Junction Box Manufacturing Cost Analysis: The Connection Equation

What is Junction Box?
The junction box, generally made from plastic, metal, or composite materials, houses wire connections, terminations, and protective components to allow the safe distribution and routing of electrical circuits. The junction box will provide insulation, mechanical protection, and a secure environment to avoid accidental contact with live electrical parts, moisture intrusion, or dust accumulation. Junction boxes are central points where several cables converge, by which branching, splicing, or transitioning could be done between the circuits. They serve such important functions as maintaining electrical safety, meeting code requirements, and supporting reliable power across residential, commercial, industrial, automotive, and solar photovoltaic systems.
Key Applications Across Industries:
The junction box plays a key role in electrical infrastructure, industrial automation, renewable energy, automotive systems, telecommunications, and building services. In residential and commercial buildings, junction boxes are used in both concealed and surface-mount wiring for connection organization and to support lighting circuitry, switches, and sockets while offering protection against possible environmental or mechanical damage to splices. They enable electricians to locate fault points easily and perform maintenance or upgrading work with minimal effort.
Junction boxes in industrial plants are normally rated to survive severe environments, often using IP-rated or explosion-proof enclosures. They protect sensor wiring, motor control connections, automation interfaces, and field instrumentation while allowing for safe signal transmission within factories, refineries, and chemical plants.
In the solar industry, photovoltaic junction boxes are mounted on solar panels to house bypass diodes and cable terminations, enabling efficient energy transfer and protecting modules from hot-spot damage. These solar junction boxes are designed for UV, heat, and weather resistance.
In the automotive industry, junction boxes, often part of a body control module, organize power distribution, relay control, and signal routing for key vehicle functions including lighting, infotainment, safety systems, and sensors.
Other specialized applications include telecommunications networks, marine installations, and outdoor electrical installations that need weatherproof and corrosion-resistant designs. Junction boxes, in all sectors, ensure organized wiring, guaranteeing increased safety and long-term reliability of the electrical systems.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global junction box market reached a value of USD 4.50 Billion in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 7.40 Billion by 2033, at a projected CAGR of 5.70% during 2025-2033. The junction box market grows with increasing investments in infrastructure development, electricity distribution networks, the deployment of renewable energy, and industrial automation. One of the strongest drivers is continuous growth in the construction sector, especially in emerging economies where urbanization and commercial development require extensive electrical installation. Building codes that enforce safe wiring practices also drive up the adoption of high-quality junction boxes in residential and commercial buildings.
Another major growth catalyst is the rapid expansion of the solar photovoltaic industry. Each solar panel has a junction box, and thus the demand for PV-specific junction boxes increases correspondingly with the surge in global solar capacity, whether rooftop, utility-scale, or hybrid renewable systems. In addition, advanced junction boxes are needed for superior thermal performance, diodes, and weatherproofing because high-efficiency solar panels are the trend.
The increasing usage of sensors, control systems, and motor-driven machinery in industrial automation and manufacturing processes demands more robust enclosures that can withstand dust, moisture, chemicals, and mechanical stress. Junction boxes with IP ratings, flameproof, and explosion-proof are in high demand for oil and gas, mining, power plants, and the chemical industry. Increasing vehicle electrification and digitalization of automotive systems also influence the market. A modern vehicle relies on several power-distribution modules and junction boxes for managing complex wiring harnesses. The requirement for next-generation, heat-resistant, compact junction boxes increases because of the proliferation of EVs across the globe.
Moreover, expansion in the field of smart home technologies, telecom networks, and backup power systems (inverters, batteries, rooftop solar) is also acting in favor of the market. All in all, safety regulations, renewable energy adoption, industrial modernization, and vehicle electrification are the core drivers contributing to stable demand for junction boxes worldwide.
Case Study on Cost Model of Junction Box Manufacturing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale junction box manufacturing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed junction box manufacturing plant in India. This plant is designed to manufacture 1 million units of junction box annually.
Manufacturing Process: The manufacturing process of a junction box comprises of material selection, molding or fabrication, component assembly, and rigorous quality testing to ensure safety and durability as per electrical standards are involved. Manufacturing starts with the selection of the raw material, usually thermoplastics such as PVC, polycarbonate, or ABS, which can work for indoor applications, while for outdoor or solar applications, the material should be UV-resistant or flame-retardant polymers. For metal junction boxes, galvanized steel, aluminum, or stainless-steel sheets are used. In the case of plastic junction boxes, the material is melted and injected into precision injection-molding machines where dies shape the box body, lid, and internal mounting structures. As for the production of metal boxes, the process involves several sheet-metal fabrication steps: cutting, punching, bending, stamping, and surface finishing by galvanizing or powder coating to enhance corrosion resistance. Once the box housing is formed, fittings and accessories are added, including cable glands, terminals, grommets, conduit knockouts, and mounting brackets. Internal terminals or bus bars are manufactured by copper stamping or molding-in inserts and are assembled with automated screw-tightening or riveting systems. Solar junction boxes further include bypass diodes, potting materials, and high-temperature cables that must be installed to tolerate heat and weather conditions. Every box, after assembly, undergoes quality inspections to evaluate dimensional accuracy, mechanical strength, dielectric insulation, IP rating against dust and water protection, and flame-retardancy performance. Functional tests verify the integrity of terminals, connections, and lid-locking mechanisms. Boxes intended for high-reliability environments, such as those demanded by industrial, automotive, or photovoltaic applications, are subjected to thermal cycling, UV exposure, salt-spray resistance, and electrical stress. The junction boxes are labelled and packaged, batch-coded for traceability, and ready for sale. This manufacturing process ensures safe, durable enclosures suitable for diverse electrical installations across buildings, industries, and renewable-energy systems.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample'
Raw Material Required:
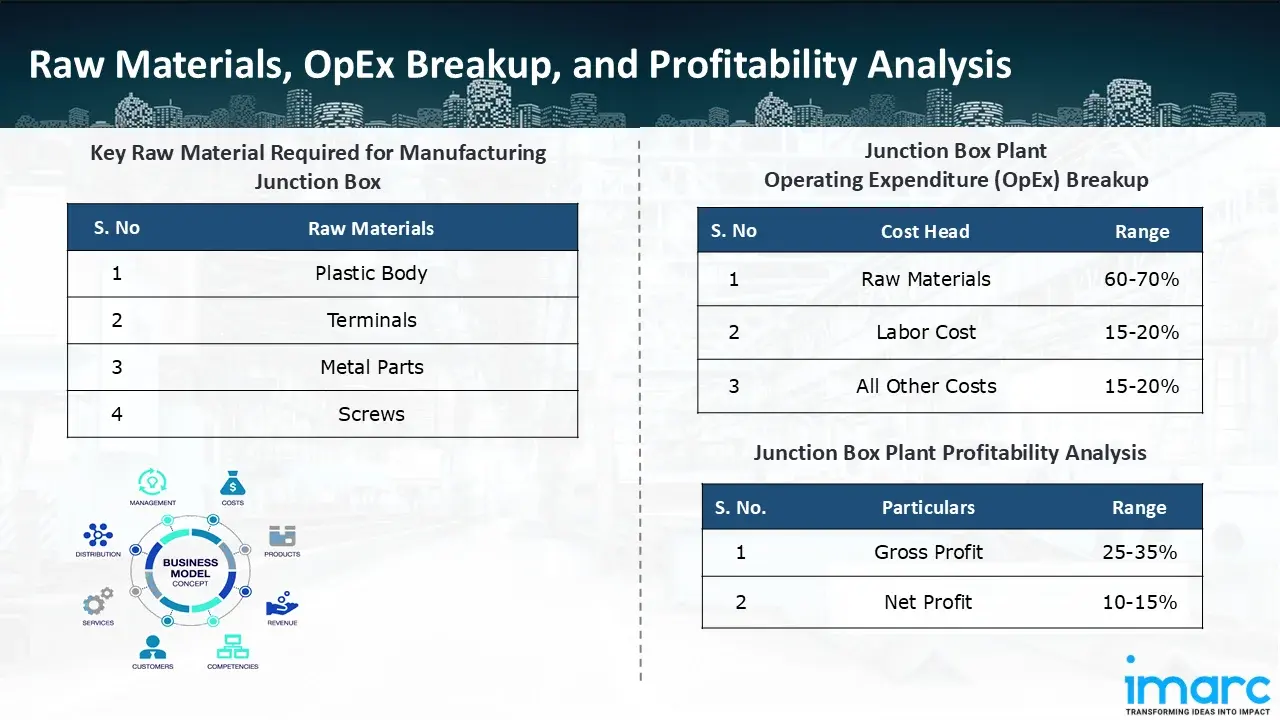
The basic raw materials required for junction box manufacturing include:
- Plastic Body
- Terminals
- Metal Parts
- Screws
Machine Section or Lines Required:
- Injection Molding
- Terminal Stamping
- Assembly
- Testing
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. Opex in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in junction box manufacturing plant ranges between 60-70%, labor cost ranges between 15% to 20%, and all other costs ranges between 15-20% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 25-35%, and net profit lie between the range of 10-15% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the junction box manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of manufacturing 1 million units of junction box annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In November 2025, a new bifacial solar panel with a 475 W output and a 23.27% power conversion efficiency has been introduced to the Australian market by Chinese company Phono. The panels have an IP 68-rated junction box, a temperature coefficient of -0.26% per degree Celsius, an operating temperature range of -40 to 85 degrees Celsius, and a maximum system voltage of 1,500 volts.
- In November 2025, Indian solar equipment producer DhaSh PV announced its plans to begin producing composite frames for solar modules as part of its next diversification strategy.
- In October 2024, GenX PV India has announced plans to establish a fully integrated aluminium frame manufacturing facility in Raipur. It is also hiking up junction box manufacturing capacity from 20 GW to 50 GW by FY 2025.
Why Choose IMARC?
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104