Australia's Textile Recycling Industry: The Role of AI in Building a Sustainable Future

AI's Revolutionary Impact: Why Textile Recycling Matters in Australia?
Australia's textile recycling sector is experiencing a technological renaissance, with 40% of SMEs currently adopting artificial intelligence (AI), marking a 5% increase compared to the previous quarter (July-Sept 2024). The percentage of businesses unaware of how to utilize AI has decreased by 2% to 21%. The integration of AI is fundamentally transforming how the nation handles its annual clothing waste, representing a paradigm shift from traditional recycling methods to sophisticated, data-driven solutions. Australian companies are leveraging machine learning (ML) algorithms to revolutionize sorting processes, with AI-powered sorting systems being utilized to efficiently sort textiles for recycling. This technology simplifies the recycling of old textiles into new goods, contributing to circular economic practices.
Smarter Solutions: How AI is Transforming Textile Recycling
In Australia, where textile waste is a pressing issue, AI is being integrated across the recycling chain to improve efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. The most groundbreaking application comes from Samsara Eco, which has developed a proprietary AI-powered platform in 2025 to develop its "library of plastic-eating enzymes". Their commercial-scale facility in Jerrabomberra utilizes a unique recycling method to retrieve nylon, polyester, and PET polymers from discarded textiles and plastics, subsequently employing enzymes to decompose them into AA, HMD, TPA, and MEG monomers. The monomers are subsequently purified and isolated from colorants and dyes prior to being delivered to polymerization partners, who transform them into nylon 6,6 and polyester.
Apart from this, the benefits of AI extend far beyond speed and accuracy. By optimizing processes, recycling facilities lower costs in the Australia textile and apparel market, reduce energy consumption, and increase recovery rates. Moreover, AI-driven solutions encourage transparency, allowing businesses and consumers to track the lifecycle of recycled products, a vital step in building trust in sustainable practices.
Market Leaders Driving Australia's Textile Recycling Renaissance:
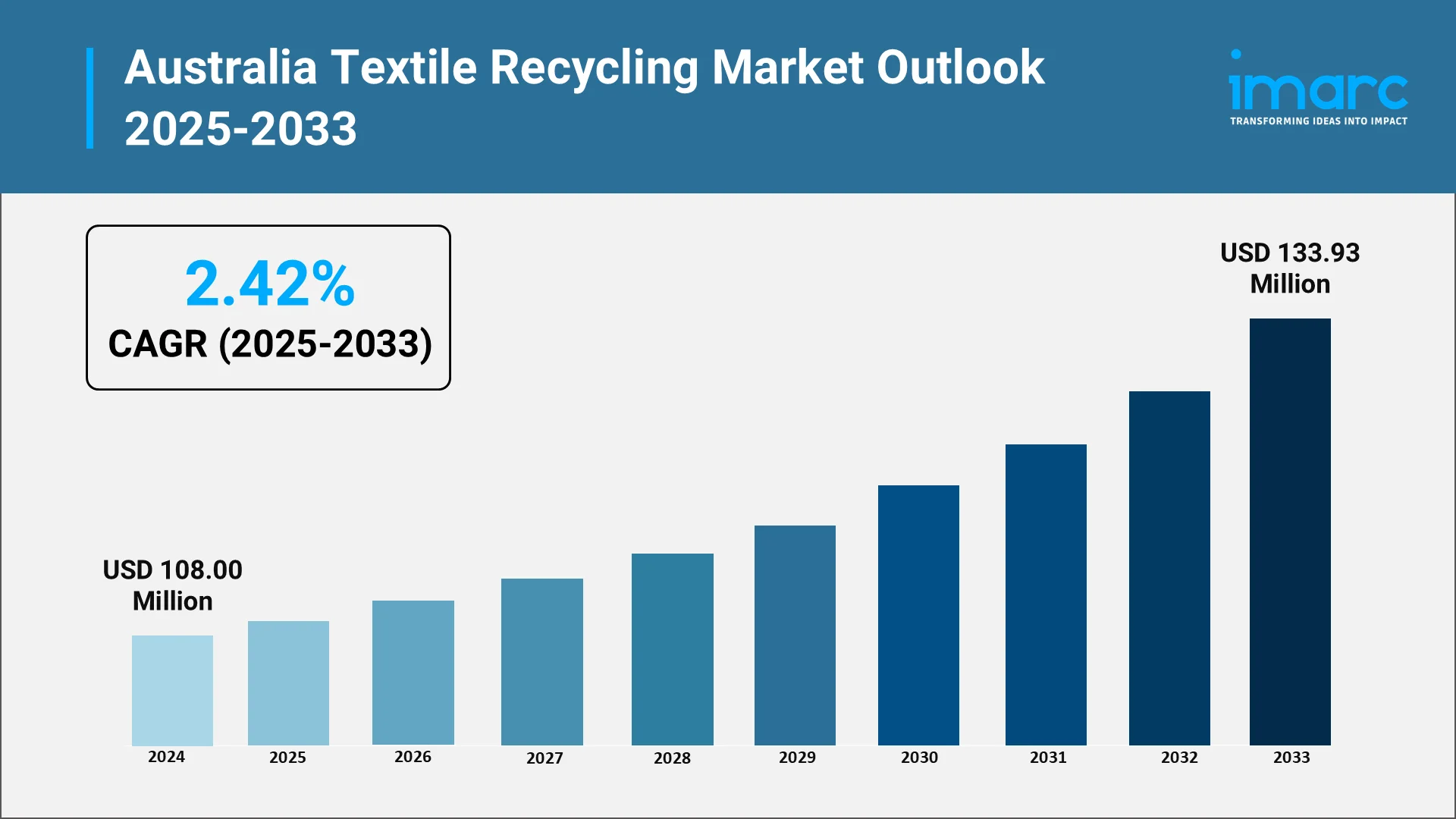
Australia's textile recycling landscape showcases a dynamic ecosystem of innovative companies leading the charge toward circularity. The IMARC Group predicts that the Australia textile recycling market size is projected to attain USD 133.93 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 2.42% during 2025-2033.
Samsara Eco dominated the innovation frontier, having raised $65 million in a fresh funding round, in 2024 with key investors including Lululemon and Hitachi Ventures. The funds were utilized by the company to enhance its enzymatic recycling capabilities, with plans to establish new commercial facilities in Southeast Asia in the upcoming years.
Citizen Wolf, based in Sydney, showcases a different innovative strategy with their zero waste, circular model where they produce only what they sell and repurpose their used garments into new fabric. They have created imaging technology enabling consumers to buy custom-fit apparel through basic online measurements.
Textile Recyclers Australia stands as one of the best textile recycling companies in Australia, dedicated to keeping textiles out of landfills and promoting circular solutions for textile waste. The company significantly reduces environmental impact by diverting materials from waste streams.
BlockTexx plays a crucial role in South Australia's recycling initiatives. In May 2025, BlockTexx® has committed to supporting Seamless, Australia’s clothing stewardship initiative aimed at promoting sustainability and circularity within the Australian apparel sector. As a stewardship program, Seamless acknowledges that brands producing or importing clothing are accountable for their complete lifecycle. The program is financed by a payment made by the clothing brands and retailers that are members of Seamless.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
Policy Powerhouse: Government Support Fueling Industry Growth
Australia's regulatory framework demonstrates unprecedented commitment to textile recycling through comprehensive policy initiatives. The 2024 National Waste Policy Action Plan sets out where Australia must focus its efforts to transition to a safe circular economy, establishing ambitious targets including 80% average resource recovery rate from all waste streams by 2030 and reducing total waste generated by 10% per person by 2030. The government's strategic focus involves a national target of plastic waste recycling by 2025 and an 80% average recovery rate from all solid waste streams by 2030 through adopting advanced recycling technologies. This policy framework directly benefits textile recycling, as synthetic fibers represent a significant portion of Australia's textile waste stream.
The "Seamless" Initiative represents a groundbreaking policy development. Australia's first National Clothing Product Stewardship Scheme came into operation in July 2024, developed by the Australian Fashion Council. This scheme places a 4 cent levy on all clothing (made locally or imported) put onto the market in Australia. The funding drives change across infrastructure, collection systems, and education campaigns.
State-level innovation showcases collaborative approaches. South Australia's Green Industries SA hosted a Circular Textiles Roundtable in May 2024 to convene interested parties actively working on various aspects of a circular textile economy. They've implemented practical programs like the "Set your clothes free" event scheduled for May 2025, partnering with local councils and charities.
Industry collaboration mechanisms include the Australian Fashion Council working with Charitable Recycling Australia, Queensland University of Technology, Sustainable Resource Use and WRAP to optimize the stewardship scheme.
The policy environment creates a compliance-driven market for Australia textile chemicals market, where companies must adapt to new requirements while benefiting from government support for innovation and infrastructure development.
Innovation Frontline: Latest Breakthroughs and Market Developments
- AI-Driven Sorting Technologies: One of the most enduring challenges to textile recycling is correctly identifying and sorting out material. Conventional systems rely almost exclusively on human labor, which is slow and error-prone. Recent developments in AI-enabled computer vision are responding. Scientists and entrepreneurs are now using AI systems that can scan fabrics at high speed, identify minute variations in fiber content, texture, and even microscopic structure. This implies polyester, cotton, and blended fabrics can be identified real-time with much higher precision. For recyclers, this technology enhances the recovery yield and makes recycled fibers of higher quality. Furthermore, machine learning software is being trained on huge collections of textile images, allowing it to improve continuously. The longer the systems run, the more accurate they become, thus cutting down on waste and improving efficiency up and down the recycling chain. Moreover, AI is employed in dye selection to produce the perfect shade of fabric from recycled bits, thereby supporting the Australia textile dyes market.
- Chemical Recycling Breakthroughs: Mechanical recycling, where fabrics are torn into strips and reused, has its limitations, mainly working with mixed materials. Enter chemical recycling, an area of keen research that is now delivering promising results. Researchers are creating methods that disassemble intricate textile mixtures into their constituent foundation elements without degrading fiber quality. For instance, polyester-cotton fabrics can be disbanded into pure cellulose and polyester, which can subsequently be recycled to create fabrics that are virtually unrecognizable from virgin fibers. Recent advancements include greener solvents and lower-energy chemical reactions, making these processes more sustainable and scalable. Although not yet ubiquitous in Australia, global advances are shaping local research and investment.
- Circular Economy Innovations: In addition to recycling techniques, recent study is centered on weaving textiles into a circular economy framework, thereby supporting the Australia textile waste management market growth. This involves creating garments that can be more readily recycled, for example, mono-material clothing or fabrics with digital labels that tell recyclers what they are made of. Australian and international startups are testing smart labeling systems based on AI and blockchain technology. The labels enable apparel to be traced from production to disposal, promoting transparency and supporting closed-loop recycling systems. These innovations have the potential to revolutionize fashion supply chains and drive waste reduction and responsible consumption.
- Market-Driven Breakthroughs: Increasing consumer demand for sustainable fashion is also driving innovation. Large fashion brands are collaborating with scientists to integrate recycled materials into their collections, establishing a direct market for these products. This commercial push encourages ongoing advancements in textile recycling, as firms look to pursue sustainability aspirations while remaining profitable. In Australia, businesses such as BlockTexx and Upparel are already trialing new recycling technologies with the backing of universities and research centers. Their success demonstrates how local industry can draw on global research while adapting solutions to Australia's specific challenges.
The Road Ahead: Navigating Challenges and Grasping Opportunities
Australia's textile recycling industry stands at a critical inflection point, with significant opportunities balanced against complex challenges. The sector's future trajectory depends on successfully navigating these dynamics while capitalizing on emerging market trends.
- Market Growth Projections: Multiple forecasts confirm robust expansion, with the Australian market anticipated to grow owing to the heightened focus on sustainability among companies. This growth is also driven by increasing government initiatives for waste reduction and the Australian Fashion Council's focus on improving textile recycling systems.
- Critical Challenges: The sector is experiencing a large number of ongoing challenges. Some of the complex issues are the diversified nature of textile wastes, which has a very high cost of advanced recycling technologies, and improved collection and sorting systems. The prevalence of synthetic, petroleum-based fibers is especially challenging, with much Australian clothing containing polyester and other man-made fibers.
- Technological Solutions: New recycling technologies provide avenues to exceed conventional constraints. Chemical recycling implies breakdown at a molecular scale through the use of chemicals to recycle and reuse complex fibers such as polyester and nylon that are mechanically less recyclable. This ability to recycle more types of textiles and obtain better purity in used fibers gives chemical recycling room for dramatic market growth.
- Infrastructure Development Opportunities: The government's promise to recover resources by 2030 provides enormous infrastructure investment requirements. Australia is utilizing available resources to the maximum through research and development investments, industry partnerships, and integrated waste management approaches.
- Fast Fashion Effect: The difficulty of 'fast fashion' trend propels spectacular expansion in textile waste levels, with enormous quantities of cheap, poorly constructed clothing rapidly produced and released repeatedly onto the market. But this is what provides a continuous supply feedstock for recycling activities.
- Competitive Landscape Evolution: Australia textile recycling industry is growing with rising environmental regulations, circular economy goals, and corporate sustainability commitments.
- Strategic Success Factors: Companies succeeding in this environment demonstrate several key characteristics: technological innovation capability, strong partnership ecosystems, regulatory compliance readiness, and scalable business models that can handle diverse textile waste streams.
- Investment Climate: Australia’s textile recycling investment climate is flourishing, driven by sustainability targets, government grants, and private equity interest. Investors favor advanced recycling technologies, circular business models, and partnerships with fashion brands to reduce landfill waste and capture value from post-consumer textiles.
The Role of AI in Advancing Sustainability within Australia’s Textile Recycling Industry:
IMARC Group assists Australia's textile recycling stakeholders in adopting AI to fuel sustainability, efficiency, and innovation. We provide the know-how to help clients adopt intelligent systems of waste reduction, material recovery, and circular value creation through:
- Market Insights: We analyze how AI is revolutionizing textile recycling via automated sorting, fiber identification, and data-driven recovery processes. Our understanding reveals future applications maximized for resource utilization and operational performance.
- Strategic Forecasting: Our forecasting capabilities chart the future of AI usage, highlighting emerging advancements in predictive maintenance, material flow optimization, and intelligent logistics in circular supply chains and zero-waste initiatives.
- Competitive Intelligence: We monitor AI-powered innovations, front-runners among recyclers, and technology suppliers. Trends in robotics, computer vision, and smart monitoring technologies reshaping competitiveness in the textile recycling industry in Australia are included in our analysis.
- Policy and Regulatory Analysis: We evaluate how AI integration fits into Australia's sustainability models and recycling requirements. Our advice ensures adherence to Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) and national circular economy goals.
- Customized Consulting Solutions: From using AI-powered material monitoring to expanding smart recycling infrastructure, our customized solutions enable organizations to amplify transparency, boost efficiency, and drive environmental stewardship.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










