
India Online Food Delivery Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Platform Type, Business Model, Payment Method, and Region, 2026-2034
India Online Food Delivery Market Summary:
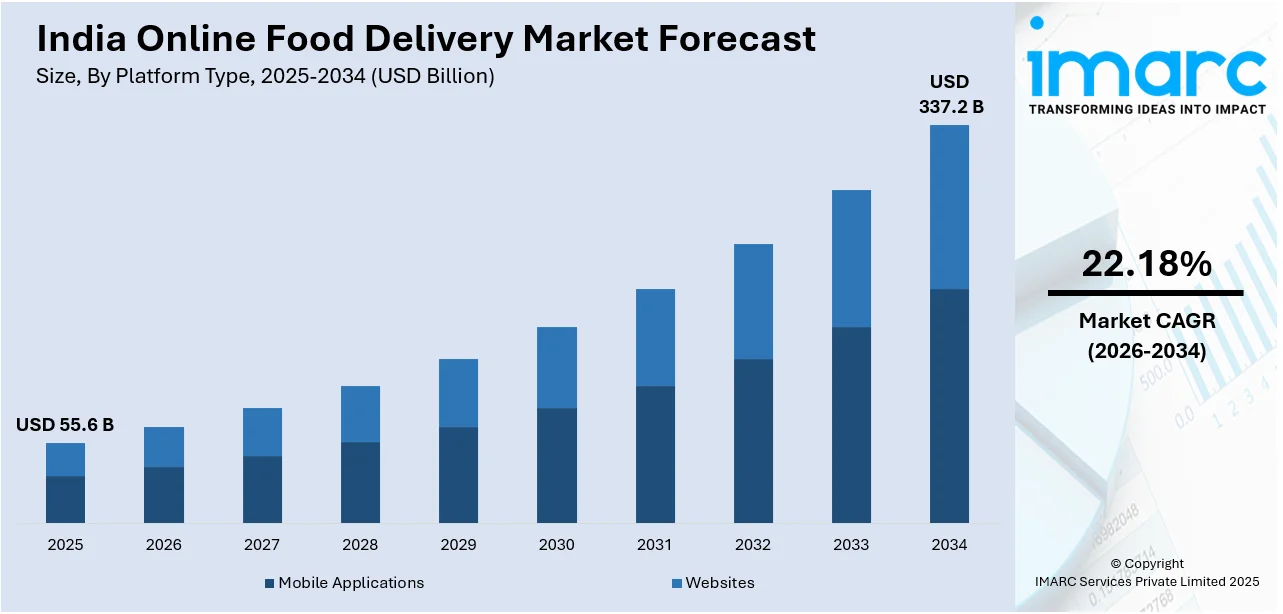
The India online food delivery market size was valued at USD 55.58 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 337.15 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 22.18% from 2026-2034.
India's online food delivery ecosystem is experiencing remarkable expansion driven by widespread smartphone adoption, evolving urban lifestyles, and the growing preference for convenience-oriented dining solutions. Apart from this, the market is thriving on technological innovation, extensive restaurant partnerships, and the increasing penetration of digital payment infrastructure across metropolitan and tier-2 cities, thereby expanding the India online food delivery market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Platform Type: Mobile applications dominate the market with a share of 79% in 2025, reflecting consumer preference for on-the-go ordering experiences and seamless mobile-first user interfaces.
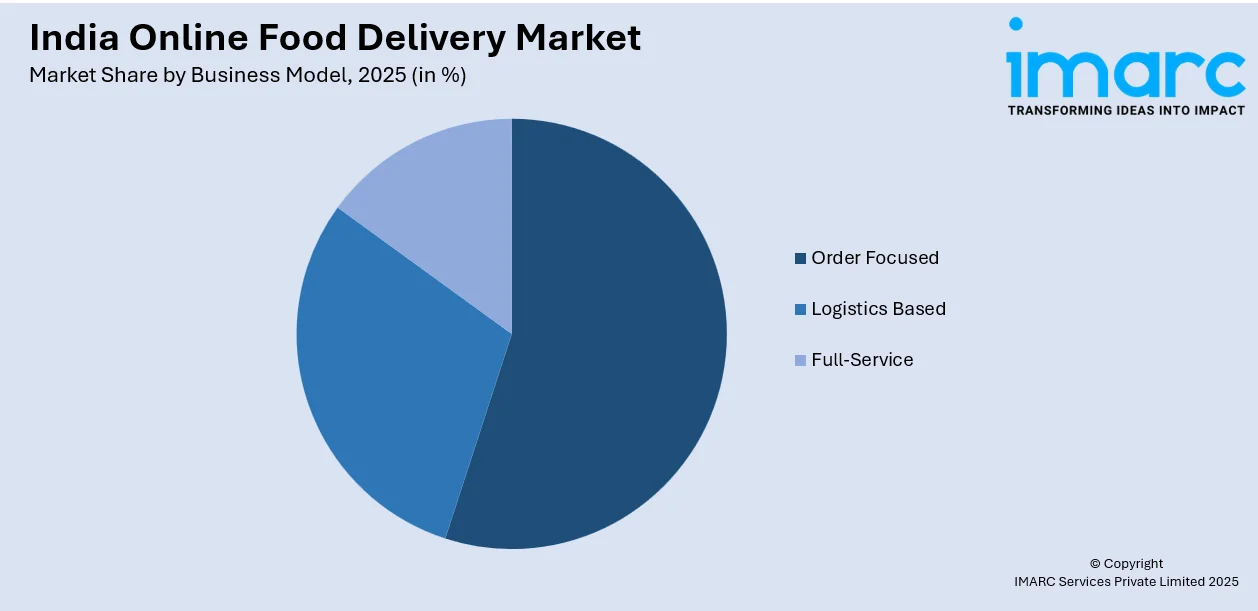
- By Business Model: Order-focused delivery system leads the market with a share of 50% in 2025, capitalizing on aggregator platforms that connect consumers with diverse restaurant choices through centralized ordering interfaces.
- By Payment Method: Online represents the largest segment with a market share of 69% in 2025, driven by digital wallet proliferation, UPI integration, and consumer trust in cashless transaction security.
- By Region: North India dominates with a market share of 30% in 2025, benefiting from high population density in Delhi NCR, strong internet connectivity, and concentrated urban consumer bases with elevated disposable incomes.
- Key Players: The competitive landscape features both established aggregators and cloud kitchen operators competing intensively for market share through aggressive discounting strategies, rapid delivery innovations, and expanded restaurant partnerships across multiple consumption occasions.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The market demonstrates accelerated growth trajectories as smartphone penetration deepens across semi-urban geographies where affordable data plans enable first-time digital ordering experiences. Cloud kitchen proliferation allows restaurant brands to experiment with multiple virtual concepts from centralized facilities, reducing operational expenditure while serving diverse culinary preferences through delivery-only models. Artificial intelligence (AI) integration enhances order prediction accuracy and route optimization, while quick commerce initiatives promise ultra-fast delivery windows that compress traditional fulfillment timeframes. Government support for digital payments infrastructure through interoperable systems strengthens transaction security and convenience. In July 2024, Rebel Foods announced INR 200 Crore investment to fortify its cloud kitchen network with plans to establish 100 EatSure food courts across major cities, demonstrating industry confidence in delivery-centric restaurant formats that bypass traditional dine-in infrastructure requirements.
India Online Food Delivery Market Trends:
Proliferation of Cloud Kitchen Operations
Cloud kitchens have emerged as transformative infrastructure enabling restaurant brands to establish delivery-focused operations without dine-in facilities. These virtual kitchen concepts eliminate front-of-house expenses including prime location rentals, interior design investments, and service staff wages, reducing capital requirements by approximately 40-50% compared to conventional restaurants. The model facilitates rapid geographic expansion as operators can launch multiple brand identities from unified production facilities, testing menu innovations with minimal financial risk while responding dynamically to local taste preferences. Technology platforms provide real-time demand analytics enabling inventory optimization and waste reduction. In 2025, Healthy food brand Salad Days intends to grow its cloud kitchen network to more than 50 sites by the conclusion of 2025, focusing on Delhi-NCR and Mumbai. This growth, driven by the latest Series A funding, seeks to satisfy increasing demand for healthy, ready-to-eat meals and improve delivery services in vital urban centers.
Expansion into Tier-Two and Tier-Three Cities
Food delivery platforms are strategically penetrating smaller metropolitan areas where improving digital infrastructure and rising disposable incomes create untapped market opportunities. These markets demonstrate faster breakeven timelines, requiring only 800 daily orders compared to 1,300 in tier-one cities due to lower operational costs and reduced competitive intensity. Platform operators are adapting business models to accommodate regional culinary preferences and price-sensitive consumer segments while establishing local restaurant partnerships. The expansion strategy encompasses investments in hyperlocal fulfillment infrastructure including micro-warehouses and last-mile delivery fleets optimized for varying urban densities. Mobile application interfaces increasingly support vernacular languages enhancing accessibility for non-English speaking populations. December 2024 witnessed WAAYU, India's first zero-commission food delivery platform supported by Open Network for Digital Commerce, launching in Hyderabad with plans to onboard 100,000 restaurants within three years, demonstrating alternative business models emerging in tier-two markets.
Digital Payment Infrastructure Dominance
Unified payment interface (UPI) technology has revolutionized transaction processing by processing 16.58 billion financial transactions in a single month. Digital payment infrastructure plays a central role in shaping India’s online food delivery market. Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has emerged as the dominant mode, supported by instant settlement, high reliability, and minimal transaction costs. Its suitability for low-value, high-frequency transactions aligns well with food delivery usage patterns, accelerating the decline of cash-on-delivery, particularly in urban and semi-urban markets. While cards and digital wallets remain available, their share of transactions continues to lag behind UPI. Leading platforms actively promote digital payments through targeted incentives, subscription benefits, and seamless checkout flows, reinforcing consumer preference for cashless transactions. For restaurant partners, digital payments improve cash flow visibility, reduce reconciliation challenges, and support formal financial reporting. For platforms, they enable richer transaction data and stronger control over the payment experience. Together, these factors have embedded digital payments as a core enabler of efficiency, scale, and user retention in India’s online food delivery ecosystem.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
Digital infrastructure advancement including 5G network deployment will enable enhanced mobile application experiences with reduced latency and improved real-time tracking capabilities. Artificial intelligence (AI) integration promises sophisticated demand forecasting, personalized menu recommendations, and dynamic pricing optimization that balances consumer value perception with restaurant profitability. The market generated a revenue of USD 55.58 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 337.15 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 22.18% from 2026-2034. Quick commerce evolution toward ultra-fast delivery windows below 15 minutes will intensify logistics investments in dark store networks positioned within immediate proximity to high-density residential clusters. Government digital payment policy support through interoperable frameworks continues strengthening transaction security while reducing cash dependency across tier-two and tier-three city populations.
India Online Food Delivery Market Report Segmentation:
|
Segment Category |
Leading Segment |
Market Share |
|
Platform Type |
Mobile Applications |
79% |
|
Business Model |
Order Focused Food Delivery System |
50% |
|
Payment Method |
Online |
69% |
|
Region |
North India |
30% |
Platform Type Insights:
- Mobile Applications
- Websites
Mobile applications dominate with a market share of 79% of the total India online food delivery market in 2025.
Mobile applications have emerged as the preferred ordering channel due to their superior user experience, personalized interfaces, and seamless integration with smartphone ecosystems. The dominance of mobile apps reflects India's mobile-first internet user base, where approximately 90% of online transactions occur through smartphones rather than desktop computers. Push notification capabilities enable platforms to drive engagement through targeted promotional offers, while location-based services facilitate accurate address detection and real-time delivery tracking.
The mobile application advantage extends beyond ordering convenience to encompass integrated payment wallets, loyalty program management, and social features that encourage repeat usage. Advanced mobile apps leverage device capabilities such as cameras for visual search, voice assistants for hands-free ordering, and biometric authentication for secure payments. The app-based model also generates valuable behavioral data that platforms utilize for algorithmic recommendations, dynamic pricing strategies, and inventory optimization, creating self-reinforcing network effects that solidify mobile's market leadership position.
Business Model Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Order Focused
- Logistics Based
- Full-Service
Order-focused food delivery system leads with a share of 50% of the total India online food delivery market in 2025.
Order-focused platforms operate as aggregators that connect consumers with restaurants while leaving delivery logistics to restaurant partners or third-party providers. This asset-light model enables rapid scaling across diverse restaurant categories without heavy capital investment in delivery fleet infrastructure. Apart from this, the approach appeals to established restaurants with existing delivery capabilities who seek additional customer channels without surrendering control over fulfillment operations or paying commission rates associated with full-service models.
The order-focused segment thrives on network effects, where platform value increases exponentially with restaurant selection breadth and customer base size. These platforms concentrate investments in technology development, customer acquisition, and brand building rather than operational logistics. The model demonstrates particular strength in markets with fragmented restaurant landscapes and established local delivery ecosystems. By maintaining neutral marketplace positioning, order-focused platforms attract premium restaurants hesitant to cede customer relationships to full-service providers while offering consumers unparalleled dining choice spanning budget to luxury segments.
Payment Method Insights:
- Online
- Cash on Delivery
Online exhibits a clear dominance with a 69% share of the total India online food delivery market in 2025.
Digital payment methods have become the predominant transaction mode as UPI infrastructure achieves near-universal acceptance and consumer trust in online transactions strengthens significantly. The online payment preference stems from multiple advantages including instant order confirmation, promotional discounts exclusively available for digital transactions, and elimination of cash handling friction for both consumers and delivery personnel. Platform incentives such as cashback rewards, loyalty points, and instant refunds further accelerate the shift toward cashless ordering.
The digital payment ecosystem's maturity enables sophisticated features like split payments among groups, scheduled payments, and integration with credit facilities that enhance purchasing power. Platforms benefit from reduced cash management costs, lower fraud exposure, and faster settlement cycles that improve working capital efficiency. The regulatory push toward formal economy participation and transaction traceability also supports online payment growth. Despite cash-on-delivery's continued relevance in tier-3 cities and among demographic segments with limited banking access, the trajectory clearly favors digital-first transaction models as financial inclusion initiatives expand and younger generations increasingly dominate consumer cohorts.
Region Insights:
- North India
- West and Central India
- South India
- East India
North India leads with a share of 30% of the total India online food delivery market in 2025.
North India's market leadership stems from the Delhi National Capital Region's massive urban agglomeration, which concentrates millions of young professionals, students, and dual-income households with high propensity for convenience-oriented food consumption. The region's extensive commercial infrastructure, well-developed road networks, and concentrated residential density enable efficient delivery economics that support competitive pricing and rapid order fulfillment. Metropolitan areas like Delhi, Gurgaon, and Noida host headquarters of major technology companies and multinational corporations, creating ideal customer segments with disposable income and digital-first consumption preferences.
The region's diverse culinary landscape spanning traditional North Indian cuisine, international dining options, and fusion concepts provides rich restaurant inventory that sustains consumer engagement across occasions. North India's early adoption of smartphone technology and digital payment systems created favorable conditions for platform penetration, while intense competition among aggregators has driven innovation in delivery speed, restaurant selection, and promotional offers. The presence of numerous educational institutions generates consistent demand from students seeking affordable meal solutions, while the region's emerging satellite cities present expansion opportunities as delivery infrastructure extends beyond core metropolitan boundaries.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the India Online Food Delivery Market Growing?
Accelerating Smartphone Penetration and Affordable Data Plans
India's smartphone user base continues expanding rapidly with 85.5% of Indian households having at least one smartphone, as device prices decline and telecom operators offer competitively priced data packages that make mobile internet accessible to broader demographic segments. The proliferation of affordable smartphones priced under USD 150 has democratized digital access, enabling millions of first-time internet users to discover online ordering platforms. Telecom sector competition has driven data costs to among the lowest globally, removing economic barriers to frequent app usage and enabling seamless browsing of restaurant menus, real-time order tracking, and multimedia content consumption. This digital infrastructure expansion creates favorable conditions for platforms to acquire users across income strata and geographic markets, extending beyond metropolitan areas into tier-2 and tier-3 cities where smartphone adoption is accelerating most rapidly.
Evolving Urban Lifestyles and Time-Constrained Consumers
Urbanization and changing workforce dynamics are fundamentally reshaping meal consumption patterns as nuclear families, working couples, and single professionals prioritize convenience over traditional home cooking. Extended work hours, lengthy commutes, and the proliferation of dual-income households have reduced available time for meal preparation, creating strong demand for ready-to-eat food solutions. The normalization of ordering meals through apps has eliminated social stigma previously associated with outsourcing food preparation, while platforms' expanded cuisine offerings and quality assurance mechanisms have built consumer confidence. Younger demographic cohorts particularly embrace on-demand food delivery as an integral lifestyle component, viewing it not as occasional indulgence but as routine solution for daily sustenance needs across breakfast, lunch, and dinner occasions. By the end of 2026, BigBasket, the grocery delivery service supported by Tata Group announced its plans to launch 10-minute food delivery across India.
Strategic Platform Investments in Delivery Infrastructure
Major aggregators are committing substantial capital toward building proprietary delivery fleets, dark stores, and cloud kitchen networks that enhance operational control and unit economics. These infrastructure investments enable platforms to reduce delivery times, improve order accuracy, and maintain quality standards across the fulfillment chain. The establishment of strategically located micro-fulfillment centers stocked with high-velocity items allows platforms to promise 15-20 minute delivery windows that create competitive differentiation. Technology investments in route optimization algorithms, demand forecasting models, and automated dispatch systems improve delivery partner productivity while reducing per-order costs. In 2025, Amazon India announced the expansion of its 10-minute delivery service Amazon Now to 100 micro-fulfilment centres (MFCs) covering most of Bangalore and parts of Mumbai and Delhi, and expanding to full city coverage in coming months.
Market Restraints:
Why is the India Online Food Delivery Market Growing?
High Customer Acquisition Costs and Profitability Pressures
Intense competition among platforms necessitates aggressive promotional spending through deep discounts, cashback offers, and free delivery incentives that significantly erode unit economics. Customer acquisition costs remain elevated as platforms vie for market share in a winner-takes-most marketplace, while low switching costs enable consumers to migrate freely toward the best promotional offers. The pressure to maintain subsidized pricing constrains platforms' ability to achieve profitability despite growing order volumes, creating tension between growth objectives and sustainable business models.
Restaurant Partner Relationship Complexities
High commission rates charged to restaurant partners generate friction as establishments struggle with compressed margins on platform orders. Many restaurants view aggregators as necessary distribution channels while resenting dependency on platforms that control customer relationships and pricing power. Commission disputes, contract negotiations, and occasional partner boycotts create operational uncertainties. The emergence of direct ordering systems and restaurant-owned delivery capabilities represents potential long-term threats to aggregator models.
Delivery Partner Retention and Labor Market Challenges
High attrition rates among gig economy delivery personnel create recruitment and training burdens while impacting service consistency. Delivery partners face income volatility, safety concerns, and limited social security benefits that reduce appeal of platform work. Regulatory discussions around gig worker classification, minimum wage requirements, and benefit mandates pose potential cost increases. Competition for delivery personnel intensifies during peak demand periods, creating capacity constraints and service quality variability during critical ordering windows.
Competitive Landscape:
The India online food delivery market exhibits intense rivalry characterized by aggressive customer acquisition strategies, extensive restaurant network development, and rapid technological innovation cycles. Major aggregators compete across multiple dimensions including delivery speed, restaurant selection breadth, user interface design, promotional intensity, and geographic coverage expansion. Platforms differentiate through subscription programs, exclusive restaurant partnerships, and premium delivery tiers while simultaneously extending into adjacent categories such as grocery delivery and quick commerce. The competitive environment features both pure-play food delivery specialists and diversified internet companies leveraging existing customer bases and logistics infrastructure. Market dynamics favor platforms achieving network effects through scale, with leadership positions reinforcing through data advantages, supplier negotiating power, and brand recognition that creates barriers to new entrant success. Some of the key players include:
- Domino's (Jubilant FoodWorks Ltd.)
- EatClub Brands Pvt. Ltd
- FreshMenu
- Rebel Foods
- Swiggy Limited
- Zomato Ltd.
Recent Developments:
- August 2025, Rapido, a well-known ride-hailing app in India, discreetly commenced beta testing its food delivery service in Bengaluru, signifying its initial significant attempt to compete with market frontrunners Swiggy and Zomato in one of the globe’s rapidly expanding delivery sectors. The decade-old startup is now testing its food delivery service in three main areas of the southern city of Bengaluru: Byrasandra, Tavarekere, and Madiwala (BTM) Layout, Hosur Sarjapura Road (HSR) Layout, and Koramangala, as confirmed by Rapido co-founder and CEO Aravind Sanka to TechCrunch.
India Online Food Delivery Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Platform Types Covered | Mobile Applications, Websites |
| Business Models Covered | Order Focused, Logistics Based, Full-Service |
| Payment Methods Covered | Online, Cash on Delivery (COD) |
| Region Covered | North India, West and Central India, South India, East India |
| Companies Covered | Domino's (Jubilant FoodWorks Ltd.), EatClub Brands Pvt. Ltd, FreshMenu, Rebel Foods, Swiggy Limited, Zomato Ltd., etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The India online food delivery market size was valued at USD 55.58 Billion in 2025.
The India online food delivery market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 22.18% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 337.15 Billion by 2034.
Mobile applications dominated the India online food delivery market with a 79% share in 2025, driven by smartphone-first consumer behavior, superior user experience design, and integrated features that facilitate seamless ordering, payment, and delivery tracking through handheld devices.
Key factors driving the India online food delivery market include rapid smartphone penetration, government digital payment infrastructure support through unified payment interface technology processing innumerable daily transactions, cloud kitchen operational efficiency reducing capital requirements, expanding tier-two and tier-three city penetration where a major percentage of e-commerce shoppers currently reside, and evolving consumer preferences toward convenience-driven meal solutions among dual-income households and young professionals with time-constrained lifestyles.
Major challenges include high customer acquisition costs that pressure profitability amid intense competitive discounting, complex restaurant partner relationships strained by commission rate disputes, delivery partner retention difficulties stemming from gig economy labor market dynamics, and operational constraints during peak demand periods affecting service consistency.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












