Cocoa Powder Cost Model: From Beans to Business
_11zon.webp)
What is Cocoa Powder?
Cocoa powder is one of the main derivatives of the cocoa bean, which is derived after cocoa butter has been extracted from it during the chocolate production process. It consists mainly of non-fat cocoa solids, which contain a high content of polyphenols, flavonoids, and alkaloids like theobromine.
Key Applications Across Industries:
Famous for its intense color, bitter-sweet taste, and antioxidant activity, cocoa powder comes in natural and alkalized (Dutch-processed) grades, each with distinctive taste profiles and functional characteristics. The manufacturing process includes cleaning, roasting, grinding, pressing, and milling cocoa beans into a powder. Cocoa powder has widespread application in chocolate confectionery, bakery items, dairy drinks, health foods, and cosmetics because of its sensory and functional attributes. In response to rising consumer needs for clean-label, plant-based, and health-focused ingredients, cocoa powder remains highly relevant to industries. Also, its potential for sustainable sourcing through fair-trade and organic certifications adds to its economic and environmental attractions. In the future, the prospects of cocoa powder tie into innovation in the customization of flavors, nutraceutical uses, and sustainable supply chains, making it a tough and lucrative commodity.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global cocoa powder market size reached USD 15.5 Billion in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 16.5 Billion by 2033. The market for cocoa powder is fueled by the world's growth in the chocolate and confectionery market, and it continues to be its largest end-use segment. Increased demand for premium bakery foods and functional drinks also supports consumption.
The wellness trend is a key driver since cocoa powder is more and more marketed as having antioxidant value, cardiovascular health benefits, and being part of plant-based diets. Increased demand for vegan and dairy-free alternatives also drives its use in non-dairy drinks and desserts. Growing Asian-Pacific and African emerging markets are driving consumption as increasing disposable incomes and urbanization spur demand. As a trend, fortified cocoa powders supplemented with proteins or vitamins are on the upswing. Furthermore, traceability programs and sustainable sourcing strategies will mold the industry in the next five years. Competitive strengths are robust brand recognition, supply chain scalability, and broad product versatility. Yet risks include volatile prices for cocoa beans and environmental issues due to deforestation. Sustainability considerations are still key, with large producers investing in fair-trade accreditation and climate-resilient agriculture. Company reactions include traceability platforms based on blockchain technology, farmer livelihood initiatives, and low-fat and sugar-free cocoa product innovations.
Case Study on Cost Model of Cocoa Powder Processing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a large-scale cocoa powder processing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed cocoa powder processing plant in Nigeria. This plant is designed to produce 100,000 tons of cocoa powder annually.
Processing Process: The production of raw cocoa beans into cocoa butter and cocoa powder consists of several steps for quality and flavor. Beans received at the plant after fermentation and drying by farmers are first cleaned to eliminate foreign particles, followed by heat treatment that blows the shells for easy separation. Shells are cracked and stripped away in the winnowing process, leaving graded cocoa nibs. These nibs can be alkalized with potassium carbonate to alter flavor and color prior to roasting, wherein hot air forms the distinctive chocolate flavor at temperatures of up to 135°C within the nibs. Roasted nibs are further ground finely using blade mills and ball mills to create cocoa liquor (particle size less than 75 μm). Here, processing in two directions occurs: pressing the liquor isolates cocoa butter from solid cocoa press cake. The butter is filtered and, as needed, deodorized by steam and vacuum for use in chocolate making. The press cake, on the other hand, is broken, kibbled, and milled into cocoa powder, with its characteristics (pH, fat percentage, color, smell) conditioned according to manufacturer requirements. Lastly, cocoa butter is warehoused and cocoa powder is packaged, both being basic ingredients for confectionery, chocolate, desserts, and baked goods.
_11zon.webp)
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
Mass Balance and Raw Material Required: The primary raw materials used in the cocoa powder producing plant are cocoa beans and potassium carbonate. For a plant producing 1 ton of cocoa powder, 2.9 tons of cocoa beans, and 0.019 ton of potassium carbonate is required. Additionally, it produces 1.2 ton of cocoa butter as by product (per ton of cocoa powder).
Machineries Required:
- Cleaning Plant
- Drum Magnet
- Dumping Station
- Podestral / Framework for Pre-screen
- Silo Plant (Single Cell) 120 cbm
- Bucket Elevator
- Drag Chain Conveyor
- Intermediate Bin
- Shell-Con Machine for Pre-treatment of Beans
- Control Cabinet
- Bucket Elevator
- De-hulling Plant / Winnower
- Service Platform (Shell Side)
- Shell Removal System
- Pneumatic Nib Conveyor
- Machine Hopper with Weigher
- Roasting Machine with Cooler and Bacteria Filter
- Electrical Control
- Utilities for the Alkalisation (Vacuum, Condensation & Process Control)
- Accessories (K2CO3 Preparation)
- Electrical Control for Reactor Plant (MCC)
- Intermediate Hoppers
- Plant Control and Monitoring System
- Cable, Cable Ducts incl. Various Materials
- Beater Blade Mill
- Extraction Device
- Level Control
- Cocoa Liquor Supply Pump
- Manually Operated 2-way Valve
- Stainless Steel Storage Tank (5000 Litre)
- Pneumatically Operated 2-way Valve
- Agitated Ball Mill
- Collecting Vessel (180 Litre)
- Vibrating Sieve
- Collecting Vessel (100 Litre)
- Discharge Pump
- In-line Magnets (Gauss-10.000)
- And Others
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Investment (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a Processing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
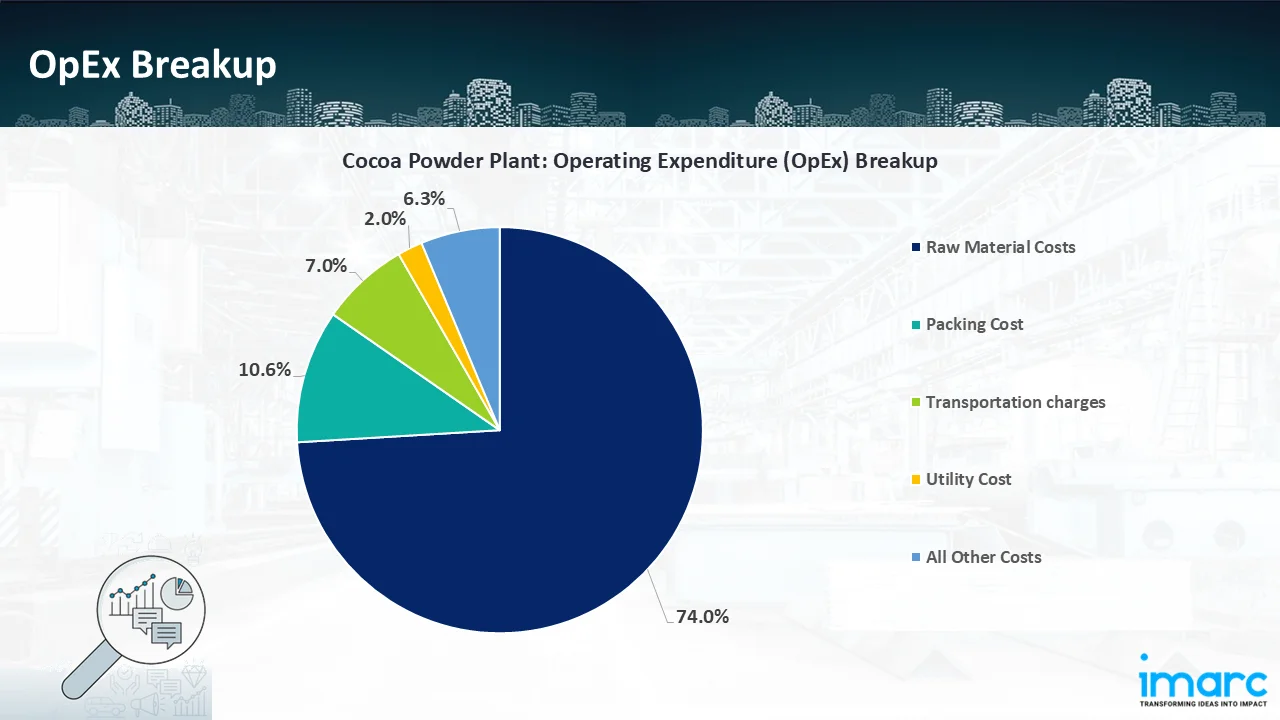
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a Processing plant effectively. Opex in a Processing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a Processing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth.
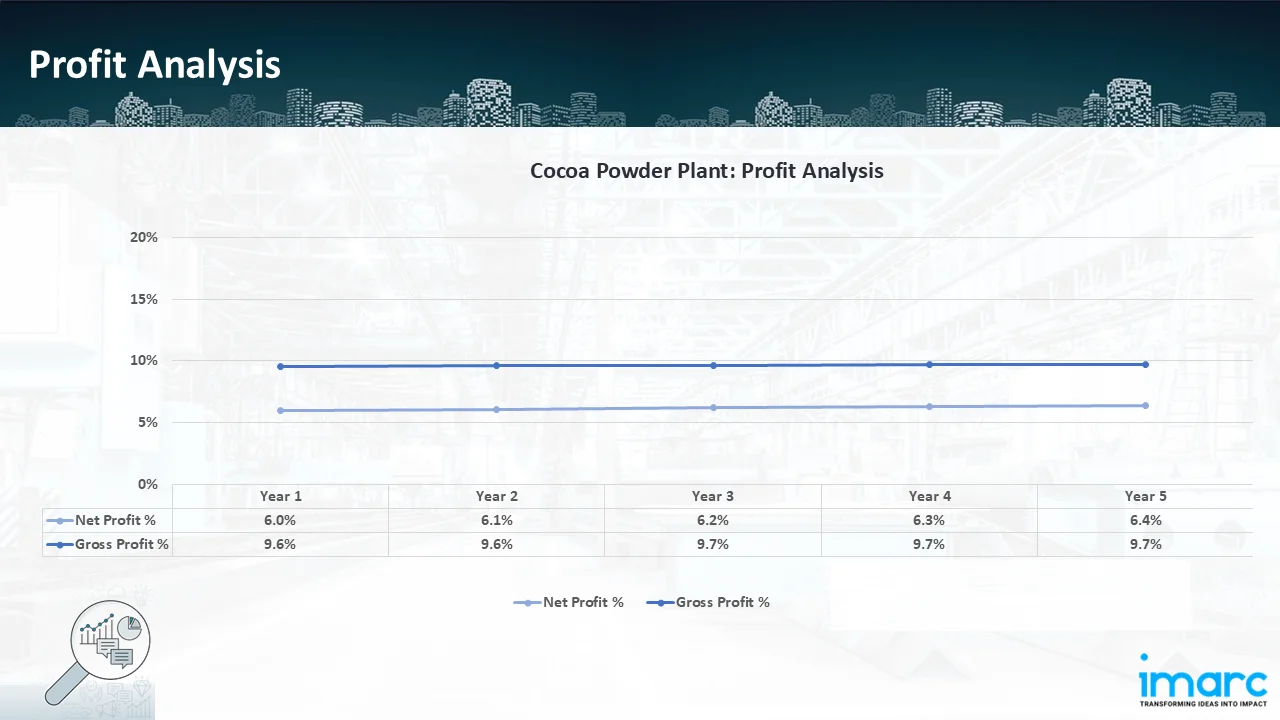
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: The proposed cocoa powder plant, with a capacity of 100,000 tons of cocoa powder annually, achieved an impressive revenue of US$ 611.9 Million in its first year. We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins improve from 9.6% to 9.7% by year 5, and net profit rises from 6.0% to 6.4%, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the cocoa powder processing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, Processing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of producing 100,000 tons of cocoa powder annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale Processing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In July 2025, California Cultured, a food technology firm that specialises in cell culture ingredients, and Barry Callebaut announced a collaboration to develop cultured chocolate on a commercial scale. It's like the idea of produced beef. In controlled conditions, scientists cultivate cocoa cells rather than cocoa trees.
- In December 2024, the first cocoa biochar project was launched in Dankwa County, Central Province, Ghana, by ofi (olam food ingredients), a prominent supplier of naturally good food and beverage ingredients, in partnership with LOTTE, Fuji Oil, and MC Agri Alliance. Wasted cocoa pod husks will be burned in biochar cone machines as part of the circular biomass project to produce biochar. Carbon from cocoa crop leftovers, which would otherwise be released back into the atmosphere through decomposition, will be locked in by biochar, which should also help the soil where the cocoa is grown.
- In October 2024, Cargill expanded its ability to produce cocoa powder and spirits for the Asian baking, ice cream and restaurant sectors by adding a new cocoa manufacturing line to its Gresik, Indonesia, facility.
Why Choose IMARC:
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the Processing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish Processing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104











