How AI is Revolutionizing Japan’s Telecom Industry?
-(1).webp)
Japan is a leader in digital transformation, known for being one of the most advanced nations in technology globally. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is becoming an integral force across various sectors, and the telecom industry is no exception. The integration of AI into telecom infrastructure is optimizing performance and reliability, and also enabling telecom companies to offer smarter, faster, and more personalized services. AI tools are enabling faster fault detection, smarter use of resources, and service plans tailored to customer usage patterns. For telecom companies, this translates into stronger operational performance, better customer retention, and a more competitive market position. The shift signals a move toward intelligent, data-driven operations that adapt quickly to business demands and deliver measurable results.
The Role of AI in Optimizing Telecom Infrastructure:
Japan’s digital economy depends on a reliable and high-performing telecom infrastructure. AI is now enhancing that backbone by enabling smarter, more responsive network management. Telecom operators are using AI systems to monitor large-scale networks in real time, detecting issues before they escalate into service disruptions.
- Predictive Monitoring and Resource Allocation
Machine learning models analyze traffic flows, identify recurring patterns, and flag unusual activity. When they forecast usage spikes, such as during national events, AI automatically adjusts bandwidth allocation to prevent congestion in specific areas. This predictive approach reduces strain on equipment, extending hardware life and minimizing the need for emergency repairs. It also allows engineers to prioritize strategic network expansions instead of constant manual troubleshooting.
- Smarter Routing for Better Performance
AI is also transforming how data moves across networks. Intelligent routing protocols assess current conditions and select the most efficient pathways for data transmission. These adjustments happen dynamically, accommodating shifts in demand or rerouting around unexpected outages.
- Impact on End Users
The result for customers is a faster, more reliable connection with fewer interruptions. For telecom companies, the technology translates into operational efficiency, lower maintenance costs, and a stronger foundation for future network upgrades. For instance, in June 2025, SoftBank announced its plans to invest in advanced technology to upgrade its network infrastructure in Japan by launching pre-commercial stratospheric telecommunications services in 2026 using Sceye’s High Altitude Platform Stations (HAPS). The initiative aims to enhance disaster recovery and rural connectivity while supporting future 6G applications. HAPS will provide faster, flexible coverage compared to traditional satellite systems.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
AI-Powered Network Management and Automation:
Japan’s telecom sector is moving closer to the concept of “zero-touch” networks, where AI systems manage the bulk of operational tasks with minimal human involvement. For instance, in February 2024, zTouch Networks announced its partnership with Rakuten Symphony to integrate its AI-powered rApps and xApps into the Rakuten Telecom Platform. This collaboration aims to enhance network management with zero-touch automation, optimizing Open RAN systems and driving energy efficiency, aligning with the vision of fully autonomous telecommunications networks. Within the growing telecom cloud environment, AI is overseeing virtual network functions, allocating resources, and ensuring seamless coordination across distributed, cloud-based infrastructures.
This intelligent orchestration optimizes performance while controlling costs. Network capacity can be scaled in real time to meet demand, and workloads can be automatically rerouted when an issue arises, reducing service disruption.
One of the most significant advancements is the deployment of self-healing capabilities. These AI-driven systems detect faults and also identify their root cause and implement corrective measures without manual intervention. This reduces downtime, cuts maintenance costs, and ensures service continuity.
As Japan expands its 5G networks and begins preparing for 6G, such automation will be critical. The complexity, density, and performance requirements of next-generation networks will demand AI-driven operational models to maintain efficiency, scalability, and reliability.
Use of AI in 5G Rollout and Network Expansion:
Japan’s nationwide 5G rollout is among the fastest and most technically ambitious globally, and AI has become a crucial enabler in meeting both scale and performance targets. Telecom firms are deploying AI-powered planning tools to determine optimal tower placement, factoring in population density, terrain, and projected demand patterns. This approach ensures broader coverage while reducing redundant infrastructure investment. For instance, in May 2025, Rakuten Mobile and Rakuten Symphony launched an AI-driven RAN Intelligent Controller in Japan's 4G and 5G networks. This innovative platform aims to reduce network energy consumption by up to 20%, enhancing sustainability and paving the way for intelligent mobile connectivity.
AI also assists in spectrum management, dynamically allocating frequencies to maximize capacity and minimize interference. During the transition phase, it coordinates seamless handovers between existing 4G networks and new 5G infrastructure, preventing service interruptions for end users.
In dense metropolitan areas where traffic spikes are frequent, AI systems monitor real-time network load and automatically adjust resource allocation to maintain low latency and high-speed connectivity. As Japan begins to lay the groundwork for 6G, AI’s role will expand to include fully adaptive networks capable of self-learning and optimizing in real time, supporting advanced applications such as autonomous mobility, immersive AR/VR, and mission-critical IoT services.
Enhancing Customer Experience through AI Solutions:
In Japan’s telecom sector, AI is becoming a core enabler of superior customer service delivery. Service assurance platforms equipped with predictive analytics can identify performance issues and resolve them before they affect end users. This proactive maintenance approach reduces service disruptions, minimizes inbound complaints, and strengthens customer confidence in the provider’s reliability.
Customer support functions are also benefiting from AI integration. Intelligent chatbots and virtual assistants can manage high volumes of routine inquiries, from account updates to basic troubleshooting, delivering accurate responses in seconds. For instance, in March 2025, KDDI announced its plans to launch the "au Support AI Advisor", a digital human service combining generative AI with voice, text, and images for enhanced customer support. This service aims to improve convenience and satisfaction, initially focusing on smartphone inquiries about Ponta points, with plans for future expansions. By automating these interactions, telecom operators reduce call center workloads, enabling human agents to focus on high-value, complex cases.
AI-driven personalization further enhances engagement. By analyzing customer usage data and behavior patterns, telecom companies can recommend tailored plans, content offerings, and targeted promotions. This improves relevance and satisfaction and also drives loyalty and reduces churn. In a competitive market, these AI-enabled capabilities give operators a measurable advantage in both customer retention and lifetime value growth.
Leveraging Big Data in Telecom with AI:
Japan’s telecom networks generate vast volumes of data every second. AI enables operators to extract actionable value from this information with speed and accuracy. Through advanced telecom analytics, machine learning models process usage data, track network performance, and uncover patterns that may not be visible through manual analysis.
These insights support strategic decisions in network expansion, service innovation, and pricing optimization. AI also strengthens security and fraud prevention by detecting anomalies, such as sudden spikes in call duration or unusual data consumption and triggering immediate action to mitigate risks.
In marketing, AI-driven segmentation goes beyond basic demographics to group customers by behavioral trends and usage profiles. This allows telecom providers to deliver targeted campaigns, recommend relevant services, and improve customer engagement. The result is more efficient resource allocation, stronger market positioning, and improved returns on both infrastructure and customer acquisition investments.
Key Telecom Providers Driving AI Integration in Japan:
- SoftBank: In November 2024, SoftBank Corp. announced the development of “AITRAS,” a converged AI-RAN solution aimed at telecom operators. Set for global deployment starting in 2026, AITRAS integrates AI and RAN workloads on NVIDIA platforms, enhancing performance, efficiency, and infrastructure investment.
- KDDI Corporation: In July 2025, expanded its partnership with Circles to enhance the global reach of povo, Japan's leading digital telecom brand. This collaboration aims to leverage innovative technology and customer-centric strategies for successful international expansion in markets like the Americas and Southeast Asia.
- NTT Docomo (and NTT Group): In March 2025, successfully demonstrated an architecture dubbed “In-Network Computing” (INC) that integrates computing with mobile network control—designed for low-latency, bandwidth-efficient services in the coming 6G/IOWN era.
- Fujitsu: In July 2025, officially launched, consolidating global network operations for enhanced flexibility. The subsidiary aims to provide innovative, high-quality network solutions through streamlined processes, addressing growing demand in telecommunications and data centers amid rising costs and AI adoption.
Data Privacy, Compliance, and AI Challenges:
Safely deploying AI in Japan’s telecom sector requires more than just technical expertise—it demands careful attention to regulatory compliance, ethical considerations, and operational transparency, which includes:
- Protecting Sensitive Telecom Data
Telecom providers in Japan handle large volumes of personal and corporate data, making robust data governance essential. Compliance with the Act on the Protection of Personal Information (APPI) and international privacy regulations requires strong encryption, controlled system access, and secure retention protocols. AI systems must be designed to process this information without creating vulnerabilities. Implementing strict cybersecurity measures, conducting regular security assessments, and ensuring data minimization practices are critical to safeguarding trust while meeting both domestic and global compliance requirements.
- Addressing Algorithmic Bias
Bias in AI models can lead to unfair or inconsistent service delivery, such as disproportionate network prioritization or unsuitable plan recommendations. These risks often stem from incomplete or non-representative training datasets. Telecom providers can address this by curating diverse and balanced data inputs, running continuous bias detection tests, and implementing governance frameworks for ethical AI use. Regular model retraining and validation ensure decisions remain equitable, protecting brand reputation and meeting rising expectations for fairness in AI-driven telecom services.
- Improving AI Transparency and Accountability
Opaque AI models, often described as “black boxes,” create challenges for compliance, customer trust, and operational oversight. To address this, telecom firms are adopting explainable AI techniques that make decision-making processes more understandable to both technical teams and regulators. Maintaining detailed audit logs and enabling traceability in AI outputs ensures accountability. These measures strengthen regulatory compliance and also build customer confidence in automated systems, reinforcing the credibility of AI-powered telecom services.
- Balancing Innovation and Governance
Sustaining AI innovation in telecom requires a structured approach to governance. Collaboration between network engineers, AI developers, legal teams, and compliance officers ensures systems remain secure, fair, and aligned with regulations. This balance allows operators to adopt advanced capabilities—such as predictive maintenance and intelligent routing—without compromising on ethical or legal standards. Establishing clear operational guidelines, monitoring frameworks, and escalation procedures helps maintain agility while safeguarding both customer interests and corporate integrity in AI deployments.
Future Outlook: AI’s Long-Term Impact on Japan’s Telecom Sector
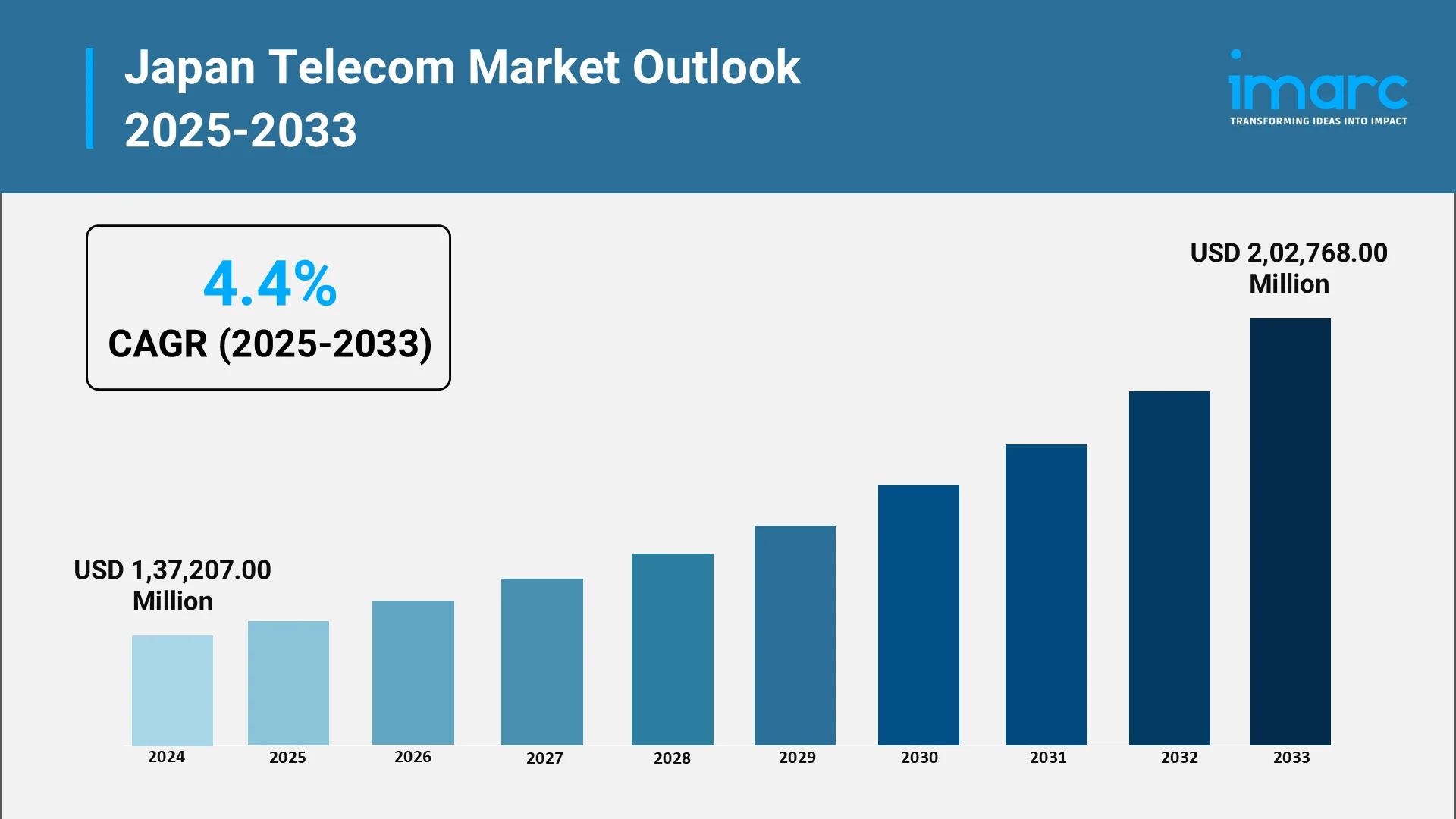
By 2033, Japan's telecom market is projected to reach USD 202768.00 Million, with AI-enabled services contributing significantly to this growth. Innovations, such as AI-enabled network slicing, intelligent edge computing, and real-time self-optimizing systems, are establishing new standards for efficiency and reliability. Additionally, AI-powered smart city integration will enhance urban infrastructure, making it more responsive and interconnected than ever before. Strategic investment in AI talent, scalable infrastructure, and cross-industry partnerships will be crucial to unlocking this potential. Telecom providers that offer seamless, secure, and highly personalized services are expected to dominate the market and solidify Japan's position as a global leader in next-generation digital infrastructure.
How IMARC Can Help:
As Japan accelerates AI adoption in its telecom sector, IMARC Group delivers the intelligence needed to navigate this transformation with clarity and precision. Our research provides stakeholders with actionable insights, enabling informed decision-making in a rapidly changing market.
- Market Insights and Forecasts: IMARC’s in-depth studies on Japan’s telecom industry include growth projections, key performance metrics, and AI integration trends. These help telecom operators, investors, and policymakers identify high-potential opportunities and shape effective strategies.
- Technology Trends: We track developments in AI-powered automation, edge computing, network slicing, and 5G optimization, giving businesses the knowledge to stay ahead of technological shifts and maintain a competitive edge.
- Competitive Landscape Analysis: Our reports feature detailed profiles of leading telecom companies in Japan, highlighting their AI-driven initiatives, strategic partnerships, and future roadmaps. This benchmarking data supports positioning and market differentiation.
- Regulatory and Policy Insights: IMARC offers timely updates on Japan’s telecom regulations, AI governance frameworks, and data privacy laws to ensure compliant and efficient implementation of AI technologies.
By leveraging IMARC’s expertise, stakeholders can accelerate AI adoption, align with Japan’s digital transformation goals, and achieve sustained growth in an increasingly AI-driven telecom environment.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










