
Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Report Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Treatment Type, End User, and Region, 2025-2033
Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Size and Share:
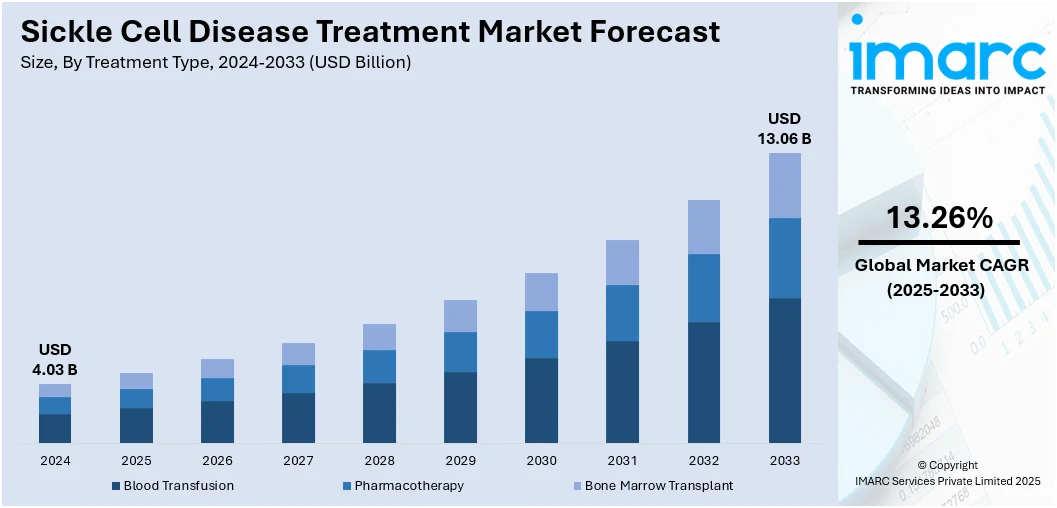
The global sickle cell disease treatment market size was valued at USD 4.03 Billion in 2024. The market is expected to reach USD 13.06 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 13.26% during 2025-2033. North America currently dominates the market, holding a significant market share of around 38.7% in 2024. The market is fueled by the rising prevalence of sickle cell disease globally, supported by expanding newborn screening programs and improved diagnostic capabilities. Besides that, growing investments in research and development, alongside advancements in gene and cell therapies, is accelerating the availability of innovative treatment options. In addition to this, supportive government policies, increased healthcare funding, and initiatives are significant factors augmenting the sickle cell disease treatment market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
|
Market Size in 2024
|
USD 4.03 Billion |
|
Market Forecast in 2033
|
USD 13.06 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 13.26% |
The market is majorly influenced by the increasing availability of advanced healthcare infrastructure in developing regions and the integration of digital health tools for remote monitoring and patient management. For instance, the University of California San Diego developed an automated electronic health record–based registry to identify sickle cell disease (SCD) patients across its health system, achieving a 92.6% positive predictive value, as of July 2024. The registry identified 31 confirmed SCD patients, with targeted outreach initiated to improve care access. Beyond patient identification, the registry is being used to monitor clinical quality metrics, track readmissions, and support care coordination. Moreover, rising collaborations between public health organizations and private entities are enhancing access to specialized treatments. Besides that, expanding clinical trial networks in high-prevalence areas are accelerating the development of region-specific therapeutic solutions. Also, growing emphasis on personalized medicine is encouraging the use of genetic profiling to guide treatment selection.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
In the United States, there strong focus on health equity initiatives to improve care access for communities disproportionately affected by sickle cell disease. As per industry reports in 2024, SCD has affected over 100,000 individuals in the United States. One of the significant sickle cell disease treatment market trends is the expansion of federal funding for research, which enables accelerated progress in innovative therapies. In addition to this, the presence of specialized treatment centers with multidisciplinary expertise ensures comprehensive disease management. Moreover, widespread adoption of electronic health records is facilitating coordinated care and continuous monitoring. Increasing partnerships between academic institutions and biotechnology firms are fostering breakthroughs in curative approaches. Additionally, favorable reimbursement frameworks for advanced treatments are supporting higher adoption rates, reinforcing the country’s leadership in sickle cell disease innovation and care delivery.
Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Trends:
Increase in the Number of Individuals Suffering from SCD
The global prevalence of sickle cell disease is steadily increasing, driven by population growth in high-burden regions, improved survival rates, and expanded newborn screening programs that identify more cases at birth. For instance, in 2025, over 20 Million individuals worldwide suffer from the SCD disorder, with over 100,000 of these patients living in the USA. Migration patterns are also contributing to a broader geographic spread of the disease, leading to increased demand for treatment in areas where SCD was previously uncommon. Besides this, advances in medical care have improved life expectancy for patients, but this also means that the healthcare system must manage a larger number of individuals living with chronic complications. Also, the growing patient base intensifies the need for diversified treatment options, including both curative and supportive care approaches. This rising prevalence is prompting governments, research institutions, and healthcare providers to strengthen resources, expand treatment infrastructure, and accelerate the development of innovative therapies to meet the evolving needs of the expanding patient population.
Rising Disposable Incomes and the Growing Awareness among Individuals
Increasing disposable incomes, particularly in emerging economies, are enabling more patients to seek timely and advanced treatment for sickle cell disease (SCD). This, in turn, is supporting the sickle cell disease treatment market growth. As per industry reports, in the United States, disposable personal income (DPI) in May 2025 was USD 22,454.6 Billion. As financial capacity improves, individuals are more likely to access specialized healthcare facilities, undergo regular diagnostic testing, and afford long-term treatment plans, including higher-cost therapies such as disease-modifying drugs or gene-based interventions. This trend is complemented by growing awareness of SCD through government-led campaigns, advocacy groups, and educational programs. Public health initiatives are disseminating information on early symptoms, preventive measures, and available treatments, leading to earlier diagnoses and more effective disease management. Besides, enhanced knowledge has also resulted in greater patient engagement, with individuals more willing to participate in clinical trials and adopt new therapies. Together, improved financial means and heightened awareness are significantly expanding the treated patient pool, stimulating market demand for both existing and innovative SCD treatments.
Fast-track Approvals by Health Regulatory Authorities
Regulatory agencies in various countries are increasingly prioritizing accelerated pathways for the approval of innovative treatments. This trend is creating a positive sickle cell disease treatment market outlook. For instance, the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) approved a new medicine in 2019 to reduce the pain experienced by adults and children with SCD. This shift is driven by the urgent need to address the significant disease burden and the limitations of existing therapeutic options. Mechanisms such as priority review, breakthrough therapy designation, and orphan drug status are being applied to promising drugs, gene therapies, and advanced cell-based interventions. These expedited processes reduce the time between clinical development and market availability, enabling patients to access potentially life-changing treatments sooner. Regulatory bodies are also enhancing collaboration with developers to provide early guidance on trial design, safety protocols, and manufacturing standards, ensuring compliance while maintaining high safety benchmarks. This proactive approach not only supports innovation but also encourages greater investment in research, as companies can anticipate faster returns and reduced development risk.
Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the global sickle cell disease treatment market, along with forecasts at the global, regional, and country levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on treatment type and end user.
Analysis by Treatment Type:
- Blood Transfusion
- Pharmacotherapy
- Bone Marrow Transplant
Blood transfusion leads the market with around 48.9% of market share in 2024. This type of treatment is one of the most widely used and accessible interventions. It helps reduce the proportion of sickled red blood cells, improving oxygen delivery and lowering the risk of severe complications such as stroke and organ damage. Transfusions are particularly important in managing acute episodes and preventing recurrent crises in high-risk patients. They are also used as a long-term preventive measure for children and adults with severe disease manifestations. While effective, regular transfusions require careful monitoring to manage risks like iron overload and transfusion reactions, which has led to the parallel growth of iron chelation therapies. In regions with limited access to advanced treatments, blood transfusion remains a cornerstone of care, reinforcing its continuing relevance in both developed and resource-constrained healthcare systems.
Analysis by End User:
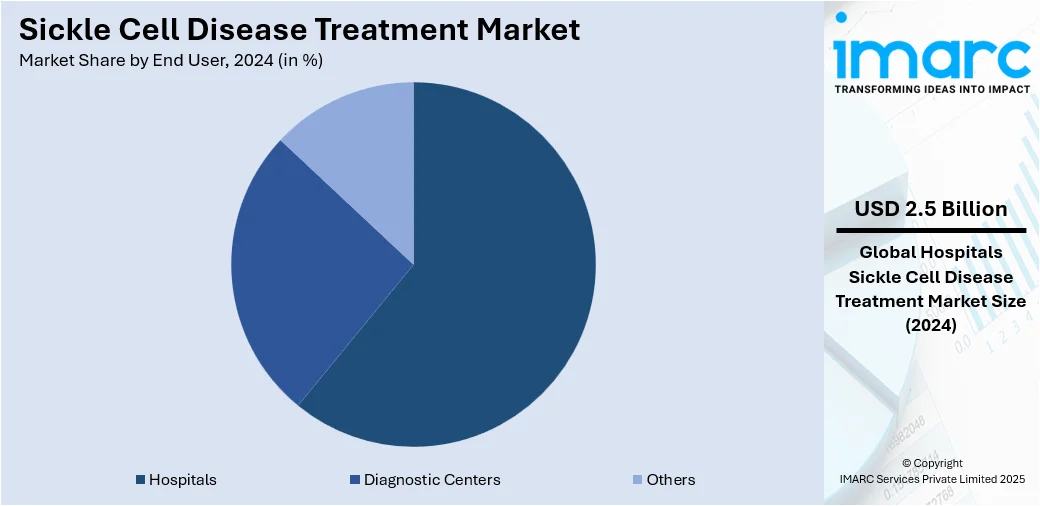
- Hospitals
- Diagnostic Centers
- Others
Hospitals lead the market with around 60.8% of market share in 2024. Hospitals are the leading centers for diagnosis, management, and specialized care. They offer holistic services, which range from emergency interventions for pain crises to administration of blood transfusions and monitoring for complications such as stroke or organ damage. Hospitals are also the main locations for specialized interventions such as stem cell transplants and gene therapy, which need sophisticated infrastructure and multidisciplinary capabilities. Additionally, they have specialized hematology departments and laboratories for ongoing monitoring of patients and management of diseases. They also play a role in patient education, counseling, and coordination of long-term care. In most areas, hospitals serve as referral centers, connecting patients with clinical trials and new treatments. Their capacity to provide both acute and preventive care makes them an important end-user segment, with direct effects on treatment accessibility, quality, and patient outcomes within the market.
Regional Analysis:
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Australia
- Indonesia
- Others
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Italy
- Spain
- Russia
- Others
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
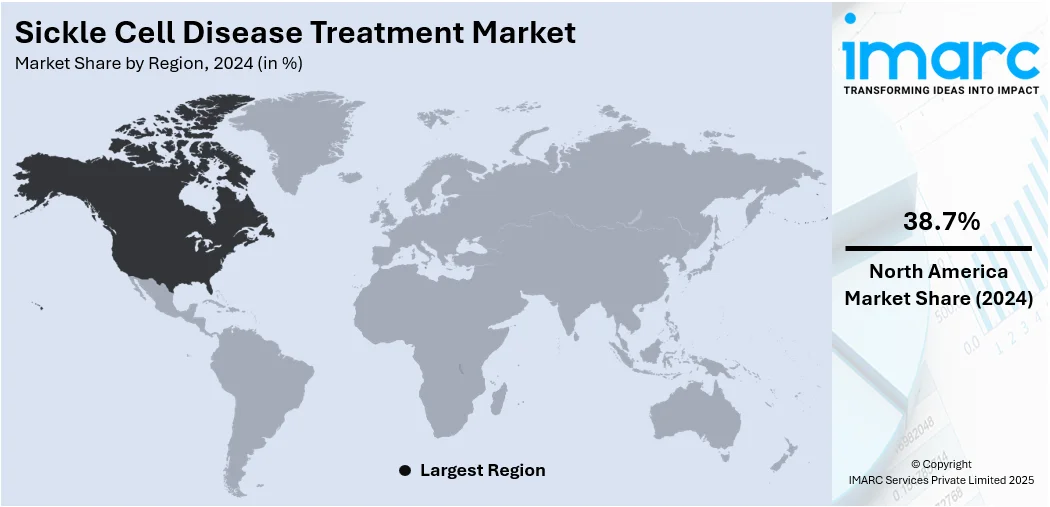
In 2024, North America accounted for the largest market share of over 38.7% due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high disease awareness, and strong research capabilities. The region benefits from established screening programs, early diagnosis, and access to a broad range of treatment options, from supportive care to cutting-edge gene and cell therapies. Significant investment in clinical research and favorable regulatory pathways support the rapid introduction of new therapies, making the region a leader in innovation. Insurance coverage and government-funded healthcare programs improve access for many patients, though disparities persist among underserved populations. The presence of specialized treatment centers and experienced healthcare professionals ensures high-quality care and ongoing monitoring. With continuous advancements and growing adoption of novel treatments, North America remains a critical market, influencing global trends and driving the pace of therapeutic development for sickle cell disease.
Key Regional Takeaways:
United States Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Analysis
In 2024, the United States holds a substantial share of around 89.00% of the sickle cell disease treatment share in North America. United States has witnessed increasing sickle cell disease treatment adoption due to the expansion of diagnostic centers across urban and rural areas. For instance, there are 32,257 businesses in the Diagnostic & Medical Laboratories industry in the United States, which has grown at a CAGR of 4.9 % between 2020 and 2025. The presence of advanced diagnostic facilities has improved early detection and monitoring of sickle cell complications, resulting in more timely therapeutic interventions. These diagnostic centers are equipped with modern tools for genetic screening and hemoglobin electrophoresis, which have made diagnosis more efficient and accessible. Moreover, rising awareness among patients and healthcare professionals about early testing is encouraging regular screenings. Insurance coverage for diagnostic procedures has further contributed to increased utilization of sickle cell treatments. Healthcare systems are increasingly integrating these services into primary care networks, ensuring faster referrals and treatment decisions.
Asia-Pacific Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Analysis
Asia-Pacific is experiencing rising adoption of sickle cell disease treatment driven by a noticeable surge in anemia cases across both urban and rural populations. According to Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) (April 2025) indicates that 67.1% of children and 59.1% of adolescent girls are anemic. Increasing awareness regarding hereditary blood disorders and rising anemia prevalence have prompted more individuals to seek medical evaluation for underlying hemoglobinopathies. Healthcare providers are responding by incorporating advanced therapeutic protocols aimed at managing sickle cell complications alongside anemia symptoms. Government health programs are also emphasizing screening initiatives that identify anemia cases potentially linked to sickle cell conditions. In rural areas, community outreach programs are facilitating diagnosis and early treatment. This increasing burden of anemia has highlighted the necessity for tailored interventions and disease management strategies.
Europe Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Analysis
The market in the Europe is growing due to several factors, including the Rare Diseases Plan implemented in 2017 within the EU, which significantly enhanced the treatment landscape for rare diseases. This initiative, along with the establishment of 24 European Reference Networks (ERNs), including the ERN on Rare Haematological Diseases (ERN-EuroBloodNet), has fostered increased collaboration among healthcare providers, researchers, and patient organizations. This network focuses specifically on rare blood-related conditions like sickle cell disease, promoting the exchange of knowledge, clinical expertise, and resources across European countries. Furthermore, the growing awareness of the disease and its impact on public health is driving initiatives in several European countries. Collaborative efforts between healthcare providers and non-governmental organizations have also led to improvements in early diagnosis and patient management.
Latin America Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Analysis
Latin America has observed a notable increase in sickle cell disease treatment adoption due to improvements in healthcare infrastructure. In countries such as Brazil and Mexico, the government and healthcare systems are focusing on raising awareness about the disease and providing essential healthcare services. Available and extrapolated data indicate that sickle cell disease (SCD) affects more than 6,000 newborns annually and between 100,000 and 150,000 individuals across Latin America. Support from international organizations, including the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), is also helping improve access to therapies and early diagnosis. The increasing availability of clinical trials for new treatments in Latin America is another significant factor fueling market growth in the region. Privatization is also driving innovation and investment in disease-specific care, including sickle cell therapies. As public-private partnerships expand, more individuals are gaining access to advanced medical services, supporting early diagnosis and sustained treatment for sickle cell complications.
Middle East and Africa Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Analysis
Middle East and Africa are experiencing rising sickle cell disease treatment adoption as a result of improved healthcare facilities across several regions. For instance, in 2025, the UAE is currently home to over 150 hospitals and has more than 5,000 healthcare facilities. Moreover, investments in new hospitals, clinics, and hematology units have allowed for better disease management and specialized care. Apart from that, expanded access to professional healthcare staff and modern diagnostic tools is accelerating timely treatment. In addition to this, as per industry reports, Africa carries the greatest burden of sickle cell disease (SCD), with prevalence reaching up to 3% of births in certain regions. This high incidence is driving market growth across the continent.
Competitive Landscape:
The market is characterized by rapid innovation, with therapies addressing both symptom control and curative potential. Existing options include supportive care, transfusions, and pharmacological agents aimed at reducing complications. Moreover, advancements in genetic and cell-based therapies are intensifying competition, as these approaches aim to correct the root cause of the disease. Market players are differentiating through safety, efficacy, and delivery methods to reduce treatment burden and improve quality of life. In addition to that, regulatory incentives and expanded clinical research pipelines are accelerating product development, though high costs and limited infrastructure in some regions pose adoption challenges. Competition is also influenced by efforts to expand access in underserved populations through targeted healthcare programs. According to the sickle cell disease treatment market forecast, rising disease awareness, improved diagnostic capabilities, and growing investment in advanced therapeutics are expected to drive strong growth over the next decade, with significant opportunities emerging in both established and resource-limited healthcare systems.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the sickle cell disease treatment market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
- AstraZeneca Plc
- Baxter International Inc.
- bluebird bio Inc.
- Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
- CRISPR Therapeutics
- Emmaus Medical Inc.
- Global Blood Therapeutics Inc.
- GlycoMimetics Inc.
- Novartis AG
- Pfizer Inc.
- Sangamo Therapeutics
Latest News and Developments:
- June 2025: The Ministry of Tribal Affairs and AIIMS, Delhi, conducted a competition for drug development aimed at treating sickle cell disease, which severely impacted India’s tribal populations. Minister Durgadas Uikey announced the initiative on World Sickle Cell Day and assured full funding and free medicine support for sickle cell disease management.
- June 2025: Beam Therapeutics reported that the U.S. FDA has granted orphan drug designation to BEAM-101, a genetically modified cell therapy aimed at treating sickle cell disease. This designation highlights the urgent need for novel treatments for the condition and reinforces the advancement of BEAM-101 through ongoing clinical development.
- May 2025: The Indian Council of Medical Research launched the ICMR-SCD Stigma Scale for India in May 2025 to address stigma associated with sickle cell disease among patients and caregivers. The scale was developed in six endemic districts and tailored to India’s socio-cultural context.
- March 2025: A novel clinical trial launched at UCSF Benioff Children's Hospital Oakland had aimed to cure sickle cell disease using CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing technology to correct the genetic mutation. Researchers had begun enrolling adult patients with sickle cell disease in California to test the safety and efficacy of this non-viral therapy.
- February 2025: CRISPR medicine was developed as the world’s first gene-editing therapy for sickle cell disease, transforming decades of laboratory research into a groundbreaking clinical treatment. Researchers including Vijay Sankaran translated early genetic insights into a life-changing therapy that offered hope to patients suffering from frequent sickle cell disease pain episodes.
Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Treatment Types Covered | Blood Transfusion, Pharmacotherapy, Bone Marrow Transplant |
| End Users Covered | Hospitals, Diagnostic Centers, Others |
| Regions Covered | Asia Pacific, Europe, North America, Latin America, Middle East and Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, Russia, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia, Indonesia, Brazil, Mexico |
| Companies Covered | AstraZeneca Plc, Baxter International Inc., bluebird bio Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, CRISPR Therapeutics, Emmaus Medical Inc., Global Blood Therapeutics Inc., GlycoMimetics Inc., Novartis AG, Pfizer Inc., Sangamo Therapeutics |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the sickle cell disease treatment market from 2019-2033.
- The sickle cell disease treatment market research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the global market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets. It further enables stakeholders to identify the key country-level markets within each region.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the sickle cell disease treatment industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
Sickle cell disease treatment market was valued at USD 4.03 Billion in 2024.
Sickle cell disease treatment market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 13.26% during 2025-2033, reaching a value of USD 13.06 Billion by 2033.
The market is driven by rising prevalence of sickle cell disease, growing adoption of gene therapies, and increased healthcare funding for rare diseases. Advancements in curative treatments, supportive government initiatives, and expanded newborn screening programs are also accelerating diagnosis and treatment access, boosting overall market growth globally.
North America currently dominates the sickle cell disease treatment market with a market share of around 38.7%. The dominance is fueled by the region’s advanced healthcare infrastructure, strong presence of biopharmaceutical companies, favorable reimbursement policies, and ongoing clinical research, alongside high awareness and early diagnosis rates that support rapid adoption of innovative therapies.
Some of the major players in the sickle cell disease treatment market include AstraZeneca Plc, Baxter International Inc., bluebird bio Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, CRISPR Therapeutics, Emmaus Medical Inc., Global Blood Therapeutics Inc., GlycoMimetics Inc., Novartis AG, Pfizer Inc., and Sangamo Therapeutics, among others.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












