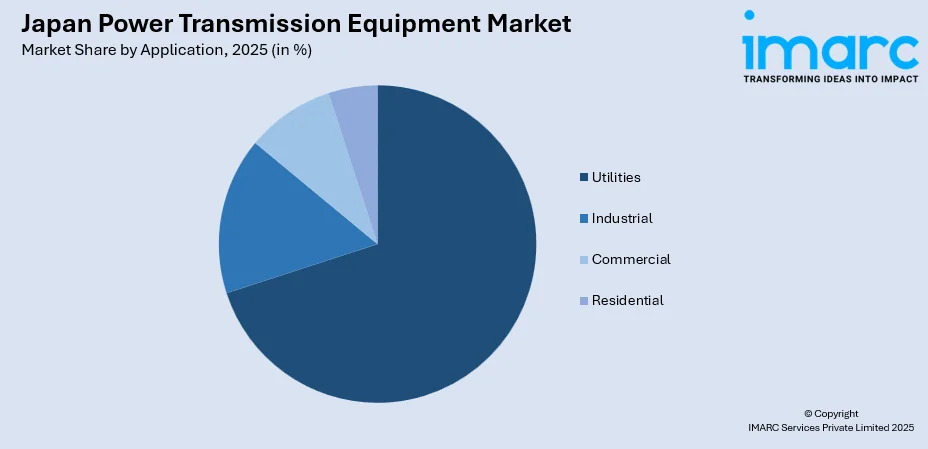
- By Application: Utilities represents the largest segment with a market share of 70% in 2025, reflecting the dominance of regional power companies in transmission infrastructure investments and ongoing grid enhancement projects.
- Key Players: The Japan power transmission equipment market features a competitive landscape characterized by established domestic manufacturers and global technology leaders, with companies focusing on advanced grid solutions, smart technologies, and sustainable equipment development to address evolving energy infrastructure requirements.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Japan's power transmission equipment market is undergoing a significant transformation as the nation accelerates its energy transition strategy. The country's unique geographical characteristics, including mountainous terrain and distributed population centers, necessitate sophisticated transmission infrastructure to ensure reliable electricity delivery. The ongoing shift toward renewable energy sources, particularly offshore wind development targeting over ten gigawatts of capacity by the end of the decade, requires substantial grid upgrades, including advanced HVDC systems and smart grid technologies. Major utilities are investing heavily in modernizing aging infrastructure while incorporating digital monitoring capabilities and automated fault detection systems. The market is also witnessing increased focus on disaster-resilient equipment designs, reflecting lessons learned from past natural disasters. Manufacturers are responding with innovative solutions, including SF₆-free switchgear and compact substation designs optimized for Japan's space constraints.
Japan Power Transmission Equipment Market Trends:
Grid Modernization and Smart Technology Integration
Japan's transmission infrastructure is embracing comprehensive digital transformation to meet future energy requirements. Utilities are deploying automated grid management systems, real-time monitoring platforms, and advanced analytics to optimize power flow and enhance network reliability. The Japan grid modernization market size reached USD 2,240.19 Million in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 12,125.70 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 20.64% during 2025-2033. The nation's unique dual-frequency electrical system necessitates upgraded frequency converters for seamless interregional power exchange. Smart meters numbering in the tens of millions enable precise demand management, while next-generation switchgear designs featuring compact and fully insulated configurations are replacing legacy equipment across substations nationwide.
HVDC Development for Renewable Energy Integration
The expansion of renewable energy capacity, particularly offshore wind installations, is driving substantial investment in high-voltage direct current transmission systems throughout Japan. HVDC technology offers superior efficiency for long-distance power transmission, reducing energy losses significantly compared to conventional alternating current lines. This technology proves essential for connecting remote generation sites, including offshore wind farms, with mainland consumption centers. Major infrastructure projects include submarine cable installations and converter station developments designed to enhance interregional transmission capacity and grid stability. For instance, in October 2023, Mitsubishi Electric was commissioned by J-Power Transmission Network to deliver a 300 MW Voltage Source Converter–based HVDC system for the Shin-Sakuma Frequency Converter Station. The new installation will strengthen the power link between Japan’s eastern and western grid regions by improving interregional transmission capability.
Disaster Resilience and Energy Security Enhancement
Japan's vulnerability to natural disasters, including earthquakes, typhoons, and tsunamis, has elevated the importance of resilient transmission infrastructure. Utilities are prioritizing investments in reinforced transmission towers, underground cabling systems, and rapid fault detection technologies to minimize outage durations. Microgrid deployments and distributed energy storage solutions provide localized power continuity when main grid connections become compromised. These initiatives align with national energy security objectives while ensuring stable electricity delivery to critical facilities during emergencies.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Japan power transmission equipment market demonstrates promising growth prospects supported by ambitious national energy policies and substantial infrastructure investment commitments. The government's Strategic Energy Plan targeting renewable energy to comprise forty to fifty percent of the power generation mix by 2040 necessitates extensive grid expansion and modernization. Offshore wind development programs, smart grid initiatives, and interregional transmission enhancement projects will sustain equipment demand throughout the forecast period. The market generated a revenue of USD 2.82 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 4.70 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 5.83% from 2026-2034.
Japan Power Transmission Equipment Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment Type | Transformers | 26% |
| Voltage Level | High Voltage (HV) | 48% |
| Application | Utilities | 70% |
Equipment Type Insights:
- Transformers
- Circuit Breakers
- Transmission Towers
- Insulators
- Conductors and Cables
- Switchgear
- Others
The transformers segment dominates with a market share of 26% of the total Japan power transmission equipment market in 2025.
Transformers constitute the foundational component of Japan's power transmission infrastructure, enabling efficient voltage conversion across the electricity supply chain. The segment benefits from ongoing grid modernization programs requiring replacement of aging assets with energy-efficient models meeting enhanced regulatory standards. Utilities are increasingly deploying advanced transformer technologies featuring improved thermal management and reduced environmental impact to support renewable energy integration objectives.
The transformer market is further stimulated by data center proliferation and industrial electrification trends driving incremental capacity requirements. The Japan transformer market size was valued at USD 4,728.36 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 9,236.45 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 7.72% from 2026-2034. Japanese manufacturers are introducing innovations, including compact designs optimized for urban substation applications and digital monitoring capabilities, enabling predictive maintenance. Recent consolidation activities within the domestic transformer industry aim to enhance production capacity and technological capabilities to address growing market demand.
Voltage Level Insights:
- High Voltage (HV)
- Extra High Voltage (EHV)
- Ultra High Voltage (UHV)
The high voltage (HV) segment leads with a share of 48% of the total Japan power transmission equipment market in 2025.
High voltage transmission equipment forms the backbone of Japan's regional electricity networks, facilitating bulk power transfer between generation facilities and distribution systems. The segment encompasses essential infrastructure components deployed across transmission corridors linking power plants with load centers throughout the country. Ongoing investment in grid reinforcement projects and renewable energy interconnection drives sustained demand for high voltage equipment.
The expansion of interregional transmission capacity represents a strategic priority requiring substantial high-voltage infrastructure deployment. Projects enhancing connectivity between Japan's major electricity service areas necessitate coordinated investment in transmission lines, substations, and associated equipment. The segment also benefits from replacement cycles as utilities upgrade aging high voltage assets to improve network reliability and operational efficiency.
Application Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Utilities
- Industrial
- Commercial
- Residential
The utilities segment exhibits a clear dominance with a 70% share of the total Japan power transmission equipment market in 2025.
Japan's ten regional electric power companies and transmission operators represent the primary demand drivers within the utilities segment. These organizations maintain extensive transmission infrastructure requiring continuous investment in equipment replacement, capacity expansion, and technological upgrades. Government policies promoting grid modernization and renewable energy integration channel substantial capital expenditure toward utility-scale transmission projects across all service territories.
The utilities segment is further propelled by strategic initiatives enhancing interregional transmission capacity to improve grid flexibility and energy security. Projects increasing interconnection between Japan's eastern and western frequency zones require specialized equipment including frequency converters and HVDC systems. Additionally, offshore wind development programs necessitate utility investment in transmission infrastructure connecting marine generation facilities with onshore grid networks.
Regional Insights:
- Kanto Region
- Kansai/Kinki Region
- Central/ Chubu Region
- Kyushu-Okinawa Region
- Tohoku Region
- Chugoku Region
- Hokkaido Region
- Shikoku Region
Kanto’s power transmission equipment demand is fueled by its dense urban centers, expansive commercial activity, and continuous electricity consumption from IT clusters, transportation systems, and large residential zones. Upgrades to grid infrastructure are essential to support rising electrification, renewable integration, and resilience against natural disasters. Major utilities are investing in advanced substations, high-voltage lines, and smart grid technology to ensure a stable supply across metropolitan Tokyo and surrounding prefectures.
Kansai’s industrial concentration, spanning manufacturing, chemical processing, and heavy engineering, drives robust requirements for reliable transmission infrastructure. The region’s energy strategy focuses on modernizing aged grid assets while enhancing interconnection capacity with neighboring areas to stabilize supply. Growing renewable installations across coastal prefectures further accelerate demand for advanced transmission equipment capable of balancing variable loads and reinforcing grid reliability for urban centers such as Osaka, Kyoto, and Kobe.
Chubu’s strong automotive and precision manufacturing base creates significant power needs, pushing utilities to invest in resilient and efficient transmission networks. The region’s mixed energy portfolio, including hydro and solar assets, requires upgraded high-voltage lines and digital monitoring systems to optimize load distribution. Ongoing development around major industrial corridors and transportation hubs also boosts the installation of modern substations and grid-stabilizing technologies to support uninterrupted operations.
Kyushu-Okinawa’s transmission market is shaped by its rapidly expanding renewable portfolio, particularly solar and geothermal projects. Integrating these variable resources into the grid necessitates advanced transmission equipment, voltage regulation systems, and enhanced inter-island connectivity. The region’s dispersed population centers and reliance on stable energy supply for agriculture, tourism, and industry further drive investment in robust transmission infrastructure equipped to handle long-distance power flow and fluctuating generation patterns.
Tohoku’s growing wind and solar generation base is the primary driver for modern transmission equipment capable of linking remote renewable sites with demand centers. Post-disaster resilience initiatives continue to influence grid reinforcement and modernization programs, emphasizing seismic-resistant infrastructure and high-efficiency transformers. Industrial revitalization efforts across inland prefectures also contribute to sustained demand for reliable power delivery and grid expansion to support new production facilities.
Chugoku’s demand is propelled by its metal processing, shipbuilding, and heavy industry sectors that require consistent energy supply. Efforts to connect large-scale renewable production—particularly from offshore wind developments—to the national grid strengthen the need for upgraded transmission lines and substations. Modernization of legacy grid assets and growing electrification in urban areas such as Hiroshima drive continuous adoption of high-performance transmission equipment and smart grid technologies.
Hokkaido’s vast geography and strong renewable energy potential, especially in wind and solar, create substantial demand for long-distance, high-capacity transmission solutions. Integrating remote generation sites with mainland Japan’s grid requires advanced interconnection systems and grid-stabilizing equipment. The region’s harsh climate conditions also necessitate weather-resistant technologies and robust infrastructure upgrades to ensure stable power supply for residential, commercial, and agricultural users.
Shikoku’s power transmission equipment market is driven by its reliance on stable energy for manufacturing clusters and widespread agricultural activities. Increasing adoption of renewable energy sources, particularly hydropower and solar, requires equipment capable of managing variable electricity inputs. Investments in grid modernization, improved disaster resilience, and enhanced inter-regional transmission links support strengthening the region’s energy reliability and ensuring consistent power delivery across its smaller but widely dispersed communities.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Japan Power Transmission Equipment Market Growing?
Accelerated Renewable Energy Integration and Grid Expansion
Japan's ambitious clean energy targets are fundamentally reshaping transmission infrastructure requirements across the country. The national Strategic Energy Plan envisions renewable sources comprising forty to fifty percent of electricity generation by 2040, necessitating extensive grid modifications to accommodate variable power inputs. Offshore wind development programs targeting substantial capacity additions require new transmission corridors and submarine cable installations connecting marine generation facilities with mainland consumption centers. Solar photovoltaic proliferation similarly demands distribution network enhancements and smart grid deployments, enabling bidirectional power flows. These renewable integration imperatives generate sustained demand for transformers, switchgear, and control systems optimized for variable generation characteristics. For instance, in October 2025, Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions Corporation (Toshiba) revealed plans to substantially increase its investment in the power transmission and distribution (T&D) equipment sector as worldwide electricity demand continues to rise. The company intends to allocate 55 billion yen by FY2027, an initiative that is projected to more than double the production capacity of its major manufacturing sites in Japan and India by FY2030 compared with FY2024 levels.
Infrastructure Modernization and Aging Asset Replacement
Japan's transmission infrastructure includes substantial equipment approaching or exceeding designed service life, creating significant replacement demand across all equipment categories. Utilities face imperative to upgrade legacy systems with modern alternatives offering improved efficiency, reliability, and digital capabilities. The transition encompasses transformers, circuit breakers, transmission towers, and associated components throughout regional electricity networks. Government policies establishing enhanced efficiency standards for distribution transformers accelerate replacement cycles while promoting energy conservation objectives. This modernization wave encompasses both equipment replacement and technological upgrades integrating smart monitoring, automated controls, and predictive maintenance capabilities into transmission operations.
Interregional Transmission Capacity Enhancement
Strategic initiatives strengthening transmission connectivity between Japan's regional electricity service areas represent a major investment driver. The country's historical grid architecture features limited interregional transfer capacity, constraining optimal resource utilization and emergency power sharing. Government-coordinated programs are expanding interconnection capacity between major load centers and generation-rich regions, requiring substantial deployment of transmission lines, substations, and frequency conversion equipment. Japan's unique dual-frequency electrical system necessitates specialized converters for power exchange between eastern and western grid zones. These capacity enhancement projects span multiple years and involve coordinated equipment procurement across participating utilities.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the Japan Power Transmission Equipment Market is Facing?
Supply Chain Constraints and Material Cost Pressures
Global supply chain disruptions and elevated raw material costs present significant challenges for transmission equipment manufacturers and project developers. Extended lead times for critical components including specialized steel, copper conductors, and transformer cores impact project timelines and budget requirements. These constraints particularly affect large-scale infrastructure projects requiring coordinated equipment deliveries across multiple categories.
Regulatory and Permitting Complexities
Japan's comprehensive environmental assessment requirements and multi-stakeholder coordination processes extend transmission project development timelines. New transmission line routing involves extensive consultations with local communities, landowners, and fishery associations, particularly for offshore interconnections. These procedural requirements, while ensuring appropriate stakeholder engagement, create implementation challenges for time-sensitive grid expansion initiatives.
Technical Workforce Availability
The specialized nature of transmission equipment installation, maintenance, and operation creates workforce availability challenges as experienced personnel retire. Training and certification requirements for high-voltage electrical work limit rapid workforce expansion. This demographic challenge affects both equipment manufacturers and utility maintenance operations, potentially constraining market growth and project execution capabilities.
Competitive Landscape:
The Japan power transmission equipment market exhibits a competitive structure featuring established domestic manufacturers alongside global technology leaders pursuing market opportunities. Major Japanese industrial conglomerates maintain strong positions across transformer, switchgear, and transmission system segments, leveraging longstanding relationships with regional utilities and a deep understanding of local requirements. International suppliers compete through advanced technology offerings, particularly in specialized areas including HVDC systems and environmentally sustainable equipment designs. The competitive landscape is characterized by ongoing consolidation activities, strategic partnerships, and capacity expansion investments as participants position for anticipated demand growth. Manufacturers are increasingly differentiating through digital solutions, service capabilities, and environmental performance credentials to address evolving customer priorities.
Recent Developments:
- In December 2024, Hitachi Energy announced plans to supply Japan's first SF₆-free 300 kV EconiQ™ circuit-breakers to Chubu Electric Power Grid, supporting the utility's zero emissions target by 2050 through environmentally sustainable switchgear technology.
- In April 2024, Hitachi Industrial Equipment Systems and Mitsubishi Electric announced an agreement to transfer Mitsubishi Electric's distribution transformer business, consolidating domestic manufacturing capabilities to address growing market demand.
Japan Power Transmission Equipment Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Equipment Types Covered | Transformers, Circuit Breakers, Transmission Towers, Insulators, Conductors and Cables, Switchgear, Others |
| Voltage Levels Covered | High Voltage (HV), Extra High Voltage (EHV), Ultra High Voltage (UHV) |
| Applications Covered | Utilities, Industrial, Commercial, Residential |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kansai/Kinki Region, Central/ Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Japan power transmission equipment market size was valued at USD 2.82 Billion in 2025.
The Japan power transmission equipment market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 5.83% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 4.70 Billion by 2034.
Transformers dominated the equipment type segment with approximately 26% market share in 2025, driven by extensive demand from grid modernization programs and renewable energy integration requirements across Japan's regional electricity networks.
Key factors driving the Japan power transmission equipment market include accelerated renewable energy integration requiring grid expansion, infrastructure modernization replacing aging transmission assets, interregional transmission capacity enhancement initiatives, and growing emphasis on disaster-resilient equipment designs.
Major challenges include supply chain constraints affecting equipment availability and project timelines, complex regulatory and permitting processes extending development schedules, technical workforce limitations as experienced personnel retire, and elevated material costs impacting project economics.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












