Can the Global Lighting Market Redefine the Future of Modern Infrastructure?

Introduction:
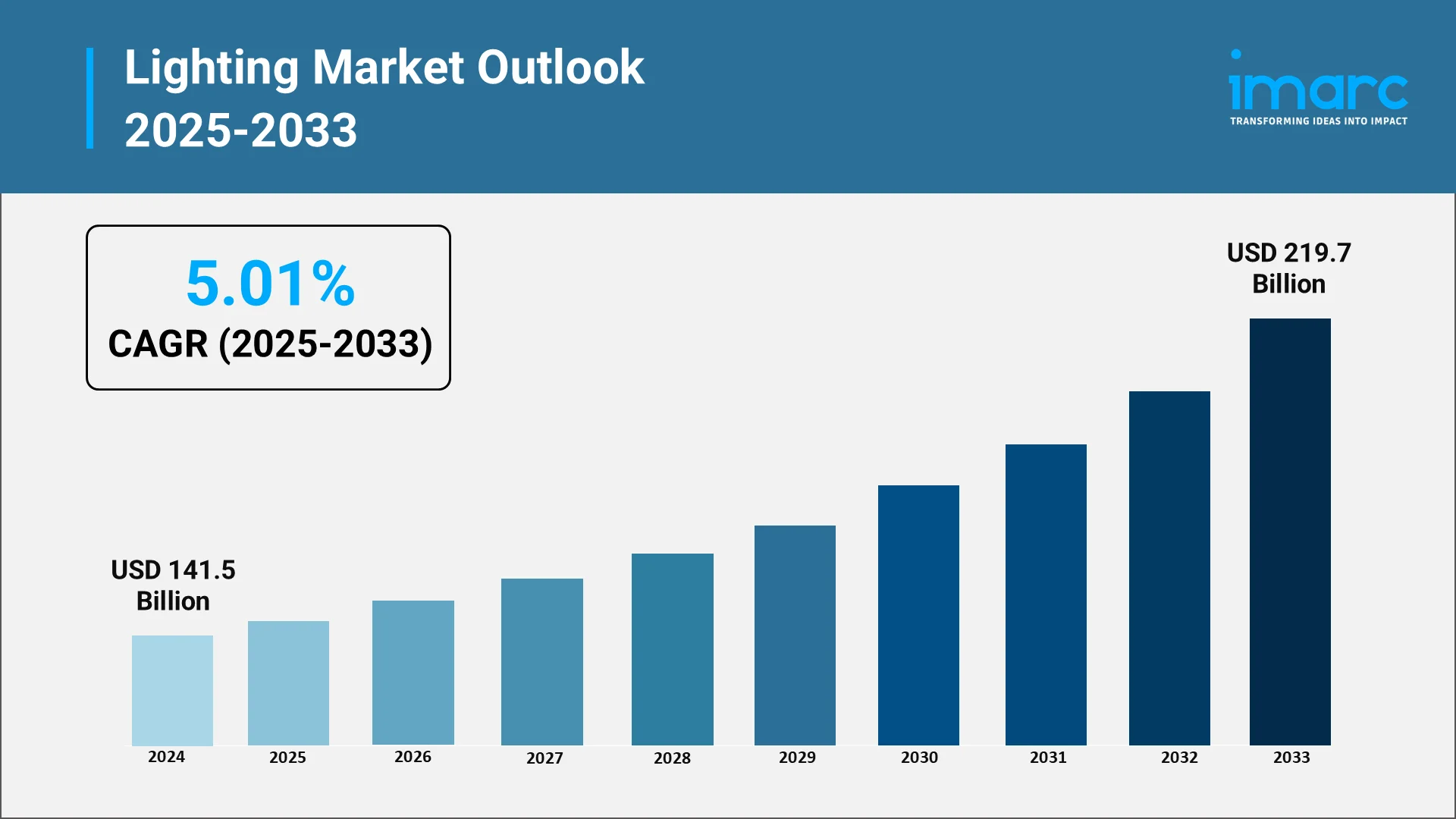
Light has long been a symbol of progress, shaping the way societies function, cities evolve, and industries thrive. The global lighting market size reached USD 141.5 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 219.7 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 5.01% during 2025-2033. As technology continues to advance, lighting has transformed from a basic necessity into a strategic enabler of innovation, efficiency, and sustainability. The evolution from incandescent bulbs to LEDs, smart systems, and intelligent lighting networks represents not just technological change but a redefinition of how energy, design, and functionality intersect in the built environment. The global lighting market stands at a critical juncture, where its integration with smart infrastructure and digital transformation is paving the way for a more connected, energy-efficient, and aesthetically advanced world. Modern infrastructure now relies heavily on adaptive lighting systems that balance design appeal with functional efficiency, forming the backbone of sustainable cities and modern industrial spaces.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
The Role, Impact, and Benefits of Lighting in Urban and Industrial Development:
Lighting is the silent architect of modern civilization. In urban areas, lighting has an impact on aesthetics, safety, and environmental quality. Streetlights light up open spaces, reduce crime, and promote mobility at night. Architectural lighting shapes city silhouettes and contributes to tourism and economic activity. Beyond visibility, lighting affects human behavior, moods, and productivity, making it a crucial component in designing and developing a city.
Lighting plays a very important role in any industrial environment for optimized performance and safety, with a view to energy consumption. The production units, factories, and warehouses need perfect illumination to maintain accuracy and continuity in the work culture. Smart lighting solutions, including automated brightness control and occupancy sensors, have further improved workplace safety and prevented any kind of downtime. In 2025 — Signify today unveiled its new EcoLink Professional Lighting line at PhilConstruct 2025, offering contractors a budget-friendly industrial lighting range that includes LED streetlights, floodlights, high-bays, panel lights and more — all featuring “VoltSafe” 2.5 kV surge protection for improved durability and lower maintenance. This also helps significantly in reducing energy bills and carbon emissions, thus aligning industries with green goals.
Besides, lighting contributes to urban resilience and digitalization. Most smart city projects are currently using lighting poles as hubs for sensors, communication networks, and surveillance systems. This convergence will convert traditional lighting into an intelligent infrastructure layer that will support transportation, environmental monitoring, and emergency response. Such innovative approaches fully prove that lighting is no longer a conventional function, but has emerged as a central pillar of modern infrastructure design.
Key Growth Drivers in the Global Lighting Market:
A combination of technology, environment, and economic reasons contributes to the growth in the lighting industry. The most prominent is the increased use of energy-efficient lighting technologies. This changing landscape of energy usage-from traditional lamps to LED system applications-has transformed the residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. LEDs consume significantly less energy, offer longer lifespans, and require minimal maintenance, making them the go-to choice for both new constructions and retrofitting projects. Reflecting the push toward smarter, integrated lighting solutions, industry-wide innovations were showcased at the GUILite (30th Guangzhou International Lighting Exhibition) in June 2025, where companies from across the LED ecosystem—such as LEDVANCE, Luminus and Nationstar—unveiled advanced LED systems for diverse applications including automotive, horticulture, and healthy-lighting.
At the same time, urbanization has accelerated global lighting demand. As cities grow and new urban centers develop, so does the demand for sustainable and intelligent lighting infrastructure. Governments and private developers are increasingly incorporating lighting systems that can adjust according to the real-time environment to minimize waste and maximize energy efficiency. This integration supports global sustainability goals and is improving the livability of urban areas.
Other driving forces include technological innovation. The rapid development of connected lighting systems using the Internet of Things has supported data-driven control of illumination. Smart lighting adjusts color temperature, brightness, and timing according to occupancy and natural lighting levels. Such solutions form an essential part of smart homes, intelligent transportation networks, and commercial complexes pursuing energy savings hand in hand with increased user experience. Further developments in wireless communication and sensors have allowed the realization of adaptive lighting ecosystems, further enhancing urban safety and comfort.
Other factors contributing to market growth include increasing industrial automation and infrastructural modernization. Industrial facilities increasingly install lighting systems that can handle automated operations and integrate with digital platforms for monitoring and control. Faced with increasing awareness of the importance of a circular economy, manufacturers have now adapted their product design to make lighting systems recyclable, which caters to global initiatives toward waste reduction and environmental responsibility.
Regulatory Framework and Policy Landscape in the Lighting Industry:
The global lighting industry works within a complex network of international standards, energy codes, and environmental regulations that touch every phase of production, distribution, and application. Most governments around the world are phasing out inefficient lighting systems and are promoting greener alternatives through strict performance and labeling requirements. Energy efficiency standards stimulate consumers and industries toward high-performance lighting solutions, while environmental policy limits toxic substances like mercury, spurring innovation with recyclable and eco-friendly materials. Also, building codes today integrate lighting efficiency into sustainability certifications like LEED and BREEAM, making sure illumination design falls within the wider scope of environmental goals. According to reports, in India, the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) released a first revision of the national lighting code (SP 72:2025), effective from October 2025, which emphasises energy-efficient technologies (especially LED) and smart lighting systems in urban, rural, industrial and indoor environments.
Simultaneously, the rise of smart cities has expanded regulatory focus toward digital and intelligent lighting systems. Governments are encouraging the use of smart grid integrations and adaptive lighting controls to improve energy management and urban resilience. This encourages collaboration between technology providers, municipal planners, and utility operators. At the same time, standardization bodies such as the International Electrotechnical Commission have continued revising global technical benchmarks to ensure safety, interoperability, and consistency in quality. Coordinated efforts like this reinforce market trust, foster the adoption of advanced technologies, and drive global transition toward efficient, sustainable, and intelligent lighting ecosystems.
Government Support / Initiatives for Global Lighting Market:
Government initiatives have been central in driving the transition toward advanced, energy-efficient lighting technologies. Through subsidies, rebates, and public awareness campaigns, most countries have been fast-tracking the replacement of obsolete lighting systems for energy consumption and carbon emissions reduction. For instance, India’s Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL) under its Street Lighting National Programme has replaced over 1.3 crore conventional streetlights with smart LED systems, significantly reducing electricity demand across cities. Smart lighting is integrated into public infrastructures like highways, transport hubs, and government buildings, thereby promoting safety and visibility while improving energy management. In smart city schemes, the networks of connected lights increasingly form the backbone for data-driven services that include traffic optimization, environmental monitoring, and coordination of emergency responses, highlighting how lighting plays its role in broader sustainability goals.
Governments also encourage the collaboration of public institutions and private companies in laying a base for innovation and technology transfer that will benefit the lighting industry. Such partnerships bring together research, finance, and technical know-how that will contribute to enhancing domestic manufacturing and the creation of advanced lighting solutions. In parallel, education and training programs are being expanded in the areas of lighting design and energy management to build professional competencies capable of supporting such a transformation. Together, these initiatives underscore the strategic role that lighting plays in sustainable infrastructure development and national growth. Such alignment of innovation, policy, and human capital development places governments in a position where lighting becomes a key enabler of future-ready, environmentally responsible economies.
Top Lighting Companies in the World:
The global lighting sector is made up of companies creating innovation, sustainability, and quality for a variety of applications, from residential and commercial to industrial and outdoor. These have been instrumental in the transition of lighting systems from conventional to intelligent and connected solutions that embrace energy efficiency with design excellence. With solid R&D, these companies provide smart lighting products combined with digital platforms to enable automation, personalization, and real-time monitoring. Using sophisticated materials and optical technologies, companies can improve the quality of lighting, increasing user comfort while minimizing environmental impact.
Strategic partnerships between architects, urban planners, and technology providers have allowed integrated solutions to emerge in the form of lighting ecosystems that are meeting urban and industrial needs. Several players are expanding their operations to emerging markets as well, by providing less expensive, long-lasting lighting for energy-constrained areas, thereby aligning growth with social responsibility. Sustainability is driving change across the value chain, from renewable-powered manufacturing and recyclable design to greener packaging. With competition increasing, only the successful integration of technology, aesthetics, and sustainability can help position these innovators front and center in a more energy-efficient and design-driven global lighting industry.
Opportunities and Challenges in the Global Lighting Market:
The transformation in global lighting demand is creating vast opportunities for innovation and growth driven by smart city development, digitalization, and sustainability goals. The market is fast adopting intelligent lighting systems that integrate sensors, connectivity, and analytics in an effort to optimize energy use and further enhance operational intelligence . For example, Signify recently partnered with Cornerstone and Dense Air in the UK to turn street-lighting infrastructure into a city-wide multi-operator wireless network for 4G/5G and IoT applications — a clear sign of lighting systems evolving into connectivity hubs rather than just illumination.
Technologies such as Li-Fi, which allows data transmission via light waves, extend the role of lighting from mere illumination to new frontiers of communication and automation. Integrated lighting networks are being developed for smart infrastructure that provides better control and more valuable data insights, along with adaptability. In line with this, LEOTEK showcased at SALC 2025 its AI-driven lighting platform, which can reduce operational and maintenance costs by up to 70% and supports functionality such as fault detection, scheduled dimming and integrated connectivity nodes — illustrating how lighting is becoming an embedded component of smart urban systems. Meanwhile, architectural and decorative lighting are gaining prominence as urban environments continue to evolve into vibrant lifestyle hubs where dynamic and aesthetically driven illumination improves mood, cultural identity, and spatial experience.
In industrial and commercial sectors, automation and predictive maintenance are driving demand for advanced lighting systems capable of real-time performance monitoring and optimization. Integration with HVAC and security systems enhances energy efficiency and comfort, while R&D efforts address challenges in standardization, interoperability, and cybersecurity. Despite supply chain and regulatory pressures, the industry’s future remains promising, with innovation focused on balancing sustainability, affordability, and technological progress. As lighting becomes integral to smart and sustainable infrastructure, it is transforming workplaces and urban environments through intelligent, interactive, and design-oriented solutions that merge technology, creativity, and environmental responsibility.
Conclusion:
The global lighting market is redefining the foundation of modern infrastructure by merging technology, design, and sustainability. As innovation accelerates through smart systems, IoT connectivity, and energy-efficient LEDs, lighting has evolved from a utility into an intelligent ecosystem that shapes urban life, industrial productivity, and environmental impact. Companies like Signify, LEOTEK, and LEDVANCE are leading this transformation with AI-driven and sensor-integrated solutions that enhance both functionality and aesthetics. Supported by strong regulatory frameworks and government initiatives, the market is poised to become a central pillar of future-ready cities, driving global progress toward a more sustainable and connected world.
Illuminate Your Strategy with IMARC’s Global Lighting Market Intelligence:
For comprehensive, data-backed intelligence on the global lighting industry, IMARC Group serves as a trusted partner, providing actionable insights that guide innovation, policy alignment, and strategic investment across residential, commercial, and industrial segments.
- Extensive Market Coverage: IMARC’s research encompasses every segment of the lighting value chain—ranging from LEDs, smart lighting systems, and Li-Fi technologies to connected urban infrastructure and industrial illumination—offering clients a 360° understanding of current and emerging market opportunities.
- Reliable Forecasting and Strategic Outlook: Using advanced forecasting tools and real-time market analytics, IMARC integrates regulatory developments, sustainability initiatives, and digital transformation trends to produce accurate projections that support business growth and product innovation strategies.
- In-Depth Competitive Landscape: Our reports deliver detailed assessments of key players such as Signify, LEDVANCE, and Acuity Brands, evaluating their technological advancements, sustainability initiatives, partnerships, and product portfolios to help stakeholders benchmark performance and identify new growth pathways.
- Regional and Sectoral Insights: IMARC’s granular analysis covers lighting demand patterns across regions, from smart city projects in Asia-Pacific to industrial retrofits in Europe and North America, helping clients uncover high-potential markets and sector-specific opportunities.
- Policy and Innovation Intelligence: We closely monitor global regulatory trends, energy-efficiency standards, and sustainability frameworks driving the lighting transition, offering clarity on how governments and corporations are aligning to build intelligent, low-carbon infrastructure.
- Trusted Global Expertise: With deep analytical capabilities and a proven track record of delivering precision-driven insights, IMARC empowers clients to navigate the evolving global lighting market confidently, turning data into decisions that shape the future of smart, sustainable illumination.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










