How are Government Policies Powering India’s Electric Car Revolution?
India's electric vehicle (EV) revolution is accelerating at a breakneck speed, powered by a strategic combination of government incentives, infrastructure investments, and manufacturing policies that are transforming the automotive landscape. The IMARC Group that the Indian electric car market reached USD 963 Million in 2024. The Government of India is at the forefront of this change, offering financial incentives to both individuals and manufacturers while creating a regulatory framework that supports EV adoption. On top of that, the rapid development of charging infrastructure is ensuring that India isn’t just following the global trend but also setting the pace in the electric mobility race.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
Electrifying India: From Central Schemes to State Solutions
FAME II: A Game-Changer in India’s EV Adoption
India’s electric vehicle policy framework has been shaped by the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme, which has significantly impacted the economics of EV ownership. Launched on April 1, 2019, with a total budget of Rs. 10,000 Crore, FAME II was designed to encourage the adoption of EV by providing substantial purchase incentives. This initiative is set to conclude on March 31, 2024, marking a critical period in India’s push toward cleaner mobility solutions.
Furthermore, in 2025, the Ministry of Heavy Industries reported notable progress under FAME II, accelerating electric mobility across India. As of October 31, 2024, 16.15 lakh EVs, including 14.27 lakh two-wheelers, 1.59 lakh three-wheelers, 22,548 four-wheelers, and 5,131 buses, had received incentives. The government allocated INR 8,844 crore under the scheme, with INR 6,577 crore dedicated to subsidies and INR 2,244 crore for infrastructure development, including 10,985 charging stations to facilitate the transition to sustainable transport.
State Level Solutions for a National Transition
State-level EV policies are essential in supporting national efforts by tackling local challenges and opportunities in the shift toward electric transportation. Numerous Indian states have implemented their specific EV policies, providing diverse incentives like tax reductions, purchase grants, and waivers from road taxes to promote the use of electric cars. These policies aim to enhance involvement from both individuals and manufacturers within the EV ecosystem. For instance, in 2025, Maharashtra announced its EV Policy 2025 aiming to make 30% of all new vehicle sales electric by 2030. The policy offers toll-free travel, tax exemptions, and registration fee waivers for EVs registered between April 1, 2025, and March 31, 2030. It also mandates charging stations every 25 km on highways and subsidies across vehicle categories.
Tax Strategy: Driving the Future of Electric Vehicles
India’s EVs benefit from lower GST rates compared to petrol and diesel cars, making them more affordable for individuals. For example, in 2025, the GST Council decided to maintain the concessional 5% GST rate on all EVs, supporting India's clean mobility goals. This ensures no price increase for both mass-market and luxury EVs under the new GST structure. The move benefits domestic and imported EVs, helping keep prices stable amid tax reforms. Additionally, the Government offers income tax deductions on loans taken to purchase EVs, further incentivizing the adoption of clean mobility. These financial benefits, combined with reduced operating costs, make EVs an attractive alternative, driving the shift towards sustainable transportation solutions across the country.
Infrastructure Investment: Building the Backbone of Electric Mobility
The growth of EVs depends heavily on the development of accessible and widespread charging infrastructure. To make EV adoption convenient and practical, it is essential to have a robust network of charging stations across the country.
- Government push for nationwide charging networks: The Government of India is systematically enhancing the charging network to facilitate the broad utilization of electric cars. This includes creating an extensive array of charging stations in important urban, rural, and industrial regions, as well as along significant highways to provide easy access for EV owners. A major advancement in this area is the announcement of the PM E-Drive scheme in 2025, which sets aside INR 2,000 crore to establish 72,000 public charging stations across the country. Designated as the nodal agency, BHEL will implement charging facilities throughout cities, airports, and key highways. This targeted investment seeks to speed up the shift towards clean transportation and diminish the nation's dependence on fossil fuels.
- Public-private partnerships in infrastructure growth: Partnerships between public and private sectors are crucial for speeding up the growth of EV charging infrastructure. Through collaboration of resources, knowledge, and technology, these alliances facilitate faster setup of charging stations, fostering innovation and ensuring the network expands effectively. This method addresses the growing need for electric cars while improving access in both urban and rural regions.
- Integration with renewable energy sources: A crucial element in building a sustainable EV ecosystem is the integration of charging infrastructure with renewable energy sources. This approach significantly reduces the overall carbon footprint of EVs, directly supporting India’s broader green mobility objectives. A notable example of this is the JOULE project, launched in 2024 by Amazon through The Climate Pledge. This $2.65 million initiative aimed to establish shared, renewable-powered EV charging stations in Bengaluru. The project, in collaboration with partners like Mahindra Logistics and Uber, projected to support over 5,500 EVs by 2030, cut emissions by 25,700 tons, and create 185 jobs, demonstrating a clear path toward a more sustainable and eco-friendly transportation sector.
- Standardization of charging infrastructure: Standardization of charging station technologies is a critical factor in enhancing the user experience and promoting widespread EV adoption. Ensuring consistent charging infrastructure allows EV owners to utilize any station, thereby increasing convenience and efficiency across diverse regions. A prime example of this strategic approach is Tamil Nadu, which in 2025 became the first state to launch dedicated EV charging infrastructure guidelines. This framework, with TNGECL as the nodal agency, aims to streamline the approval process, promote the use of renewable energy, and standardize installations. Piloted in six major cities, this initiative seeks to address the significant disparity of one charger for every 316 EVs, demonstrating a clear commitment to building a seamless and accessible charging ecosystem.
Manufacturing Momentum: PLI Schemes and 'Make in India' Drive Domestic Production
The Role of PLI in Strengthening India’s EV Manufacturing
The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) program is essential for India's approach to enhance local production of EVs and batteries. Through financial incentives, the program motivates manufacturers to improve their production skills, innovate, and eventually lessen the nation's reliance on imports. This is essential for positioning India as a frontrunner in sustainable mobility and energy storage. A significant advancement in this field took place in 2024 when Ficci urged the Indian government to implement a PLI 2.0 program. This suggested extension was designed to assist startups and smaller companies in the EV sector that currently cannot take advantage of the existing PLI framework, fostering a more inclusive and vibrant ecosystem.
Made in India, Ready for the World: The Rise of Domestic Green Mobility
The "Make in India" initiative is instrumental in stimulating domestic manufacturing and fostering a self-reliant economy by encouraging companies to produce goods within the country. This strategic focus supports industrial expansion, drives innovation, and generates employment, while reducing dependence on imports. A significant milestone in this endeavor was the 2025 inauguration of a major green mobility project in Hansalpur, Gujarat. During the event, Prime Minister Narendra Modi unveiled the e-VITARA, Suzuki's first "Made-in-India" global EV, which is now slated for export to 100 countries. This initiative also included the commencement of local hybrid battery electrode production, further solidifying India's position as a global hub for green technology and clean energy.
Roadmap to the Future: 2033 Vision and Long-term Sustainability Goals
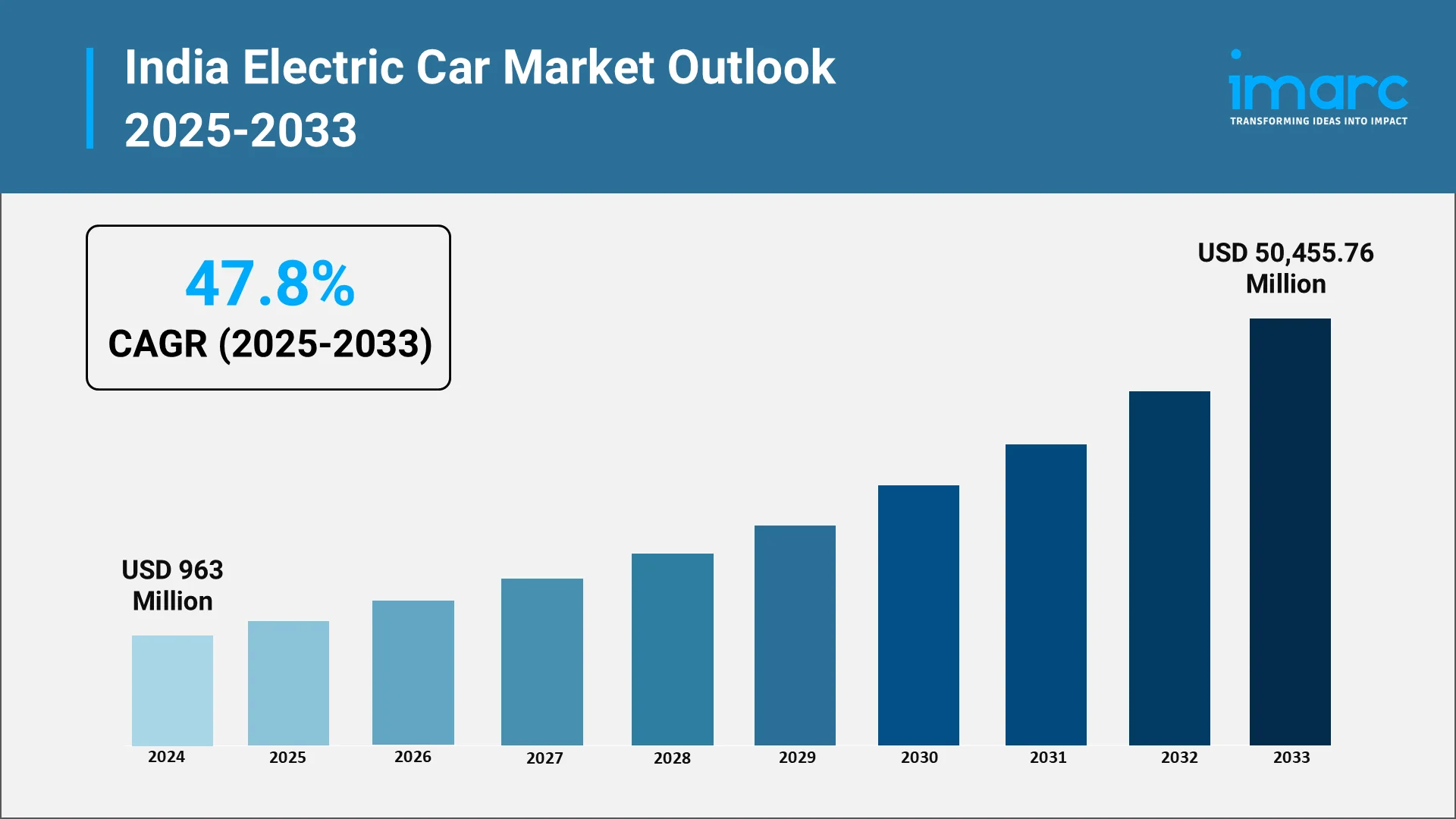
India's electric car market is set for rapid growth, with projections from IMARC Group estimating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 47.8% from 2025 to 2033, reaching USD 50,455.76 Million by 2033. This growth is propelled by increasing government incentives, advancements in EV technology, expanding charging infrastructure, and a growing environmental consciousness among individuals. The rise of EVs is not just a trend but a strategic shift toward a more sustainable future.
Additionally, India's electric car penetration targets are among the most ambitious globally, aiming for 30% EV sales penetration by 2030. The NITI Aayog has outlined specific targets for various vehicle categories, including:
- 30% of private car sales to be electric by 2030
- 40% of the bus fleet to be electrified by 2030
- 70% of commercial vehicles to be electric by 2030
- 80% of two-wheelers and three-wheelers to be electric by 2030
These targets reflect India's strong commitment to achieving clean and sustainable mobility, reducing dependence on fossil fuels, and addressing the nation's growing air pollution challenges.
Apart from this, long-term sustainability goals also play a pivotal role in the market growth. The push for green mobility is not limited to vehicle electrification but also extends to renewable energy integration for EV charging infrastructure. As seen with Tata Power’s launch of Mumbai’s largest EV MegaCharger hub in 2025, the initiative powered entirely by renewable energy, India is focusing on creating a self-sustaining ecosystem. The hub, designed for private car owners and ride-hailing fleets, serves as a step towards ensuring that electric mobility runs on clean energy.
Furthermore, India’s future roadmap also envisions a strong push for domestic manufacturing, with a goal of local production of EVs and components under the ‘Make in India’ initiative. This is expected to not only reduce import dependence but also enhance the country’s position as a global hub for EV production. The continuous development of green technologies and infrastructure, including the expansion of EV charging networks, is central to achieving these long-term goals.
Driving the Future: IMARC’s Blueprint for India’s EV Takeoff
IMARC Group empowers stakeholders in India’s electric car industry with actionable intelligence to thrive in the rapidly growing market. Our research and services guide clients in identifying new opportunities, mitigating risks, and driving innovation across product development, services, and market strategies.
- Market Insights: Track domestic and global trends shaping user demand in India, such as the shift toward eco-friendly vehicles, government incentives for electric cars, and the rise of sustainable mobility solutions.
- Strategic Forecasting: Anticipate emerging trends in EV adoption, from advancements in battery technologies and charging infrastructure to policy changes and environmental regulations across key regions.
- Competitive Intelligence: Analyze competitive forces within India’s EV market, assess vehicle and battery innovations, and monitor breakthroughs in autonomous driving, smart features, and sustainable energy solutions.
- Policy and Regulatory Analysis: Gain insights into how national initiatives and regulations, such as India’s EV policy, subsidies, and environmental mandates, affect market dynamics, compliance, and access to new opportunities.
- Tailored Consulting Solutions: Receive support in developing customized market entry strategies, financial modeling, and partnership evaluations. IMARC’s consulting services help clients create India-specific market plans in a sector that’s evolving with technological advancements, regulatory shifts, and increased user awareness.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










