Solar Glass Manufacturing Cost Analysis: Harnessing Light, Measuring Costs
_11zon.webp)
What is Solar Glass?
Solar glass is a type of specialty glass that has high transmittance and is designed exclusively for use in solar energy systems. Unlike regular flat glass, solar glass is designed to have maximum light transmission with minimal losses due to reflection and absorption. Solar glass is normally produced from low-iron raw materials to increase its optical clarity and may also have textured surfaces or anti-reflective coatings to enhance solar energy harvesting. Solar glass also has high mechanical strength, thermal stability, and resistance to environmental stress. This makes it suitable for protecting photovoltaic components while allowing maximum sunlight to hit solar cells.
Key Applications Across Industries:
Solar glass is mainly applied in photovoltaic (PV) modules, where it acts as the front cover protecting solar cells and allowing efficient light transmission. In crystalline silicon solar panels, solar glass is the outermost layer, protecting solar cells from dust, moisture, mechanical damage, and ultraviolet radiation. The optical properties of solar glass have a direct impact on the power output and efficiency of solar modules.
In addition to traditional solar panels, solar glass is applied in building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV). In this case, solar glass is used as a building material and an energy conversion surface. It is applied in building façades, roofs, skylights, windows, and curtain walls, which enable buildings to produce electricity while retaining architectural functionality.
Solar glass is also used in solar thermal energy systems, where it covers solar collectors used for heating water or industrial purposes. In such applications, the solar glass needs to be able to resist high temperatures while remaining clear and durable. Solar glass is also being used in agrivoltaic systems, greenhouse roofs, and solar canopies, where the ability to transmit light and resist the environment is essential.
New uses for solar glass include bifacial solar panels, which employ solar glass on both sides of the panel to transmit reflected and diffused sunlight. This gives solar glass a more active role in solar panel performance, going beyond its traditional role of protection. Solar glass enables a variety of applications in the energy and infrastructure sectors related to the use of solar energy.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global solar photovoltaic glass market reached a value of USD 17.30 Billion in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 78.50 Billion by 2033, at a projected CAGR of 17.39% during 2025-2033.
The primary driving factor for the global solar glass market is the fast-growing adoption of solar energy around the world. As nations shift towards a low-carbon economy, solar energy has become a backbone of a renewable energy plan. This, in turn, leads to a growing demand for solar photovoltaic modules, as solar glass is a crucial raw material for solar module manufacturing.
Government policies and regulations are key drivers for the solar glass market. Supportive policies for the adoption of renewable energy, long-term strategies for a low-carbon economy, and energy security issues lead to large-scale solar energy investments. Such policy-led developments create a stable demand for solar modules and, consequently, solar glass. In several regions, ‘Make in the Country’ developments also support the manufacturing of solar glass.
Advances in solar module technology also promote the market. The trend towards high-efficiency solar modules, bifacial solar modules, and building-integrated photovoltaics boosts the demand for solar glass in terms of quantity and quality. The industry requires the provision of glass with high transparency, improved surface treatment, and increased mechanical strength, which promotes value-added growth rather than just volume growth.
Urbanization and infrastructure development also promote the market. The growth of urban centers and the adoption of energy-efficient designs for buildings promotes the use of solar glass in construction materials. In addition, the increasing demand for electricity and the instability of fossil fuel markets accelerates the adoption of solar energy as a stable source of electricity in the long term.
In terms of sustainability, solar glass has the advantage of aligning with global environmental objectives. The use of solar glass in facilitating the generation of clean energy makes it a strategic material in the energy transition. As such, government support, technological advancements, infrastructure development, and sustainability drivers are contributing to the solar glass production market globally.
Case Study on Cost Model of Solar Glass Manufacturing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale solar glass manufacturing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed solar glass manufacturing plant in India. This plant is designed to manufacture 1,000 tons of solar glass per day.
Manufacturing Process: The solar glass manufacturing process is a precision-based process aimed at creating glass with high optical quality, strength, and durability for solar energy applications. The solar glass manufacturing process starts with the selection and batching of raw materials, mainly high-quality silica sand with very low iron content, soda ash, and limestone. Low iron content is essential in this process as it ensures low absorption of light, resulting in high solar transmittance.
The raw materials are then melted in a high-temperature furnace at temperatures above 1,600°C to create a molten glass. The molten glass is then processed using the float glass technique, where the molten glass is floated on a bath of molten tin to create a flat sheet of glass with high thickness precision. The glass thickness is precisely controlled to meet solar module requirements.
The glass is then cooled in an annealing lehr to remove stresses. However, for solar energy applications, the glass is further processed, mainly through surface texturing or acid etching, to increase light trapping. Anti-reflective coatings are also applied to the glass to improve optical properties.
The glass is then tempered by heating and rapidly cooling to enhance its mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance. This process is critical in ensuring the glass is durable enough to withstand outdoor environmental conditions. The final processes involve cutting, edge treatment, and quality checks, where the glass is tested for parameters such as transmittance, strength, flatness, and defects. The solar glass is then packaged and delivered to photovoltaic module manufacturers.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
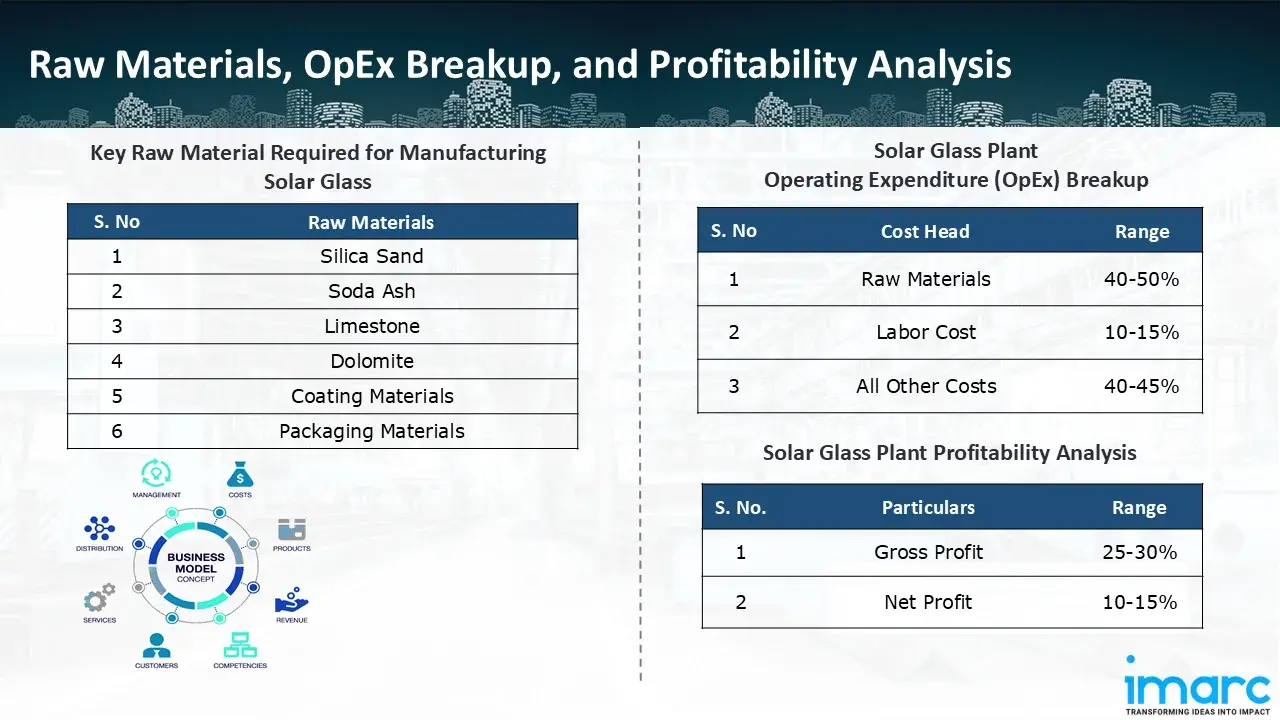
Raw Material Required:
The basic raw materials required for solar glass manufacturing include:
- Silica Sand
- Soda Ash
- Limestone
- Dolomite
- Coating Materials
- Packaging Materials
Machine Section or Lines Required:
- Batch Mixing
- Melting
- Tin Bath
- Annealing
- Coating
- Cutting
- Packing
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. OpEx in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in solar glass manufacturing plant ranges between 40-50%, labor cost ranges between 10% to 15%, and all other costs ranges between 40-45% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 25-30%, and net profit lie between the range of 10-15% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the solar glass manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of manufacturing 1000 tons of solar glass per day, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In April 2025, Almaden, a major Chinese producer of solar glass with headquarters in Changzhou, Jiangsu province, has announced intentions to construct a 500,000-ton solar glass production facility in the United Arab Emirates as part of a larger strategic move into international markets.
- In March 2025, Borosil Renewables announced a INR 900 crore investment in order to increase its solar glass production capacity to 10 GW by 2026. The action is intended to boost domestic manufacturing capacity, lessen reliance on imports, and assist India's expanding solar energy industry. The development will assist in fulfilling the growing national demand for solar glass in renewable energy projects.
- In January 2025, Gold Plus, a manufacturer of float glass, announced putting into service a new facility that can produce 109,500 metric tonnes of solar glass annually. With new facility, Gold Plus has expanded the range of products it offers by joining the solar glass market and increasing its capacity for float glass.
Why Choose IMARC?
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104











