
Philippines Higher Education Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Component, Deployment Mode, Course Type, Learning Type, End User, and Region, 2026-2034
Philippines Higher Education Market Overview:
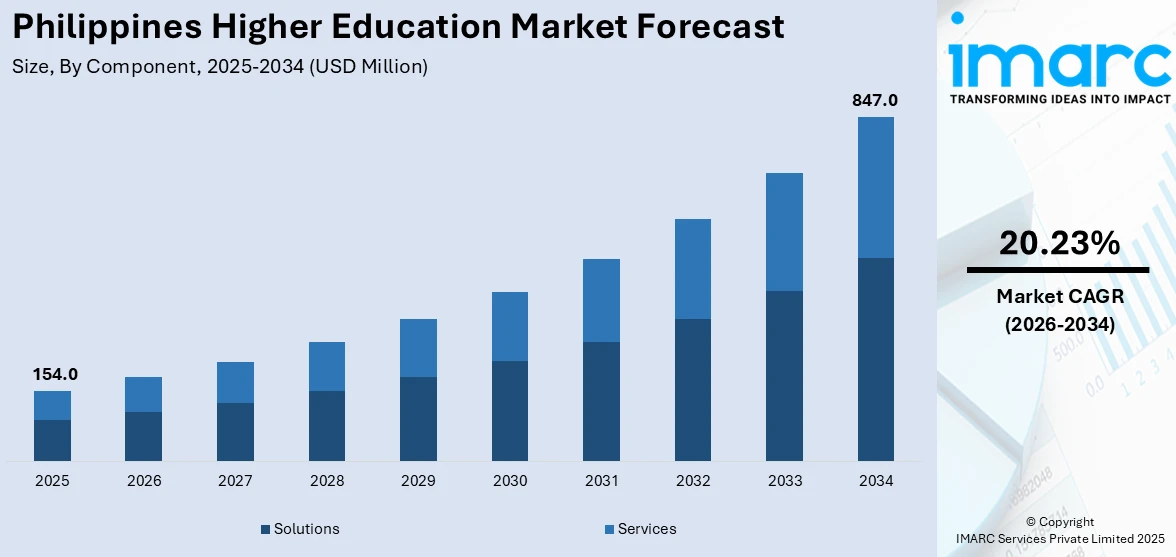
The Philippines higher education market size reached USD 154.0 Million in 2025. The market is projected to reach USD 847.0 Million by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 20.23% during 2026-2034. The market is driven by a growing youth population, rising demand for skilled professionals, and expanding private sector participation. The increasing adoption of digital technologies and international collaborations transforming traditional learning models and government initiatives aimed at improving quality and access are also driving growth. The market comprises a mix of public and private institutions offering diverse programs, reflecting the evolving dynamics and competitive participation in the Philippines higher education market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 154.0 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 847.0 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 20.23% |
Key Trends of Philippines Higher Education Market:
International Partnerships
International collaboration is becoming a defining feature of the Philippines higher education sector. Universities are actively pursuing cross-border programs, dual-degree offerings, and student exchange agreements with institutions in countries like Australia, the US, Japan, and South Korea. For instance, in February 2024, the US launched the Php1.6-billion UPSKILL Program aimed at enhancing Philippine higher education through innovation and workforce development. This five-year initiative, announced by Presidents Biden and Marcos, involves collaboration between U.S. universities and Philippine agencies to improve educational outcomes and career prospects for Filipino graduates. These partnerships enhance academic quality, promote global exposure, and help institutions align with international standards. Joint research initiatives, faculty training, and virtual exchange programs are also on the rise, driven by digital infrastructure improvements. The Commission on Higher Education (CHED) supports these efforts through mobility programs and recognition of foreign credentials. As Filipino students increasingly seek globally competitive qualifications, institutions that offer international pathways are gaining a competitive edge. These collaborations not only improve academic outcomes but also attract foreign students and investments, contributing to the overall Philippines higher education market growth and enhancing its relevance in the regional academic landscape.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Rising Focus on STEM and Tech
The Philippines is placing greater emphasis on STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education to align with industry demands and global workforce trends. Educational institutions are expanding STEM course offerings, investing in updated lab facilities, and forming partnerships with tech companies to ensure practical, industry-relevant training. Government programs, such as scholarships and grants for STEM students, aim to address skills shortages in high-demand sectors like IT, engineering, and data science. For instance, in June 2024, the Technological University of the Philippines (TUP) announced its partnership with the Commission on Higher Education (CHED) to enhance research and innovation in Philippine higher education. The collaboration, initiated during a recent visit by CHED representatives, aims to empower universities through funding programs and support for competitive research initiatives. Tech-enabled learning environments and curriculum enhancements are being implemented to promote innovation and problem-solving skills. Coding, robotics, and AI-related modules are increasingly introduced even at the undergraduate level. This focus is critical not just for domestic employment but also for preparing graduates for overseas opportunities in STEM fields. Strengthening STEM education is a key pillar of the Philippines’ strategy to boost higher education relevance and economic competitiveness.
Growth Factors of Philippines Higher Education Market:
Expanding Private Sector Involvement
The Philippine private education sector is playing a central role in expanding the scope and quality. Private colleges and universities are offering specialized courses, state-of-the-art facilities, and new methods of instruction to woo students. Competitive fees, flexible class schedules, and industry tie-ups are enabling these colleges and universities to gain an edge. With more control over curriculum development, private schools can move more quickly toward responding to market needs and incorporating new areas of study into their curriculum. This competitive atmosphere benefits students as the overall quality of education is enhanced, faculty development is promoted, and research opportunities are increased. With the continued increase in demand for quality higher education, the increased prominence of private schools will continue to be the major catalyst for determining the country's academic scene.
Demand for Postgraduate and Professional Programs
The Philippine job market increasingly values advanced academic qualifications, driving demand for postgraduate and professional degree programs. Many professionals are enrolling in MBAs, master’s degrees, and law or healthcare-related postgraduate courses to strengthen their credentials and advance their careers. Employers also view higher-level qualifications as a competitive advantage, leading to better job placements and salary growth. This demand extends beyond traditional degrees to include executive education and industry-specific certifications. Universities are responding by offering flexible class schedules, modular programs, and online learning options to accommodate working professionals. As industries evolve and competition intensifies, the pursuit of advanced education is becoming a necessity for career growth, fueling steady enrollment and contributing to the sustained expansion of the higher education market.
Adoption of Digital and Hybrid Learning Models
Technological advancements have paved the way for the widespread adoption of digital and hybrid learning in Philippine higher education. Universities are integrating online platforms, interactive learning tools, and virtual classrooms to provide more flexible and inclusive education. Hybrid models combine the benefits of face-to-face interaction with the convenience of remote access, making it possible for working students and those in remote areas to pursue degrees without compromising their schedules. This digital shift also enables universities to offer international collaborations, webinars, and online research projects. By embracing technology-driven learning, institutions can reach a broader audience, improve engagement, and enhance the overall quality of education delivery. This trend is transforming the learning experience while increasing the sector’s long-term growth potential.
Opportunities of Philippines Higher Education Market:
Growth in Lifelong Learning and Upskilling
Rapid changes in technology and industry demand are fueling the need for continuous learning and professional upskilling in the Philippines. Universities can capitalize on this trend by offering short courses, certification programs, and online training modules tailored for working professionals. Programs in digital marketing, data analytics, healthcare administration, and project management are in high demand. These offerings provide flexibility in duration, cost, and delivery mode, making them accessible to a wider audience. By addressing skill gaps and aligning programs with industry requirements, institutions can generate new revenue streams while supporting workforce development. This trend also strengthens alumni engagement, as graduates return for further studies, reinforcing long-term relationships between universities and their student communities.
Development of Niche Academic Programs
The growing need for specialized expertise is creating opportunities for Philippine universities to introduce niche academic programs, which is driving the Philippines higher education market demand. Fields such as renewable energy, cybersecurity, creative industries, marine sciences, and sustainable development are gaining global attention. By developing unique curricula in these areas, universities can differentiate themselves and attract students interested in future-oriented careers. These programs not only cater to local industry needs but also position institutions to serve the international student market. Partnerships with businesses, NGOs, and research bodies can further enhance program relevance and employability outcomes. As global markets shift toward specialized skills, universities that invest in niche programs will strengthen their reputation, increase enrollment, and contribute to the country’s competitiveness in emerging industries.
Expansion into ASEAN Student Market
The Philippines’ English-based instruction, affordable tuition fees, and cultural hospitality create strong potential to attract students from ASEAN countries. Neighboring nations with limited higher education capacity are seeking opportunities abroad, and the Philippines can serve as a competitive alternative to Western universities. By offering internationally recognized programs, student exchange opportunities, and scholarship packages, Philippine universities can tap into this growing regional demand. Marketing efforts through education fairs, digital campaigns, and bilateral agreements with ASEAN governments can enhance visibility. Additionally, the country’s tourism appeal can serve as a draw for international students seeking both education and cultural experiences. This expansion not only increases enrollment but also promotes cross-cultural collaboration, strengthening the country’s academic and economic position within Southeast Asia.
Challenges of Philippines Higher Education Market:
Quality Disparities Across Institutions
While top universities in the Philippines uphold strong academic standards, many institutions—especially in rural or less-developed areas—struggle with outdated curricula, inadequate facilities, and limited faculty training. These disparities result in inconsistent graduate competencies, making it harder for employers to assess skills. The uneven distribution of resources and technology limits access to quality education for a large portion of the population. Students from disadvantaged backgrounds may face reduced career opportunities due to substandard training. Addressing this challenge requires nationwide policy reforms, better funding allocation, and stronger accreditation systems to ensure that all institutions meet minimum quality benchmarks. Without improvements in quality parity, the higher education sector risks widening socio-economic gaps and reducing its overall competitiveness in the regional and global academic landscape.
Graduate Employability Gap
Many graduates in the Philippines face difficulties finding jobs that match their qualifications, reflecting a persistent mismatch between academic programs and labor market demands. Some universities focus heavily on theory, offering limited practical training or industry exposure, leaving students underprepared for real-world challenges. Employers often report skill gaps in areas like critical thinking, problem-solving, and technical expertise. According to the Philippines higher education market analysis, this disconnect affects both career progression for graduates and the overall productivity of the workforce. Universities need to strengthen internship programs, industry partnerships, and competency-based learning approaches to address the gap. If left unresolved, graduate underemployment could discourage enrollment, weaken higher education’s value proposition, and hinder the country’s ability to meet its human capital development goals in an increasingly competitive regional job market.
Affordability and Financial Barriers
While tuition in the Philippines is generally lower than in many Western countries, higher education can still be financially out of reach for many families, especially when factoring in living expenses, transportation, and learning materials. Limited access to scholarships, student loans, or financial aid exacerbates the problem. Students from low-income households may drop out before completing their degrees, reducing overall graduation rates and workforce readiness. This financial strain also pushes many to work part-time while studying, which can impact academic performance. Expanding government-backed education financing programs, private scholarships, and flexible payment schemes is essential to improving access. Without addressing affordability, the sector risks excluding a significant portion of the population from higher education, perpetuating inequality and slowing national socio-economic progress.
Government Supports of Philippines Higher Education Market:
Free Tuition and Financial Aid Programs
The Philippine government has implemented policies such as the Universal Access to Quality Tertiary Education Act, which provides free tuition in state universities and colleges. This initiative aims to remove cost barriers for students from low- and middle-income households, encouraging higher enrollment rates. Additional scholarship programs and grants from government agencies support specialized fields like engineering, agriculture, and teacher education. These measures also help reduce student loan dependency, making education more accessible and equitable. By expanding coverage to more institutions and increasing stipends for living expenses, the government can further boost participation rates. Such financial support strengthens human capital development, ensures a more inclusive education system, and enhances the nation’s ability to compete in a knowledge-driven global economy.
Capacity-Building for Faculty and Institutions
The government actively invests in faculty development through training grants, international exchange programs, and research funding. These initiatives aim to improve teaching quality, enhance research output, and keep educators updated with global best practices. Institutional capacity-building programs also fund laboratory upgrades, library modernization, and the integration of digital learning infrastructure. Through agencies like CHED (Commission on Higher Education), the government sets quality assurance standards and accreditation guidelines to ensure institutions maintain competitive academic offerings. Such initiatives not only elevate local academic performance but also position Philippine universities to participate in international collaborations. Strengthening faculty skills and institutional resources directly contributes to producing globally competitive graduates and fostering a stronger national innovation ecosystem.
Internationalization and Academic Exchange Initiatives
The government promotes international collaboration through scholarship schemes like the Philippine-California Advanced Research Institutes (PCARI) program and participation in ASEAN academic networks. These efforts facilitate student and faculty exchanges, joint research projects, and cross-border academic programs. By encouraging partnerships with foreign universities, the Philippines aims to enhance its global academic reputation and expand learning opportunities for students. Internationalization policies also help align local curricula with global standards, improving graduate competitiveness in the international job market. Moreover, such programs attract foreign students, contributing to cultural exchange and economic growth. Government-backed internationalization serves as both a driver of educational quality and a strategic tool for strengthening the Philippines’ role in the regional and global higher education landscape.
Philippines Higher Education Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2026-2034. Our report has categorized the market based on component, deployment mode, course type, learning type, and end user.
Component Insights:
- Solutions
- Student Information Management System
- Content Collaboration
- Data Security and Compliance
- Campus Management
- Others
- Services
- Managed Services
- Professional Services
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the component. This includes solutions (student information management system, content collaboration, data security and compliance, campus management, and others) and services (managed services and professional services).
Deployment Mode Insights:
- On-premises
- Cloud-based
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the deployment mode have also been provided in the report. This includes on-premises and cloud-based.
Course Type Insights:
- Arts
- Economics
- Engineering
- Law
- Science
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the course type have also been provided in the report. This includes arts, economics, engineering, law, science, and others.
Learning Type Insights:
- Online
- Offline
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the learning type have also been provided in the report. This includes online and offline.
End User Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
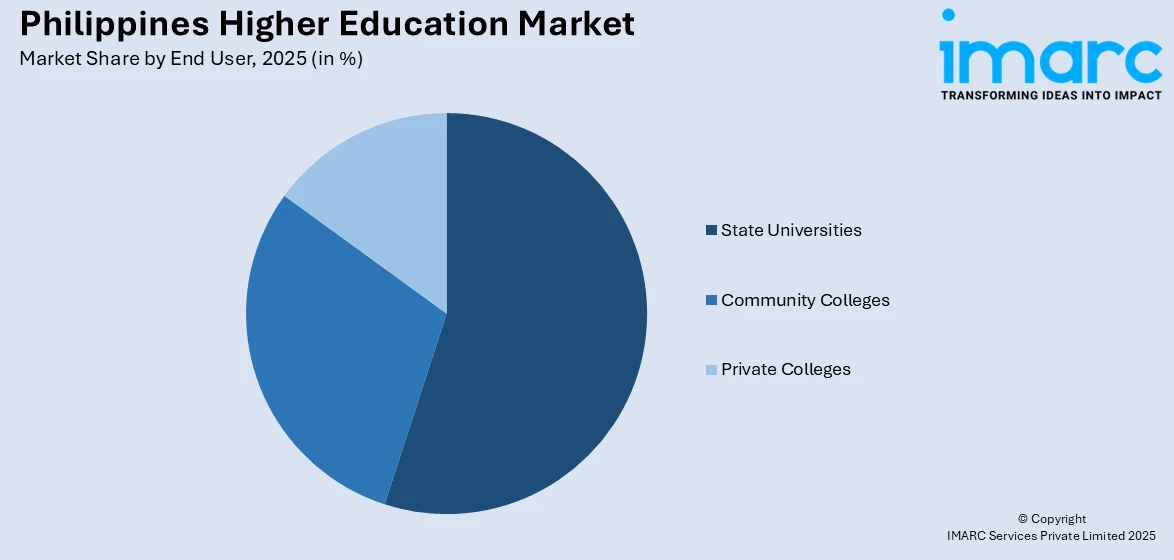
- State Universities
- Community Colleges
- Private Colleges
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the end user have also been provided in the report. This includes state universities, community colleges, and private colleges.
Regional Insights:
- Luzon
- Visayas
- Mindanao
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Philippines Higher Education Market News:
- In March 2025, the Commission on Higher Education (CHED) and PhilHealth signed a memorandum of understanding to enhance healthcare access for 500,000 underprivileged students in state universities. The partnership integrates PhilHealth services with CHED’s financial assistance programs, aiming to streamline healthcare delivery through accredited SUC facilities and improve students’ health services access.
- In January 2025, the Philippine government announced its plans to attract foreign higher education institutions by offering incentives for establishing branch campuses in the country. The Board of Investments has released new guidelines that provide tax holidays and increased deductions for partnerships with local entities. This initiative aims to enhance international collaboration and develop local talent, in line with the Transnational Higher Education Act.
- In May 2024, Twenty-one Australian educational institutions participated in a business mission to the Philippines exploring transnational education opportunities. The mission, led by Austrade, aimed to enhance collaboration between Australia and the Philippines, focusing on meeting local educational needs amid rising demand for high-quality qualifications.
Philippines Higher Education Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Components Covered |
|
| Deployment Modes Covered | On-Premises, Cloud-Based |
| Course Types Covered | Arts, Economics, Engineering, Law, Science, Others |
| Learning Types Covered | Online, Offline |
| End Users Covered | State Universities, Community Colleges, Private Colleges |
| Regions Covered | Luzon, Visayas, Mindanao |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Philippines higher education market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Philippines higher education market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Philippines higher education industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The higher education market in the Philippines was valued at USD 154.0 Million in 2025.
The Philippines higher education market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 20.23% during 2026-2034.
The Philippines higher education market is projected to reach a value of USD 847.0 Million by 2034.
The Philippines higher education market is currently shaped by strong push toward digital transformation and online learning, increased international partnerships for global competitiveness, and rising focus on STEM and tech programs to meet industry demands.
The Philippines higher education market is growing due to rising youth population, increasing demand for skilled professionals to meet industry needs, and expanding private sector participation. Government initiatives supporting digital transformation and international collaborations also significantly drive market growth.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












