Electric Vehicle Charging Station Cost Model: Station Economics Review

What is Electric Vehicle Charging Station?
An EV charging station represents the necessary main infrastructure that allows electrical energy to be transferred from the power grid into electric vehicles to enable their use for transportation. Unlike conventional fueling stations that offer liquid fuels, EV charging stations provide electric power through the use of standardized connectors and smart control systems.
Key Applications Across Industries:
The core components include a power conversion unit, which transforms alternating current from the grid into direct current for the vehicle battery; a charging controller controlling communication between the charger and the EV; and a connector or plug matched to the vehicle's charging interface. EV charging stations are categorized into two main classifications: AC chargers, which include Level 1 and Level 2, and DC fast chargers, categorized under Level 3. AC chargers are normally applied for residential, or workplace charging and offer slower replenishment, whereas DC chargers would be appropriate for commercial and highway corridors due to their capability for rapid charging. Modern charging stations integrate smart grid integration, load balancing, and renewable energy connectivity for efficient energy management. It also includes digital communication technologies enabling authentication, billing, and monitoring through various mobile applications or the RFID system. Increasingly, they are integrated with solar panels, battery energy storage, and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technologies to enhance sustainability and stabilize the grid. As the global automotive industry moves toward increased electrification, EV charging infrastructure has emerged as a critical component of clean mobility ecosystems. Manufacturing companies focus on scalability, modular design, and interoperability across various vehicle platforms to deliver accessibility and convenience to consumers with support for the greater energy transition to decarbonized transportation.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global electric vehicle charging station market reached a value of USD 21.6 Billion in 2025. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 213.7 Billion by 2034, at a projected CAGR of 28.15% during 2026-2034. The global electric vehicle charging station market is driven by a combination of technological innovation, environmental regulation, and policy-driven electrification initiatives. A major driver is the carbon-neutral movement happening around the globe because governments across the world have set ambitious targets for emission reduction and have begun phasing out internal combustion engine vehicles. Such policies, abetted by subsidies and mandates, speed up not only EV adoption but also, in turn, the corresponding development of charging infrastructure.
Furthermore, the cost of lithium-ion batteries keeps going down as efficiency grows, making electric vehicles more economical and viable, and hence directly increasing demand for accessible and reliable charging networks. EV charger integration into parking lots, highways, and residential complexes by city planners is another critical factor in boosting urban mobility. The growing demand arising from the increased popularity of ride-sharing, electric fleets, and delivery services is additionally pushing demand for high-capacity, fast-charging solutions to minimize any kind of downtime. Advances in technology like ultra-fast charging up to 350 kW, wireless charging systems, and AI-enabled energy management platforms are remolding the market with improved convenience and efficiency in charging. Coupled with this, the integration of renewable energy into charging infrastructure falls in line with global efforts toward reducing grid emissions, thus allowing green charging powered by solar or wind energy. Another significant catalyst to growth is private sector participation, wherein energy companies, automotive manufacturers, and technology firms enter into strategic alliances to further expand charging networks. Meanwhile, vehicle-to-grid (V2G) and bidirectional charging technologies are emerging as pivotal developments that enhance grid resilience and open new revenue streams. Overall, the combination of environmental imperatives, supportive regulations, and technological evolution continues to position EV charging infrastructure as a foundation of the global transition toward sustainable, electrified transportation.
Case Study on Cost Model of Electric Vehicle Charging Station Manufacturing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale electric vehicle charging station manufacturing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed electric vehicle charging station manufacturing plant in India. This plant is designed to manufacture 15,000 units of electric vehicle charging station annually.
Manufacturing Process: The manufacturing of an EV charging station involves a mix of electrical engineering, precision assembly, and rigorous quality control to ensure safety, reliability, and compatibility with diverse electric vehicle platforms. The process starts at the design and prototype phase where engineers develop schematics that define the station's power output, communication protocols, and enclosure design. This involves selecting the appropriate standard relevant to the market, such as CCS, CHAdeMO, or Type 2, and integrating smart functionalities like billing systems, connectivity modules, and user interfaces. Once the design has been validated, sourcing of components commences-key components includes power electronic systems like rectifiers, inverters, and transformers; charging connectors; control boards; metering devices; and protective systems like circuit breakers and surge suppressors. This involves assembling the power module, which converts AC power from the grid to DC for fast charging or regulates the supply for AC-based chargers. These modules are then mounted onto heat sinks and cooling systems for thermal load management during operations. Installation of the control system and communication units, comprising microcontrollers, sensors, and wireless modules, is conducted to manage energy exchanges and communicate with vehicles and central servers. Fabrication of the enclosure follows next, whereby metal or composite housings are cut, welded, and powder-coated to achieve weather resistance and electrical safety. The completely assembled units are tested and calibrated regarding electrical load tests, checks on insulation, and software validation for meeting safety standards such as IEC and UL. On approval, packaging and shipment of the stations to site installations ensue, followed by final integration and commissioning. This process ensures that every EV charging station delivers reliable, efficient, and safe charging performance in real-world conditions.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
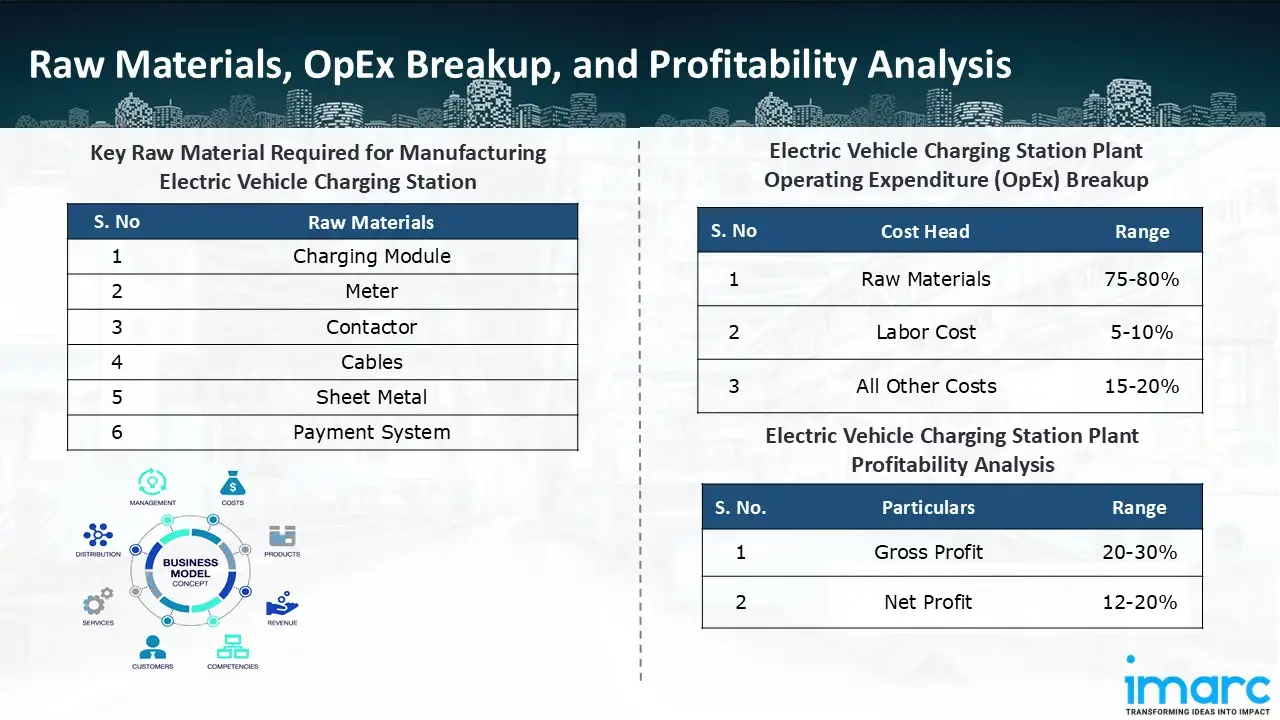
Raw Material Required:
The basic raw materials required for electric vehicle charging station manufacturing include:
- Charging Module
- Meter
- Contactor
- Cables
- Sheet Metal
- Payment System
Machineries Required:
- Assembly
- Wiring
- Software Integration
- Testing
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. Opex in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in electric vehicle charging station manufacturing plant ranges between 75-80%, labor cost ranges between 5% to 10%, and all other costs ranges between 15-20% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 20-30%, and net profit lie between the range of 12-20% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the electric vehicle charging station manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of manufacturing 15,000 units of electric vehicle charging stations annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In October 2025, Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA) and Dubai Taxi Company (DTC) have inked a long-term agreement to install 208 ultra-fast EV charging stations throughout the emirate in an effort to reduce transportation emissions and accelerate the electrification of the taxi fleet. The agreement, which is a component of DEWA's EV Green Charger program, was inked during WETEX 2025.
- In July 2025, states in the United States have constructed less than 400 EV charging stations through April under US$ 7.5 billion federal infrastructure initiatives as reported by the Government Accountability Office. According to GAO, a joint office in charge of the program "has not defined performance goals with measurable targets and time frames for its activities." As of April 2025, 384 charging ports were in use at 68 stations throughout 16 states.
- In February 2025, TATA.ev launched a groundbreaking initiative to raise the number of electric vehicles charging points in India to 400,000 by 2027. The firm is also expanding its collaboration with leading Charging Point Operators (CPOs) to set up around 30,000 new public charging points.
Why Choose IMARC:
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104











