
Philippines Mental Health Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Disorder, Service, Age Group, and Region, 2025-2033
Philippines Mental Health Market Overview:
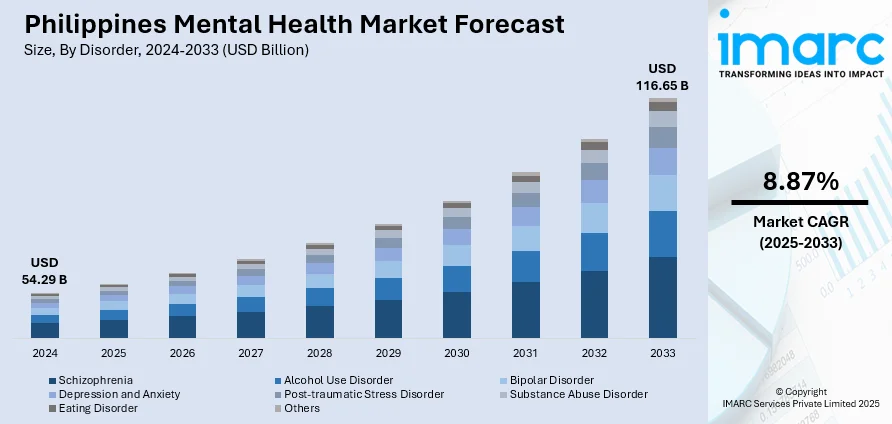
The Philippines mental health market size reached USD 54.29 Billion in 2024.The market is projected to reach USD 116.65 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 8.87% during 2025-2033. The market is fueled by the passage of the Mental Health Act in 2018, which has enhanced service access and lowered stigma. Government programs, such as the Philippine Council on Mental Health, facilitate policy implementation and resource allocation. Economic drivers, in the form of increased disposable incomes and an expanding middle class, allow more people to pay for mental health services. Technological progress has promoted the expansion of telehealth services, providing easy access to health care, while cultural changes driven by awareness campaigns, leading to a better supporting environment for mental health contribute to the Philippines mental health market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 54.29 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 116.65 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 8.87% |
Key Trends of Philippines Mental Health Market:
Digital Transformation of Mental Health Services
The Philippines is witnessing a dramatic transformation to digital mental health services with the nation's high smartphone penetration and internet connectivity. The teletherapy, online counseling, and mental health apps platforms have been emerging as options from which individuals can access mental health services in an easy and confidential manner across the country. This digital revolution staked its claim in the remote and underprivileged areas where it really is difficult to have established mental health care to patients. This whole ease and confidentiality of going digital have also helped in stamping out stigma of seeking mental health treatment. Several consumers are thus seeking assistance with their issues, and this has resulted in a more open and accepting atmosphere for mental health conversations. This is in keeping with international trends toward tech integration into healthcare, globalization of mental health service reach, and enhancement of its impact that further spurs the Philippines mental health market growth.
To get more information of this market, Request Sample
Government Initiatives and Policy Support
The Mental Health Act of 2018 was passed by the Philippine government because it recognizes the importance of mental health. In addition to protecting the rights of those who suffer from mental illness, the law aims to raise awareness of mental health issues and guarantee that mental health services are both inexpensive and easily accessible. Apart from the Mental Health Act, the government has initiated a number of programs to treat mental illnesses, such as providing mental health hotlines and integrating primary care with mental health services. Associations with international organizations that provide financing and technical assistance, such as the United Nations Development Programme and the World Health Organization, support the efforts.
Cultural Transformation and Public Consciousness
Cultural perspectives on mental health in the Philippines are changing, with more public awareness and acceptance. Disorders of mental health were once stigmatized, and people suffered discrimination. Yet, due to advocacy and the media, attitudes have been changing lately. Added to this are several celebrities and public figures who openly shared their experiences with mental illness, helping further in normalizing such conversations. Moreover, some schools have appointed classes for mental health, building an aware and compassionate generation. These cultural changes serve as a crucial foundation for creating a welcoming atmosphere where people feel free to ask for assistance and discuss mental health in an honest manner. This kind of acceptance will surely serve as an impetus for further demand for the country's mental health services and aid.
Growth Drivers of Philippines Mental Health Market:
Expanding Corporate Wellness Programs
Corporate wellness programs in the Philippines are increasingly incorporating mental health initiatives as organizations recognize the direct link between employee well-being and productivity. Companies are investing in counseling services, stress management workshops, and mental health awareness campaigns to reduce burnout, absenteeism, and workplace conflicts. Many firms are also partnering with external mental health providers to offer confidential employee assistance programs (EAPs). These initiatives not only enhance employee morale but also contribute to talent retention and a positive workplace culture. The growing acceptance of mental health support in the corporate sector reflects a shift toward holistic employee care. As more organizations adopt wellness frameworks, demand for professional mental health services within corporate settings is expected to rise significantly in the coming years.
Integration into Primary Healthcare
The integration of mental health services into primary healthcare is making support more accessible to the general population in the Philippines, driving the Philippines mental health market demand. Routine health check-ups increasingly include basic psychological screenings, while community health centers are offering counseling alongside general medical services. This approach reduces stigma by normalizing mental health care as part of overall well-being. It also benefits rural and underserved communities where specialized mental health facilities are scarce. Training primary care physicians and nurses in mental health assessment enables early detection of conditions such as anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders. By embedding mental health into frontline healthcare, the system ensures timely intervention, reduces the burden on specialized facilities, and promotes a more inclusive, preventive approach to mental health management nationwide.
Rising Demand for Specialized Professionals
The Philippines is witnessing a growing need for specialized mental health professionals, including psychiatrists, psychologists, and licensed counselors, to meet increasing public demand for mental health services. As awareness and acceptance improve, more individuals are seeking therapy, psychiatric care, and specialized interventions. This surge is driving the expansion of academic programs, professional certifications, and skills training in mental health disciplines. Universities and training institutes are responding by introducing advanced curricula and offering scholarships to encourage careers in this field. Additionally, international collaboration is helping raise local professional standards through knowledge exchange and training partnerships. Addressing this demand will not only improve service availability but also ensure a higher quality of care across the country’s mental health ecosystem.
Opportunities of Philippines Mental Health Market:
Mental Health Tourism
The Philippines holds strong potential to develop as a mental health tourism destination, offering affordable yet high-quality therapy, counseling, and rehabilitation services in a tranquil, scenic environment. With its natural landscapes, warm climate, and reputation for hospitality, the country can appeal to international clients seeking recovery in a restorative setting. Competitive service costs compared to Western nations make it attractive for those looking for cost-effective treatment without compromising care quality. Additionally, integrating wellness retreats, holistic therapies, and cultural activities can enhance the therapeutic experience. Partnerships with resorts, hospitals, and mental health professionals could create specialized packages that combine clinical treatment with relaxation and wellness. Such initiatives can generate foreign revenue while boosting the country’s reputation in the global health and wellness market.
Growth in School-Based Interventions
Expanding mental health programs in schools and universities presents a significant opportunity for early intervention and prevention of long-term psychological issues. By integrating counseling services, peer support groups, and mental health education into the curriculum, educational institutions can help students identify and manage emotional challenges early. According to the Philippines mental health market analysis, this approach not only supports academic performance but also fosters resilience, self-awareness, and healthy coping skills among young people. Partnerships between schools, local governments, and mental health professionals can improve access to trained counselors and facilitate workshops for teachers to recognize early warning signs. With the increasing awareness of student well-being, schools can serve as critical touchpoints for providing accessible and stigma-free mental health services, ultimately shaping healthier future generations in the Philippines.
Expansion of Private Sector Clinics
Rising demand for mental health services in the Philippines is creating substantial opportunities for the growth of private clinics and specialized therapy centers. Increasing awareness, a growing middle class, and shifting cultural attitudes toward seeking help are encouraging more individuals to invest in mental well-being. Private practices can offer diverse services such as psychotherapy, psychiatric consultations, group therapy, and alternative treatments tailored to specific needs. Strategic location choices in urban hubs and developing areas can help clinics capture both premium and mid-range markets. Moreover, partnerships with corporations for employee wellness programs and insurance providers can expand client reach. By prioritizing service quality, confidentiality, and modern facilities, private sector clinics can position themselves as trusted providers in the country’s evolving mental health landscape.
Challenges of Philippines Mental Health Market:
Shortage of Mental Health Professionals
The Philippines faces a significant shortage of trained mental health professionals, including psychiatrists, psychologists, and licensed counselors, which limits the availability of specialized services. This gap is especially pronounced in rural and remote areas, where residents often have little to no access to qualified practitioners. As a result, individuals may experience long waiting times, inadequate diagnosis, or receive treatment from untrained personnel. The concentration of professionals in urban centers exacerbates the disparity, forcing rural patients to travel long distances for care. This shortage not only hinders early intervention but also contributes to worsening conditions due to delays in treatment. Addressing this challenge requires expanding training programs, offering incentives for rural deployment, and integrating mental health services into primary care systems.
Stigma and Misconceptions
Persistent stigma and misconceptions about mental health remain major barriers to care in the Philippines. Many individuals fear being judged, discriminated against, or labeled as “weak” if they seek professional help. Cultural beliefs and a lack of accurate information often lead to the dismissal of mental health symptoms as temporary mood swings or personal failings. This mindset discourages people from accessing services, resulting in untreated conditions that may worsen over time. Misconceptions are further reinforced by inadequate mental health education in schools and limited public discourse. Overcoming these challenges requires continuous awareness campaigns, integrating mental health literacy into education systems, and encouraging open conversations within communities to normalize help-seeking behaviors and foster a supportive environment.
Uneven Service Distribution
Mental health services in the Philippines are heavily concentrated in urban areas, leaving many underdeveloped provinces with limited or no access to care. Major cities have hospitals, clinics, and specialists, while rural regions often rely solely on general healthcare providers with minimal mental health training. This imbalance forces individuals in remote locations to travel long distances, incur higher costs, or forgo treatment altogether. Such uneven distribution deepens the disparity in mental health outcomes, particularly among low-income populations. Infrastructure limitations, lack of transportation, and minimal government presence in these regions compound the problem. Solutions include expanding community-based clinics, deploying trained professionals to underserved areas, and leveraging telehealth platforms to bridge the accessibility gap between urban and rural populations.
Government Initiatives in Philippines Mental Health Market:
Funding for Community-Based Care
The allocation of dedicated budgets toward community-based mental health care is transforming service accessibility in the Philippines. By establishing local facilities such as counseling centers and rehabilitation units within municipalities and barangays, individuals can seek help closer to home, reducing travel time and associated costs. These localized services are particularly beneficial for rural and underserved areas where specialized facilities are scarce. Community-based care also fosters a more inclusive approach, enabling early detection and treatment through collaboration with local leaders, schools, and health workers. This model not only increases reach but also strengthens social support networks, creating a safer environment for individuals to address their mental health needs without stigma, while ensuring that care is integrated into everyday community life.
Training for Frontline Health Workers
Capacity-building programs for frontline health workers are essential to expanding the Philippines’ mental healthcare coverage. Through specialized training, general healthcare staff, such as nurses, midwives, and barangay health workers, gain the skills to identify early signs of psychological distress, provide basic counseling, and refer patients to specialists when necessary. This approach helps bridge the gap in mental health service availability, particularly in areas lacking psychiatrists or psychologists. Regular workshops and certification programs also equip health workers with updated knowledge on emerging mental health challenges, such as stress-related disorders or post-pandemic trauma. Empowering these frontline providers ensures that mental health support becomes an integral part of primary healthcare, enabling faster intervention, reducing the treatment gap, and improving long-term outcomes for patients.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Nationwide public awareness campaigns are playing a critical role in reshaping attitudes toward mental health in the Philippines. These initiatives use television, radio, social media, and community events to promote understanding of mental wellness, break cultural stigmas, and encourage individuals to seek help early. By highlighting real-life stories, expert advice, and practical coping strategies, campaigns make mental health conversations more relatable and accessible. Collaborations with schools, workplaces, and influencers amplify their reach, targeting both younger and older audiences. The goal is to normalize mental health discussions, reduce misconceptions, and foster supportive environments where individuals feel safe to speak up. Over time, these campaigns help build a society that prioritizes psychological well-being alongside physical health.
Philippines Mental Health Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on disorder, service, and age group.
Disorder Insights:
- Schizophrenia
- Alcohol Use Disorder
- Bipolar Disorder
- Depression and Anxiety
- Post-traumatic Stress Disorder
- Substance Abuse Disorder
- Eating Disorder
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the disorder. This includes schizophrenia, alcohol use disorder, bipolar disorder, depression and anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, substance abuse disorder, eating disorder, and others.
Service Insights:
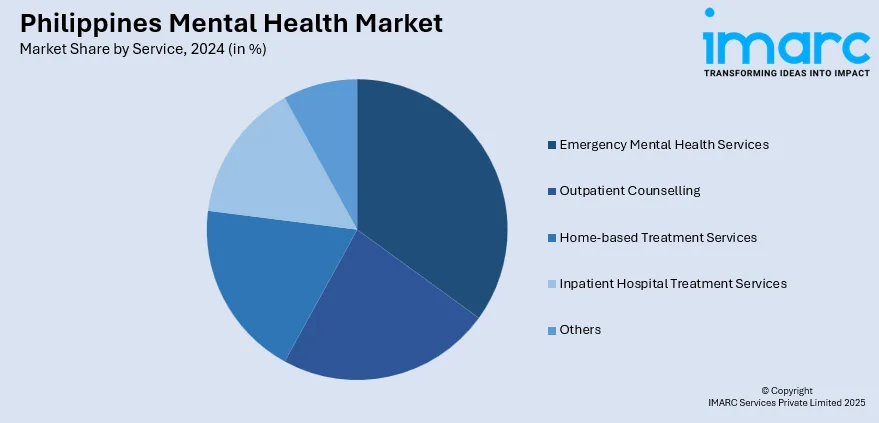
- Emergency Mental Health Services
- Outpatient Counselling
- Home-based Treatment Services
- Inpatient Hospital Treatment Services
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the service has also been provided in the report. This includes emergency mental health services, outpatient counselling, home-based treatment services, inpatient hospital treatment services, and others.
Age Group Insights:
- Pediatric
- Adult
- Geriatric
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the age group has also been provided in the report. This includes pediatric, adult, and geriatric.
Regional Insights:
- Luzon
- Visayas
- Mindanao
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major country markets, which include Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Philippines Mental Health Market News:
- In October 2023, the Department of Health (DOH) and the World Health Organization (WHO) unveiled the 2024–2028 Philippine Council for Mental Health (PCMH) Strategic Framework to direct the creation and execution of mental health policies, programs, and services aimed at addressing the substantial impact of mental illness and enhancing mental health and well-being throughout the nation.
Philippines Mental Health Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Disorders Covered | Schizophrenia, Alcohol Use Disorder, Bipolar Disorder, Depression and Anxiety, Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, Substance Abuse Disorder, Eating Disorder, Others |
| Services Covered | Emergency Mental Health Services, Outpatient Counselling, Home-Based Treatment Services, Inpatient Hospital Treatment Services, Others |
| Age Groups Covered | Pediatric, Adult, Geriatric |
| Regions Covered | Luzon, Visayas, Mindanao. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Philippines mental health market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Philippines mental health market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Philippines mental health industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The mental health market in the Philippines was valued at USD 54.29 Billion in 2024.
The Philippines mental health market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 8.87% during 2025-2033.
The Philippines mental health market is projected to reach a value of USD 116.65 Billion by 2033.
The key trends of the Philippines mental health market include increased public awareness and reduced stigma, driven by the 2018 Mental Health Act. There is also rapid digital transformation, with growing adoption of teletherapy and mental health apps to address the severe shortage of mental health professionals. Furthermore, the integration of mental health into primary care and a rising focus on preventive and holistic wellness are gaining traction.
The Philippines mental health market is growing due to rising prevalence of mental health disorders, coupled with a shortage of professionals, boosting demand for accessible solutions like telehealth and digital platforms. Government support and economic growth also play significant roles.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












