India Foreign Exchange Market: Key Trends, Regulatory Landscape, and Future Outlook

How India’s Forex Market is Expanding and Changing:
India’s foreign exchange market has emerged as a crucial component of the nation's financial system. Over the past decade, its scale, depth, and liquidity have expanded significantly, fueled by increasing international trade volume, attracting foreign investments (FDI and FII), and facilitating outbound remittances. This growth underscores the market's importance and reflects India's integration into the global economy. The market now supports a diverse range of participants—from banks and corporates to retail investors and fintech platforms—each playing a role in currency exchange, hedging, and risk management. As the economy liberalizes further and capital flows become more dynamic, an efficient forex ecosystem is becoming increasingly essential.
Get sample data, market projections (2025–2033), segmentation insights, and key player profiles in the India Foreign Exchange Market Report
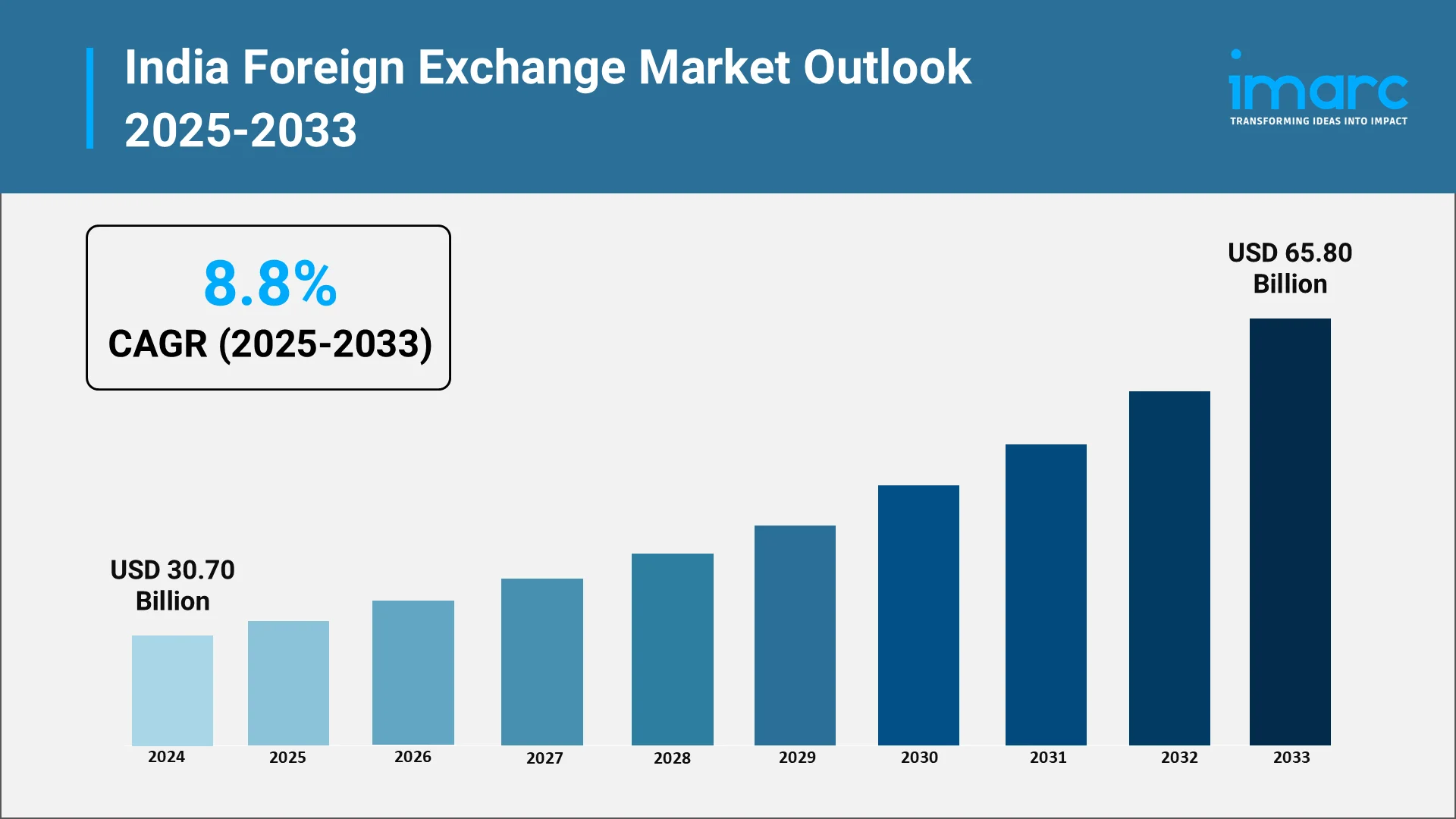
In 2024, India’s forex market was estimated at USD 30.70 Billion, marking a sharp rise from prior years. This growth supports commercial flows and central bank operations. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively uses the forex market to manage currency volatility and ensure monetary stability.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
Rapid Growth in India’s Forex Market: Key Drivers:
India’s foreign exchange market is witnessing a wave of change with increased participation, growing adoption of tech, and a shifting global landscape. Some of the most crucial trends driving the market today and what they mean for businesses, investors, and policymakers Include:
Rising Retail Participation in Forex Trading
The proliferation of digital platforms and increased awareness among retail investors have significantly democratized forex trading. This surge in retail involvement is adding depth and liquidity to the market, a notable shift from its traditionally institutional dominance. User-friendly digital platforms, seamless onboarding, and live price feeds have lowered entry barriers. A younger, tech-savvy investor base is trading major currency pairs, often using demo accounts, margin tools, and broker-provided learning modules. Once dominated by institutions, the market is now witnessing individual traders grow in number and impact. The foreign exchange market in India is witnessing a clear shift toward broader individual participation. In April 2025, RBI Governor emphasized fair treatment for small forex buyers and increased retail participation in government securities at a recent conference. He highlighted the need for better liquidity in the call money market and warned against banks collaborating with unauthorized forex platforms. This shift has pushed brokerages to invest in better platforms, while regulators are paying closer attention to investor protection, transparency, and the use of leverage by inexperienced participants.
Role of RBI and Policy Interventions
The RBI continues to anchor the forex market through direct intervention and macroprudential policy. Its toolkit includes managing interest rate differentials, adjusting liquidity conditions, and using forex reserves tactically. The central bank’s bi-monthly reviews provide cues for banks and corporates managing currency risk. For instance, in January 2025, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) revised the regulations under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) to facilitate cross-border transactions. Key changes include allowing Indian exporters to open foreign currency accounts with overseas banks and enabling Special Non-Resident Rupee accounts, aimed at enhancing the Indian rupee's global competitiveness and facilitating international trade and investment. RBI also steps in during global turmoil, using swaps or selling dollars to calm markets. Its approach balances exchange rate flexibility with targeted intervention, reinforcing confidence among international investors and domestic stakeholders.
INR Volatility from Global Macro Events
The Indian rupee remains highly sensitive to external shocks. US Federal Reserve rate changes, crude oil price volatility, and regional geopolitical tensions have caused sharp swings in currency levels. With India being a major energy importer, any rise in oil prices fuels dollar demand, putting downward pressure on the rupee. In periods of global risk aversion, capital outflows further amplify volatility. To manage this, corporates increasingly rely on hedging tools, while the RBI steps in to smooth excessive fluctuations. Stability in this environment has become a shared responsibility between firms and the central bank.
Rise in Hedging and Derivative Usage
Corporates are now more proactive in managing currency risk. The use of derivatives—like forwards, options, and swaps—has grown sharply. Exporters, importers, and firms with foreign revenue exposure routinely hedge to protect against currency fluctuations. Stock exchanges such as NSE and BSE have expanded their forex derivative offerings, drawing interest from even mid-sized enterprises. Greater access to structured products, rising financial awareness, and stronger advisory support from banks and consultants have accelerated this trend.
Trade Deficit and Reserve Pressures
India’s persistent trade deficit continues to strain forex reserves. A wide gap between imports and exports increases dollar demand, weakening the rupee and triggering RBI interventions. In recent months, surges in energy and electronics imports have widened the gap, despite partial relief from strong services exports and remittances. This imbalance affects reserve strength and limits monetary flexibility. For businesses, currency fluctuations driven by trade dynamics directly influence procurement costs and profitability. Long-term solutions lie in expanding export capacity, managing import dependence, and diversifying trade partners.
Technology-Driven Market Transformation
Technology has reshaped how currency markets operate in India. Mobile apps, AI-enabled tools, and machine learning models are changing how trades are executed and analyzed. Banks and fintechs now offer instant quotes, predictive analytics, and real-time execution—reducing slippage and boosting transparency. Institutional desks rely on automation and APIs for high-speed order flows. Retail platforms increasingly use chatbots for service and voice-command features for order placement. This integration of tech has lowered costs, increased accessibility, and improved decision-making across all user segments. These innovations have played a key role in expanding the India foreign exchange market share by drawing in both institutional and retail participants. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is actively fostering this innovation, as evidenced by its commitment in May 2025 to develop a framework for the responsible and ethical adoption of AI in the financial sector, ensuring secure and sustainable growth. This proactive regulatory stance, alongside India's fintech industry being valued at an estimated USD 150 Billion as of 2025, underscores the profound impact of these advancements.
Who Trades What: Mapping India’s Forex Market Structure:
India’s foreign exchange market has expanded beyond traditional players, evolving into a layered, multi-participant environment where institutions and individuals operate side by side. Understanding the structure of this market who trades, what they trade, and how- is essential for grasping its current direction and emerging opportunities.
Market Participants: Institutions Vs Retail
Institutional entities remain the backbone of India’s forex market. These include public and private sector banks, foreign banks operating through Indian branches, hedge funds, NBFCs, and large corporate treasuries. Their trades involve large volumes and complex products, often tied to global market strategies or cross-border business operations.
However, retail investors have started to make a noticeable impact. Powered by app-based trading, real-time charting tools, and simplified onboarding, individual participation has grown quickly. While institutional players still account for the lion’s share of volume, retail activity especially in exchange-traded derivatives is reshaping the market’s lower end. Increased financial awareness and access to education tools are pushing more individuals to explore forex as an alternative asset class.
Types of Forex Instruments:
India’s forex market supports a diverse mix of currency instruments, tailored to the needs of both hedgers and speculators:
- Spot Transactions: These involve immediate settlement based on prevailing exchange rates. Used by banks, importers/exporters, and corporates needing urgent conversions.
- Forwards: Customized contracts to lock in an exchange rate for a future date, helping businesses mitigate currency risk linked to receivables or payables.
- Swaps: Complex instruments involving the simultaneous buying and selling of currencies over different settlement periods. Common among financial institutions managing liquidity or interest rate exposures.
- Derivatives (Futures & Options): Exchange-traded products used to hedge or speculate on currency movements. Futures offer standard contracts, while options provide flexibility to define risk thresholds. Growing interest among both institutional desks and retail traders is pushing volumes higher on platforms like NSE and BSE.
Key Players and Their Roles:
The Indian forex market operates through a well-regulated network of entities:
- Banks: Central to both interbank and client-side transactions, banks handle high-volume trades, hedging mandates, and bulk forex settlements. They also facilitate retail forex needs via branches and digital platforms. According to recent India foreign exchange market news, banks have played a central role in managing liquidity and supporting currency stability during periods of heavy central bank intervention. For example, in March 2025, the Reserve Bank of India bought a net USD 14.36 Billion in the spot forex market, purchasing USD 41.52 Billion and selling USD 27.16 Billion. This intervention contributed to a 2% rally in the Indian rupee against the US Dollar, as reported in the RBI’s monthly bulletin. These interventions, executed primarily through the banking system, underscore the critical role banks play in transmitting central bank actions into market liquidity and currency stability.
- NBFCs: Non-Banking Financial Companies offer services like overseas remittances, travel cards, and small-value conversions. Their reach has expanded in urban and semi-urban centers.
- Forex Dealers & Authorized Money Changers: These players focus on over-the-counter forex transactions — largely for tourism, education, and individual remittances. Strictly regulated by the RBI, they add flexibility and last-mile connectivity to the ecosystem.
The segmentation of India’s forex market reveals a dynamic interplay between scale-driven institutional flows and technology-enabled retail participation. With new instruments and platforms emerging, this balance is expected to shift further making segmentation insights critical for anyone analyzing future market movements or building forex-related financial products.
Forecasting the Next Decade: Growth Vectors in India’s Forex Market
India’s foreign exchange market is expected to maintain strong momentum over the next decade, supported by rising global integration and sustained regulatory support. India foreign exchange market size is anticipated to grow USD 65.80 Billion by 2033, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.8% during 2025-2033. Growth will be driven by volume and the market’s structural shift toward wider participation, deeper instruments, and technology-first execution models.
Key growth drivers include:
- Global Expansion of Indian Firms
Indian companies are scaling operations beyond domestic borders—opening overseas offices, acquiring global assets, and billing in foreign currencies. This expansion increases the need for currency conversions, hedging contracts, and offshore fund management. Recent data from the Reserve Bank of India highlights this trend, with India's outward foreign direct investment (OFDI) commitments nearly doubling to $6.8 Billion in April 2025, up from $3.58 Billion in April 2024, demonstrating a robust growth for global ventures. From IT services to pharma and manufacturing, firms are embedding forex management into their treasury strategies. For example, India is expected to export $210 Billion worth of IT in FY2024–2025, which will result in significant cross-currency needs as these companies cater to a global clientele. As more businesses operate in multi-currency environments, forex demand will rise in volume and complexity, driving sustained growth across both spot and derivative markets.
- Rising FDI and FII Inflows
Foreign institutional and direct investors continue to view India as a long-term growth market. Increased investments in equity, debt, infrastructure, and private ventures create constant demand for currency access and repatriation channels. With FDI inflows supporting business expansion and FII flows adding to market liquidity, forex transactions linked to capital market activity are growing. These inflows also encourage more sophisticated hedging, reserve management, and regulatory compliance—all of which drive forex market development and institutional engagement. India foreign exchange market analysis indicates stronger FII inflows are influencing INR volatility patterns.
- Broader Use of Liberalized Remittance Schemes (LRS) by Individuals
The Liberalized Remittance Scheme (LRS) has become a key driver of retail forex activity. Indians are increasingly using LRS to invest abroad, fund overseas education, pay for medical treatment, or purchase property. Fintech platforms and private banks have made cross-border transactions easier, faster, and more transparent. This growing retail usage boosts forex volume and encourages product diversification—spurring demand for forex cards, digital remittances, and small-ticket hedging instruments tailored for individual users.
- Shift Toward Non-Dollar Settlements
India is entering more bilateral trade agreements that reduce dollar dependency. Settling transactions in currencies like AED, RUB, and CNY offers cost advantages, faster processing, and strategic flexibility. These shifts support the government’s push to internationalize the rupee and enhance trade resilience. As non-dollar settlements become more common, they create demand for multi-currency platforms, broader currency pairs, and cross-border liquidity solutions—widening the scope of forex trading and strengthening India’s influence in the global currency ecosystem.
- Policy and Regulatory Support
Proactive regulatory reforms are making forex markets more accessible and stable. RBI initiatives—like allowing INR pairs on exchanges, easing FEMA rules, and promoting rupee invoicing—enhance market efficiency. The Ministry of Finance’s clarity on tax norms, reporting, and investor eligibility has boosted confidence among corporates and individuals alike. These reforms reduce friction and encourage transparency, long-term participation, and innovation in forex products. Regulatory credibility is now a core factor behind sustained growth in the Indian forex market.
India’s forex market is positioned to grow in volume and mature in function. The next decade will likely see it evolve into a more resilient, tech-led, and globally aligned segment of India’s broader financial ecosystem.
Driving Informed Decisions in India’s Foreign Exchange Market: How IMARC Group Delivers Strategic Intelligence and Tailored Advisory
IMARC Group supports stakeholders across India’s foreign exchange market with data-backed intelligence and practical advisory. Our services help clients respond to currency fluctuations, navigate regulatory shifts, and make informed strategic decisions in a fast-moving financial environment.
We assist banks, institutional investors, corporate treasuries, and fintech firms in unlocking new opportunities, reducing exposure to risk, and strengthening their currency management strategies through:
- Market Insights: Track developments across the Indian and global forex landscape—rising cross-border flows, evolving trade patterns, RBI market interventions, and external shocks. Our analysis covers spot, forward, and derivatives segments, offering clarity on exchange rate drivers, liquidity trends, and trading behavior.
- Strategic Forecasting: Plan ahead with forward-looking analysis on INR movement, interest rate differentials, inflation trends, and policy direction. Our forecasting tools incorporate macroeconomic data, geopolitical signals, and regulatory cues to help clients act decisively in volatile conditions.
- Competitive Intelligence: Keep pace with innovations in trading systems, algo-execution platforms, and digital forex services. We provide insight into peer strategies, institutional hedging practices, and shifts in investor behavior, helping clients refine their market positioning and operational efficiency.
- Policy and Regulatory Analysis: Understand the implications of regulatory changes, including updates to FEMA rules, ECB guidelines, capital account regulations, and liberalized remittance schemes. We assess how these policies impact market dynamics, capital access, compliance obligations, and risk exposure.
- Customized Consulting Solutions: Whether entering the Indian forex market, managing currency exposure, or enhancing trading operations, we offer tailored consulting aligned with your strategic goals. Our support spans policy advisory, risk strategy, operational benchmarking, and product innovation.
As India’s foreign exchange market grows in scale and complexity, IMARC Group remains a trusted knowledge partner—offering sharp insights, strategic foresight, and practical support that empowers clients to succeed.
Conclusion:
India’s foreign exchange market stands at a crucial inflection point. With volumes rising, instruments diversifying, and participation widening, it’s no longer just a trade settlement tool it’s a core component of India’s financial architecture. According to the foreign exchange market overview, this growth is being driven by regulatory support, technology integration, and India’s increasing global business exposure. From corporates managing cross-border exposure to individuals using digital platforms for remittances and investments, the use cases are expanding fast. Policy reforms, greater transparency, and increased access are creating a more inclusive and efficient environment. For stakeholders, the opportunity lies in staying agile, well-informed, and strategically positioned in this fast-moving landscape.
For a comprehensive analysis of market size, forecasts, segmentation, and competitive landscape, access our full India Foreign Exchange Market Report
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
-(1)_11zon.webp)










