How to Set Up a Manufacturing Plant in Saudi Arabia: Strategic Roadmap and Comprehensive Guide

Establishing a manufacturing plant in Saudi Arabia presents a unique gateway to Middle East’s largest economy, backed by abundant resources, robust logistics infrastructure, and a forward-looking economic diversification agenda Creating a manufacturing facility in Saudi Arabia opens a unique gateway to Middle East's biggest economy, supported by vast resources, strong logistics infrastructure, and a visionary economic diversification policy.
Saudi Arabia offers unparalleled advantages such as tax incentives, access to low-cost energy, and strong regulatory reforms. However, entering this market requires careful planning, understanding local regulations, and alignment with national development strategies. This guide walks you through the full process, from choosing an optimal site to securing licenses and mitigating operational risks.
Leading Industries Driving Saudi Arabia’s Manufacturing Growth:
- Automotive and EV Manufacturing: With Lucid Motors and Ceer establishing local plants, the automotive ecosystem is rapidly expanding.
- Petrochemicals and Advanced Materials: Anchored by SABIC and Aramco, Saudi is a global leader in downstream chemicals and plastics.
- Pharmaceuticals and Biotech: Vision 2030 targets 70% local drug production by 2030, with players like SPIMACO and Sudair Pharma scaling up.
- Renewable Energy and Green Hydrogen: NEOM’s USD 8.4 Billion hydrogen project is the world's largest under development.
- Construction Materials and Steel: Urbanization and mega-projects fuel demand for cement, steel, and smart materials.
- Food and Beverage Processing: Local players like Almarai and international brands are expanding food processing to meet rising domestic and regional demand.
Why Saudi Arabia is the Manufacturing Powerhouse of the Future?
-
Vision 2030 and Industrial Transformation
Saudi Arabia is transforming into a global manufacturing powerhouse under Vision 2030. With initiatives like the National Industrial Development and Logistics Program (NIDLP), the Kingdom is actively attracting foreign manufacturers through streamlined regulations and funding schemes. In March 2025, the Saudi Ministry of Industry and Mineral Resources launched “Made in Saudi” expansion strategy to promote local production, especially in strategic sectors like automotive, pharmaceuticals, and renewable energy.
Mega-projects such as NEOM and the King Salman Energy Park (SPARK) are redefining the industrial landscape with cutting-edge infrastructure, smart city planning, and investment facilitation.
-
Gateway to the MENA and African Markets
Strategically located at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, Saudi Arabia offers direct access to over 2.5 Billion consumers. The presence of top-tier ports like King Abdulaziz Port (Dammam) and King Abdullah Port (KAEC), as well as expansive road and rail links under the Gulf Railway Project, enhances trade routes to UAE, Egypt, and other GCC nations.
Manufacturers in Saudi Arabia enjoy tariff-free exports across the region, with free trade agreements (FTAs) under the Greater Arab Free Trade Area (GAFTA) and bilateral pacts.
-
Stable Policies and Investment-Driven Governance
Saudi Arabia offers a stable legal and economic environment. Regulatory bodies such as the Saudi Arabian General Investment Authority (SAGIA, now part of MISA) and the Saudi Industrial Development Fund (SIDF) actively support foreign investment. In early 2025, Saudi Arabia introduced a 5-year Golden Residency Program to attract skilled professionals and investors in manufacturing sectors.
Recent collaborations with UNIDO and the World Economic Forum on sustainable industrialization further showcase the Kingdom’s commitment to ethical and innovation-led development.
How long does it take to build a factory in Saudi Arabia?
Timelines vary based on location, industry, and scale:
- Standard Facilities (12–20 Months): Suitable for F&B or consumer goods production.
- Pre-Approved Zones (8–14 Months): Industrial parks with ready infrastructure can fast-track timelines.
- High-Tech or Customized Facilities (20–36 Months): Required for pharma, petrochemicals, or energy tech manufacturing.
Unlocking Manufacturing Potential in Saudi Arabia:
1. Government Incentives and Financial Support
Saudi Arabia offers extensive support for manufacturing plant setup through:
- Capital Grants and Soft Loans: SIDF offers financing of up to 75% of project costs for strategic sectors.
- Customs Exemptions: On machinery, equipment, and raw materials used in production.
- Industrial Land at Subsidized Rates: Industrial cities under MODON offer long-term leases at competitive prices.
- Tax Benefits: 20-year tax holidays in Special Economic Zones (SEZs) like Ras Al Khair and King Abdullah Economic City.
- Green Manufacturing Incentives: Financial support for renewable-powered facilities and hydrogen-based production systems.
2. State-of-the-Art Infrastructure and Industrial Ecosystems
Industrial zones such as Jubail Industrial City and the Advanced Manufacturing Hub in NEOM offer plug-and-play facilities, integrated utilities, and tech-ready spaces. Riyadh’s dry port, Dammam’s intermodal network, and fast-developing smart warehousing in KAEC ensure seamless logistics.
For example, Lucid Motors’ EV manufacturing plant in KAEC is equipped with smart assembly lines and is integrated with port operations for direct global shipments.
3. Abundant and Cost-Effective Energy Resources
Saudi Arabia offers one of the lowest industrial energy costs globally. Natural gas and electricity are subsidized for manufacturers. The Kingdom is also rapidly expanding its solar and hydrogen infrastructure under the Saudi Green Initiative, which benefits energy-intensive industries.
In 2024, the SABIC-Hyundai partnership leveraged these advantages to establish a green ammonia production plant, optimizing energy efficiency and reducing carbon emissions.
4. Competitive Labor Market and Skill Development
Saudi Arabia has ramped up workforce training through the Human Capability Development Program (HCDP). In July 2025, Saudi Arabia introduced a skill-based work permit system classifying expatriates into high-skill, skilled, and basic categories. This reform supports Vision 2030 by aligning workforce planning with economic goals. Vocational institutes like the Saudi Technical and Vocational Training Corporation (TVTC) and partnerships with foreign universities support skill-building in manufacturing tech.
Reforms under the Saudization policy are balanced by visa reforms that allow skilled expatriates to fill technical roles. Programs like Tamheer and Maharat offer subsidies for employee training.
5. High Demand and Regional Export Potential
The Kingdom’s domestic market, driven by a growing population and mega-infrastructure projects, fuels demand in sectors like construction materials, electronics, food processing, and energy tech.
Additionally, strategic location and FTAs provide access to markets in Africa, the Middle East, and South Asia. For instance, Almarai’s dairy and food processing expansion serves both local demand and exports to the UAE, Oman, and Jordan.
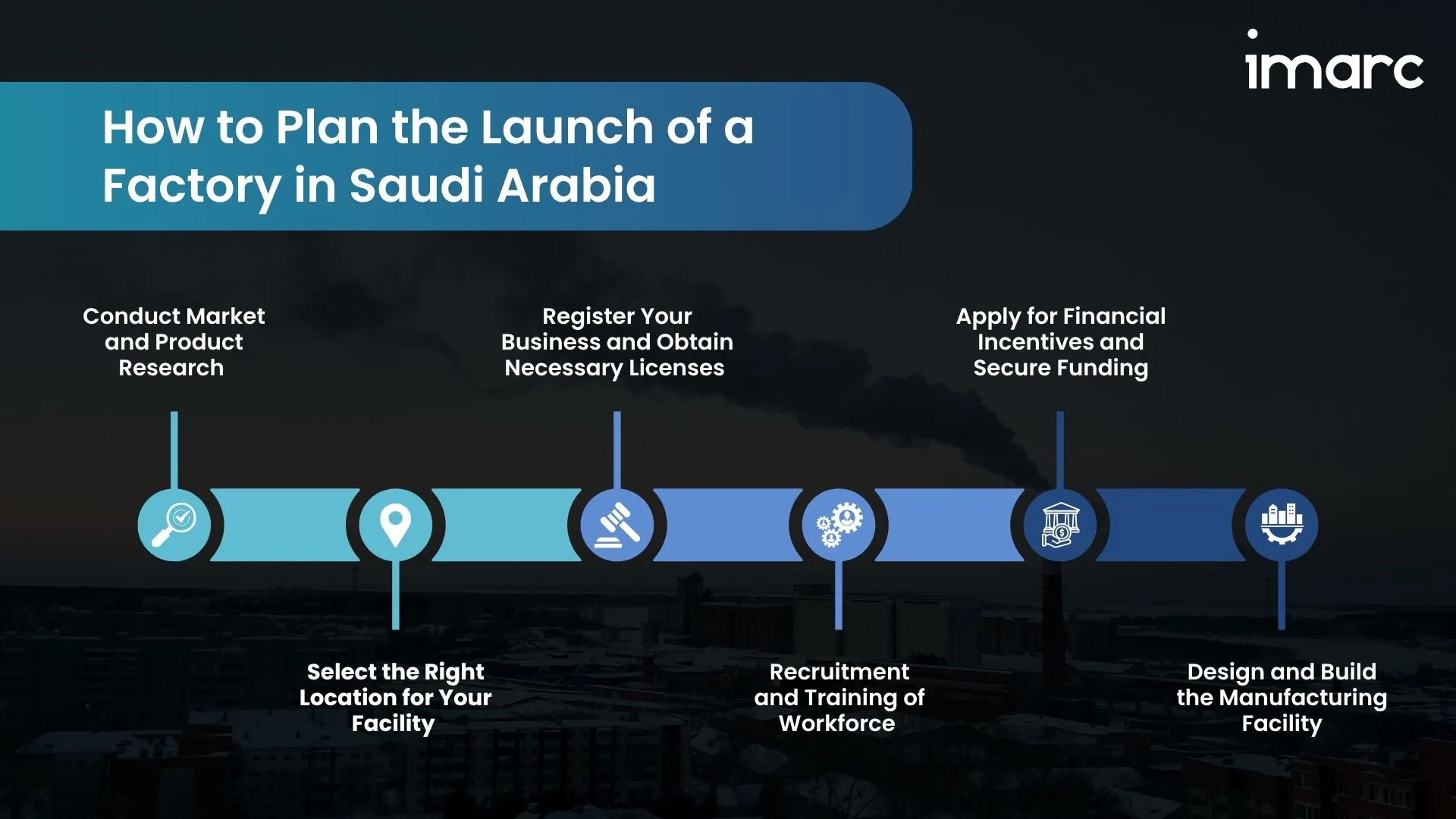
How to Plan and Execute the Launch of a Factory in Saudi Arabia?
Setting up a manufacturing facility in Saudi Arabia offers unique opportunities due to its strategic location, growing infrastructure, and business-friendly policies. Below is an in-depth blueprint for launching a successful manufacturing operation in the Kingdom.
1. Conduct Comprehensive Market and Product Research
Before starting any manufacturing venture, market research is crucial for identifying business opportunities and understanding the competitive landscape. It involves conducting detailed demand forecasting, pricing analysis, and evaluating competitor strategies to gain a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics. Key elements include:
- Demand Analysis: Utilize data from Saudi authorities like MISA, NIDLP, and the Saudi Export Development Authority to predict market demand trends and align your product offerings accordingly.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Assess the competitive landscape to identify key players, pricing strategies, and gaps in the market that your product can fill.
- Product Adaptation: Analyze the compatibility of your products with local regulations, and consumer preferences, and ensure that your product meets the required certifications and standards.
- Import Regulations: Understand the Saudi customs laws and leverage any Free Trade Agreements (FTA) advantages that can make your products more competitive in the market.
2. Select the Right Location for Your Facility
The location of your manufacturing plant is a critical decision that will impact logistics, labor, and operational costs. Saudi Arabia boasts several industrial hubs with unique advantages for different types of industries. You’ll need to consider factors like proximity to raw materials, transportation infrastructure, labor availability, and government incentives. Some of the key regions include:
- Jubail: Known for its strong petrochemical and heavy industry presence, Jubail is ideal for industries such as chemicals, construction materials, and manufacturing.
- NEOM and KAEC: These regions are geared towards technology-driven manufacturing, with a focus on sustainability, smart manufacturing, and innovation.
- Sudair and Dammam: Offering strong logistics connections and proximity to key ports, Sudair and Dammam are excellent for businesses in FMCG manufacturing and logistics-heavy sectors.
Your site selection should be aligned with your industry’s needs. Evaluate logistics access (ports, railways, highways), labor availability, and proximity to suppliers to ensure that you’re positioned for long-term success.
3. Register Your Business and Obtain Necessary Licenses
Once you’ve conducted your research and selected a location, the next step is business registration and obtaining the required licenses. Saudi Arabia has streamlined processes for foreign investments, but it's crucial to follow the regulatory steps. Key steps include:
- Legal Entity Registration: The most common structures are LLC (Limited Liability Company) or joint ventures with local partners. The Ministry of Investment (MISA) will guide you through this process.
- Industrial Licensing: Depending on your industry, you may need licenses from the Ministry of Industry (MODON) to operate legally in the country.
- Environmental and Zoning Approvals: Ensure that your facility complies with local environmental laws and zoning regulations.
- Work and Immigration Permits: You will need work permits for any foreign employees, which are issued through GOSI (General Organization for Social Insurance) and Jawazat (Saudi Passport Office).
4. Recruitment and Training of Workforce
A key challenge when establishing a manufacturing plant is hiring and training a skilled workforce. Saudi Arabia offers various programs to help foreign companies recruit local talent. Key recruitment sources include:
- National Job Portals: Use local job portals to recruit engineers, technicians, and administrative staff.
- Educational Institutions: Collaborate with vocational colleges and technical academies to train your workforce. Programs like Tamheer provide subsidized internships for young Saudis, helping them gain practical experience.
- Skill Development Subsidies: Government programs support training programs, helping bridge any skills gap in your workforce.
- Saudization Compliance: Ensure that your workforce adheres to the local employment quotas as part of Saudi Arabia’s Saudization initiative, which mandates a specific number of local hires.
Having a well-trained and skilled workforce is critical to the smooth operation of your factory.
5. Apply for Financial Incentives and Secure Funding
Saudi Arabia offers various financial incentives to attract foreign investment, particularly in key industrial sectors. Here’s how you can access funding and subsidies:
- SIDF Loans: The Saudi Industrial Development Fund (SIDF) provides loans for industrial projects, offering favorable interest rates for eligible businesses.
- MODON and Land Support: The Ministry of Industry and Mineral Resources (MODON) provides support for land acquisition and facility construction in designated industrial zones.
- SEZ Incentives: Manufacturers in Special Economic Zones (SEZs) can benefit from tax holidays, fast-track services, and other financial advantages.
- Aramco Namaat Program: Aramco’s program offers co-investment in priority sectors such as renewable energy, logistics, and high-tech manufacturing.
Working with government agencies and financial institutions ensures that you can reduce costs and access the financial support necessary for setting up a successful manufacturing operation.
6. Design and Build the Manufacturing Facility
The design and construction phase is vital for the successful operation of your manufacturing plant. Consider the following:
- Hire Local EPC Contractors: Work with experienced Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) contractors familiar with Saudi regulations and standards.
- Compliance with Safety and Construction Standards: Ensure compliance with GACA (General Authority of Civil Aviation) and Civil Defense regulations to ensure worker safety and building security.
- Smart Manufacturing Integration: Design the facility to integrate cutting-edge automation and smart technologies such as AI, IoT, and robotics.
- Sustainability Considerations: Plan for energy-efficient systems and adhere to environmental regulations to minimize operational costs and impact.
Ensure that your facility design allows for flexibility, scalability, and future-proofing in line with Industry 4.0 standards.
Real World Challenges to Plan For:
- Regulatory Navigation: While reforms are active, processes still require thorough documentation and local legal guidance.
- Saudization Compliance: Specific quotas apply for local hires; planning workforce strategy is essential.
- Climatic Conditions: High temperatures affect construction and operations—energy-efficient building design is critical.
- Cultural and Legal Sensitivity: Business practices are relationship-oriented; Arabic legal documents and advisors are essential.
- Logistics Costs: Inland transportation remains costly; optimize through proximity to ports or rail corridors.
How IMARC Supports Manufacturing Expansion in Saudi Arabia:
IMARC helps clients navigate operational complexities of setting up in Saudi Arabia with detailed research, clear feasibility studies, and practical support.
IMARC helps in:
- Analyze market demand, competition, and pricing trends in Saudi and GCC regions, utilizing trade agreements for effective market entry.
- Evaluate project feasibility, aligning with Vision 2030, and calculate local vs. import costs with detailed CAPEX/OPEX and ROI models.
- Select optimal manufacturing sites based on infrastructure, logistics, workforce availability, and government incentives for cost-efficient operations.
- Maximize financial efficiency with forecasting, identifying subsidy opportunities, and securing grants from SIDF, MODON, and SEZ.
- Navigate regulatory processes, including business registration, licensing, labor law compliance, and obtaining environmental and safety certifications.
- Streamline workforce recruitment with local job portals, technical colleges, and government-backed training programs for skill development.
We helps clients build successful manufacturing operations in Saudi Arabia with tailored services ranging from feasibility studies and site selection to regulatory compliance and financial modeling. Whether you are entering automotive, energy, food processing, or chemicals, our Saudi-specific team ensures a seamless setup journey.
Ready to establish your manufacturing plant in Saudi Arabia?
Contact IMARC Group today for a customized feasibility study, location strategy, and end-to-end consulting support.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104










