
Japan Waste to Energy Solutions Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Technology, Waste Type, and Region, 2026-2034
Japan Waste to Energy Solutions Market Summary:
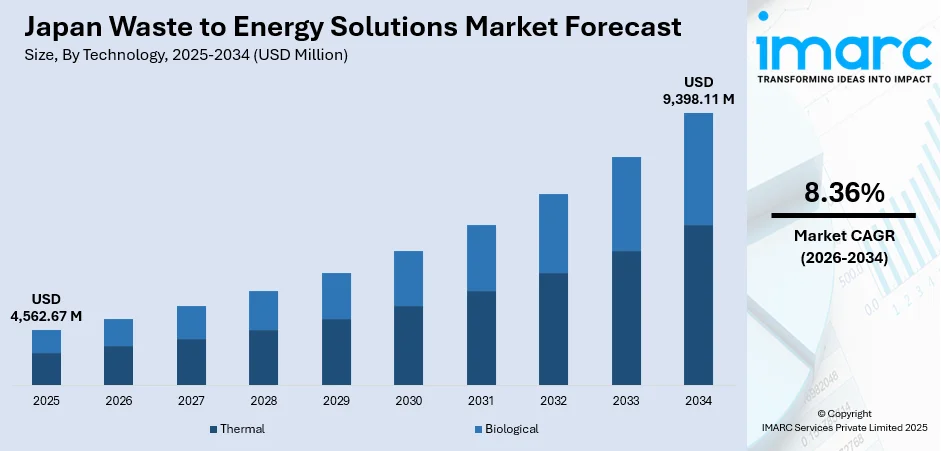
The Japan waste to energy solutions market size was valued at USD 4,562.67 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 9,398.11 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 8.36% from 2026-2034.
The Japan waste to energy solutions market is expanding as the country prioritizes sustainable waste management practices and accelerates its decarbonization efforts. Robust government policies supporting renewable energy adoption, combined with stringent environmental regulations, are driving investments in advanced thermal and biological conversion technologies. Japan's limited landfill capacity and high population density necessitate efficient waste processing solutions that simultaneously address waste management challenges and energy security concerns. The integration of waste-to-energy systems within urban infrastructure is strengthening adoption rates, while technological innovations in incineration and gasification are enhancing energy recovery efficiency, positioning the market for sustained expansion and contributing to the Japan waste to energy solutions market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Technology: Thermal technology dominates the market with a share of 80% in 2025, reflecting Japan's extensive investment in advanced incineration and gasification infrastructure for efficient municipal waste processing.
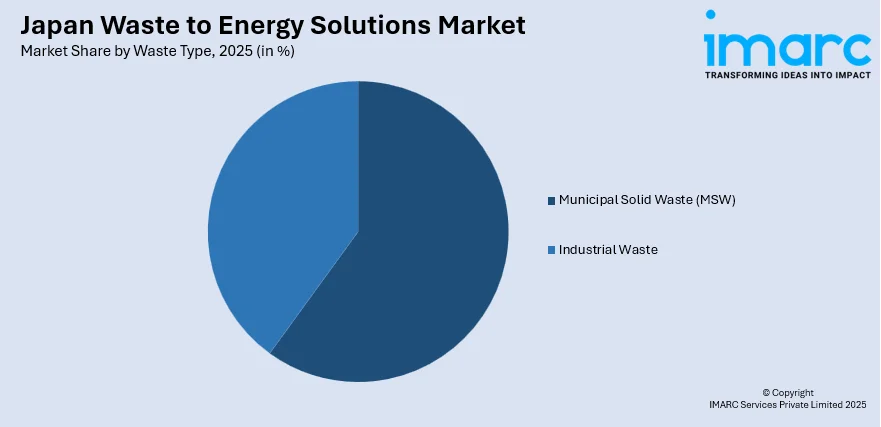
- By Waste Type: Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) leads the market with 60% share in 2025, driven by high urban waste generation volumes and comprehensive municipal waste management frameworks across major metropolitan regions.
- Key Players: The Japan waste to energy solutions market exhibits significant competitive activity, with major engineering conglomerates expanding their technology portfolios, investing in next-generation thermal systems, and pursuing strategic partnerships to enhance market presence and technological capabilities.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The Japan waste to energy solutions market is progressing as municipalities, industrial operators, and private enterprises embrace advanced waste processing technologies to meet sustainability objectives. Government support through the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) under the Green Innovation Fund, with a budget of JPY 44.5 billion, is funding carbon-neutral waste and resource-circulation systems, including high-efficiency incineration with emissions control and advanced biogas/CCUS technologies. Advanced incineration systems with high-efficiency power generation capabilities are being deployed across urban centers, while biogas technologies are gaining traction for organic waste processing. The convergence of waste management imperatives, energy security priorities, and environmental commitments is positioning waste-to-energy solutions as integral components of Japan's sustainable energy infrastructure.
Japan Waste to Energy Solutions Market Trends:
Advanced Thermal Conversion Technologies
Japan is witnessing significant advancements in thermal conversion technologies, with manufacturers developing high-efficiency stoker systems and gasification units that optimize energy recovery while minimizing environmental impact. Direct melting systems and advanced incineration technologies are being deployed to reduce final landfill waste to approximately 3% compared to 15% from conventional grate systems. For instance, in June 2024, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Environmental & Chemical Engineering received a JPY 67.68 billion contract from Yokohama City to rebuild the Hodogaya Plant using proprietary V-type stoker technology with a disposal capacity of 1,050 tonnes per day. These developments are supporting Japan waste to energy solutions market growth by enhancing operational efficiency and environmental performance.
Biogas Integration and Circular Economy Initiatives
The integration of biogas technologies within municipal waste management frameworks is accelerating as Japan advances circular economy principles. Anaerobic digestion facilities are being established to convert food waste, sewage sludge, and agricultural residues into renewable energy while producing valuable digestate for agricultural applications. The Sagamihara Biogas Power Plant, operational since August 2023, exemplifies this trend by converting pig feed waste and food waste into 4,500 MWh of renewable electricity annually through anaerobic digestion. This approach aligns with Japan's MIDORI Strategy, which emphasizes sustainable resource utilization and organic waste valorization across agricultural and urban systems.
Smart Grid Integration and Combined Heat and Power Systems
Modern waste-to-energy facilities in Japan are increasingly incorporating smart grid technologies and combined heat and power systems to maximize energy utilization efficiency. The Japan smart grid market size reached USD 3.6 Billion in 2025. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 10.7 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 13.07% during 2026-2034. Advanced facilities generate electricity while supplying thermal energy to district heating networks, industrial processes, and community facilities. Tokyo’s network of advanced incineration plants reflects this integrated strategy, producing significant revenue through electricity generation while supplying heat to nearby public facilities such as swimming pools and greenhouses. The introduction of AI-enabled remote monitoring and automated control systems is further strengthening operational efficiency, improving plant reliability, and lowering overall operating costs.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Japan waste to energy solutions market is positioned for substantial expansion as the country intensifies decarbonization efforts and modernizes aging waste management infrastructure. Government commitments to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050 and reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 46% by 2030 are driving substantial investments in advanced conversion technologies. Municipal reconstruction projects addressing superannuated facilities are creating significant opportunities for technology upgrades and capacity expansion. The market generated a revenue of USD 4,562.67 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 9,398.11 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 8.36% from 2026-2034.
Japan Waste to Energy Solutions Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Thermal | 80% |
| Waste Type | Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) | 60% |
Technology Insights:
- Thermal
- Biological
Thermal technology dominates the market with 80% share of the total Japan waste to energy solutions market in 2025.
Japan has emerged as a global frontrunner in thermal waste-to-energy technologies, supported by a vast network of modern incineration facilities. Its highly developed thermal infrastructure enables the effective conversion of municipal waste into usable energy, helping reduce reliance on landfills. Through continuous innovation, strict environmental standards, and strong government support, the country has built an efficient system that emphasizes energy recovery, sustainability, and responsible waste management as core pillars of its national waste strategy. Thermal technologies including stoker incinerators, fluidized bed systems, and gasification units, are deployed across municipalities to address waste management requirements while generating reliable baseload electricity.
Technological innovations are enhancing thermal system performance and environmental compliance. For instance, in April 2023, MHIEC received an order from the Clean Authority of Tokyo to rebuild the Kita Incineration Plant using V-type stoker technology achieving Japan's highest power generation efficiency levels. The facility incorporates high-efficiency power generation capabilities while reducing unburned combustibles in post-combustion ash. Advanced emission control systems utilizing bag filters, activated carbon injection, and catalytic decomposition ensure compliance with stringent dioxin and pollutant regulations.
Waste Type Insights:
Access the Comprehensive Market Breakdown Request Sample
- Municipal Solid Waste (MSW)
- Industrial Waste
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) leads the market with a 60% share of the total Japan waste to energy solutions market in 2025.
Municipal solid waste processing constitutes the foundation of Japan's waste-to-energy sector, driven by high urban population density and comprehensive waste collection infrastructure. Japan’s municipalities handle a substantial volume of waste each year, supported by well-structured collection systems that cover almost all major urban areas. The treatment of household, commercial, and non-recyclable waste through advanced thermal and biological processes helps reduce overall waste volumes while contributing to the country’s goals for renewable energy production and sustainable resource management.
Government regulations mandating municipal waste management plans and restricting landfill disposal are strengthening MSW processing infrastructure investments. Tokyo's integrated waste management system processes approximately 8,000 tonnes of household waste daily through 19 advanced incineration plants, achieving complete collection rates while generating electricity for grid supply. Japan’s limited and steadily shrinking landfill space underscores the growing importance of waste-to-energy solutions. With disposal sites nearing capacity, the country is prioritizing technologies that reduce waste volumes while generating usable energy. This shift supports long-term sustainability goals, strengthens resource efficiency, and ensures more resilient waste management across municipalities.
Regional Insights:
- Kanto Region
- Kansai/Kinki Region
- Central/Chubu Region
- Kyushu-Okinawa Region
- Tohoku Region
- Chugoku Region
- Hokkaido Region
- Shikoku Region
High population density and huge municipal waste volumes in Tokyo and surrounding prefectures drive WtE demand. Limited landfill space and strong local air-quality regulations push modernization of incinerators with energy recovery and stricter emissions controls. Urban energy demand and circular-economy policies make rooftop/onsite heat and power recovery and ash-reuse technologies commercially attractive.
Kansai’s industrial and urban mix (Osaka, Kyoto, Hyogo) increases both industrial and municipal waste streams, prompting investment in high-efficiency thermal WtE and material recovery systems. Regional government programs and environmental education encourage cleaner incineration tech, heat networks and resource recovery to support local manufacturing and reduce landfill reliance. Grid integration and utility partnerships accelerate electricity export from WtE plants.
Chubu’s manufacturing base (Aichi/Nagoya) and strong local energy players foster WtE projects that supply process heat and grid power. Industrial symbiosis, using recovered energy on-site, and utility decarbonization roadmaps encourage advanced combustion, CHP and ash-to-material solutions. Ongoing plant renewals and orders for modern facilities show municipalities replacing small, inefficient units with large, efficient WtE installations.
Island geography and growing regional energy needs (including tourism in Okinawa) raise the value of decentralized, reliable energy from waste. Constraints on landfill area and high logistics costs for waste transport push local WtE deployment, co-generation for district heating/cooling, and small modular plants. Regional renewal efforts and disaster-resilient energy systems further favor on-island WtE solutions.
Tohoku’s post-disaster reconstruction and resilience priorities, plus dispersed populations, make local WtE attractive for stable energy and waste capacity. Investment focuses on modern, low-emission incinerators, heat recovery for community use, and technologies that handle seasonal organic waste. Policy emphasis on regional self-sufficiency and environmental restoration accelerates projects that combine energy recovery with robust emissions control.
Chugoku’s mix of smaller cities and industrial clusters drives demand for medium-scale WtE facilities that prioritize efficient heat recovery and ash recycling for construction use. Limited landfill space and aging plants necessitate upgrades to meet national emissions standards. Municipal consolidation of waste services and public–private partnerships encourage investment in modern thermal treatment and materials-recovery technologies.
Cold climate and long distribution distances raise local energy value, so WtE plants that provide district heating and reliable winter power are prioritized. Sparse populations and remote communities favor modular, multi-service WtE solutions (electricity + heat). Harsh weather and logistics constraints also encourage ash reuse and local processing to reduce transport and bolster regional energy security.
Shikoku’s smaller, spread-out municipalities face landfill constraints and higher per-capita waste transport costs, making regionalized WtE hubs attractive. Drivers include municipal cost sharing, emphasis on emission-controlled incineration, and conversion of waste heat for local industrial or district uses. Plant modernization and consolidation help achieve economies of scale while meeting national environmental standards.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Japan Waste to Energy Solutions Market Growing?
Government Policy Support and Carbon Neutrality Commitments
Japan's ambitious decarbonization agenda is driving substantial investments in waste-to-energy infrastructure as the country pursues carbon neutrality by 2050 and targets 46% greenhouse gas emission reductions by 2030. The government has positioned waste-to-energy as a critical component of both waste management and renewable energy strategies, providing financial subsidies, tax incentives, and regulatory support to accelerate technology deployment. Japan's updated energy plan emphasizes renewable energy expansion with renewables expected to constitute 40-50% of the energy mix by 2040. For instance, the Ministry of the Environment's medium-to-long-term scenario for the waste and resource recycling sector, presented in August 2021, outlines pathways for achieving carbon neutrality through enhanced energy recovery from waste. These policy frameworks are creating favorable conditions for market expansion while ensuring alignment with national climate objectives.
Technological Innovation and Energy Security Imperatives
Continuous technological advancement in thermal and biological conversion systems is strengthening market growth by enhancing efficiency, safety, and environmental performance. Japan's engineering expertise is driving innovations in incineration, gasification, and anaerobic digestion technologies that optimize energy recovery while meeting stringent emission standards. The country's emphasis on energy security following past supply disruptions has elevated the importance of domestically sourced energy production. For instance, in November 2024, Powerhouse Energy Group announced the granting of Japanese Patent 7577260 for its Thermal Conversion Chamber technology producing synthesis gas from non-recyclable wastes. Additionally, in February 2024, Hitachi Zosen Corporation proposed the Development of High CO2 Concentration Waste Incineration Technology under NEDO's carbon neutrality project, focusing on capturing and separating CO2 emissions from incineration processes. These technological developments reinforce Japan's position as a global leader in waste-to-energy solutions.
Limited Landfill Capacity and Stringent Environmental Regulations
Japan's geographic constraints and limited landfill availability are fundamental drivers of waste-to-energy adoption, as the country seeks alternatives to land-intensive disposal methods. Mountainous terrain and dense urban development restrict landfill expansion, compelling municipalities to prioritize waste volume reduction through thermal processing. Stringent waste management regulations require municipalities to develop long-term waste processing plans and maintain comprehensive treatment capabilities. As of March 2024, Japan's remaining landfill capacity stood at approximately 95.75 million cubic meters, representing 24.8 years of remaining capacity. These constraints, combined with regulatory frameworks promoting waste reduction, recycling, and energy recovery, are accelerating infrastructure investments and driving market expansion across all regions.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the Japan Waste to Energy Solutions Market is Facing?
High Capital Investment Requirements
The substantial upfront capital investment required for waste-to-energy facility construction presents challenges for smaller municipalities and private investors. Advanced thermal systems with high-efficiency power generation and comprehensive emission control capabilities demand significant financial resources for design, construction, and commissioning. These capital constraints can delay project implementation and limit market expansion in regions with constrained municipal budgets.
Complex Regulatory Processes and Approval Timelines
Japan's comprehensive regulatory framework governing waste-to-energy facility development involves complex approval processes and extended timelines that can impede project advancement. Environmental impact assessments, community consultations, and multi-agency permitting requirements add complexity and duration to project development cycles. These procedural requirements, while ensuring environmental protection and community engagement, can delay facility commissioning and market growth.
Public Perception and Community Concerns
Community opposition to waste-to-energy facilities based on concerns regarding air emissions, health impacts, and visual aesthetics can present obstacles to project development. Despite advanced emission control technologies that significantly reduce pollutant releases, historical perceptions of incineration facilities persist in some communities. Effective stakeholder engagement and community education programs are essential for building public acceptance and enabling successful project implementation.
Competitive Landscape:
The Japan waste to energy solutions market is characterized by active competition among established engineering conglomerates and specialized environmental technology providers. Market participants are focusing on technological differentiation through advanced thermal systems, improved energy recovery efficiency, and enhanced emission control capabilities. Strategic partnerships between technology providers and municipal authorities are facilitating project development and operational excellence. Companies are investing in research and development to advance next-generation technologies including gasification, biogas production, and carbon capture integration. Long-term operation and maintenance contracts are strengthening customer relationships while creating recurring revenue streams and reinforcing market positions across the competitive landscape.
Recent Developments:
- May 2025: JFE Engineering partnered with four major restaurant chains in Japan, including Akindo Sushiro and Food & Life Companies, to generate electricity from biogas sourced from food waste. The initiative sells the power it produces back to participating restaurant establishments, demonstrating circular-economy principles in the foodservice industry.
- February 2025: Asahi Kasei and Kurashiki City inaugurated a biogas purification system at the Kojima Sewage Treatment Plant in Okayama Prefecture. The system uses zeolite and pressure-vacuum swing adsorption technology to separate CO2 and produce high-purity biomethane from sewage sludge biogas, supporting carbon neutrality and renewable energy objectives, with commercialization expected around 2027.
Japan Waste to Energy Solutions Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Technologies Covered | Thermal, Biological |
| Waste Types Covered | Municipal Solid Waste (MSW), Industrial Waste |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kansai/Kinki Region, Central/ Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Japan waste to energy solutions market size was valued at USD 4,562.67 Million in 2025.
The Japan waste to energy solutions market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 8.36% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 9,398.11 Million by 2034.
Thermal technology, accounting for 80% market share in 2025, dominates due to Japan's extensive investment in advanced incineration and gasification infrastructure for efficient waste processing and energy recovery across municipal applications.
Key factors driving the Japan waste to energy solutions market include government carbon neutrality commitments, limited landfill capacity, stringent environmental regulations, technological innovations in thermal systems, and energy security imperatives driving domestic renewable energy production.
Major challenges include high capital investment requirements for advanced facilities, complex regulatory approval processes, extended project development timelines, public perception concerns regarding emissions, and community engagement requirements for facility siting.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












