Key Challenges and Opportunities Shaping the Diesel Engine Industry
The diesel engine industry is standing at a transformative crossroads. As global markets are pushing for sustainability, stricter emissions compliance, and cutting-edge innovations, diesel powertrains are facing both immense pressure and promising potential. This in-depth article explores the key forces reshaping the diesel engine landscape, analyzing the challenges, opportunities, and future direction of an industry that continues to power critical sectors around the globe.
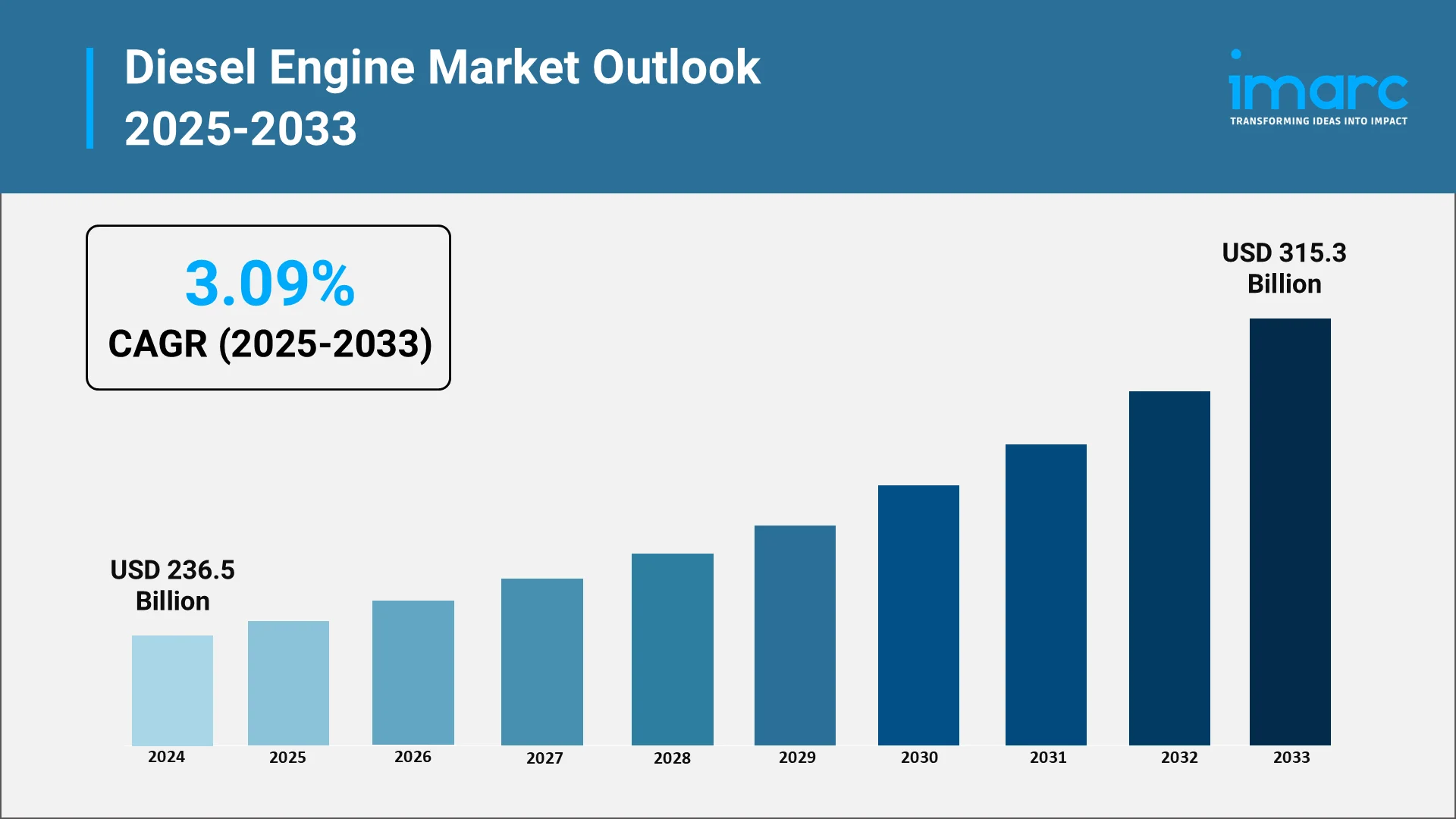
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
Driving Global Progress: Understanding Diesel’s Ongoing Role Across Industries
The diesel engine industry is continuing to play a crucial role in powering the world’s infrastructure. From transportation and construction to agriculture and power generation, diesel engines are maintaining their reputation for durability, fuel efficiency, and torque-rich performance.
Despite the surge in electric vehicle (EV) development, diesel technology is remaining deeply embedded in sectors where high power output, reliability, and longevity are essential. Heavy-duty trucks, freight trains, marine vessels, and off-highway equipment are still relying heavily on diesel engines due to their superior energy density and lower operational costs per unit of power. On April 20, 2024, the 2024 World Congress on Internal Combustion Engines began in Tianjin, China. It signifies a critical turning point for the sector. Weichai Power captured attention by revealing an unprecedented accomplishment. The world’s inaugural diesel engine featuring an inherent thermal efficiency of 53.09%.
Global demand is persisting in regions where infrastructure is still developing and where alternatives like electric charging stations are lacking. In various underdeveloped areas, diesel continues to be the backbone of logistics and transportation networks.
The significance of diesel engines is also reflecting in industrial applications. Mining operations, remote construction projects, and emergency power generators are depending on diesel’s self-sufficiency and efficiency in environments where grid-based solutions are unavailable or unreliable. In 2025, Cummins Inc., a worldwide frontrunner in power technology, revealed the successful launch of advanced low carbon fuel test cells, signifying a key milestone in its collaborative initiative with Vale and Komatsu to create a surface mining haul truck powered by ethanol/diesel, focused on lowering greenhouse gas emissions. This accomplishment highlights the firms’ joint dedication to reducing carbon emissions in the mining industry and promoting sustainable energy options.
However, this reliance is coexisting with mounting pressures for cleaner energy alternatives. Stakeholders, including original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), governments, and consumers, are increasingly expecting more sustainable solutions, which is reshaping how the diesel engine industry is operating and evolving.
Moreover, with climate targets becoming more aggressive, diesel engine manufacturers are now being expected to not only comply with environmental standards but also lead innovations in combustion efficiency and emissions reduction.
This continuing global reliance on diesel, juxtaposed with sustainability pressures, is creating a dual narrative: while some are predicting diesel’s slow fade-out, others are investing in its reinvention. The industry's next phase depends on how it is adapting to meet environmental, economic, and technological expectations while preserving the core advantages of diesel technology.
Facing the Heat: Diesel Engine that Are Redefining the Industry
The diesel engine industry is currently grappling with a host of challenges that are testing its adaptability and resilience. At the forefront are increasingly stringent emissions regulations. Governments across the globe are implementing tighter limits on nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. Compliance with regulations like Euro VI in Europe, EPA Tier 4 in the United States, and Bharat Stage VI in India is requiring manufacturers to invest significantly in advanced after-treatment systems, exhaust gas recirculation, and selective catalytic reduction technologies. In 2025, The western Indian state of Maharashtra has established a committee to examine a plan to prohibit petrol and diesel vehicles in Mumbai due to deteriorating air quality, permitting only electric or gas-powered vehicles, as stated in an order.
In parallel, the accelerating momentum of electric vehicles (EVs) is putting pressure on diesel engines in the automotive sector. EVs are emerging as cleaner, quieter, and increasingly affordable alternatives. Public transit systems in cities are shifting to battery electric or hydrogen fuel cell buses, while light-duty diesel passenger vehicles are facing reduced demand due to government incentives for electric mobility.
Public perception is also shifting. In many urban centers, diesel engines are being associated with pollution and health risks, creating consumer hesitancy. Several cities have announced future bans on diesel-powered vehicles, sending clear signals to manufacturers and buyers alike.
Additionally, global supply chain disruptions, especially those affecting semiconductor and emission-control component availability, are delaying production timelines and increasing costs across the board.
Fuel Prices and Efficiency Challenges Impacting Diesel Demand:
Fuel efficiency and fluctuating fuel prices are continuing to exert a profound impact on the diesel engine industry. As global crude oil markets remain volatile, diesel prices are swinging in ways that are affecting both consumers and industrial operators. These fluctuations are influencing purchasing decisions, operating costs, and total cost of ownership.
Operators are now prioritizing fuel economy more than ever. Higher fuel prices are compelling fleet owners to re-evaluate the cost-effectiveness of diesel engines. As a result, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) are under pressure to innovate and offer more fuel-efficient engine designs without compromising on power or reliability.
However, improving fuel efficiency is not a straightforward task. Engineering cleaner combustion, reducing friction losses, and optimizing injection timing are requiring precise calibration and sophisticated engineering tools. These improvements often come at a cost, potentially making newer diesel engines more expensive and less accessible for small-scale users.
The challenge becomes even more pronounced in regions where fuel subsidies are being reduced or phased out. Governments, aiming to promote cleaner energy adoption, are removing diesel subsidies, thereby making fuel prices less predictable and less economically attractive.
Despite these concerns, diesel engines are continuing to demonstrate strong performance in long-haul and heavy-load applications, where energy density and refueling speed still matter. For these users, fuel-efficient diesel engines remain indispensable, even as alternatives are growing in appeal.
Therefore, the future of diesel demand is being shaped not just by technology, but by broader economic and policy decisions related to fuel pricing, taxation, and infrastructure. The industry must continue navigating this dynamic pricing environment while innovating to maintain fuel economy leadership.
Reinventing Diesel: Unlocking Opportunities Through Cleaner and Smarter Technologies
While challenges are mounting, the diesel engine technology is simultaneously uncovering exciting opportunities driven by innovation. Engine manufacturers are investing in next-generation technologies that are making diesel engines cleaner, more efficient, and smarter than ever before.
One major area of opportunity is the development of advanced combustion systems. Techniques like Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) and advanced fuel injection systems are enabling more complete combustion with lower emissions. These innovations are allowing diesel engines to meet or exceed stringent emissions regulations without compromising on performance.
Additionally, integration of electronic control units (ECUs) and real-time monitoring systems is enabling smarter engine management. These digital systems are optimizing fuel delivery, air-fuel ratio, and after-treatment processes dynamically, resulting in better fuel economy and lower emissions.
Another promising avenue is the use of synthetic and bio-based fuels. Second-generation biodiesels and renewable diesel options are offering cleaner-burning alternatives that work within existing diesel infrastructure. These fuels are reducing lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions and providing a viable pathway for decarbonizing diesel-powered fleets.
Hybrid diesel-electric systems are also gaining momentum, particularly in applications like buses, construction equipment, and port machinery. These hybrid systems are reducing idling times, improving torque at low speeds, and enabling partial electrification without the range anxiety of full electric solutions. These engines are also coming with advanced thermal efficiency. For example, in 2024, During the 2024 World Congress on Internal Combustion Engines held in Tianjin, China, the company presented a heavy-duty diesel engine featuring a BTE of 53.09%. This accomplishment received formal acknowledgment from the German testing body TÜV SÜD and the China Automotive Technology & Research Center. Both organizations provided product testing reports and certificates to Weichai Power, verifying the company’s new world record regarding thermal efficiency in diesel engines.
Collectively, these diesel engine opportunities are proving that diesel engines still have room for innovation. By embracing cleaner combustion, hybrid integration, and intelligent controls, the diesel industry is redefining what’s possible and extending its relevance into the next era of mobility.
Merging Worlds: How Hybridization, Alternative Fuels, and Digitalization Are Reshaping Diesel Engines
Emerging trends are now merging the traditional strengths of diesel engines with the innovations of the digital and sustainable era. Hybridization, alternative fuels, and digitalization are not just enhancing diesel engines, they are transforming them.
Hybrid diesel systems are blending the high torque and fuel efficiency of diesel with the regenerative capabilities and quiet operation of electric motors. This synergy is particularly effective in stop-and-go urban applications and in vehicles that require power during idle or low-speed operations. By reducing fuel consumption and emissions during idling and low-load conditions, hybrid diesel solutions are offering a practical middle ground between full electrification and traditional combustion.
Simultaneously, the exploration of alternative fuels is gaining traction. Green ammonia, hydrogen-based fuels, and advanced biofuels are showing potential as drop-in or near drop-in solutions for existing diesel engines. OEMs are now experimenting with dual-fuel engines and flexible-fuel platforms that can operate efficiently across different fuel types, thereby reducing dependence on fossil-based diesel.
Digitalization is playing a key role in this transformation. Smart sensors, IoT connectivity, and AI-based analytics are providing real-time insights into engine performance, maintenance needs, and operational efficiency. These tools are not only enhancing reliability but are also enabling customized tuning for different driving conditions and usage patterns.
These converging trends are pushing the diesel engine beyond its mechanical roots and into the realm of intelligent, sustainable mobility solutions. The challenge now is scaling these technologies across markets and applications while maintaining cost-effectiveness and reliability.
Gazing Ahead: Where Growth, Sustainability, and Opportunity Meet
The future of the diesel engine industry is not about extinction—it’s about evolution. While regulatory and market pressures are real, opportunities for growth are continuing to emerge, especially in developing regions, aftermarket segments, and sustainability-focused innovations.
Developing markets in Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America are continuing to demand diesel-powered equipment for critical infrastructure projects. These regions are valuing diesel’s reliability, simplicity, and low operating costs, especially where electrification is not yet viable.
At the same time, the aftermarket industry is flourishing. There is growing demand for retrofitting older engines with emissions control technologies, upgrading components for better diesel engine fuel efficiency, and integrating digital solutions. This is opening new revenue streams for service providers and component manufacturers.
Sustainability is also creating opportunities. Companies adopting Science-Based Targets or pursuing ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) initiatives are looking for cleaner diesel solutions as transitional tools. Diesel engines running on renewable fuels or integrated into hybrid platforms are serving as interim solutions until full electrification becomes practical.
Industry collaborations are accelerating innovation. Joint ventures between engine manufacturers, tech firms, and fuel providers are helping to speed up development cycles and bring new technologies to market more quickly.
In conclusion, while the diesel engine industry is facing undeniable challenges, it is far from obsolete. It is transforming, adapting, and preparing to serve new roles in a rapidly changing energy ecosystem. The key lies in embracing change, investing in technology, and reimagining what diesel engines can be—not just for today, but for the sustainable future ahead.
Driving Progress: IMARC Group’s Insights into the Global Diesel Engine Industry
IMARC Group is delivering critical intelligence on the evolving diesel engine market, guiding stakeholders across automotive, industrial, agricultural, and marine sectors in adapting to tightening emission standards and shifting energy trends. Our research and consulting services support informed strategies for technology development, investment, and regulatory alignment through:
- Market Intelligence and Insights: Detailed examination of the global diesel engine landscape, including emission trends, fuel efficiency innovations, and adoption patterns across key industries. Analysis covers performance optimization, aftertreatment systems, and emerging hybrid diesel-electric technologies.
- Strategic Forecasting: Forward-looking evaluations of market growth trajectories, investment opportunities, and the transition toward low-emission power solutions. Forecasts assess how cleaner combustion systems, biofuels, and digital engine technologies are redefining competitiveness and sustainability.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Continuous monitoring of global manufacturers, component suppliers, and emerging start-ups shaping the diesel engine sector. Assessments focus on innovation pipelines, R&D capabilities, and strategic alliances driving technological modernization and cost efficiency.
- Policy and Regulatory Analysis: Comprehensive review of emission standards, carbon regulations, and government initiatives influencing diesel engine production and export. Our analysis supports compliance strategies aligned with Euro VI, EPA Tier 4, and evolving national policies targeting decarbonization.
- Tailored Consulting Solutions: Customized guidance designed to enhance operational performance, support clean energy integration, and build resilience in supply chains. IMARC Group’s solutions connect technological advancement with sustainability objectives, helping clients optimize investments, adopt hybrid models, and position competitively in a transitioning energy landscape.
Through actionable data, forward planning, and continuous benchmarking, IMARC Group empowers businesses to navigate regulatory pressures, adopt cleaner technologies, and seize opportunities in the next generation of diesel engine innovation.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










