Australia's Agribusiness Industry Driven by Sustainability and Government Initiatives

Introduction:
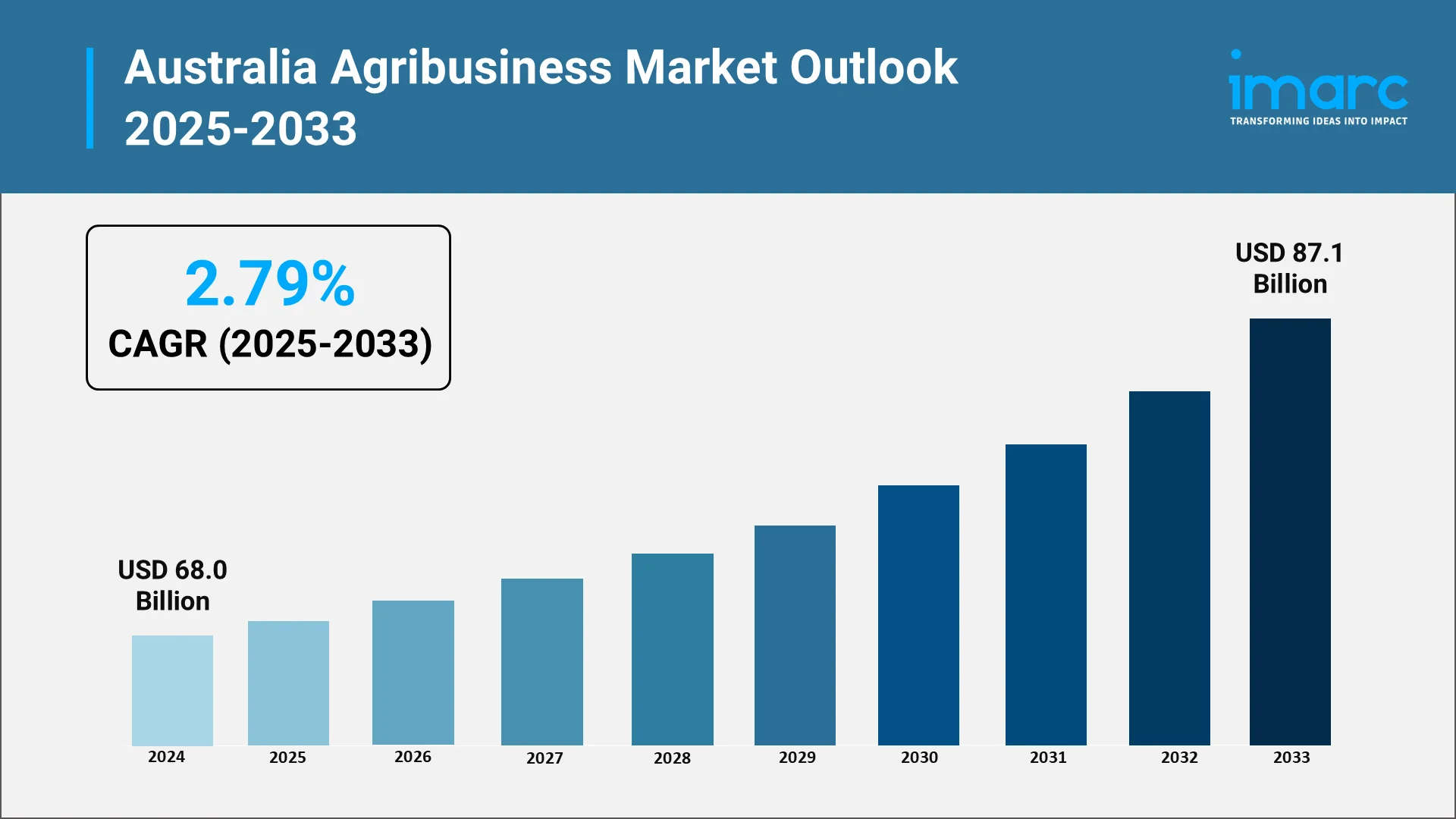
Australia's agribusiness sector is at a crossroads, combining its historic advantage in bulk farming with new-generation technologies and green practices. The industry is pivotal to the nation's economy, adding billions to GDP and underpinning exports to overseas markets. Increasing food security demands and climate change pressures have compelled Australian farmers and agribusiness companies to take up innovation at an unprecedented scale. From AI integration and precision farming to agricultural biological use, the market is witnessing a speedy revolution. Government incentives, sustainability targets, and demand for environmentally friendly products from consumers are prominent drivers of this transformation. Furthermore, the rise of the Australia agritech market, the Australia Agricultural biologicals market, and the Australia agricultural equipment market reflects how digitalization, green farming, and automation are transforming the agricultural sector in Australia. Through firm government policies and innovation from the private sector, Australia stands a good chance of becoming a world leader in sustainable agribusiness.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
Role of AI, Impact, and Benefits in the Australian Agribusiness Industry:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing Australian agriculture by enabling farmers to optimize crop yields, manage resources efficiently, and reduce operational costs. AI-driven tools, including predictive analytics and machine learning models, monitor soil health, weather patterns, and pest infestations in real time, supporting informed decision-making and minimizing waste. Drones and AI-powered imaging systems provide precise data on crop conditions, allowing targeted interventions that reduce chemical use—AI systems at Dookie agricultural campus, for example, have cut herbicide usage by up to 80%.
In addition to crop farming, AI facilitates supply chain openness, allowing agribusinesses to follow products from farm to plate, enhancing food safety and satisfying consumer requirements for traceability. In animal husbandry, AI tracks animal health and wellbeing, helping to prevent disease risks. Adoption of AI in farming machinery additionally automates processes, decreasing labor dependence and enhancing efficiency. In terms of sustainability, productivity, and international competitiveness, AI is shaping Australia's agritech industry into a contemporary, high-technology, and sustainable sector.
Government Initiatives / Support in the Australian Agribusiness Industry:
The Australian government has launched a number of programs to build the agribusiness sector, emphasizing innovation, sustainability, and competitiveness in the global market. Initiatives like the National Agricultural Innovation Agenda are specifically designed to drive research and development in agri-technologies to support innovation in automation, data analysis, and biotechnology. Grants and subsidies are provided to farmers embracing sustainable production practices such as precision irrigation, renewable energy sources, and low carbon emission production.
Export policies are also central, enabling Australian growers to access export markets while upholding excellent standards of safety and quality. The government has also invested in digital agriculture programs, providing connectivity for regional and rural areas in support of technology adoption. Biosecurity frameworks also protect the industry from pests and diseases, upholding Australia's reputation for high-quality produce. Support for the agricultural biologicals industry involves research funding for environmentally friendly crop protection and soil conditioning products. With these interventions, the government makes sure that agribusiness is resilient, technologically driven, and focused on long-term sustainability objectives.
Some of the key initiatives are:
- The $72.7 million Agribusiness expansion initiative (ABEI) supports Australian agribusinesses to grow and diversify exports. Delivered by Austrade and DAWE, it provides scaled-up export services, improved market intelligence, grants for industry collaboration, and technical expertise to expand access. Agriculture Counsellors worldwide supply key insights, published via Austrade’s portal. Recent updates include tariff changes in Thailand, extended beef shelf-life in Saudi Arabia, and new export opportunities in Sri Lanka, Taiwan, Argentina, and Europe.
- The Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), with the Australian Government, launched the Australia-India Critical Agriculture Skills Pilot Project to modernize India’s agriculture sector. Implemented in Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, it introduced roles like Digital Agriculture Extension Promoter and Carbon Farming Practitioner. Developed with ICAR, ASCI, ACAH, and industry partners, the initiative aligns with SDGs, fostering sustainability, innovation, and international skill collaboration to strengthen India’s agricultural workforce.
Top Companies in the Australian Agribusiness Industry:
The Australian agribusiness landscape is shaped by a mix of established players and innovative startups. Some of the top companies include:
- GrainCorp Limited – A leader in grain handling, storage, and marketing with a strong export presence.
- Elders Limited – Offering diversified agribusiness services, including real estate, livestock, and financial services.
- Nufarm Limited – Specializing in crop protection products and actively investing in agricultural biologicals.
- Costa Group – Australia’s largest horticultural company with a focus on sustainable fruit and vegetable production.
- AACo (Australian Agricultural Company) – A dominant player in cattle farming and beef exports.
- AgriWebb – A leading agritech startup providing digital farm management solutions.
- The Yield – An AI-driven platform offering predictive insights into weather and crop management.
These companies represent the synergy of tradition and innovation, with established firms ensuring scale and global market reach, while startups drive digital transformation and sustainability across the value chain.
Opportunities and Challenges in the Australian Agribusiness Industry:
Opportunities:
- Sustainability and Biologicals Market Growth
Australia’s agribusiness sector is experiencing rising opportunities through the expansion of the agricultural biologicals market. Consumer demand for organic, chemical-free, and eco-friendly produce is driving growth, creating new revenue streams for farmers and agribusinesses. Innovations in biofertilizers, biopesticides, and soil health enhancers are reducing reliance on traditional chemicals while improving long-term sustainability. This aligns with both environmental goals and government policies that prioritize carbon-neutral farming. By capitalizing on Australia’s reputation for clean, green, and safe food, producers can capture premium market segments locally and internationally. With strong R&D support and consumer-driven momentum, agricultural biologicals offer a pathway for agribusinesses to meet sustainability demands while unlocking higher margins and global recognition.
- Export Potential and Global Competitiveness
Australia’s agribusiness industry is strategically positioned to capitalize on booming export markets, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region, where growing middle-class populations demand premium, traceable, and sustainable food products. Approximately 70% of Australia’s agricultural production is exported, with grains, oilseeds, and pulses as major contributors. The country’s reputation for quality and safety provides a competitive edge, while digitalized supply chains, powered by AI and blockchain, enhance transparency and trust. Government trade agreements and export promotion schemes improve market access, and a focus on carbon-neutral, climate-resilient farming aligns with global sustainability trends. This export-driven growth strengthens economic resilience and positions Australia as a global leader in environmentally responsible and high-quality food production.
- Agritech and Equipment Market Expansion
The rapid adoption of agritech and smart agricultural equipment is revolutionizing productivity in Australian farming. Precision tools, AI-driven analytics, drones, and automated machinery are transforming resource management and yield optimization. The Australia Agricultural equipment market, fueled by this shift, presents strong opportunities for companies offering solutions that improve efficiency while reducing operational costs. Government grants and incentives further encourage farmers to adopt modern equipment, ensuring widespread penetration across regions. These advancements address challenges like labor shortages and climate variability by enabling scalable, data-driven farming practices. For startups and established equipment providers, Australian innovation-friendly environment offers fertile ground to develop and deploy technologies that set global benchmarks for sustainable and high-tech agriculture.
Challenges:
- Climate Change and Resource Constraints
Climate change is a major challenge for Australian agribusiness, with extreme weather events, prolonged droughts, bushfires, and unpredictable rainfall disrupting crop yields and livestock production. Agriculture accounts for approximately 70% of Australia’s total water use, and climate change is exacerbating water scarcity, with projections suggesting up to a 25% decrease in major dam water flows by 2070 if emissions continue. This intensifies pressure on irrigation systems and necessitates advanced water management strategies. Farmers face rising costs to implement climate-adaptive technologies while maintaining productivity and sustainability. Without scalable solutions for water efficiency and climate resilience, the sector’s long-term viability, profitability, and competitiveness in domestic and international markets are at risk, threatening food security and economic stability.
- Rising Costs and Market Volatility
Australian agribusinesses are under pressure from escalating input costs, including fertilizers, labor, fuel, and energy. These expenses strain financial sustainability, particularly for small and medium-sized producers. At the same time, global market volatility adds another layer of uncertainty. Fluctuating commodity prices, trade restrictions, and geopolitical tensions create unstable revenue streams for exporters. Such challenges limit farmers’ ability to plan long-term investments in technology and sustainability. The financial burden is further compounded by supply chain disruptions and rising logistics costs. Together, these factors weaken profitability, reduce resilience, and make it difficult for agribusinesses to maintain competitiveness in global markets.
- Biosecurity and Technology Adoption Barriers
Biosecurity is a major concern for Australian agribusiness, as pests, diseases, and invasive species threaten crop and livestock health, potentially harming the country’s global reputation for safe, high-quality produce. At the same time, digital transformation offers efficiency gains, but adoption is hindered by poor connectivity in rural, regional, and remote areas, where approximately 30% of Australia’s population resides. High costs of advanced equipment and limited technical expertise further restrict innovation, slowing the adoption of precision farming and smart agriculture. Small and medium-sized farmers face particular challenges in balancing sustainability with profitability. Addressing these obstacles requires coordinated government policies, targeted private-sector investment, and collaborative research initiatives to strengthen biosecurity measures, improve digital access, and foster innovation, ensuring long-term resilience and competitiveness in the Australian agribusiness sector.
Future Outlook: Australian Agribusiness Industry
The future of the Australian agribusiness industry is poised for significant growth, driven by sustainability, technology, and global market demand. The adoption of AI, robotics, and precision farming will redefine agricultural efficiency, while agricultural biologicals will reduce chemical reliance and enhance soil health. Export opportunities in Asia-Pacific are expected to expand, especially as consumers seek premium, traceable, and eco-friendly food products. Government support through policy reforms, infrastructure investments, and innovation funding will further accelerate industry transformation. The Agricultural equipment market will see rapid automation, with smart tractors, drones, and robotic harvesters becoming mainstream. Moreover, carbon-neutral farming and renewable energy integration will align the industry with Australia’s broader climate goals. Despite challenges like climate variability and global trade complexities, the industry’s resilience, combined with innovation, positions Australia as a global leader in sustainable agribusiness by 2033. The coming decade will be marked by modernization, sustainability, and global competitiveness.
From Sustainable Farms to AI-Powered Agribusiness:
IMARC’s Guide to Unlocking the Australian agricultural market. IMARC Group empowers farmers, investors, and policymakers to navigate the Australia agribusiness landscape as artificial intelligence, digital transformation, and sustainability reshape the industry. Our expertise enables stakeholders to harness AI for precision farming, transparent supply chains, and eco-friendly innovations driving resilience, competitiveness, and long-term growth.
- Market Insights: Explore emerging AI-driven trends in the Australia agritech market, Agricultural biologicals market, and Agricultural equipment market. IMARC tracks adoption patterns, predictive analytics, and green farming practices shaping Australia’s agribusiness outlook for 2025 and beyond.
- Strategic Forecasting: Anticipate market growth, assess the Australia agribusiness market size through 2033, and identify opportunities across exports, technological adoption, and consumer preferences.
- Competitive Intelligence: Track leading agribusiness companies, startups, and global entrants pioneering AI in sustainable farming.
- Policy & Regulatory Analysis: Decode Australia’s sustainability mandates, biosecurity frameworks, and digital agriculture strategies driving the sector.
- Tailored Consulting: Deliver customized strategies to scale AI adoption, optimize production cycles, and unlock untapped potential in the Australian agribusiness industry.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










