Hemp Processing Cost Analysis: Costs, Conversion & Profitability

What is Hemp?
Hemp is a versatile, fast-growing variety of the Cannabis sativa plant, which is cultivated for industrial and nutritional purposes. Compared to the psychoactive cannabis strains, hemp contains very low levels of tetrahydrocannabinol, therefore making it non-intoxicating and legally distinct in many regions. The plant is valued for its strong fiber, nutrient-rich seeds, and cellulose-rich stalk, which can be processed into textiles, bioplastics, building materials, food ingredients, cosmetics, and wellness products. Hemp grows with minimal pesticides, improves soil quality, and captures significant carbon, making it an environmentally sustainable agricultural crop with wide industrial relevance.
Key Applications Across Industries:
The versatility of seeds, stalks, fibers, and flowers makes hemp one of the most multifunctional crops, with uses across diverse industries. In the textile industry, hemp fibers are spun into yarn for making clothes, shoes, ropes, and industrial fabrics and are known for their durability, breathability, and mold resistance. The fibers also support automotive and aeronautical industries in the manufacture of lightweight interior parts, insulation panels, and biocomposite parts using hemp-based composites.
In the construction industry, hemp hurds are combined with lime to form "hempcrete," a lightweight, insulating, and fire-resistant alternative to traditional building materials. Acoustic panels, insulation mats, and fiberboard are other manufactured products made from hemp fibers. Its other major use is in the manufacture of paper, for which hemp provides higher cellulose content and quicker renewability than wood.
The notable food and nutraceutical applications of hemp seeds and oil are because of their rich contents of proteins, essential fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals. These are being value-added into protein powders, snacks, cold-pressed oils, and functional foods. Hemp oil in cosmetics finds applications in lotions, soaps, serums, and balms, mainly for its moisturizing and anti-inflammatory action. Besides, hemp flowers are processed to extract the non-psychoactive cannabinoids such as CBD, which are finding wide applications in wellness supplements, topicals, and therapeutic formulations.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global industrial hemp market reached a value of USD 6.2 Billion in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 20.9 Billion by 2033, at a projected CAGR of 14.5% during 2025-2033. The global hemp market is growing at a great pace, driven by some critical factors: regulatory changes, sustainability priorities, technological innovations, and increasing consumer demand for natural and eco-friendly products. Among the primary drivers are legalization and deregulation with respect to industrial hemp cultivation in many countries, unlocking large-scale commercial opportunities in agriculture, textiles, construction, food, and wellness sectors. These recent changes in regulations have motivated farmers to diversify into hemp cultivation and industries to research hemp as a renewable alternative to synthetic or resource-intensive materials.
Another major driver is the increasing emphasis on sustainable and carbon-neutral manufacturing. Hemp has a low environmental footprint in that it requires fewer chemical inputs, regenerates the soil, naturally suppresses weeds, and absorbs considerable carbon during its growth. Hemp fibers, biocomposites, and hempcrete see extensive adoption in product development within industries looking to reduce reliance on plastics, wood, and fossil fuel-based materials. This goes in line with global trends in green building, circular economy transitions, and environmentally responsible packaging. Consumer interest in plant-based and functional nutrition is also driving demand for hemp seeds, protein powders, oils, and CBD-based wellness products. Given the nutritional profile of hemp and perceived health benefits, its application in food, beverages, and supplements has been widening. Besides, cosmetics and personal care industries are embracing hemp-derived ingredients, with increased demand for natural, chemical-free formulations. The technological advancements made in fiber decortication, extraction, biopolymer blending, and automated processing have been helping to reduce the production cost and improve the quality of the product, allowing hemp to compete with conventional materials. In addition, global investment in hemp research, supply-chain development, and industrial-scale processing is improving the commercialization landscape. All these factors position hemp as a high-potential crop that drives innovation across different industries in the emerging bioeconomy.
Case Study on Cost Model of Hemp Processing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale hemp processing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed hemp processing plant in India. This plant is designed to process 1,500 tons of hemp annually.
Processing Flow: Processing of hemp consists of a succession of agricultural, mechanical, and industrial steps in order to separate and commercially utilize the main components of the plant: fiber, hurd, seeds, and flowers. These different parts correspond to different markets. It starts with the harvesting, when plants reach optimal maturity for either fiber or seed production. In the case of fiber-type hemp cultivation, it is cut near the ground, left to lie in the field, and then subjected to a process called retting, a microbial or moisture-induced process that degrades the pectin binding the fibers to the woody core of the stalk. Retting can be field-based, water retting, chemical retting, or enzyme-assisted, depending on the intended quality of the final product. Subsequently, after retting, the stalks are dried and passed through a decortication machine, which mechanically separates long bast fibers from the inner woody hurds. The bast fibers are cleaned, carded, and aligned to be used for textile purposes, biocomposites, and industrial materials, while hurds are processed further into hempcrete, bedding, paper, and insulation. For value-added seed processing, hemp seeds are cleaned, dried, and dehulled after harvesting. Seeds can then undergo cold pressing to extract hemp oil; the remaining cake is ground into hemp protein powder. If hemp flowers are harvested, biomass is dried and subjected to extraction via CO2, ethanol, or a solventless method to separate cannabinoids for wellness and therapeutic uses, such as CBD. Quality control throughout this processing chain ensures standards related to moisture, purity, and cannabinoid composition are met or exceeded. In many cases, integrated processing operations combine these functions, maximizing the value that can be extracted from hemp to supply multiple industries with efficient, sustainable, and scalable processing chains.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
Raw Material Required:
The basic raw materials required for hemp processing include:
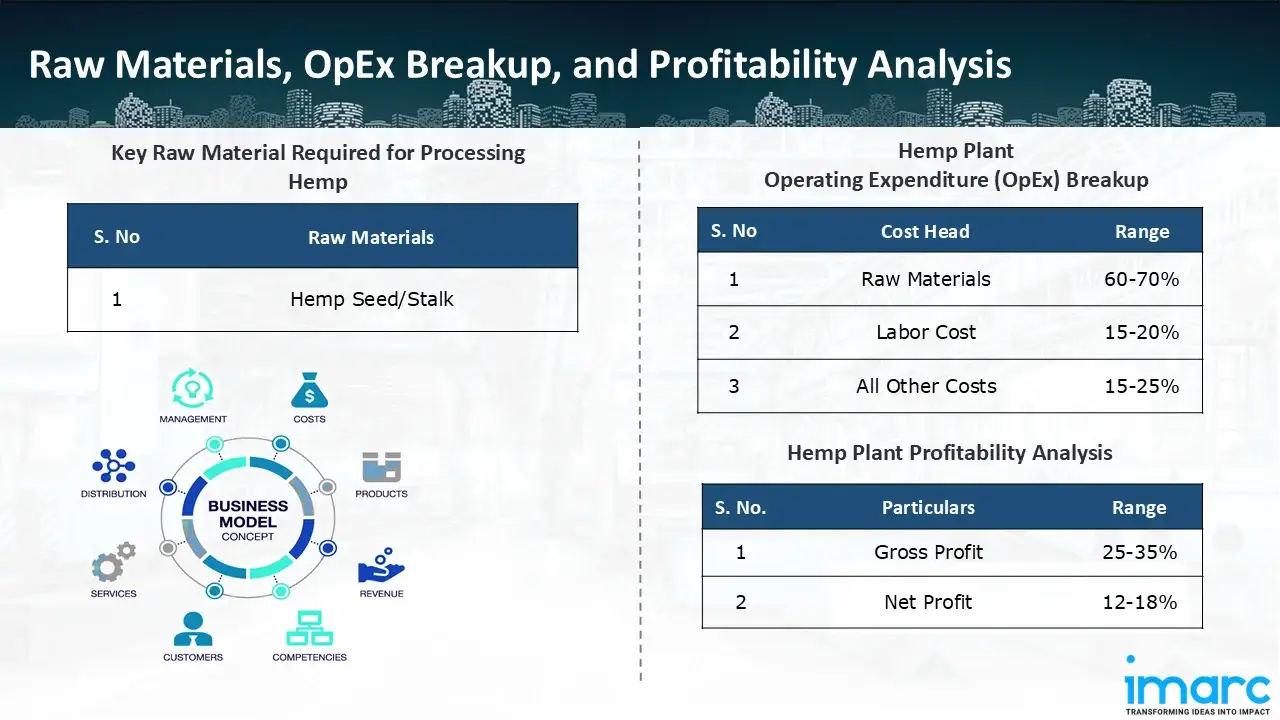
- Hemp Seed/Stalk
Machine Section or Lines Required:
- Decorticator
- Separator
- Oil Press
- Refining
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a processing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a Processing plant effectively. Opex in a processing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a processing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in hemp processing plant ranges between 60-70%, labor cost ranges between 15% to 20%, and all other costs ranges between 15-25% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 25-35%, and net profit lie between the range of 12-18% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the hemp processing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, processing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of processing 1,500 tons of hemp annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale processing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In November 2025, the relocation of Christchurch hemp maker and processor Rubisco to an Ashburton site is anticipated to open the door for a US$ 20–US$ 30 million expansion plan. The company has started raising cash in order to add more processing equipment and produce more wool and hemp into building, interior ornamental, biocomposites, clothing, textile, furnishing, geotextile, and other products.
- In May 2025, Minnesota’s Office of Cannabis Management is introducing a new registration period for businesses selling hemp-derived cannabinoid products, including beverages and gummies. Companies not registered to sell these products will face significant fines and penalties.
- In May 2025, Ukraine is entering the European hemp market with the opening of its largest industrial processing facility, with the goal of reviving a once-thriving industry and demonstrating resilience through innovation. The Ma'Ryzhany Hemp Company has started running what is currently the largest hemp processing facility in Ukraine, according to a statement from the Ministry of Economy.
Why Choose IMARC?
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104