Emerging Opportunities in the Japan Lead Acid Battery Industry
_11zon.webp)
Introduction to Japan's Lead Acid Battery Market:
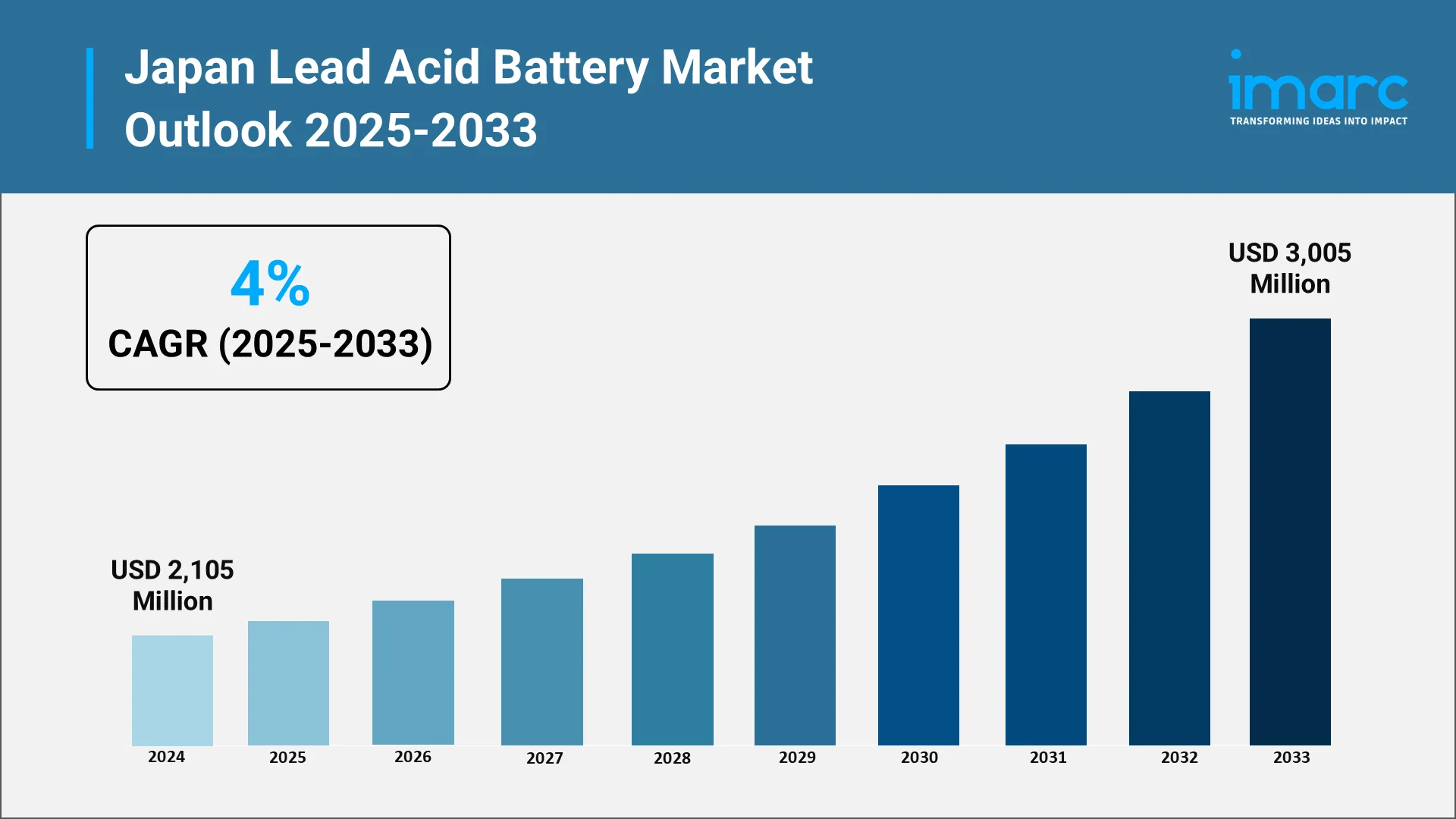
Japan's lead acid battery market stands as a cornerstone of the nation's energy storage infrastructure, demonstrating remarkable resilience and adaptability in an era dominated by rapid technological evolution. Despite the global shift toward lithium-ion technologies, the Japanese lead acid battery sector continues to thrive, driven by its unmatched cost-effectiveness, proven reliability, and exceptional recyclability. The market, valued at approximately USD 2,105 Million in 2024, is projected to reach USD 3,005 Million by 2033, expanding at a compound annual growth rate of 4% during the forecast period (2025-2033).
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
This consistent growth pattern mirrors Japan's strategic acknowledgment of lead acid batteries as crucial elements in many industries. Being one of the world's top vehicle manufacturing countries with global giants Toyota, Honda, Nissan, and Mazda calling the country home, Japan has a strong demand for starting, lighting, and ignition (SLI) batteries powering millions of cars. The country's sophisticated industrial base, combined with its focus on energy security and reliability, also supports the essential position of lead acid batteries in telecommunications, uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, and reserve power uses.
Rising Demand from Automotive and Industrial Applications:
The automotive sector remains the primary demand driver for Japan lead acid battery market, accounting for significant share of total battery applications in 2024. The automotive lead acid battery market specifically is experiencing remarkable growth, with projections indicating expansion from USD 13.6 Billion in 2024 to USD 16.4 Billion by 2033, representing a robust CAGR of 2.11% during 2025-2033.
This automotive demand is concentrated across several key regions within Japan. The Kanto region, encompassing Tokyo and surrounding areas, holds the largest market share due to its dense vehicle population and well-developed service networks. The Kansai region, including major cities like Osaka, Kyoto, and Kobe, contributes significantly to the national market, driven by significant commercial vehicle fleets and strong aftermarket ecosystems
Modern vehicles increasingly incorporate start-stop systems designed to improve fuel efficiency by automatically shutting off engines during idle periods. These systems place significantly higher demands on batteries, requiring frequent cycling and superior charge acceptance capabilities. Enhanced Flooded Batteries (EFB) and Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) batteries have emerged as preferred solutions for these applications, offering performance characteristics specifically engineered to withstand the rigorous demands of start-stop technology while maintaining competitive pricing compared to lithium-ion alternatives.
Outside of automotive use, industrial applications drive immense demand for lead acid batteries. Warehousing and material handling activities utilize lead acid batteries heavily to operate forklifts and automated guided vehicles (AGVs), where cost savings and infrastructure investment turn them into the choice solution. The telecommunications industry continues to have essential reliance on lead acid backup battery systems to provide network stability and continuity. Data centers, banks, hospitals, and other mission-critical sites use lead acid batteries in UPS systems, delivering vital power protection against failures and voltage variations.
Role of Renewable Energy and Backup Power Solutions:
Japan's ambitious renewable energy targets are creating new opportunities for lead acid batteries in energy storage applications. The government's 6th Strategic Energy Plan, adopted in 2021, elevated renewable energy targets from 22-24% to 36-38% of electricity generation by 2030, with longer-term goals targeting 40-50% renewables by 2040 and carbon neutrality by 2050. These aggressive targets are anchored in the nation's Green Transformation (GX) strategy, which emphasizes the critical role of energy storage in achieving environmental sustainability while maintaining grid stability and energy security.
The intermittent nature of renewable energy sources—particularly solar power, which has experienced the most significant growth in Japan's renewable sector—necessitates robust energy storage solutions. During peak solar generation periods, excess electricity must be captured and stored for use during evening hours and periods of low generation. Lead acid batteries, with their proven track record in stationary applications and established recycling infrastructure, are well-positioned to address portions of this storage demand, particularly in distributed energy resources and smaller-scale installations.
Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) introduced the "Storage Battery Industry Strategy" in August 2022, outlining three transformative roles for batteries: driving carbon neutrality through electrification, powering renewable energy integration through large-capacity storage, and backing up critical infrastructure including 5G communication networks and data centers. This strategic framework recognizes energy storage as fundamental to Japan's energy transition, with policy measures including substantial subsidy schemes offering up to 30% capital expenditure support for large-scale battery energy storage systems (BESS) through national programs, and up to 50% support through Tokyo Metropolitan Government initiatives.
The Feed-in Premium (FiP) scheme, introduced in 2022, adds market-linked premiums to renewable electricity prices while allowing co-located storage systems, providing developers flexibility to shift output without affecting base pricing. These policy instruments aim to embed energy storage deeply within Japan's energy architecture, creating market conditions favorable for lead acid battery deployment in applications where their cost advantages and reliability prove most valuable.
Uninterruptible power supply system represents another critical application domain for lead acid batteries in Japan. The market for UPS applications, valued at USD 8.51 Billion in 2024, is projected to reach USD 12.74 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 4.35% during 2025-2033. These systems provide essential backup power to critical facilities including hospitals, data centers, telecommunications infrastructure, and financial institutions. The reliability, cost-effectiveness, and established performance characteristics of lead acid batteries make them particularly suitable for UPS applications where instantaneous power availability and long-term durability are paramount requirements.
Japan's vulnerability to natural disasters—including earthquakes, typhoons, and tsunamis—further amplifies the importance of reliable backup power solutions. Lead acid batteries play crucial roles in emergency power systems, ensuring continuity of critical services during infrastructure disruptions and supporting disaster response capabilities.
Government Regulations and Recycling Initiatives:
Battery collection, recycling, and disposal are all governed by a thorough regulatory framework in Japan, which places special focus on resource conservation and the control of hazardous substances. In order to manage dangerous compounds like lead and cadmium and to promote resource efficiency, the Act on the Promotion of Effective Utilization of Resources, which went into effect in 2001, requires relevant manufacturers to collect and recycle tiny rechargeable batteries.
Lead acid batteries benefit from one of the most successful recycling infrastructures globally, with recycling rates consistently exceeding 95% in developed markets including Japan. This exceptional recyclability provides significant environmental advantages, enabling recovery and reuse of approximately 97% of a lead acid battery's component, including lead and sulfuric acid. The closed-loop recycling system for lead acid batteries represents a mature circular economy model, with recycled lead providing approximately 60% of global lead usage, with roughly 80% utilized in battery manufacturing.
Japan's battery collection system operates through multiple channels. Municipalities collect dry batteries through dedicated collection boxes at public institutions or as non-combustible waste, typically processing them in non-ferrous metal smelters with focus on mercury and other metal recovery. The Japan Portable Rechargeable Battery Recycling Center (JBRC), a branch organization of the Battery Association of Japan (BAJ), handles collection and recycling of small rechargeable batteries including certain lead acid batteries used in portable applications.
In Japan, specific guidelines for the handling, storage, and disposal of lead and sulfuric acid components are enforced by environmental rules. Smaller businesses may find these regulations onerous, while larger firms have made significant investments in recycling and sustainable production methods. With the introduction of extensive permission requirements and compliance obligations, the regulatory environment places a strong emphasis on safety issues, especially with regard to fire prevention and hazardous material management.
Lead acid batteries' high degree of recyclable nature makes them a great fit for Japan's circular economy programs and worldwide environmental goals. The importance of this environmental benefit is growing as governments and businesses place more emphasis on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals. The proven capacity of lead acid batteries to function in closed-loop systems, along with their affordability and dependability, puts them in a favorable position in markets where economic viability and environmental responsibility must coexist.
Technological Advancements Enhancing Battery Performance
The lead-acid battery market is continually evolving through sophisticated innovations that boost performance, durability, and efficiency, maintaining its competitiveness against alternative technologies.
Key advancements include:
- Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM): This technology uses a glass mat separator to hold the electrolyte, making batteries spill-proof with high charge acceptance and superior cycle life. They are now the standard for modern Start-Stop vehicles.
- AGM2 (Next-Gen AGM): This incorporates Thin Plate Pure Lead (TPPL) technology (using 99% pure, ultra-thin plates) and advanced chemistry, delivering up to twice the power and three times the lifespan of conventional AGM batteries by significantly increasing plate surface area.
- Enhanced Flooded Batteries (EFB): Offering a cost-effective intermediate option, EFB features increased paste density, nonwoven scrim materials, and carbon additives to minimize sulfation and improve cycle life, making them ideal for mass-market microhybrid applications.
Further innovations involve advanced material science and smart technology. Improved grid alloys and electrode designs, including calcium and carbon additives, enhance conductivity and extend cycle life. Crucially, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology enables real-time diagnostics, adaptive charging, and predictive maintenance, enhancing overall reliability and extending service life. Manufacturers like GS Yuasa are at the forefront, evidenced by their SLR-1000 Nano-Carbon Lead Acid battery, engineered for deep cycle applications to deliver an unprecedented 5,000 cycles at 70% depth of discharge.
Future Opportunities and Market Outlook to 2033:
The Japan lead-acid battery market is projected for steady growth through 2033, underpinned by several significant opportunities. A major driving force is the focus on the Circular Economy, with the overall battery recycling market (which includes lead-acid components) expected to reach USD 3,005 billion by 2033, representing a 4% CAGR from 2025. Consistent revenue streams are guaranteed by the Automotive Aftermarket, as Japan's large and aging vehicle fleet (over 78 million) ensures robust replacement demand, particularly in cold climate regions. Furthermore, the industrial segment offers expansion potential as manufacturing and logistics modernize, increasing the need for cost-effective, reliable power for AGVs and robotic systems.
Beyond traditional sectors, new opportunities arise from infrastructure modernization. The rollout of 5G networks and other telecommunications infrastructure requires extensive, dependable, and cost-effective backup power, a role perfectly suited to lead-acid batteries. Similarly, while lithium-ion batteries dominate large-scale grid projects, lead-acid technology remains competitive in distributed energy resources and smaller commercial/residential backup systems within the renewable energy sector due to its lower capital cost and established recycling network. Finally, Japanese manufacturers can leverage their reputation for quality to pursue export opportunities across growing Asian markets.
However, the market's growth will be constrained by significant challenges. The most prominent is the intense competition from lithium-ion batteries, which continues to erode market share, especially in the rapidly expanding Electric and Hybrid Vehicle segments. Manufacturers also face threats from price volatility in raw materials, particularly lead, which can squeeze profitability, and increasing regulatory pressures concerning environmental protection and lead content. Despite these headwinds, the lead-acid market's inherent strengths—its technological maturity, proven reliability, cost-effectiveness, and near-perfect recyclability—ensure its sustained relevance across multiple application domains, rewarding a strategic focus on innovation and sustainability.
Choose IMARC Group: Your Strategic Partner in Lead Acid Battery Market Intelligence
Unlock Comprehensive Market Insights with Unmatched Expertise
- Data-Driven Market Research: Deepen your understanding of the Japan lead acid battery market through comprehensive research reports covering market size projections, demand dynamics across automotive and industrial sectors, technological innovations in AGM, EFB, and TPPL batteries, competitive landscape analysis, and regional market segmentation across Kanto, Kansai, Chubu, and Kyushu regions.
- Strategic Growth Forecasting: Anticipate emerging trends in lead acid battery applications, from advanced start-stop automotive systems and renewable energy integration to telecommunications infrastructure and industrial automation. Access detailed projections for market evolution through 2033, identifying high-growth segments and emerging opportunities before your competitors.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Analyze competitive dynamics within the Japan lead acid battery market, review product portfolios and technological capabilities of major players including GS Yuasa, Panasonic, and global manufacturers, monitor breakthrough innovations in battery chemistry and manufacturing processes, and understand pricing strategies and market positioning across different segments.
- Policy and Infrastructure Advisory: Stay informed about regulatory frameworks governing battery recycling, environmental compliance, and hazardous material management. Track government subsidy programs supporting energy storage deployment, monitor changes in automotive regulations affecting battery specifications, and understand how Green Transformation (GX) policies impact market opportunities.
- Custom Reports and Consulting: Receive tailored insights aligned with your specific organizational objectives—whether you're launching new battery products, investing in manufacturing capacity expansion, evaluating market entry strategies, or seeking partnership opportunities with Japanese manufacturers and distributors.
At IMARC Group, our mission is to empower industry leaders with the clarity and intelligence required to navigate the evolving lead acid battery landscape. Join us in driving sustainable energy storage solutions—because reliable power matters for business continuity, economic growth, and environmental stewardship. To check full report, click: https://www.imarcgroup.com/japan-lead-acid-battery-market
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










