How AI is Powering Japan’s 3D Printing Revolution
Japan’s artificial intelligence (AI)-driven three-dimensional (3D) printing startups are redefining manufacturing by merging speed, sustainability, and precision. Japan’s additive manufacturing scene is moving beyond prototypes—it's rewriting how industries build, design, and innovate. From ecofriendly, AIoptimized 3Dprinted housing projects to 3D Printing Corporation’s seamless designtoproduction platforms, the country is proving that smart manufacturing can also be sustainable. Cutting-edge collaborations like Phase3D’s realtime quality monitoring are raising reliability standards, while speeding up R&D cycles, slashing costs, and making mass customization a reality. And the momentum keeps growing—just this April 2025, West Japan Railway Company revealed the world’s first 3D printed train station, nestled in rural Osaka, a bold testament to how technology can blend tradition with transformation. From construction to aerospace, Japan is crafting a future where manufacturing is not just faster and smarter—but greener, bolder, and truly nextgen.
Also, the KOKONI unveiled the world’s first 3D printer with instant AI 3D modelling, bridging the gap between the virtual and real worlds. With the KOKONI EC-1, customers may utilize a smartphone and its user-friendly app to build photorealistic 3D models straight from 2D photographs without the need for costly scanners or complicated software. Powered by advanced AI algorithms, fast printing technology, and a user-friendly design, it empowers beginners, hobbyists, and experts to transform imagination into tangible creations effortlessly.
AI and the Rise of the Japan 3D Printing: Where tradition meets transformation
Japan has long been a global manufacturing powerhouse, and its 3D printing industry is rapidly becoming a key pillar of the country’s next-gen production ecosystem. AI is acting as the catalyst for this transformation — accelerating design processes, streamlining material discovery, and enhancing the precision and efficiency of additive manufacturing. According to industry reports, Japan’s 3D printing market is projected to grow steadily as AI-driven tools reshape workflows, making production smarter, faster, and more cost-effective.
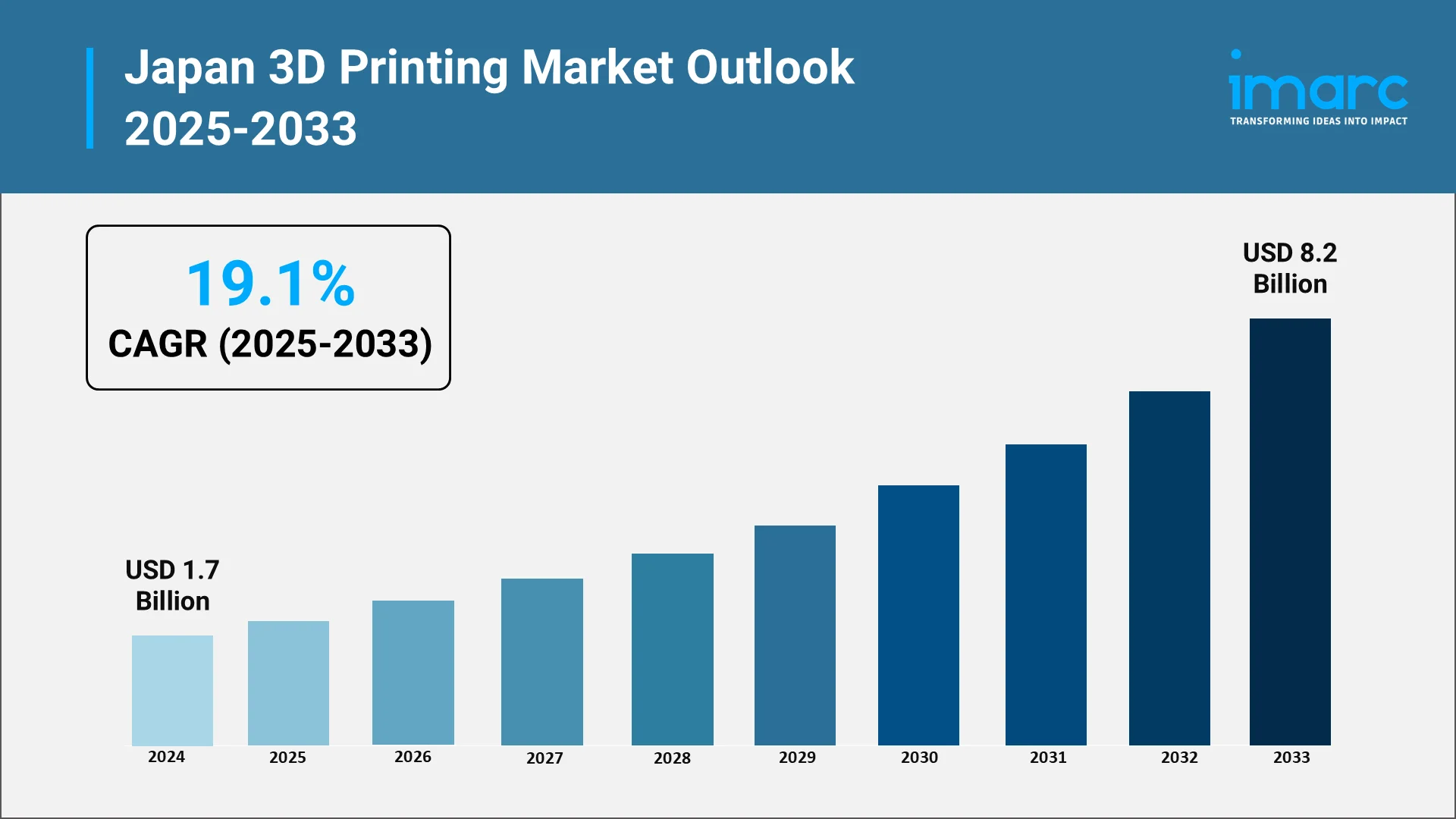
According to IMARC, Japan’s 3D printing market was valued at approximately USD 1.7 Billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 8.2 Billion by 2033, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.1% between 2025 and 2033. As Japan continues to integrate AI into every layer of additive manufacturing, including material research, design optimization, and post-processing, it is solidifying its position as a global leader in intelligent, sustainable, and digitally driven manufacturing.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
Next-Gen Materials: AI at the Core of Japan’s 3D Printing Innovation
- Machine Learning for Material Simulation and Selection: Machine learning is transforming material simulation and selection by analyzing vast datasets of molecular properties to predict how new alloys, composites, and polymers will perform. This AI-driven approach eliminates much of the trial-and-error in traditional research, enabling scientists to rapidly identify optimal material combinations, dramatically shortening R&D timelines and accelerating innovation in Japan’s 3D printing ecosystem.
- Optimizing High-Performance Materials: AI is transforming Japan’s approach to high-performance 3D printing materials. By leveraging advanced algorithms, manufacturers are fine-tuning metal powders for lightweight aerospace components, ceramics for heat-resistant industrial parts, and bio-compatible polymers for medical implants. In 2024, a leading industry survey found that AI algorithms can reduce 3D printing material waste by up to 25% and improve part accuracy by as much as 40% through intelligent process control. This data-driven optimization not only accelerates material development but also ensures components meet Japan’s rigorous quality standards, empowering industries to deliver stronger, safer, and more efficient solutions for the global market.
- Smart Composites and Polymers: Smart composites and polymers are revolutionizing Japan’s 3D printing landscape, thanks to AI-powered material innovation. By analysing complex molecular interactions, AI helps create self-healing materials, ultra-lightweight composites, and customized polymers engineered for highly specific applications. From aerospace components demanding strength-to-weight optimization to medical implants requiring biocompatibility, these AI-designed materials enable manufacturers to deliver next-generation, performance-driven solutions, accelerating innovation across industries.
AI-Powered Plastics: The Next Frontier in Japan’s 3D Printing Evolution
- Improving Material Strength, Quality, and Recyclability: Japan’s AI-driven advancements in 3D printing plastics center on enhancing material strength, quality, and recyclability. Machine learning algorithms are increasingly used to analyze microstructural data, allowing early detection of material weaknesses and enabling targeted structural improvements for greater durability. At the same time, AI optimizes polymer formulations to boost recyclability without compromising performance, fostering the development of high-strength, sustainable plastics. Supporting this innovation, Japan’s Ministry of the Environment has set a target for recycled plastics to comprise at least 15% of materials used in new vehicles by 2036–2040. This directive is accelerating eco-friendly progress across the automotive, healthcare, and electronics industries.
- Applications Across Industries: AI-optimized plastics are revolutionizing Japan’s manufacturing landscape by enabling sector-specific innovations. In automotive production, they power the creation of ultra-light yet durable components for improved fuel efficiency. In healthcare, they support the development of bioresorbable implants tailored for patient safety and faster recovery. Meanwhile, in electronics, high-precision, heat-resistant parts are enhancing device performance—showcasing how AI-driven material design is reshaping industries with smarter, purpose-built solutions.
- Emerging Trends: Japan is experiencing a growing shift toward biodegradable polymers and recycled feedstocks, fueled by sustainability goals and advanced AI-driven material engineering. These intelligent systems optimize formulations for consistent printability, durability, and performance, overcoming traditional limitations of eco-friendly materials. This synergy of AI and green innovation is enabling manufacturers to create high-quality, sustainable 3D-printed products, aligning with Japan’s broader circular economy and carbon-neutrality ambitions.
From Concept to Creation: AI’s Role in Enhancing Speed and Accuracy in 3D Printing
AI is unlocking unprecedented efficiency in Japan’s additive manufacturing processes:
- Process Control and Defect Detection: In Japan’s evolving 3D printing landscape, AI-powered computer vision systems are transforming process control. These systems use real-time monitoring to detect micro-defects—such as cracks, warping, or layer misalignment—during printing. By identifying issues instantly, manufacturers can halt production or make in-process corrections, reducing waste and ensuring superior product quality. This proactive approach also minimizes costly post-production inspections and reprints. Such intelligent defect detection not only improves efficiency but also boosts reliability for industries like aerospace, medical devices, and automotive manufacturing, where flawless production is non-negotiable. AI-driven defect detection is becoming a cornerstone of Japan’s next-gen additive manufacturing workflows.
- Print Optimization: Artificial intelligence is redefining print optimization in Japan’s 3D printing sector by fine-tuning critical parameters like temperature, layer thickness, printing speed, and material flow. Through machine learning, AI models analyze previous print data and predict the optimal settings for each material and design, ensuring high precision and repeatability. This level of customization minimizes human trial-and-error, reducing material wastage and boosting overall efficiency. For complex parts—whether in medical prosthetics, aerospace components, or consumer electronics—AI ensures consistent performance across production batches. By automating optimization, manufacturers can deliver higher-quality products with tighter tolerances, giving Japan a competitive edge in advanced additive manufacturing.
- Accelerated Production: AI-enabled print optimization and process automation are cutting time-to-market for Japanese manufacturers. By streamlining design iterations, predicting potential failures, and optimizing print parameters, AI significantly reduces production cycles. This allows companies to create functional prototypes and end-use products much faster while maintaining uncompromised quality. For industries such as healthcare, automotive, and consumer electronics, where rapid innovation is vital, this acceleration translates to a competitive advantage. Furthermore, AI reduces dependency on skilled labor for constant monitoring, enabling scalable production with fewer resources. This efficiency ensures that, Japan’s 3D printing ecosystem can stay ahead in delivering innovative, reliable, and market-ready solutions.
Who’s Leading Japan’s AI-Driven 3D Printing Revolution?
- Ricoh: Leveraging AI for real-time quality monitoring and advanced prototyping in 3D printing solutions. In May 2025, Ricoh introduced an advanced 3D inkjet printing technology that produces biocompatible resin parts with full-color precision and enhanced mechanical strength, compliant with JIS T 10993-1 standards. Currently piloted in dental and eyewear manufacturing, this innovation expands possibilities for high-quality, functional additive production in medical and consumer sectors.
- JSR Corporation: JSR Corporation is at the forefront of AI-driven photopolymer resin development, creating materials designed for high-precision 3D printing applications. By leveraging machine learning, the company can predict and fine-tune resin properties—such as curing speed, flexibility, and durability—to meet the stringent demands of sectors like electronics, medical devices, and automotive manufacturing. In August 2024, JSR unveiled smart photopolymer microspheres that mimic biomolecular behavior through synthetic chemistry, enabling precise antibody recognition. This breakthrough, both cost-effective and highly adaptable, opens doors for next-gen biosensors and medical-grade 3D printing materials, transforming both healthcare diagnostics and precision manufacturing.
- Mitsubishi Chemical: A pioneer in AI-enabled high-performance materials, from automotive-grade polymers to bio-based plastics. In April 2025, Mitsubishi Chemical showcased its bio-based engineering plastic DURABIO™ at Expo 2025 Osaka, featuring 3D-printed algae-based stools. Known for its optical clarity, mechanical strength, and 3D printing compatibility, DURABIO™ highlights Mitsubishi’s push toward sustainable, high-performance materials for next-generation manufacturing.
- ORIX Rentec: Taking the “what-if” out of 3D printing, ORIX Rentec is rewriting the modeling game with 3D-FABs—the industry’s first AI-powered online simulation platform for additive manufacturing. Launched in May 2023, 3D-FABs lets users upload 3D CAD data, experiment with different materials and printer settings, and get instant cost estimates—24/7, without the back-and-forth of traditional quoting. With AI suggesting optimal print strategies and archiving every simulation, the platform is turning complex modeling into an on-demand, insight-driven experience. It’s not just a tool—it’s a virtual lab for anyone looking to speed up innovation and cut down development headaches.
Japan’s Innovation Network: Startups and Research Hubs Advancing AI-Driven 3D Printing
Japan’s competitive landscape in AI-powered 3D printing is evolving into a dynamic collaborative engine, driven by the fusion of cutting-edge research, government-backed initiatives, and cross-industry partnerships. Established manufacturers, agile startups, and R&D hubs are jointly accelerating innovation by leveraging AI for smarter material design, enhanced print precision, and scalable production. This synergy fosters rapid prototyping, cost-efficient workflows, and breakthroughs in bio-compatible polymers, high-performance composites, and sustainable materials. The ecosystem thrives on shared infrastructure, open innovation platforms, and policy incentives aimed at bolstering digital transformation. As Japan integrates AI deeper into additive manufacturing, its collaborative approach ensures a strong competitive edge, positioning the nation as a global leader in high-value, next-generation manufacturing solutions.
Emerging Opportunities in Japan’s 3D Printing Landscape:
A Future Fueled by Intelligence
The demand for customized medical devices, lightweight automotive components, and high-performance electronics parts is expected to drive Japan’s 3D printing market forward. AI’s role in scaling production, reducing costs, and personalizing products offers manufacturers a strong competitive edge in both domestic and global markets.
In addition to this, the Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) is supercharging its Green Growth and digital transformation agenda with bold incentives—offering subsidies and tax breaks for manufacturers embracing AI-powered 3D printing and advanced materials. The initiative goes beyond funding, aiming to reshape Japan’s industrial future by accelerating R\&D, reinforcing supply chains, and driving scalable innovation across automotive, electronics, and bio-manufacturing sectors—positioning Japan at the forefront of smart manufacturing.
Challenges and the Road Ahead:
Bridging the Gap to Global Leadership
Despite its progress, Japan’s 3D printing sector faces challenges such as high costs of AI adoption, data standardization issues, and the need for expanded digital infrastructure. However, by leveraging AI for process automation, predictive analytics, and resource optimization, Japan can solidify its position as a leader in advanced additive manufacturing and help shape the future of global production.
- High Costs of AI Adoption: AI integration into 3D printing processes necessitates a large investment in hardware, software, and qualified staff. For many small and mid-sized manufacturers, these expenses remain prohibitive, slowing adoption. Without scalable cost-sharing models or government-backed incentives, the financial burden could hinder Japan’s ability to fully capitalize on AI-driven additive manufacturing.
- Data Standardization Issues: A lack of unified standards for data collection, processing, and interoperability poses a major barrier. Fragmented systems across manufacturers, suppliers, and research hubs complicate collaboration and slow innovation. Establishing common frameworks for data exchange is crucial for enabling seamless integration of AI tools and accelerating cross-industry 3D printing advancements.
- Need for Expanded Digital Infrastructure: Japan’s existing digital backbone struggles to meet the demands of AI-powered additive manufacturing. High-speed, secure networks and robust cloud systems are essential for real-time data processing, remote collaboration, and large-scale production. Expanding digital infrastructure is vital for supporting the next generation of smart, AI-driven 3D printing ecosystems.
- Shortage of Skilled Talent: A skills gap has been brought about by the quick development of AI and 3D printing technology. Engineers, data scientists, and specialists who can manage AI-integrated production processes are in short supply. Without targeted training programs and academic-industry collaboration, this talent shortage could limit Japan’s competitive edge in advanced manufacturing.
AI + 3D Printing: Japan’s Blueprint for a Smarter Manufacturing Future
Japan’s 3D printing revolution is no longer a vision it’s a rapidly unfolding reality, powered by the seamless integration of artificial intelligence. From material discovery to defect-free manufacturing, AI is enabling Japanese industries to produce stronger, lighter, and more sustainable components at unprecedented speed and precision. Government initiatives like METI’s Green Growth and Digital Transformation strategies are fueling this shift, offering subsidies, tax incentives, and regulatory support to accelerate innovation. While challenges such as high adoption costs, talent shortages, and data standardization remain, AI-driven solutions are turning these obstacles into opportunities. By leveraging predictive analytics, real-time optimization, and collaborative innovation ecosystems, Japan is positioning itself as a global leader in the AI + 3D printing space. This convergence of advanced technology and forward-thinking policy marks a new era where Japan doesn’t just keep pace with global manufacturing trends but sets them.
Insight to Impact: IMARC’s Guide to Japan’s AI-Driven 3D Printing Future
IMARC Group supports businesses, researchers, and policymakers navigating Japan’s rapidly evolving 3D printing and artificial intelligence ecosystem. Our expertise enables stakeholders to harness the power of AI-driven additive manufacturing for innovation, efficiency, and growth.
- Market Insights: Analyse emerging trends in 3D printing adoption, AI-integrated design workflows, and material advancements across industries.
- Strategic Forecasting: Anticipate market growth, sector specific opportunities, and the transformative effects of AI on Japan’s additive manufacturing landscape.
- Competitive Intelligence: Monitor leading players, from industry giants to startups, driving AI-enabled 3D printing innovation in Japan.
- Policy & Regulatory Analysis: Decode government initiatives, R&D incentives, and industrial strategies shaping Japan’s 3D printing ecosystem.
- Tailored Consulting: Deliver customized strategies for material optimization, production scalability, and leveraging AI for competitive differentiation.
As Japan’s 3D printing market accelerates toward an AI-powered future, IMARC Group stands as a trusted partner—providing actionable insights to help clients unlock new opportunities and lead in the next wave of manufacturing innovation.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
-(1)_11zon.webp)










