Japan Foreign Exchange Market Expected to Reach USD 111.9 Billion by 2033 - IMARC Group
Japan Foreign Exchange Market Statistics, Outlook and Regional Analysis 2025-2033
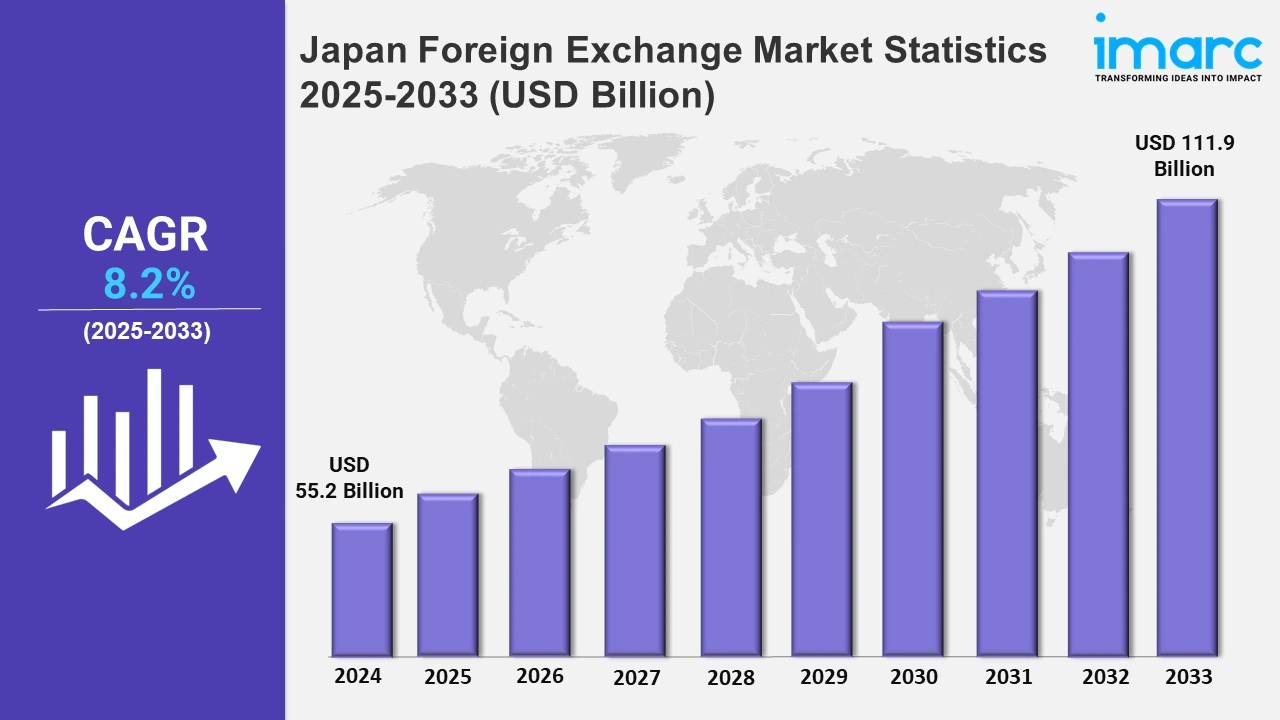
The Japan foreign exchange market size was valued at USD 55.2 Billion in 2024, and it is expected to reach USD 111.9 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 8.2% from 2025 to 2033.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Direct access to Japan's bank payment clearing network indicates expanding prospects for foreign financial enterprises to improve cross-border payment efficiency, reduce transaction expenses, and boost their position in Japan's dynamic financial ecosystem, which prioritizes innovation and integration. For example, in October 2024, one of the British fintech firms, Wise, received approval for direct access to Japan's bank payment clearing network. This milestone enabled the company to offer more efficient and cost-effective cross-border payment services in Japan becoming the first foreign financial company to do so.
Moreover, the shift by local banks away from in-house retail FX services demonstrates the growing engagement with specialized suppliers that meet consumer demands. Partnerships guarantee that customers continue to have access to simple travel money options while also improving their advantages through savings and streamlined service offerings. For instance, in May 2024, U.K.-based foreign exchange brand Travelex launched an FX affiliate referral program in partnership with local Japanese banks. With financial institutions reducing in-house retail FX services, the program directs customers needing travel money to Travelex, offering discounts for purchases using bank cards. Furthermore, the market is experiencing an increase in demand for hedging products owing to increased currency volatility and trade uncertainty. Companies are increasingly using FX swaps and forward contracts to stabilize their operations and reduce the risks associated with shifting currency rates. This has created tremendous opportunities for financial institutions to provide bespoke solutions. For example, leading Japanese multinational firms, such as Toyota and Sony, regularly employ forex futures to hedge their worldwide exposure. Toyota, in particular, uses forward contracts to ensure revenues from North America and Europe, providing consistent profitability despite erratic yen movements. This increased dependence on advanced forex instruments highlights the need for innovative financial solutions that meet the changing demands of enterprises involved in international trade and commerce.
Japan Foreign Exchange Market Statistics, By Region
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include the Kanto region, Kinki region, Central/Chubu region, Kyushu-Okinawa region, Tohoku region, Chugoku region, Hokkaido region, and Shikoku region. The fiscal policy, along with extensive investment in R&D activities, is one of the growth-inducing factors.
Kanto Region Foreign Exchange Market Trends:
The Kanto region, especially Tokyo, is Japan's financial capital, where algorithmic trading is gaining popularity. Companies such as Nomura Securities use automated trading systems to perform large-scale deals effectively. Tokyo's reputation as a worldwide financial hub draws a varied range of players, including overseas investors, who use innovative technology to improve liquidity and trading speed. This trend emphasizes Kanto's key role in developing Japan's foreign exchange industry through technical improvements.
Kinki Region Foreign Exchange Market Trends:
In Osaka, part of the Kinki region, businesses are actively managing forex risks through hedging. Kansai Electric Power hedges currency fluctuations to stabilize costs for importing energy resources. The industrial strength of Osaka drives this trend, as companies prioritize financial strategies to ensure operational predictability. By integrating forex risk management, the Kinki region highlights the importance of financial tools for stability in a dynamic economic environment.
Central/Chubu Region Foreign Exchange Market Trends:
The Central/Chubu region, anchored by Nagoya, sees forex strategies as critical for its export-heavy industries. Toyota uses forward contracts to lock in exchange rates and protect earnings from foreign markets. As a key manufacturing area, Chubu’s reliance on exports necessitates robust currency management to navigate exchange rate uncertainties. This trend reflects the region’s focus on ensuring profitability for active businesses.
Kyushu-Okinawa Region Foreign Exchange Market Trends:
The Kyushu-Okinawa region, close to major Asian markets, experiences growing forex activity due to its trade connections. Saibu Gas employs currency swaps to stabilize costs associated with importing energy. The region’s strategic location fosters cross-border commerce, requiring reliable forex solutions. This trend demonstrates Kyushu-Okinawa’s role as a trade hub, where financial tools support businesses engaged in international transactions.
Tohoku Region Foreign Exchange Market Trends:
Tohoku, known for agriculture, witnesses farmers and cooperatives using forex to support export growth. ZEN-NOH protects revenue by employing forex options to manage currency risks from markets. With rising agricultural exports, forex strategies are critical for financial stability. This trend highlights the importance of currency management in rural economies, ensuring that Tohoku’s agricultural producers remain competitive internationally.
Chugoku Region Foreign Exchange Market Trends:
In Hiroshima, part of the Chugoku region, manufacturing firms like Mazda Motors rely on forex swaps to manage production costs tied to markets. The region’s export-focused industries depend on effective currency management to maintain profitability. This trend showcases how forex strategies play a vital role in supporting manufacturers in regions heavily integrated into the economy.
Hokkaido Region Foreign Exchange Market Trends:
Hokkaido’s growing tourism industry relies on forex services to handle international revenues. JR Hokkaido, for example, adapts to increasing foreign visitors by implementing multi-currency systems to streamline operations. The surge in international tourism highlights Hokkaido’s need for efficient currency management. This trend emphasizes how foreign exchange tools are shaping financial practices in tourism-driven regions.
Shikoku Region Foreign Exchange Market Trends:
Shikoku's small exporters play an important role in FX activities. Kikusui Chemicals employs outright forwards to secure currency rates for their foreign sales. This region's concentration on smaller-scale sectors highlights the need for specialized FX instruments to assist niche exporters. Shikoku's emphasis on financial stability for SMEs highlights its distinct position in the Japan foreign currency market.
Top Companies Leading in the Japan Foreign Exchange Industry
Some of the leading Japan foreign exchange market companies have been included in the report. Competitive analysis, such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant, has been covered in the report.
Japan Foreign Exchange Market Segmentation Coverage
- Based on the counterparty, the market has been classified into reporting dealers, other financial institutions, and non-financial customers. Reporting dealers, including major banks, stimulate market activity by enabling interbank and client transactions. Other financial institutions, such as hedge funds and asset managers, engage in active trading for investment or speculation. Non-financial customers use forex for international trading and hedging.
- Based on the type, the market has been categorized into currency swap, outright forward and FX swaps, and FX options. Currency swaps are used to regulate interest rates and provide long-term finance. Outright forward and FX swaps provide for set future exchange rates and liquidity by combining spot and forward currency contracts. FX options provide flexibility in controlling exchange rate risks through specified strike prices.
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 55.2 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 111.9 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 8.2% |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Predictive Market Assessment:
|
| Counterparties Covered | Reporting Dealers, Other Financial Institutions, Non-financial Customers |
| Types Covered | Currency Swap, Outright Forward and FX Swaps, FX Options |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kinki Region, Central/Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email |
Browse IMARC Related Reports on Foreign Exchange Market:
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.





.webp)




.webp)












