
Microinsurance Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Product Type, Provider, Model Type, and Region, 2026-2034
Microinsurance Market Size and Share:
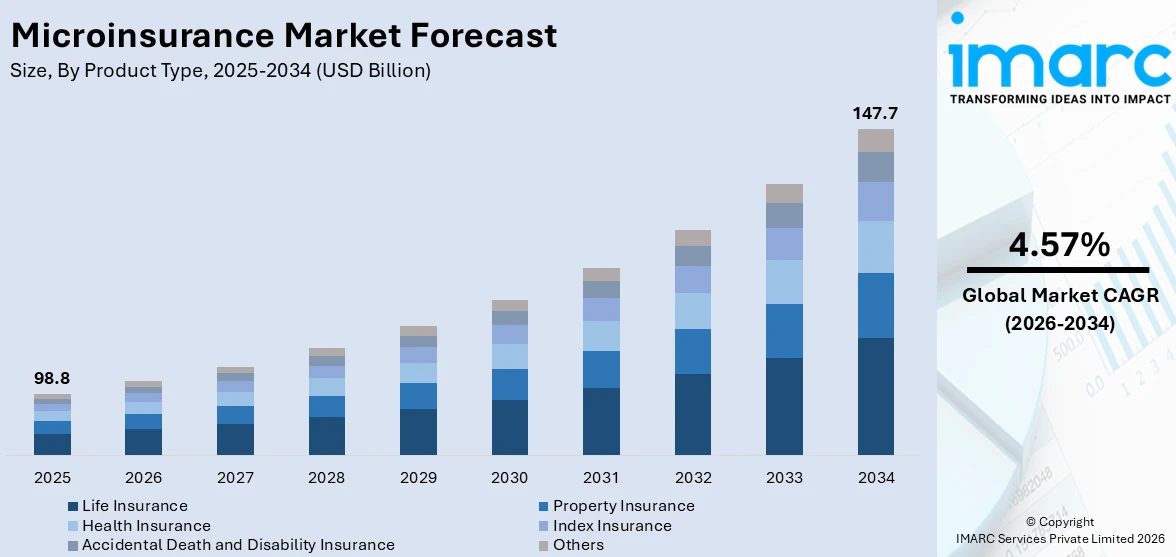
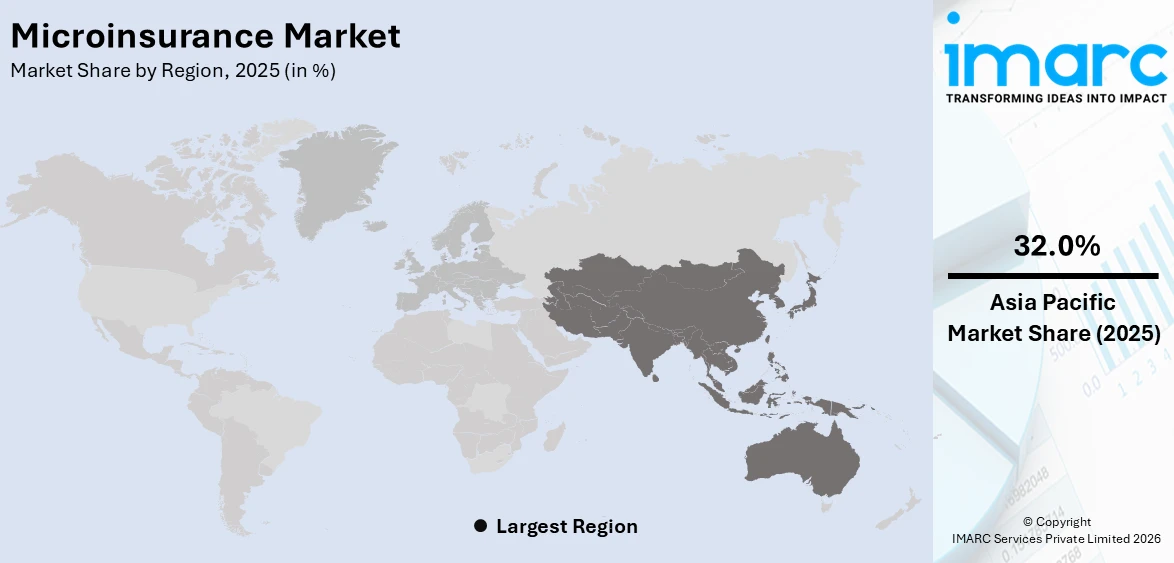
The global microinsurance market size reached USD 98.8 Billion in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach USD 147.7 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 4.57% during 2026-2034. Asia Pacific currently dominates the market with 32.0% of the total market share. The market is experiencing steady growth driven by the rising focus on maintaining financial inclusion by governing agencies, increasing integration of big data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI), and rising number of public awareness campaigns to educate citizens.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
|
Market Size in 2025
|
USD 98.8 Billion |
|
Market Forecast in 2034
|
USD 147.7 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 4.57% |
The global microinsurance market is driven by the rising awareness of financial security among low-income population, particularly in emerging economies. In line with this, the increasing focus of insurers on underserved markets is creating lucrative opportunities in the market. Along with this, governments and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) increasingly promoting microinsurance as a tool for poverty alleviation, thereby accelerating market adoption. Continual technological advancements, such as mobile-based platforms and digital payment systems, are simplifying policy distribution and claim processing, making microinsurance more accessible, which is positively influencing the market. On 23rd May 2024, the government of India announced the launching of the National Health Claim Exchange (NHCX) portal, developed under the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM). It streamlines health insurance claims processing nationwide. It is designed for interoperability and transparency and will integrate with 40-45 insurers and 200-250 hospitals, enabling seamless data exchange in a standardized, FHIR-compliant format. Major insurers such as Paramount TPA, Tata AIG and Bajaj Allianz have already completed integration. Additionally, the growing need for risk management solutions in sectors such as agriculture, healthcare, and small enterprises is propelling demand. Furthermore, strategic collaborations between insurers and microfinance institutions enhance product reach and affordability, which is broadening the market scope.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The United States stands out as a key regional market, primarily driven by the growing emphasis on social equity and financial inclusion. Besides this, the increasing cost of traditional insurance products resulting in the higher demand for affordable alternatives tailored to underserved communities is resulting in a higher product uptake. In addition, partnerships between insurers and community organizations are fostering trust and expanding awareness about microinsurance solutions. Concurrently, regulatory initiatives aimed at promoting accessible financial products are encouraging innovation in this sector. The rise of gig and freelance economies is increasing the need for tailored microinsurance policies covering health, liability, and income protection in the country. Furthermore, numerous enhancements in data analytics and AI-driven underwriting processes enabling insurers to offer customized, low-cost solutions effectively is further creating a positive outlook for the market.
Microinsurance Market Trends:
Increasing Demand for Financial Inclusion
Financial inclusion is a critical factor driving various financial services markets, including microinsurance. It ensures that a broader segment of the population can access insurance services. Financially inclusive microinsurance schemes often create a sense of community and social cohesion. In many cases, community-based organizations or microfinance institutions are involved in delivering microinsurance services. This in turn fosters trust and solidarity among community members, as they collectively share risks and support each other during difficult times. Governments in many developing countries are recognizing the importance of financial inclusion in improving the well-being of their citizens. They are implementing policies and regulations that promote the growth of microinsurance and other financial inclusion initiatives. According to a report from the World Bank, financial inclusion has improved significantly and is recorded to have reduced the numbers of adults without access to an account from 2.5 billion in 2011 to 1.7 billion in 2017, then to 1.4 billion in 2021. As of 2021, 76% of individuals globally had an account.
Growing Technological Advancements
The proliferation of mobile devices and internet connectivity is revolutionizing microinsurance. Mobile technology is enabling insurers to reach previously inaccessible populations in remote areas. Through mobile apps and digital platforms, individuals can easily access and purchase microinsurance policies. Many insurance companies are doing innovations in their product and way they sell insurance. Toffee Insurance, for example, is developing a business strategy in which it provides products according on each individual customer's unique needs. Over 115K Indians, 80% of whom are first-time buyers, are subject to the organization's selling policies. Additionally, Turtlemint provided insurance agents with an innovation stage to offer products, and as of right now, it has about 75,000 partners/agents (PoS) operating throughout India. Technological innovations including data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) are imparting a profound impact on microinsurance. Insurers now use advanced data analytics to assess risks more accurately. This enables them to tailor insurance products to the specific needs of their customers and price policies more competitively. AI-powered chatbots and automated processes are streamlining customer interactions and claims processing, making microinsurance more efficient and cost-effective. Besides this, blockchain technology is enhancing the transparency and security in microinsurance. Smart contracts on blockchain platforms can automate policy issuance and claims processing, reducing administrative overhead and the risk of fraud. Moreover, blockchain can create immutable records of transactions, ensuring the integrity of insurance policies and claims history.
Government Initiatives and Regulation
Many governments in emerging economies recognize the social and economic benefits of microinsurance in reducing poverty and promoting financial stability. As a result, they have introduced policies and regulations that encourage the development of microinsurance products. These regulations often focus on product design and licensing requirements, creating a conducive environment for insurers to operate and expand their microinsurance offerings. Government regulations often include provisions for protection in microinsurance. These regulations ensure that policyholders are treated fairly and transparently. Governments often foster partnerships between microinsurance providers and microfinance institutions (MFIs). MFIs have an established presence in many underserved communities and can act as distribution channels for micro insurance products. Government support for such partnerships can significantly expand the outreach of microinsurance to rural and remote areas. Moreover, governing agencies are investing in public awareness campaigns to educate citizens about the benefits of microinsurance. These campaigns can include workshops, seminars, and outreach programs to inform individuals about the importance of financial protection and the availability of microinsurance options. The focus of governments across the world on financial inclusion is further driving the market growth. For instance, The Indian government introduced a number of financial inclusion programs, including the Venture Capital Fund for Scheduled Castes under the Social Sector Initiatives, the Credit Enhancement Guarantee Scheme (CEGS) for Scheduled Castes (SCs), the Jan Dhan Yojana, and the Jeevan Suraksha Bandhan Yojana. As per the latest figures provided by banks to the government, the total number of Jan Dhan accounts had reached 50 crores as of 9th August 2023. Of these accounts, 67% were opened in rural or semi-urban areas, and 56% were held by women.
Microinsurance Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the global microinsurance market, along with forecast at the global, regional, and country levels from 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on product type, provider, and model type.
Analysis by Product Type:
- Property Insurance
- Health Insurance
- Life Insurance
- Index Insurance
- Accidental Death and Disability Insurance
- Others
Life insurance leads the market with 48.0% of the market share in 2025. Life insurance offers financial protection to beneficiaries in the event of the death of the policyholder. It can also serve as an investment tool with various types, such as term, whole life, and universal life insurance policies. It provides safety to loved ones and helps with estate planning, making it a cornerstone of financial security for many. Whole life and universal life insurance policies often accumulate cash value over time. Policyholders can access this cash value through loans or withdrawals, providing a savings component in addition to the death benefit.
Analysis by Provider:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
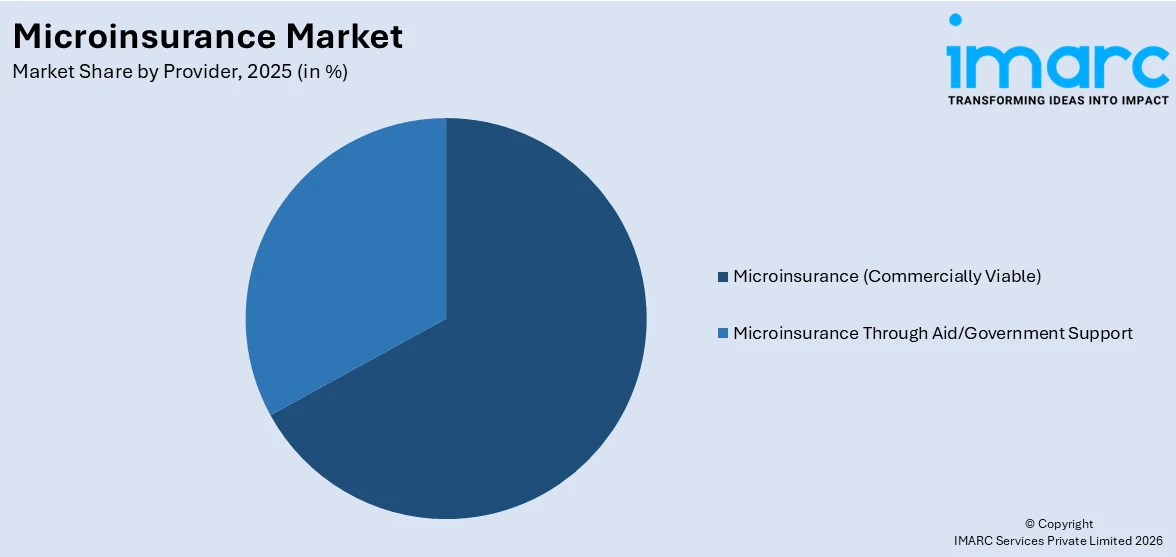
- Microinsurance (Commercially Viable)
- Microinsurance Through Aid/Government Support
Microinsurance (commercially viable) leads the market with 67.0% of the market share in 2025. Microinsurance offered by commercially viable providers refers to insurance products provided by private insurance companies or microinsurance-focused entities. These providers operate on a for-profit basis and design microinsurance products that are financially sustainable without significant external subsidies. They leverage market-based approaches to reach low-income and underserved populations, often using technology and innovative distribution channels to make microinsurance products accessible and affordable. This segment represents the largest share of the microinsurance market and is characterized by a focus on profitability while serving the insurance needs of vulnerable communities.
Analysis by Model Type:
- Partner Agent Model
- Full-Service Model
- Provider Driven Model
- Community-Based/Mutual Model
- Others
The partner agent model involves collaborating with local agents, such as microfinance institutions, cooperatives, or retail outlets, to distribute microinsurance products. These agents act as intermediaries between insurance providers and policyholders, helping with product sales, premium collection, and claims processing. This model capitalizes on existing networks and trusted relationships within communities, making it an efficient way to reach underserved population and expand the overall microinsurance coverage.
The full-service model encompasses a comprehensive approach to microinsurance, where insurance providers directly manage all aspects of the insurance process, ranging from product design and distribution to claims handling. This model allows for greater control over the customer experience and ensures that policies align with the specific needs of the target market. While it may require more extensive resources, the full-service model can be effective in providing tailored microinsurance solutions to a wide range of customers, improving customer satisfaction, retention, and trust, thereby encouraging broader adoption.
The provider-driven model facilitates healthcare or service providers offering microinsurance directly to customers. This approach allows for the seamless integration of insurance with healthcare services, ensuring timely care and reduced out-of-pocket expenses for beneficiaries. It is particularly relevant in regions where formal insurance infrastructure is limited. By aligning insurance with essential services, this model builds trust and meets immediate needs, driving growth by improving access to affordable healthcare and demonstrating tangible benefits to underserved communities.
Community-based/mutual model involves policyholders forming a mutual or cooperative to collectively pool their resources and share risks. Members contribute premiums to a communal fund, and when a member faces a covered loss, they receive compensation from the pool. This model fosters a sense of ownership and community solidarity as members collectively manage the insurance program. It often serves as an effective means of self-insurance among marginalized communities, particularly in rural areas where formal insurance may be less accessible, which is impelling growth in this segment.
Regional Analysis
To get more information on the regional analysis of this market Request Sample
- Asia Pacific
- North America
- Europe
- Middle East and Africa
- Latin America
In 2025, Asia Pacific accounted for the largest segment, with a market share of 32.0%. The Asia Pacific microinsurance market is largely driven by the rising focus on maintaining financial inclusion and social protection goals. Governing agencies in the region are implementing regulatory frameworks that encourage the development of microinsurance products and providers. Besides this, mobile-based insurance distribution and payments are making it easier for insurers to reach remote and underserved areas. Moreover, data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) are being used to assess risks and design customized microinsurance products, enhancing efficiency and affordability. The Asian Pacific region has recently seen an increase in microfinance institutions, banks, and other local organizations partnering with insurers to distribute microinsurance products. Such partnerships avail existing networks and channels of reaching customers for easier and more convenient access to and buying coverage.
Key Regional Takeaways:
United States Microinsurance Market Analysis
In 2025, the US accounted for around 87.90% of the total North America microinsurance market. Growing awareness of financial inclusion among marginalised people is driving the microinsurance sector in the US. There is still a big market opportunity because some 25 million Americans lack insurance or have inadequate coverage, as per industry reports. Rising healthcare costs have also resulted in a higher demand for affordable microinsurance products that include health, life, and property risk protection. Healthcare costs rose to over USD 4.9 Trillion in 2023, according to data from Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. More than 75% of customers buy their policies online, which is why digital transformation has become the most important enabler in the insurance sector. Microinsurance is now more accessible due to collaboration among fintech companies and insurers, particularly through mobile apps. Government initiatives that make reasonably priced insurance available coupled with financial literacy programs propel its adoption. Some of the large insurers, such as Prudential Financial and MetLife, have introduced microinsurance plans targeting gig workers; this market has increased to over 60 million in 2023, according to industry reports.
Europe Microinsurance Market Analysis
Among Europe's low-income labor-class demographic, microinsurance is rapidly gaining pace, particularly among the migration-driven population. The rising pressure of affordability in relation to access to financial security defines microinsurance's growth imperative. In fact, as figures from the European Commission have it, 94.6 million EU citizens were at risk of poverty or social exclusion in 2023, accounting for 21.4% of the total population. In 2023, women represented more likely victims of poverty or social exclusion in the EU compared to males with 22.3% to 20.3%. Key is played by government policies encouraging inclusive insurance and assistance from non-governmental organizations. The percentage of adults in the region having a bank account, excluding high-income economies, increased from 65 percent in 2017 to 78 percent in 2021, above the average of 71 percent for emerging economies, according to the most recent edition of the Global Findex, which includes data for 2021, which displays a positive outlook for the microinsurance industry. The growth of parametric insurance solutions, especially for climatic and agricultural risks, is propelling markets in nations such as Germany, the UK, and France forward.
Asia Pacific Microinsurance Market Analysis
The substantial and economically underserved population, particularly in rural regions, serves as a significant advantage for the Asia-Pacific microinsurance sector. There is great market potential since a new analysis from the International Labour Organisation (ILO) estimates that 1.6 billion people in Asia and the Pacific lack adequate access to social health protection. Subsidized insurance schemes have been implemented by governments in countries such as Indonesia and India. One such scheme is India's Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana, which has enrolled more than 34 crore people as of May 2023, according to data from the Ministry of Finance, Indian Government. Mobile-based microinsurance solutions are increasingly popular in India. Nations including the Philippines, vulnerable to natural disasters, are demanding weather-indexed microinsurance plans.
Latin America Microinsurance Market Analysis
Due to Latin America's heightened vulnerability towards natural catastrophes as well as vulnerable economies, the use of microinsurance has increased lately in the region. This comes at the wake of nearly 30 percent of individuals earning sub-poverty incomes with poverty lines still running relatively low in many places as deduced by data coming out from the World Bank. According to a report by Microinsuarance Network, a total of 15.2 million policies and between 14 and 40 million individuals were covered by microinsurance across the eight Latin American and Caribbean (LAC) nations. Access is being made easier by the adoption of mobile technology; in metropolitan areas, smartphone prevalence is above 60% in 2022, as per industry reports. The international NGOs are now co-operating with the regional insurers to expand their rural coverage.
Middle East and Africa Microinsurance Market Analysis
Climate change and economic hardship are two prime movers of the micro-insurance industry in the Middle East and Africa. Microinsurance is an essential financial product as more than 90 percent of the population in sub-Saharan Africa has no formal type of insurance, including health insurance, according to reports from the industry. This includes agricultural microinsurance among the most recognized, one that protects smallholder farmers against crop failures due to floods or droughts. Mobile-based platforms are growing in this region with the support from alliances with telecom companies. Another product gaining popularity in countries such as Egypt and Nigeria is the Islamic microinsurance, or takaful, due to cultural preferences for Sharia-compliant products.
Competitive Landscape:
Key players in the microinsurance market are actively engaged in various strategies and initiatives that expand their reach and improve access to microinsurance products. They are using technology to make processes simpler, enhance distribution channels, and tailor offerings for underserved populations. Many microinsurance providers are venturing into partnerships with microfinance institutions, banks, and mobile network operators for them to reach more extensive markets. They are investing in public education and awareness campaigns to make low-income populations understand the importance of having insurance. Top companies are also experimenting with new pricing models and assessment techniques of risk to lower microinsurance costs and hence its sustainability in the long run, which contributes towards achieving financial inclusion and protection for all.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the microinsurance market with detailed profiles of all major companies.
Latest News and Developments:
- October 2024: Egypt's first microinsurance firm was established by AXA and Post for Investment. The goal of this project is to give low-income individuals and small enterprises in Egypt access to accessible and reasonably priced insurance options. The microinsurance company seeks to increase resilience and encourage financial inclusion among marginalized communities by providing coverage for property, health, and other necessities.
- February 2024: A new parametric flood resilience insurance policy has been introduced by WRMS Global and MIC Global to assist Indian merchants. When predetermined flood conditions are fulfilled, this creative system employs parametric triggers to quickly reimburse insured parties, reducing financial losses and business interruptions. The goal of the coverage is to make small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) more resilient to the rising hazards of flooding brought on by climate change.
Microinsurance Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Product Types Covered | Property Insurance, Health Insurance, Life Insurance, Index Insurance, Accidental Death and Disability Insurance, Others |
| Providers Covered | Microinsurance (Commercially Viable), Microinsurance Through Aid/Government Support |
| Model Types Covered | Partner Agent Model, Full-Service Model, Provider Driven Model, Community-Based/Mutual Model, Others |
| Regions Covered | Asia Pacific, Europe, North America, Latin America, Middle East and Africa |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, microinsurance market forecast, and dynamics of the market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the global microinsurance market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the microinsurance industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
Microinsurance is a financial service designed to offer affordable insurance coverage to low-income individuals and underserved communities. It addresses specific risks such as health, life, property, or agriculture, typically through simplified policies, low premiums, and innovative distribution methods.
The global microinsurance market was valued at USD 98.8 Billion in 2025.
IMARC estimates the global microinsurance market to exhibit a CAGR of 4.57% during 2026-2034.
Key factors driving the market include increased awareness of financial security among low-income populations, technological advancements such as mobile-based platforms and AI-driven underwriting, and strong government and NGO initiatives promoting financial inclusion.
Life insurance represented the largest segment by product type, driven by its dual role as financial protection and an investment tool.
Microinsurance (commercially viable) leads the market by provider due to its focus on profitability and the use of innovative technologies for reaching underserved communities.
On a regional level, the market has been classified into North America, Asia Pacific, Europe, Latin America, and Middle East and Africa, wherein Asia Pacific currently dominates the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












