
Middle East Renewable Energy Market Size, Share, Trends, and Forecast by Type, End User, and Country, 2026-2034
Middle East Renewable Energy Market Overview:
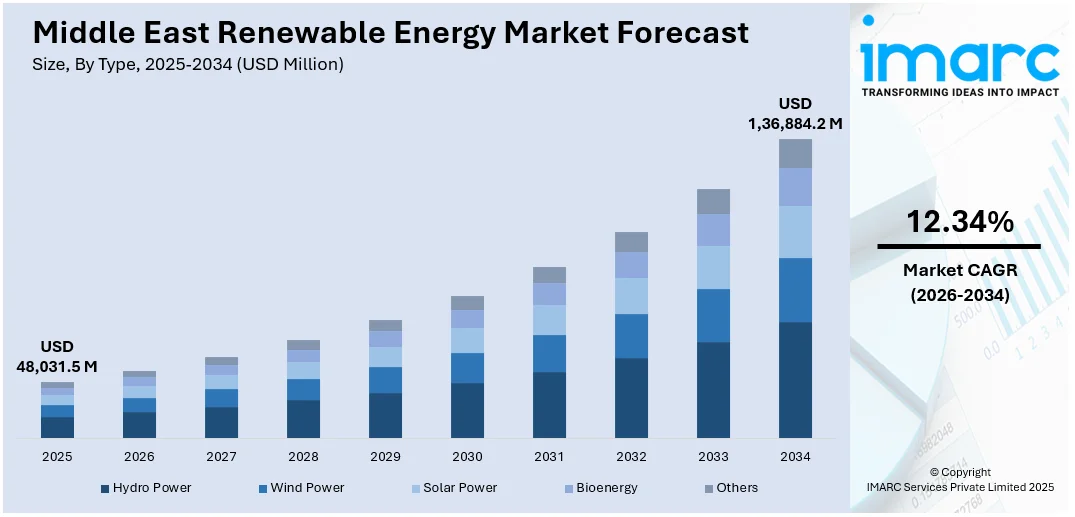
The Middle East renewable energy market size was valued at USD 48,031.5 Million in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 1,36,884.2 Million by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 12.34% during 2026-2034. Iran currently dominates the market with around 33.3% of market share, supported by abundant solar and wind resources, rising energy consumption, and strong government initiatives to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Infrastructure investments and favorable policies continue to accelerate renewable energy deployment across the country, further accelerating the overall Middle East renewable energy market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 48,031.5 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 1,36,884.2 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 12.34% |
The Middle East renewable energy market is gaining momentum due to growing energy diversification efforts, rising electricity demand, and an urgent need to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. For instance, as per industry reports, in 2024, energy demand in the Middle East increased by 2.2%, largely driven by a notable rise in electricity consumption. Governments across the region, particularly in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Egypt, are investing heavily in solar and wind projects as part of national energy strategies like Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 and the UAE Energy Strategy 2050. Abundant solar irradiance makes photovoltaic (PV) technology especially viable, while declining costs of solar panels and improved grid infrastructure are accelerating deployment. International collaborations, green hydrogen initiatives, and public-private partnerships are also expanding access to funding and technical expertise. As countries seek to meet their Paris Agreement targets and support sustainable development, renewables are becoming central to regional energy planning, shaping a positive Middle East renewable energy market outlook.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Increased investment in renewable energy is also being driven by the Middle East's push toward economic diversification and long-term resilience. Energy-intensive industries such as desalination, aluminum smelting, and manufacturing are transitioning to cleaner energy sources to meet ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals and improve cost-efficiency. Regulatory support, such as feed-in tariffs, tenders, and net metering, is encouraging private sector involvement. Additionally, innovation in energy storage and smart grid technologies is improving renewable energy reliability and integration. The emergence of regional clean energy hubs, such as NEOM in Saudi Arabia and Masdar City in Abu Dhabi, signals a broader shift toward low-carbon economies. With a young population, growing urbanization, and rising environmental awareness, there is a clear socio-economic incentive to adopt renewable solutions, positioning the Middle East as an emerging global clean energy leader.
Middle East Renewable Energy Market Trends:
Government-Led Sustainability Initiatives and Emissions Reduction Targets
The Middle East is experiencing a surge in renewable energy adoption driven by heightened environmental awareness and ambitious governmental sustainability goals. A prime example is the UAE’s National Demand Side Management (DSM) Programme, which reduced 11.2 million tonnes of CO₂ emissions by 2023. Targeting sectors like the built environment, the DSM aligns with the UAE’s Net Zero Strategy and aims to significantly cut energy use by 2050. Regional governments are also offering supportive incentives, such as tax credits, feed-in tariffs, and subsidies, to attract private sector investment in renewables. These policy frameworks are not only promoting cleaner energy but also positioning renewables as essential tools for long-term environmental compliance and resilience in energy-intensive sectors across the region.
Green Financing and Institutional Investment Momentum
Robust financial backing from regional sovereign wealth funds and institutions is catalyzing renewable energy growth across the Middle East. Saudi Arabia’s Public Investment Fund (PIF), for instance, raised USD 3 billion in green bonds in 2022 and USD 5 billion in 2023, with over USD 5.2 billion allocated to environmentally focused initiatives by mid-2024. This capital is being directed toward large-scale projects in solar, wind, and related clean technologies, accelerating the region’s transition from fossil fuels. Such financing instruments reflect a growing trend of green capital markets and align with broader ESG strategies. Given these developments, the Middle East renewable energy market forecast suggests sustained growth in clean energy investments, driven by strong policy support and evolving private sector involvement.
Technological Advancements and Decentralized Energy Models
Rapid improvements in renewable technologies are transforming the feasibility and scalability of clean energy in the Middle East. The IEA predicts that by 2030, photovoltaic (PV) power generation in the region will contribute over 10% of global new renewable capacity. Advances in solar panel efficiency, wind turbine output, and energy storage solutions are reducing the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE), making renewables cost-competitive with fossil fuels. Additionally, the shift toward distributed generation, enabled by smart grids and microgrid technologies, is reshaping the traditional power landscape. Decentralized systems enhance energy security, reduce transmission losses, and empower local communities to manage their own sustainable energy mix, especially in remote or off-grid areas, further driving the Middle East renewable energy market growth.
Middle East Renewable Energy Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Middle East renewable energy market, along with forecasts at the regional, and country levels from 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on type, and end user.
Analysis by Type:
- Hydro Power
- Wind Power
- Solar Power
- Bioenergy
- Others
Solar power stands as the largest component in 2025, holding around 53.8% of the market. This leadership is driven by the region’s abundant solar resources, favorable climatic conditions, and declining costs of photovoltaic (PV) technology. Countries such as the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Egypt have launched large-scale solar initiatives, including utility-scale solar farms and residential rooftop programs. Technological advancements in PV efficiency, energy storage integration, and smart grid compatibility have further accelerated adoption. Moreover, supportive government policies, long-term power purchase agreements (PPAs), and competitive bidding processes have encouraged private sector participation. Solar power's scalability, low maintenance, and alignment with national sustainability goals make it the cornerstone of the region’s clean energy transition.
Analysis by End User:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Industrial
- Residential
- Commercial
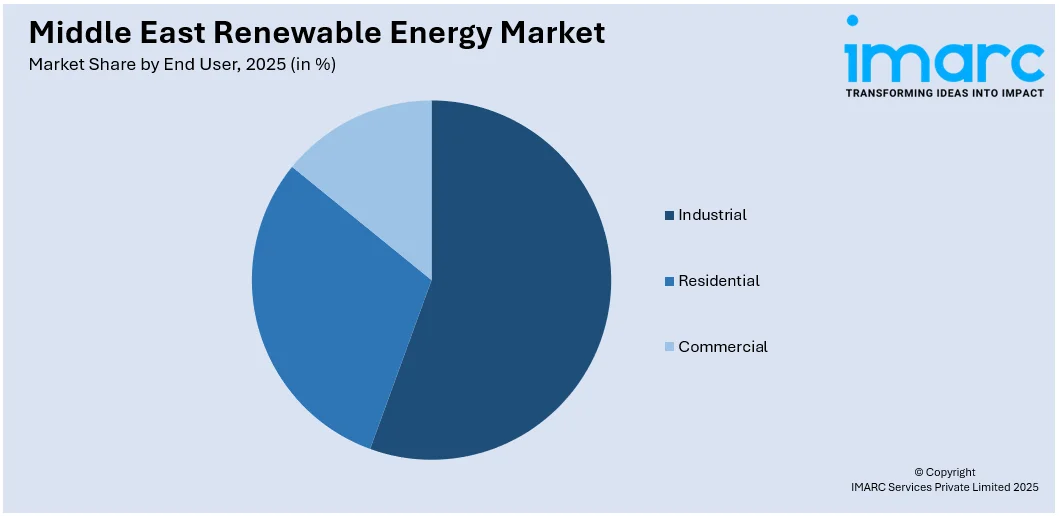
Industrial leads the market with around 50.9% of market share in 2025. This dominance is largely attributed to the region’s heavy reliance on energy-intensive industries such as petrochemicals, cement, aluminum, and manufacturing. With growing pressure to reduce carbon emissions and improve sustainability practices, industrial players are increasingly investing in renewable energy solutions, including solar and wind power. Many companies are also adopting corporate power purchase agreements (PPAs) to secure stable, clean energy at competitive prices. Government incentives, green financing mechanisms, and regulatory mandates for emissions reduction are further accelerating this transition. Additionally, renewable energy enhances energy security and operational resilience, making it a strategic asset for industrial growth and long-term competitiveness across the Middle East.
Country Analysis:
- Saudi Arabia
- Turkey
- Israel
- United Arab Emirates
- Iran
- Iraq
- Qatar
- Kuwait
- Oman
- Jordan
- Bahrain
- Others
In 2025, Iran accounted for the largest market share of over 33.3%. This leadership is driven by Iran’s abundant natural resources, particularly its high solar irradiance and vast wind corridors, which position the country favorably for large-scale renewable energy projects. The government’s strategic push to diversify its energy mix, reduce reliance on fossil fuels, and improve energy security has spurred significant investment in solar and wind infrastructure. For instance, in May 2025, In May 2025, Iran installed 600 MW of solar power, quadrupling its previous annual average as part of a government effort to meet rising electricity demand. The Energy Ministry plans to develop 5,000 MW of solar capacity, importing equipment internationally to meet deadlines. Construction has started on 297 MW of projects across five provinces, supported by $96 billion in government funding. The administration is also advancing a 500 MW renewable expansion, promoting industrial self-generation and rooftop solar with incentives for households. Iran's growing energy demand, coupled with rising environmental concerns and international pressure to curb emissions, has further fueled the adoption of renewable sources. Additionally, domestic manufacturing capabilities and supportive policies have lowered project costs, making renewables increasingly viable and attractive across the country.
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape of the Middle East renewable energy market is characterized by a mix of international developers, regional utilities, and government-backed entities actively investing in large-scale projects. Market participants are focusing on strategic collaborations, long-term power purchase agreements (PPAs), and vertically integrated operations to strengthen their positions. The market is witnessing intense competition in utility-scale solar and wind tenders, often awarded based on low levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) bids. Governments are playing a crucial role by offering regulatory support, subsidies, and streamlined approval processes, attracting both foreign direct investment and local participation. Innovation in storage technologies, digital energy management, and grid integration is also emerging as a key area of competition, as companies aim to offer more reliable and efficient renewable solutions.
For instance, in June 2025, Saudi Arabia's Voluntary Carbon Market (VCM) signed a landmark agreement with Enowa, NEOM’s energy and water subsidiary, to deliver over 30 million tons of carbon credits by 2030. The deal supports Saudi Arabia’s net-zero goals and helps offset emissions from renewable energy development. Carbon credits will be sourced globally, primarily from the Global South. This partnership marks a major step in scaling the region’s carbon market and was facilitated through Saudi’s new carbon credit exchange platform, launched in 2024.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the Middle East renewable energy market with detailed profiles of all major companies.
Latest News and Developments:
- May 2025: KEZAD Group and Broaden Energy signed a 50-year land lease for an 80,000-square-meter hydrogen manufacturing facility in Abu Dhabi's KEZAD Area A. The AED 455M project will focus on hydrogen, solar, and wind energy solutions, creating 1,000 jobs and supporting the UAE’s renewable energy goals.
- April 2025: Desay Battery showcased its latest energy storage solutions at Middle East Energy Dubai, featuring lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries, modular systems, and large-scale infrastructure. The company emphasized its commitment to supporting the region’s energy transition with products designed for high-temperature environments, further expanding its presence in renewable energy.
- April 2025: Masdar, Abu Dhabi’s future energy company, completed the acquisition of 100% of Greece’s Terna Energy. This follows a USD 3.5 Billion deal, marking Masdar's largest European energy transaction. The acquisition strengthens Masdar’s renewable energy portfolio, supporting its goal to reach 100GW capacity by 2030.
- March 2025: Oman has five of the ten largest low-carbon hydrogen plants planned to be operational by 2030. Major projects include ACME Duqm Phase 2 and POSCO Consortium Duqm, leveraging Oman’s renewable energy resources for sustainable growth.
- March 2025: Saudi Aramco acquired a 50% stake in Blue Hydrogen Industrial Gases Co., a joint venture with Air Products Qudra. This move advances low-carbon hydrogen production in Jubail Industrial City, supporting Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 and goals for net-zero emissions by 2060 and a circular carbon economy.
- January 2025: Masdar and EWEC launched the world's first 24/7 solar PV and battery storage gigascale project in Abu Dhabi. This groundbreaking initiative combines a 5.2GW solar plant with a 19GWh battery storage system to provide 1GW of clean, uninterrupted power daily, setting a global benchmark in renewable energy.
Middle East Renewable Energy Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Predictive Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Hydro Power, Wind Power, Solar Power, Bioenergy, Others |
| End Users Covered | Industrial, Residential, Commercial |
| Countries Covered | Saudi Arabia, Turkey, Israel, United Arab Emirates, Iran, Iraq, Qatar, Kuwait, Oman, Jordan, Bahrain, Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Middle East renewable energy market from 2020-2034.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Middle East renewable energy market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Middle East renewable energy industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The renewable energy market in the Middle East was valued at USD 48,031.5 Million in 2025.
The Middle East renewable energy market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 12.34% during 2026-2034, reaching a value of USD 1,36,884.2 Million by 2034.
Key factors driving the Middle East renewable energy market include rising environmental awareness, government-led sustainability initiatives, technological advancements in solar and wind energy, declining renewable energy costs, supportive regulations such as subsidies and tax incentives, and increasing investments in large-scale renewable projects aimed at reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Iran holds the largest share of around 33.3% of the Middle East renewable energy market, driven by significant solar and wind energy potential, government support for renewable initiatives, rising domestic energy demand, and efforts to diversify energy sources. Strategic investments and favorable geography further boost the country's renewable energy development.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












