LED Light Manufacturing Cost Analysis: Lighting Up Production Economics
.webp)
What is LED Light?
An LED light is an illuminating device that utilizes Light Emitting Diodes as its source of light, generating light through a semiconductor-based process called electroluminescence. When electrical current flows across the semiconductor material of the diode, electrons emit energy as photons and thus produce highly efficient and concentrated illumination. LED lights are far more energy-efficient than incandescent or fluorescent lamps, emitting very low heat and having remarkably long operation lives. They are fabricated into bulbs, tubes, panels, strips, and industrial fixtures, each featuring driver, heat sink, optics, and housing to effect desired lighting attributes and performance characteristics.
Key Applications Across Industries:
LED lighting finds broad applications in residential, commercial, industrial, automotive, horticultural, and public infrastructure settings owing to its energy efficiency, reliability, and design flexibility. LEDs have been applied in ceiling fixtures, lamps, kitchen lighting, outdoors, and decorative systems within homes. Smart LED lights now, with the integration of wireless connectivity, support dimming, color tuning, scheduling, and voice control-things that form the backbone of modern home automation.
LED panels, downlights, and linear fixtures are used in several commercial settings, such as offices, retail stores, hotels, hospitals, and educational institutions, to achieve uniform illumination with reduced energy bills and enhanced visual comfort. LEDs are also used in hospitality for display lighting, signage, and ambiance creation.
Industrial high-bay and flood LED luminaires also offer long-life, high-lumen solutions in a number of industrial applications-from warehouses, factories, and refineries to cold storage units. Resistance to vibration, coupled with their long lifespan and reduced maintenance needs, make them ideal in continuous-use environments.
LEDs play an important role in street lighting, transportation hubs, airports, and parking lots, enhancing safety and better visibility while reducing municipal energy use. They find applications in automotive functions like headlights, taillights, interior lights, and digital displays. Specialized applications involve horticulture lighting, where LEDs provide the tailored spectrum for plant growth, and medical/technical lighting, including surgical lamps, UV disinfection systems, and precision optical devices.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global LED lighting market reached a value of USD 90.3 Billion in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 183.7 Billion by 2033, at a projected CAGR of 8.2% during 2025-2033. The factors such as rapid technological advancement, regulatory pressures on energy consumption, widespread infrastructure development, and growing traction for smart lighting solutions are acting as drivers to the global LED lighting market. One of the main market drivers is the global push toward energy efficiency, as governments implement tough standards in terms of lighting and phase out inefficient incandescent and halogen lamps. Compared to conventional lighting sources, LED lights use very minimal electricity, creating a perfect solution both for utility-driven efficiency programs and cost-conscious consumers.
Other significant drivers include urbanization and growth in construction. As cities are expanding and commercial, residential, and industrial buildings are developed anew, a great demand arises for modern lighting systems. Retrofit projects in already existing buildings also play a significant role in this, as property owners upgrade to LEDs to achieve compliance with evolving building codes and reduce long-term operating costs.
The improvements in technology, such as smart lighting, IoT connectivity, tunable white light, Li-Fi communication, and superior thermal management, drive adoption. Smart LED systems enable automation, remote monitoring, adaptive lighting, and integration with building management systems, which appeal to commercial buildings and smart cities.
Large-scale street lighting upgrade initiatives led by municipalities and governments further boost demand, as well as airport expansions and installations of public safety lighting. Similarly, the industries are moving toward LED high-bay and task lighting to align themselves with safety, productivity, and operational efficiency. Falling LED component costs and advances in semiconductor manufacturing have increased affordability, which has helped expand the technology's adoption into emerging markets. Additionally, long-term growth is supported by sustainability trends, carbon-reduction commitments, and growing awareness of LED recyclability. Collectively, these drivers position LED lighting as a dominant technology that shapes modern illumination across global markets.
Case Study on Cost Model of LED Light Manufacturing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale LED light manufacturing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed LED light manufacturing plant in India. This plant is designed to manufacture 3 million units of LED lights annually.
Manufacturing Process: The process of making an LED light starts with the LED chip, which is produced by epitaxial growth of semiconductor layers, usually gallium nitride (GaN) on substrates like sapphire or silicon carbide. In MOCVD (Metal-Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition), numerous microscopic layers are laid down to form the diode structure. After wafer processing, the wafer is diced into small LED chips, each of which is mounted on a lead frame or ceramic substrate and wire-bonded in order to create electrical connections. A phosphor coating can then be added to the chip, which converts the blue or ultraviolet LED emission into white light in a range of color temperatures. These packaged LED chips are assembled onto a printed circuit board through automated surface-mount technology. The PCB also includes electronic components for the driver circuit, which converts AC electricity into steady DC power while providing current regulation, surge protection, and flicker control. Effective thermal management is important; thus, the PCB is attached to a heat sink made of aluminum or thermally conductive composites to dissipate heat and prolong LED life. A light beam is formed by adding optical elements, such as lenses, diffusers, or reflectors. The final assembly is put into a metal, plastic, or polycarbonate housing, depending on the intended application. Quality testing involves lumen output, color accuracy, thermal behavior, electrical safety, and lifecycle performance evaluation of the finished LED light. Once approved, the lights are packaged and distributed for residential, commercial, or industrial use.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
Raw Material Required:
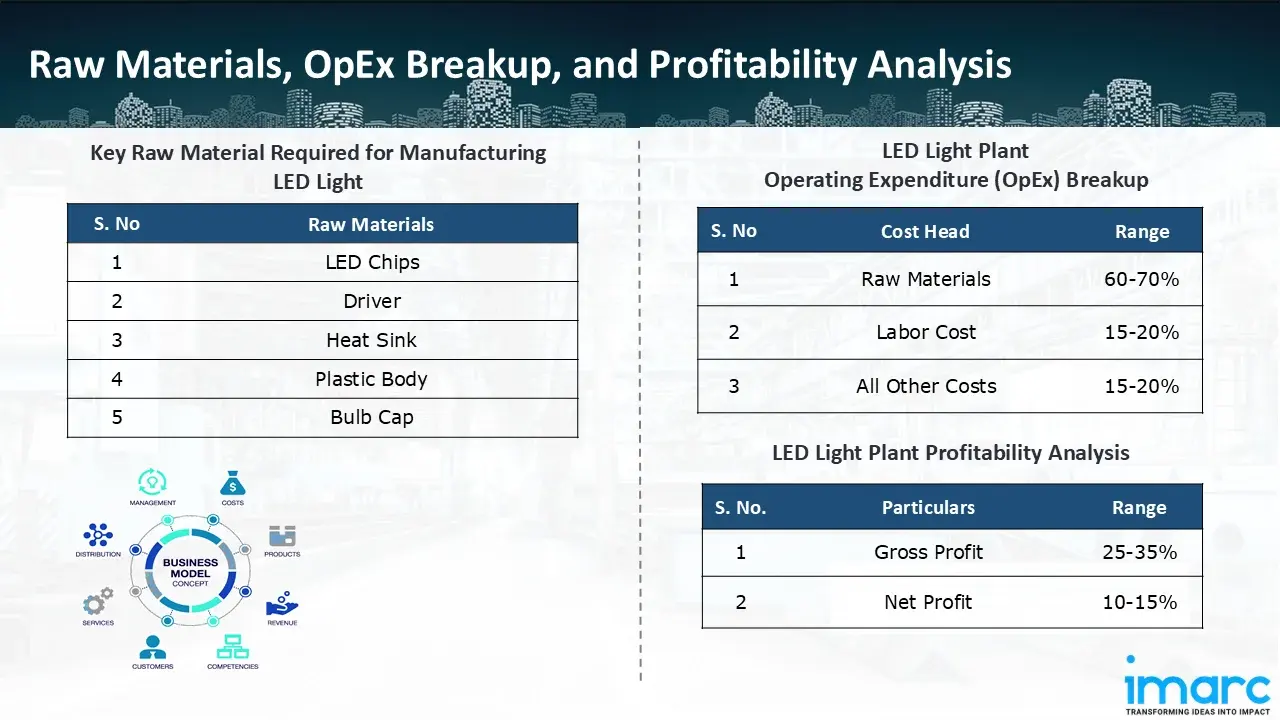
The basic raw materials required for LED light manufacturing include:
- LED Chips
- Driver
- Heat Sink
- Plastic Body
- Bulb Cap
Machine Section or Lines Required:
- SMT Line
- Assembly
- Aging
- Testing
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. Opex in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in LED light manufacturing plant ranges between 60-70%, labor cost ranges between 15% to 20%, and all other costs ranges between 15-20% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 25-35%, and net profit lie between the range of 10-15% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the LED light manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of manufacturing 3 million units of LED light annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In November 2025, VELO Lighting, a UK-based leader in professional sports illumination, has announced the launch of its next-generation LED floodlights designed to combine great performance with unsurpassed energy efficiency and sustainability.
- In November 2025, Bridgelux, a leading developer and manufacturer of high-performance LED lighting systems, today announced the immediate availability of its Generation 2 F90 Chip-on-Board (COB) series. The new series boasts remarkable color-point consistency throughout operational temperatures while delivering CRI 90 efficacy levels that meet or exceed standard CRI 80 solutions.
- In September 2024, LEDVANCE announced continuing to be the sole licensee of the OSRAM trademark for general illumination lamps. In addition, the license arrangement will be expanded to cover luminaires in general lighting outside of P.R. China.
Why Choose IMARC?
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104