How Japan is Strengthening Cybersecurity in the Digital Age

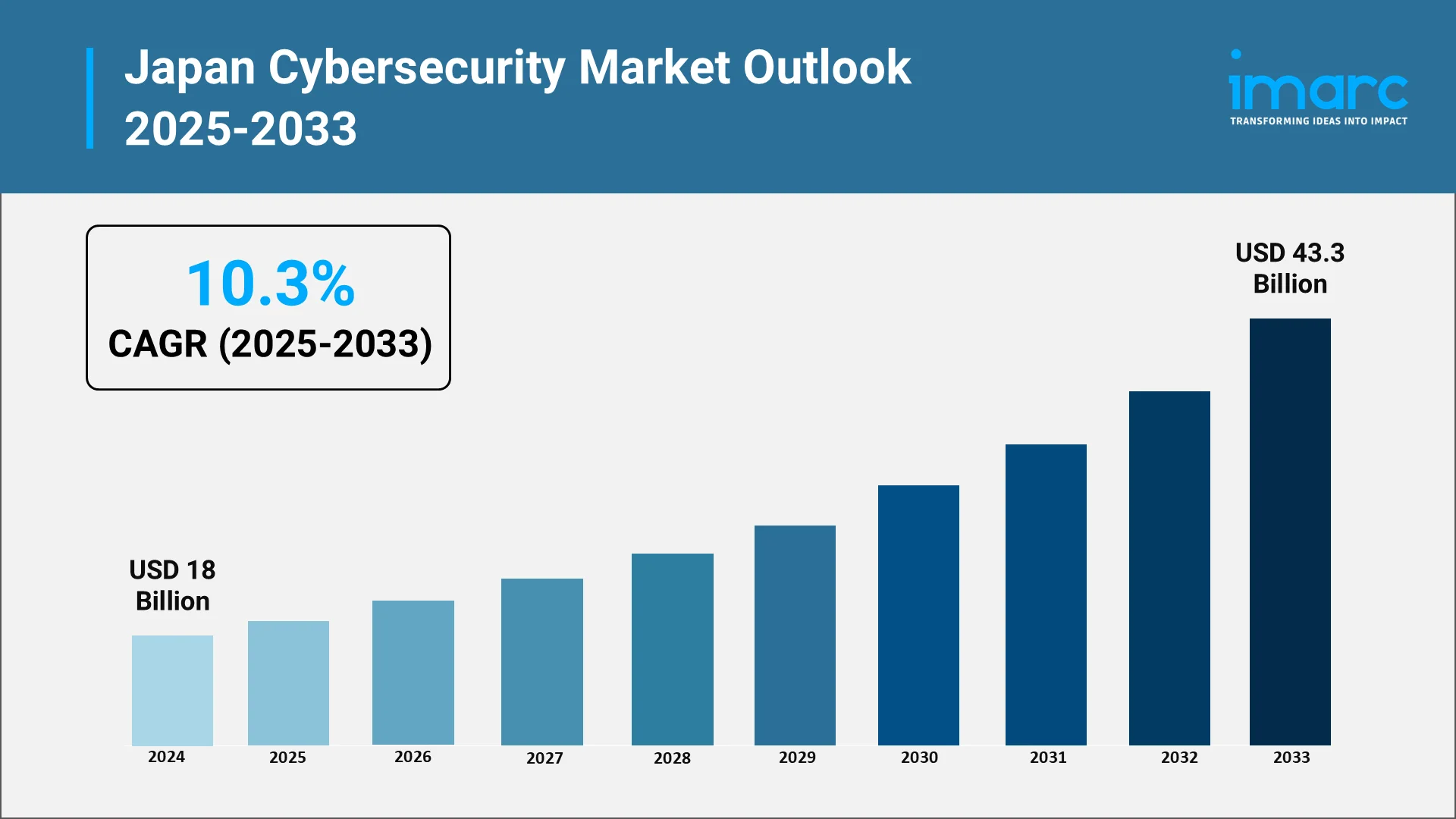
As a global leader in technology and innovation, Japan has increasingly recognized the critical importance of cybersecurity to protect its digital infrastructure. As per IMARC Group projections, the cybersecurity market in Japan was valued at USD 18 Billion in 2024 and is projected to experience a robust growth rate of 10.3% CAGR, reaching USD 43.3 Billion by 2033. This rapid expansion highlights Japan's ongoing efforts to enhance its cybersecurity landscape.
In response to the rising frequency and sophistication of cyber threats, Japan’s government, alongside private-sector companies, is taking decisive actions to strengthen its digital defenses. Moreover, with the increasing reliance on digital technologies across industries, ensuring cybersecurity has become essential to maintaining national security, economic stability, and consumer trust. The nation’s comprehensive approach is focused on building a resilient, secure digital ecosystem that can effectively withstand emerging challenges in the Japan cyber threat landscape.
Let us dive into Japan's comprehensive cybersecurity initiatives and strategies, key challenges, and future outlook.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
Government Policies, Strategies, and Cybersecurity Law:
Japan’s government has established a robust legal framework and comprehensive policies to strengthen cybersecurity across the nation. Below are key elements of cybersecurity strategy:
- Japan National Cybersecurity Center (NISC): NISC plays a central role in overseeing Japan’s national cybersecurity framework. NISC works with multiple sectors—public and private—ensuring all parts of the nation’s infrastructure are protected from cyber threats. It coordinates cybersecurity policies, incident response efforts, and the integration of cybersecurity technology.
- Cybersecurity Basic Act: This legislation serves as the backbone of Japan's cybersecurity efforts. It mandates that critical infrastructure sectors, such as telecommunications, energy, transportation, and finance, must implement stringent cybersecurity measures to defend against attacks. The act ensures that operators of critical systems prioritize cybersecurity in their operations, which significantly mitigates potential vulnerabilities.
- Ongoing Policy Updates: The dynamic nature of cybersecurity threats means that Japan continuously updates its policies. With the rise of artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and 5G technologies, the Japanese government’s digital policy regularly revises its laws and strategies to incorporate new security measures that align with technological advancements. These updates ensure that the country’s legal framework remains responsive to evolving digital risks.
- In May 2025, Japan passed the Active Cyber Defense Law, which marked a significant shift in Japan cybersecurity strategy. This legislation enhances public-private collaboration, establishes a Cyber Council, and empowers government agencies to proactively counter cyber threats.
- In April 2024, Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI) announced plans to implement a cybersecurity rating system by fiscal year 2025. The system categorizes corporate cyber defense measures, enhancing transparency and encouraging improved cybersecurity practices across businesses.
- In April 2024, METI and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC) released the "AI Guidelines for Business Ver 1.0." These non-binding guidelines provide businesses with principles and practices for the safe and secure development and use of AI technologies.
- In April 2024, Microsoft revealed a major investment of USD 2.9 Billion to enhance cloud infrastructure and AI capabilities in Japan. This initiative aims to bolster the country's cybersecurity, expertise, and research, with plans to collaborate with the government on cybersecurity services.
Japan’s proactive policy and legal framework are crucial in ensuring the country’s preparedness to address future cybersecurity challenges effectively.
Key Projects and Developments:
Several ongoing government initiatives and technological advancements are directly shaping Japan’s cybersecurity future:
- Critical Infrastructure Protection Program: The government has identified certain sectors as particularly vulnerable to cyber threats. The protection of these critical infrastructures is of national importance. Some of the areas targeted include:
- Energy: Power grids and energy production systems must be secure from cyber intrusions to ensure continuous service to citizens and businesses.
- Telecommunications: The telecommunications infrastructure is pivotal for Japan’s communication systems, including emerging 5G networks. Ensuring the security of this infrastructure is critical for national security.
- Finance: Japan’s financial system must be resilient against cyberattacks to preserve its stability, protect sensitive financial data, and maintain consumer confidence.
- Transportation: Transportation networks, including railways and airports, are essential for Japan’s economy. Cybersecurity measures help ensure the smooth and secure operation of these systems.
- Smart Cities and IoT Security: The concept of smart cities, where everyday objects and systems are interconnected, provides significant opportunities for cybersecurity firms. The Smart Japan-Asean Mobility Partnership (JAMP) study focused on IoT security for mobility and transport. As digital infrastructure grows, Japan prioritizes cybersecurity to protect citizens’ data and secure smart systems.
- 5G Network Security: The global rollout of 5G networks has heightened the need for robust security. Japan is focusing heavily on securing its 5G infrastructure to prevent large-scale attacks that could disrupt critical services. This includes ensuring that 5G networks supporting everything from autonomous vehicles to industrial control systems remain secure.
These projects highlight Japan’s determination to secure its digital and physical infrastructure, laying the foundation for a resilient and secure technological future.
Challenges and Roadblocks:
Despite these significant efforts, Japan still faces a number of challenges in strengthening its cybersecurity defenses:
- Skilled Workforce Shortage: There is a critical shortage of cybersecurity professionals in Japan, which poses a significant challenge to the country’s defense against sophisticated cyberattacks. Japan is making efforts to close this gap by offering specialized education programs, but the demand for skilled professionals continues to outstrip supply.
- Legacy Systems: Many industries and critical infrastructures in Japan rely on legacy systems that were not built with modern cybersecurity threats in mind. Upgrading these outdated systems is both expensive and time-consuming. Moreover, these systems often cannot manage the scale and complexity of contemporary cyber threats.
- Geopolitical Risks: The nation’s geopolitical standing in the Asia-Pacific region makes it a target for cyber espionage and state-sponsored cyberattacks. The complexity and scale of these cyberattacks in Japan require continuous adaptation and innovation in cybersecurity strategies.
- Fragmented Funding: Japan’s cybersecurity efforts are sometimes hindered by fragmented funding across different government departments. While the government has allocated resources for cybersecurity, these investments are not always coordinated, which can delay the implementation of a unified national cybersecurity strategy.
Addressing these challenges is essential to ensuring that Japan's cybersecurity efforts remain robust and adaptive to new threats.
Opportunities and Future Outlook:
The future of Japan cybersecurity market is bright, with ample opportunities for innovation and growth in the following areas:
- AI and Machine Learning: As Japan continues to embrace AI and machine learning, these technologies are expected to play a significant role in cybersecurity. AI can be used to predict, detect, and respond to threats in real-time, making security systems more proactive and efficient. AI tools can analyze large volumes of data to identify patterns and detect anomalies, enhancing the overall defense system.
- Growth of 5G and IoT Security: The demand for secure networks and systems will increase with 5G technology becoming more prevalent. Companies and the government alike will need to invest in securing these new high-speed networks. Additionally, the rise of IoT in various sectors, from healthcare to transportation, will require specialized security solutions to protect the devices and the data they generate.
- Cybersecurity for Aging Populations: Japan has one of the world’s fastest-aging populations. This demographic shift creates an opportunity for cybersecurity solutions tailored to older adults. From secure online banking to digital healthcare services, creating cybersecurity solutions for seniors will be an increasingly important niche market.
Japan’s cybersecurity industry is poised to see substantial growth and innovation with the rise of these technologies.
Impact and National Benefits:
The long-term benefits of strengthening cybersecurity in Japan are wide-ranging:
- Economic Stability: Japan ensures the continued smooth operation of its economy by securing vital sectors such as finance, energy, and telecommunications. A secure digital infrastructure boosts consumer and investor confidence, enabling economic growth and stability.
- National Security: Japan’s cybersecurity measures help protect its national interests, including government systems and military assets. Securing digital infrastructure from espionage and cyberattacks is crucial for maintaining national security in an increasingly interconnected world.
- Global Competitiveness: Japan’s reputation as a technology leader is enhanced by its commitment to cybersecurity. As businesses worldwide look for secure partners, Japan’s strong cybersecurity posture positions the country as a key player in the global tech ecosystem.
Cybersecurity Companies and Manufacturers in Japan:
The country is home to several leading Japan cybersecurity companies that play a critical role in the nation's efforts to secure its infrastructure:
- Trend Micro: Known globally for its cybersecurity solutions, Trend Micro provides protection against a wide range of threats, from malware to ransomware, and plays an integral role in Japan’s cybersecurity landscape.
- Fujitsu: Fujitsu offers end-to-end cybersecurity services for large enterprises, providing solutions ranging from risk management to incident response. The company helps organizations implement secure systems to guard against cyber threats.
- Rakuten Mobile: As a significant player in the mobile communications sector, Rakuten Mobile focuses on ensuring the security of mobile networks. It plays a vital role in securing Japan’s digital communication infrastructure.
These companies, along with startups and emerging cybersecurity firms, are at the forefront of securing Japan’s digital landscape.
How IMARC Can Help:
As Japan continues to grow its cybersecurity market, IMARC Group offers invaluable insights into this evolving industry. With detailed reports on the cybersecurity industry in Japan, IMARC provides:
- Market Insights and Projections: IMARC’s research covers trends, growth projections, and the key players in Japan’s cybersecurity sector. These insights can guide businesses in making informed decisions and identifying lucrative investment opportunities.
- Emerging Technologies: IMARC tracks the latest developments in cybersecurity, including the rise of AI, IoT, and 5G security. Businesses can use IMARC’s reports to stay ahead of technological shifts and leverage emerging innovations.
- Strategic Guidance: Whether expanding into Japan or enhancing current cybersecurity operations, IMARC provides data-driven insights that help businesses navigate Japan’s complex cybersecurity market.
By leveraging IMARC’s expertise, stakeholders stay informed and make strategic decisions that align with Japan’s cybersecurity goals, ensuring long-term success.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
-(1)_11zon.webp)










