How Smart Agriculture Market is Shaping the Global Agriculture Industry: Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities

The smart agriculture market is revolutionizing the global agriculture industry through the integration of cutting-edge technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, sensors, and big data analytics. As the world population continues to grow, farmers and agribusinesses face mounting pressure to increase productivity while minimizing environmental impact. Smart agricultural technologies offer transformative solutions to address these challenges by enhancing operational efficiency, optimizing resource utilization, and enabling data-driven decision-making across the entire crop cycle.
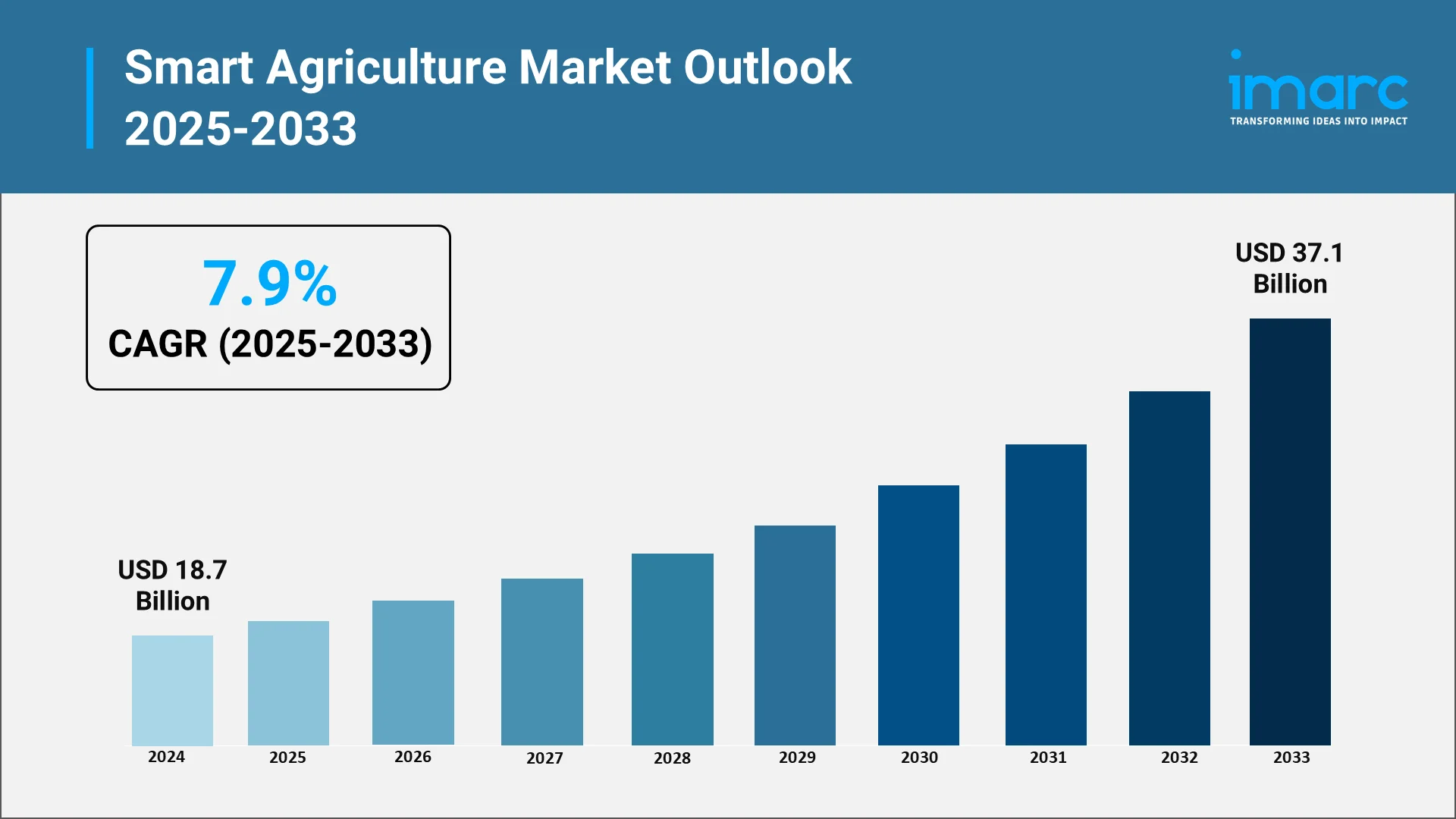
The global smart farming industry has witnessed remarkable growth in recent years. According to IMARC Group’s report, global smart agriculture market reached USD 18.7 Billion in 2024. It is projected to reach USD 37.1 Billion by 2033, demonstrating a growth rate of 7.9% during 2025-2033, thereby underscoring the accelerated adoption of smart agricultural technologies worldwide.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
How Smart Agriculture is Redefining Global Food Production:
Smart agriculture is reshaping traditional farming through intelligent, automated, and data-driven systems. It enables real-time monitoring of crop health, soil conditions, weather, and machinery, allowing timely decisions that improve productivity and efficiency.
- Resource Optimization and Sustainability:
Precision irrigation using soil sensors cuts water use by up to 30%, while variable fertilizer application reduces runoff and pollution by targeting inputs based on soil and crop data. These technologies lower costs and support sustainable farming practices.
- Enhanced Productivity and Yield Quality:
Data analytics and drone imaging detect pests, diseases, and nutrient issues early, preventing yield losses and maintaining quality. Automated machinery improves efficiency during planting and harvesting, maximizing output.
- Labor Efficiency and Cost Reduction:
Autonomous equipment and AI tools reduce manual work by up to 40%, allowing larger-scale management with fewer workers. Integrated platforms simplify data handling and streamline decision-making.
- Climate Resilience and Risk Management:
Real-time forecasts and predictive analytics strengthen adaptation to climate variability, helping farmers plan irrigation, harvests, and risk responses more effectively.
Global Momentum: Key Drivers Accelerating Smart Agriculture Adoption
Several interconnected factors are propelling the rapid expansion of the smart agriculture market, creating a favorable environment for technology adoption across diverse agricultural segments.
- Rising Global Food Demand: Feeding a growing population requires major productivity gains as farmland faces urban and environmental pressures. The FAO projects food production must rise 70% by 2050, making technology-driven efficiency crucial for food security.
- Integration of IoT and AI Technologies: Over 220 million acres are now connected through digital platforms using IoT sensors and AI analytics. Machine learning delivers real-time insights on planting, pest control, and harvest timing, enabling precision decisions once impossible.
- Government Support and Policy Initiatives: Governments worldwide are funding digital agriculture. India’s INR 2,817 crore Digital Agriculture Mission, the USDA’s $1.5 billion climate-smart initiative, and China’s plan to digitalize 32% of its farms by 2028 highlight strong policy backing.
- Climate Change Pressures: Rising weather risks have made resilience essential. Smart irrigation, forecasting tools, and soil sensors help farmers optimize resources and protect crops from unpredictable conditions.
- Economic Imperatives: High input and labor costs drive technology use, with precision systems often paying off within one to two years through lower waste and higher yields.
- Expansion of Autonomous Systems: Affordable robotics, from self-driving tractors to automated irrigation, now enable continuous, precise, and labor-efficient farming.
Regulatory Framework and Policy Landscape in the Smart Agriculture Industry:
The regulatory environment for smart agriculture encompasses data governance, environmental standards, technology safety protocols, and agricultural support mechanisms. Different regions have adopted varied approaches that reflect local priorities and agricultural contexts.
- European Union Common Agricultural Policy (CAP):
Implemented in 2023 under Regulation (EU) 2021/2115, the CAP promotes a smart, competitive, and climate-resilient agricultural sector. It sets Good Agricultural and Environmental Condition (GAEC) standards and offers financial incentives for sustainable practices. After 2024 farmer protests, Regulation (EU) 2024/1468 simplified compliance while preserving environmental goals. The CAP dedicates a large share of the EU budget to support technology adoption, training, and rural infrastructure.
- United States Regulatory Approach:
The USDA emphasizes voluntary, market-based participation backed by funding and technical aid. The Inflation Reduction Act allocated $19.5 billion for conservation, including $4.95 billion for climate-smart programs. The 2025 Technical Guidelines established voluntary standards for tracking greenhouse gas outcomes, enabling farmer participation in carbon markets.
- Data Governance and Privacy:
Regulators are defining data ownership, privacy, and cybersecurity standards for digital farming. Emerging policies ensure farmers control their operational data while allowing research and policy use.
- Product Safety and Environmental Standards:
New frameworks regulate autonomous farm equipment and promote precision applications of pesticides, fertilizers, and water. Technologies proven to lower environmental impact receive regulatory incentives and faster adoption pathways.
- Government Support and Initiatives for the Smart Agriculture Industry
Governments worldwide have implemented substantial programs to accelerate smart agriculture adoption, recognizing its importance for national food security, economic development, and environmental sustainability.
- India's Digital Agriculture Mission: Approved by the Union Cabinet on September 2, 2024, this comprehensive initiative represents one of the most ambitious national smart agriculture programs globally. The mission's three major Digital Public Infrastructure components include:
- AgriStack: A farmer-centric database creating digital identities for 11 crore farmers through Farmer IDs linked to land records and demographic information
- Krishi Decision Support System: Integration of remote sensing data on crops, soil, weather, and water resources into a comprehensive geospatial system supporting precision agriculture market
- Soil Profile Mapping: Detailed soil profile maps on a 1:10,000 scale for approximately 142 million hectares of agricultural land
The Digital General Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES) will provide precise yield estimates through scientifically designed crop-cutting experiments, improving agricultural production accuracy and supporting data-driven policy decisions.
- United States Federal Programs: The USDA has deployed multiple initiatives supporting smart agriculture adoption:
The Partnerships for Climate-Smart Commodities program initially invested $3.1 billion across 135 projects nationwide, though this was later restructured as the Advancing Markets for Producers initiative with revised criteria. The program focuses on creating market opportunities for climate-smart agricultural commodities while providing direct benefits to farmers.
The Regional Conservation Partnership Program (RCPP) received historic funding of $1.5 billion in fiscal year 2024, supporting partner-driven conservation and climate solutions. Priority areas include climate-smart agriculture, urban agriculture, conservation, and environmental justice initiatives.
The Conservation programs funded through the Inflation Reduction Act provide additional support, with $1.65 billion for the Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP), $472 million for the Conservation Stewardship Program (CSP), and funding for precision agriculture practices.
- Chinese National Strategy: China's Smart Agriculture Action Plan 2024-2028 aims to digitally integrate over 32% of agriculture by 2028, expanding from the previous 2019-2025 digitalization initiative. The plan emphasizes AI, robotics, and big data integration to enhance productivity, sustainability, and resource management. Substantial government investment supports infrastructure development, research institutions, and technology transfer mechanisms.
- Brazilian Agricultural Investment: Brazil's record funding for the 2024/25 Crop Plan allocated R$ 475.5 billion (approximately $88.2 billion), representing a 9% increase from the previous year. This substantial financial commitment supports agricultural modernization, technology adoption, and Brazil's position as a global agricultural leader.
- European Innovation Support: The European Commission allocates approximately €1.3 billion under Horizon Europe for sustainable agricultural research and development. Additionally, the CAP provides member states with flexibility to support precision agriculture investments through rural development programs and eco-schemes that incentivize adoption of environmentally beneficial technologies.
Industry Leaders Steering the Smart Farming Revolution:
The smart agriculture market features a competitive landscape dominated by established agricultural equipment manufacturers, technology companies, and emerging agtech startups. Leading players have invested billions in developing comprehensive precision agriculture ecosystems.
Deere & Company (John Deere): The global market leader commands approximately 15-18% market share through its comprehensive portfolio of autonomous tractors, precision planting equipment, and the John Deere Operations Center digital platform. In fiscal year 2024, the company reported net income of $7.1 billion on revenue of $51.7 billion. Despite market challenges, John Deere continues investing substantially in technology development. In January 2024, the company partnered with SpaceX to deliver Starlink satellite communications services, enabling farmers in rural areas with limited connectivity to fully leverage precision agriculture technologies. The company's S7 Series combines feature advanced automation packages addressing labor shortages and operational efficiency challenges.
AGCO Corporation: Beyond the PTx Trimble joint venture, AGCO maintains strong market presence through its portfolio of agricultural machinery brands including Fendt, Massey Ferguson, Challenger, Valtra, and Precision Planting. The company reported net sales of approximately $14.4 billion in 2023. AGCO's strategic focus on retrofit solutions enables precision agriculture capabilities across multiple equipment brands, expanding addressable market opportunities beyond proprietary machinery sales.
Trimble Inc.: While contributing its agriculture business to the PTx Trimble joint venture, Trimble retains a 15% ownership stake and continues supplying certain GNSS and guidance technologies. The company's broader portfolio in positioning, modeling, connectivity, and data analytics supports the joint venture's technological capabilities.
Other players operating in the industry include AG Leader Technology, AgJunction Inc. (Kubota Corporation), CLAAS KGaA mbH, CropMetrics LLC (CropX inc.), DICKEY-john, Farmers Edge Inc., Gamaya, Granular Inc. (Corteva Inc.), and Raven Industries Inc. (CNH Industrial N.V.).
Opportunities and Challenges: The Dual Path of Progress
The smart agriculture market offers major growth potential across the global value chain but also faces key implementation challenges.
Opportunities
- Addressing Labor Shortages Through Automation:
Global labor shortages caused by urbanization and aging rural populations are accelerating adoption of autonomous machinery, robotic systems, and AI-driven tools. These technologies help reduce manual work and sustain productivity in both advanced and emerging markets where rural migration is high.
- Sustainability and Environmental Stewardship:
Consumers and regulators are demanding sustainable farming practices. Precision agriculture technologies that optimize fertilizer, pesticide, and water use not only cut costs but also reduce environmental impact. Digital tools verifying sustainable practices allow farmers to access carbon credit markets and earn premiums for eco-friendly production.
- Market Expansion in Developing Regions:
North America leads the sector, but Asia Pacific offers the fastest growth, projected at around 16% CAGR from 2025–2030. Government-led initiatives in India, China, Indonesia, Vietnam, and Thailand are promoting digitalization and modern farming. Localized solutions for small farms, varied crops, and diverse infrastructure will drive regional expansion.
- Data-as-a-Service Models:
The data generated by sensors and connected equipment enables predictive analytics, benchmarking, and advisory services. Aggregated farm data supports R&D and allows input suppliers and buyers to improve offerings. Emerging monetization systems that reward farmers for shared data open new revenue opportunities.
- Integration with Food Supply Chains:
Consumers increasingly demand transparency. Blockchain-enabled and IoT-linked systems allow traceability, quality control, and sustainability verification, helping farmers gain market access and command higher prices.
- Climate Adaptation Solutions:
Climate variability is creating strong demand for adaptive technologies like weather-integrated crop modeling, irrigation management, and regional tools for drought and flood resilience. These help stabilize yields and ensure long-term food security.
Challenges
- High Initial Investment Costs:
Implementing full-scale smart farming systems can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars, making adoption difficult for small and medium farms. Despite favorable ROI, limited access to financing slows implementation.
- Digital Infrastructure Gaps:
Many rural regions lack reliable broadband, restricting real-time monitoring and automation. Bridging this gap requires major investment and collaboration between governments and telecom providers.
- Data Ownership and Privacy:
Farmers remain cautious about how companies use operational data. The absence of clear regulations on ownership and privacy limits participation. Establishing transparent frameworks will be crucial for trust and adoption.
- Complexity and Learning Curves:
Smart systems require technical know-how in analytics, GPS, and IT. Farmers need accessible training, intuitive interfaces, and dependable technical support to operate efficiently.
- Interoperability Issues:
Different equipment brands and software platforms often fail to integrate, causing inefficiencies. Open standards and interoperability protocols are essential to unlock full value from smart farming systems.
- Cybersecurity Threats:
Digitized agriculture faces growing risks of hacking and data breaches. The sector must adopt security protocols, authentication systems, and awareness programs to safeguard operations.
- Skills Gap and Education Needs:
A new generation of farmers must combine agronomy with data science and systems management. Updated curricula and certification programs will help bridge the skill divide.
- Environmental and Ethical Considerations:
Continuous machine operation can disturb ecosystems, and drone use raises privacy concerns. Ethical deployment of new technologies must align with both environmental protection and public acceptance.
Conclusion: Smart Agriculture as the Foundation of Future Food Systems
The Smart Agriculture Market is reshaping global food production through digital technologies, automation, and data-driven tools. Valued between $37–85 billion by 2033 with over 10% annual growth, it has moved from experimentation to mainstream use worldwide. Growth is fueled by rising food demand, labor shortages, climate challenges, and government programs. Companies like John Deere, AGCO, Trimble, and Bayer are building integrated precision ecosystems, supported by major initiatives such as India’s Digital Agriculture Mission and the USDA’s climate-smart programs.
Key barriers include high investment costs, limited rural connectivity, and data governance gaps. Collaborative efforts among technology providers, agribusinesses, governments, and farmers are essential. Accessible financing, clear regulations, training, and user-friendly solutions will drive adoption. Smart agriculture enables higher productivity, resource efficiency, and sustainability—transforming farming into a climate-resilient and innovation-led global food system.
Why Partner with IMARC Group:
- Data-Driven Market Intelligence: Gain actionable insights into Smart Agriculture Market trends, including Smart Agricultural Technologies, Precision Agriculture segmentation, and regional growth. Our research covers autonomous equipment, IoT sensors, AI analytics, and digital farming shaping the Global Smart Farming Industry.
- Strategic Growth Forecasting: Predict trends in agricultural technology with analytics on autonomous machinery, drone monitoring, irrigation, and data platforms. Explore regional forecasts on North America’s maturity, Asia Pacific’s growth, Europe’s regulations, and Latin America’s infrastructure.
- Competitive Intelligence and Benchmarking: Assess key Smart Agriculture players, product pipelines, partnerships, R&D, and strategies.
- Policy and Infrastructure Advisory: Understand regulations, data governance, subsidies, and public investments shaping smart agriculture policies worldwide.
- Custom Reports and Consulting Services: Access tailored insights for product launches, investments, and smart agriculture implementation.
IMARC Group empowers global agribusinesses and investors with the intelligence for sustainable growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










