Key Challenges and Opportunities Shaping the Soft Skills Training Market

Introduction: The Evolving Landscape of Workforce Development
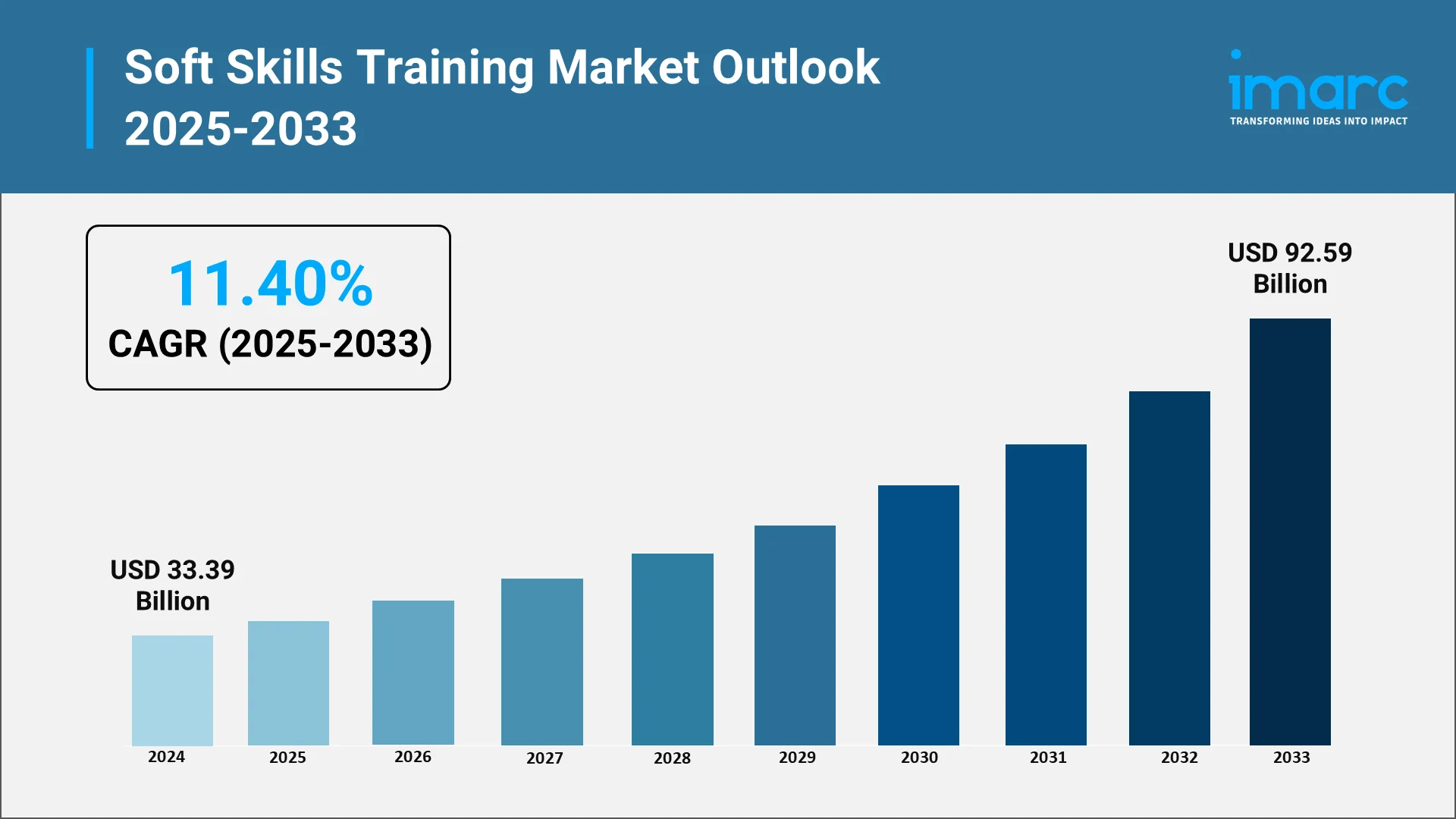
The global soft skills training market size was valued at USD 33.39 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 92.59 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 11.40% during 2025-2033. This substantial growth reflects a fundamental shift in how organizations approach workforce development, as the recognition of soft skills as strategic assets rather than supplementary competencies becomes universal across industries.
The acceleration of this market is driven by converging forces: technological disruption requiring enhanced human capabilities, demographic shifts creating multigenerational workplaces, and evolving business models demanding unprecedented levels of adaptability and collaboration. North America currently dominates the market, holding a significant market share of over 32.9% in 2024, driven by strong demand for leadership development, communication skills, and workforce adaptability.
Yet beneath these promising figures lie complex challenges that organizations must navigate. From quantifying return on investment to integrating emerging technologies, from managing constrained budgets to balancing personalization with scale, the soft skills training sector is at a critical inflection point where strategic decisions today will determine competitive positioning tomorrow.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
Skills Gap Crisis in Modern Workforce:
The skills gap has evolved from an HR concern into a strategic business threat with quantifiable economic consequences. Nearly 75% of C-level executives report a skills gap, with 70% of directors and 64% of VPs acknowledging their companies operate with skills deficiencies. This widespread acknowledgment reflects a crisis that transcends organizational hierarchy and industry boundaries.
The Magnitude of the Challenge
The global skills gap is reshaping labor markets and threatening long-term growth. Most companies already face talent shortages or expect them soon, especially in data analysis, project management, AI, and software development. The U.S. alone could lose hundreds of billions in unrealized output over the next decade. Yet the most urgent deficit lies in soft skills: strategic thinking, communication, decision-making, and problem-solving. These human capabilities are increasingly vital for leadership, innovation, and adaptability, yet remain the hardest to teach and measure, leaving many organizations unable to translate technical expertise into effective performance.
Demographic and Structural Pressures
A shrinking labor force is compounding the skills crisis. Retiring Baby Boomers, declining birth rates, and lower participation rates are leaving major workforce gaps, particularly in healthcare, hospitality, and service sectors. At the same time, automation and digital transformation demand new technical competencies across every industry, from finance to manufacturing. Education systems lag behind these shifts, producing graduates without job-ready skills. The result is a persistent disconnect between industry demand and available talent, forcing companies to compete for fewer qualified workers and to rethink workforce planning, upskilling, and recruitment strategies.
Technology Integration and Digital Transformation:
The integration of advanced technologies into soft skills training represents one of the most transformative shifts in corporate learning and development. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, virtual reality, and gamification are no longer experimental tools—they are becoming foundational elements of effective training ecosystems.
- AI-Powered Personalization and Adaptive Learning: AI-driven training platforms use machine learning and natural language processing to tailor learning paths to individual needs. They analyze learner behavior and performance to deliver targeted feedback, adjust pacing, and provide additional support where needed. This adaptive approach improves engagement, closes skill gaps faster, and enhances overall training efficiency. In October 2025, Infosys launched the Customer Experience Suite for Salesforce, integrating its Topaz™ AI-first services with Salesforce’s agentic AI to accelerate enterprises’ digital and agentic transformation. The suite automates customer service, sales, and employee support functions while enhancing personalization and real-time decision-making, helping companies achieve measurable efficiency gains. With successful case studies like VTT’s AI-driven sales transformation, the initiative strengthens demand for leadership, communication, and customer engagement skills in AI-augmented workplaces.
- Emerging Technologies Reshaping Training Delivery: Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) enable employees to practice real-world scenarios safely and repeatedly, enhancing practical skill application. Gamification elements like points, badges, and leaderboards increase motivation and retention. Together, these tools turn passive learning into active, immersive experiences that improve outcomes and participation rates. In May 2024, VirtualSpeech partnered with Strivr to expand virtual reality (VR) soft skills training through integration on Strivr’s enterprise XR platform. The collaboration adds VirtualSpeech’s AI-driven communication and leadership modules—covering real-time roleplays for sales, interviews, and negotiations—to Strivr’s library of over 2 million training experiences and 1 million learners. This partnership strengthens the soft skills training market, driving large-scale adoption of AI-powered immersive learning to enhance employee engagement, productivity, and performance across global enterprises.
- Digital Learning Platforms and Ecosystem Integration: Digital platforms now serve as integrated ecosystems combining content, analytics, and collaboration. They link with HR and performance systems to align training with business goals and track skill development across teams. For instance, in October 2025, Vinci Compass Investments Ltd. announced an agreement to acquire a 50.1% stake in Verde Asset Management, one of Brazil’s oldest multi-strategy investment firms managing R$16 Billion in assets. The transaction, valued at approximately R$ 46.8 Million in cash and 3.1 Million Class A shares, will strengthen Vinci Compass’ Global Investment Products and Solutions (Global IP&S) platform by expanding discretionary mandates and multi-strategy offerings. The acquisition enhances Vinci Compass’ performance analytics capabilities across asset allocation, risk management, and portfolio construction, positioning the firm as a leading player in Brazil’s asset management and investment analytics landscape. This connected approach supports data-driven decisions and scalable, personalized learning.
- AI Teaching Assistants and Real-Time Support: AI teaching assistants provide instant guidance, answer questions, and help navigate learning materials anytime. They personalize feedback and highlight areas where learners struggle, improving content quality and learner progress. By automating routine support, they allow trainers to focus on higher-value instruction. For instance, in May 2025, Udemy launched Role Play, an AI-powered platform designed to enhance workplace communication and leadership skills through real-time simulations. The platform enables professionals to practice negotiation, feedback, and conflict management, with over 2,000 interactive Role Plays published within two weeks of its debut. By integrating adaptive AI coaching with expert content, Udemy aims to bridge the soft skills gap.
- Challenges in Technology Adoption: Despite the promise, technology integration presents obstacles. Organizations face challenges related to digital literacy among both learners and facilitators, infrastructure requirements, data privacy concerns, and the need to maintain human connection in increasingly digital learning environments. Successfully leveraging technology requires not only selecting appropriate tools but also cultivating organizational cultures that embrace continuous learning and experimentation. The most effective approaches blend technology with human interaction. Hybrid models combining AI-driven personalization with instructor-led sessions, peer collaboration, and mentoring leverage the strengths of both domains—the scalability and data intelligence of technology with the empathy, context, and judgment of human facilitators.
- Future Trajectory: Advances in generative AI, NLP, and predictive analytics are redefining digital learning experiences. These tools will enable conversational, responsive, and anticipatory training environments. Companies that focus on learning impact rather than novelty will gain a lasting edge in workforce capability and adaptability. In March 2024, Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) unveiled an AI-native portfolio co-developed with NVIDIA, offering end-to-end solutions for generative AI training, tuning, and deployment. The launch included two full-stack GenAI solutions, a Machine Learning Inference Software preview, and an enterprise RAG reference architecture, accelerating AI project scalability and reducing model fine-tuning time for a 70 billion parameter Llama 2 model to six minutes on a 16-node system. By integrating AI infrastructure with consulting services, HPE aims to address the AI skills gap, reinforcing demand for soft skills training in leadership, adaptability, and AI-driven collaboration across enterprises.
ROI Measurement and Performance Analytics:
Measuring the return on investment for soft skills training remains one of the most persistent challenges facing learning and development professionals. Unlike technical training, where outcomes can often be quantified through certifications, productivity metrics, or error reduction, soft skills improvements manifest in subtle, interconnected ways that resist simple measurement.
The Measurement Imperative
High-performing learning and development professionals are significantly more likely to measure the ROI of learning and upskilling programs, and when making technology purchases, buyers expect to see returns on investment within short timeframes. This expectation creates pressure to demonstrate value quickly, even as the most significant benefits of soft skills development, improved collaboration, enhanced leadership, stronger organizational culture, accrue over longer timeframes. The stakes are substantial. Without robust measurement frameworks, training budgets remain vulnerable during economic downturns or strategic realignments.
Core Measurement Challenges
Data collection and analysis presents a cumbersome process, with many organizations struggling with data silos that make compiling necessary information for ROI calculations challenging. Performance improvements rarely result from a single intervention; isolating the specific impact of training from other factors, market conditions, process improvements, technology implementations, proves exceptionally difficult. Time lag compounds attribution challenges, as benefits of training may not be immediately apparent, with significant delays between training delivery and measurable results.
Measurement Frameworks and Methodologies
Organizations employ multiple frameworks to assess training effectiveness. The Kirkpatrick Model remains widely used, measuring training across four levels: reaction (participant satisfaction), learning (knowledge acquisition), behavior (application of skills), and results (business impact). While comprehensive, implementing all four levels requires significant resources and sophisticated measurement systems.
Data-Driven Approaches and Analytics
Advanced analytics platforms are transforming ROI measurement from art to science. Learning management platforms offer tools to track and analyze training participation, completion rates, and post-training performance data, with analytics providing insights that enable data-driven decision-making. Machine learning algorithms can identify correlations between training engagement and performance outcomes, surfacing patterns invisible to manual analysis.
Financial Metrics and Business Impact
The standard ROI formula calculates: ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) × 100, where Net Profit equals the gain from investment minus the cost of investment. Applying this formula to soft skills training requires monetizing benefits: increased sales, reduced turnover costs, productivity gains, quality improvements, and comparing them to total training costs including development, delivery, opportunity costs, and ongoing support.
Overcoming Measurement Barriers
Success requires institutional commitment to measurement as a strategic capability, not administrative burden. Organizations must invest in data infrastructure that integrates learning, performance, and business systems. They need to define clear objectives before training initiatives launch, establishing what success looks like and how it will be measured.
Starting with the "why" ensures talent development professionals connect programs to business objectives from the outset, as research shows executives want to see business connections and sometimes ROI, not merely what participants need to know or do.
Budget Allocation and Resource Management:
Financial constraints represent persistent obstacles for learning and development initiatives, with soft skills training particularly vulnerable to budget cuts during economic uncertainty. Research shows that resource and budget constraints rank as a top challenge for technology leaders, followed by talent retention and talent recruitment concerns. This creates a paradoxical situation: organizations need training to address talent challenges, yet budget limitations prevent adequate investment in the solutions required. When organizations face financial pressure, training budgets often face disproportionate cuts. Leadership perceives training as discretionary spending rather than strategic investment, especially when ROI remains difficult to quantify.
This short-term thinking generates long-term costs: under-skilled workforces, reduced productivity, increased turnover, and diminished competitive positioning. When financial constraints arise, companies tend to limit spending by downsizing, trimming expenses, or postponing employee training. These measures may offer temporary relief but often worsen underlying issues, as a smaller or inadequately trained team is forced to handle extra duties, resulting in heavier workloads and higher burnout rates.
Effective budget management begins with strategic prioritization. Not all training initiatives deliver equal value; organizations must identify which skills have greatest impact on business outcomes and concentrate resources accordingly. This requires understanding critical capability gaps, analyzing competitive requirements, and forecasting future skill demands. Data-driven prioritization enables informed decisions.
Personalization vs. Scalability Balance:
One of the most complex challenges facing the soft skills training market is achieving equilibrium between personalization and scalability. Personalized learning delivers superior outcomes by adapting content, pace, and methodology to individual needs, learning styles, and contextual requirements. However, developing and delivering highly customized training for thousands of employees presents logistical and financial challenges that can prove prohibitive without sophisticated infrastructure.
The Case for Personalization: Personalized soft skills training recognizes that individuals enter programs with diverse backgrounds, competencies, and learning preferences. A recent graduate requires different leadership development than a mid-career manager transitioning to executive roles. Cultural contexts shape communication styles and expectations, requiring training that acknowledges these differences rather than imposing universal templates.
Research consistently demonstrates that personalized learning improves engagement, retention, and application. When learners perceive training as relevant to their specific challenges and career trajectories, motivation increases substantially. Adaptive platforms that assess baseline capabilities, identify gaps, and recommend targeted interventions maximize efficiency by eliminating redundant content while addressing genuine development needs.
Personalization also supports diverse learning modalities. Some individuals thrive in collaborative environments, while others prefer self-paced reflection. Findings show 67% of employees considering switching jobs say learning opportunities are a key factor; over 80% of daily generative AI users expect efficiency gains. Visual learners benefit from infographics and video, while kinesthetic learners require interactive simulations and role-playing. Personalized approaches accommodate these preferences, optimizing learning effectiveness across populations.
The Imperative of Scalability: Organizations employing thousands—or tens of thousands—cannot deliver entirely bespoke training to each individual without prohibitive costs. Scalability enables broad access to development opportunities, ensuring that frontline employees receive similar quality training as executive leadership. Standardized components create consistency in organizational culture, shared language around key concepts, and baseline competencies across teams. Scalable solutions leverage technology to reach distributed workforces efficiently. Cloud-based platforms deliver content globally, eliminating geographic constraints. Asynchronous learning accommodates diverse schedules and time zones, preventing training from disrupting operational continuity. Standardized assessments provide benchmarking data that informs organizational strategy and identifies systemic development needs.
Cost considerations make scalability essential. Developing custom content for each role, function, or individual quickly exhausts budgets. Economies of scale in content development, platform licensing, and facilitation reduce per-learner costs, making comprehensive training programs financially viable for organizations of all sizes. More than 80% of workers who use generative AI daily expect it to make their time at work more efficient in the next 12 months. Half (49%) of all users expect it to lead to higher salaries.
What are the Challenges and Opportunities in Soft Skills Training Market?
The soft skills training market stands at a critical juncture where persistent challenges intersect with transformative opportunities. Understanding this duality enables organizations to navigate complexities strategically while capitalizing on emerging possibilities that promise to reshape workforce development.
Persistent Market Challenges:
- Engagement and Application Gaps: High engagement during training doesn’t always lead to behavioral change. Without reinforcement or supportive cultures, learned skills fade quickly. Technical industries often undervalue soft skills, requiring careful communication strategies to drive acceptance.
- Quality and Standardization Issues: The market’s fragmentation leads to wide variation in quality and instructor competence. With no universal benchmarks, organizations often rely on marketing claims instead of evidence-based evaluations. Soft skills certifications lack consistent credibility, limiting professional recognition.
- Cultural and Contextual Adaptation: Soft skills are shaped by culture, so training designed for one region may not resonate in another. Western-developed programs often need adaptation to fit local communication styles and norms. Global firms must balance localization with maintaining consistent organizational culture.
Emerging Market Opportunities:
- Microlearning and Just-in-Time Development: Short, focused modules fit into busy schedules and keep learning relevant. Employees can access quick lessons before real-world interactions, enhancing retention and application. Mobile delivery ensures training is available at the moment of need.
- Integration with Performance Management and Career Development: Organizations are embedding soft skills into job evaluations and promotion criteria. Linking development to career progression increases motivation and accountability. It also helps leaders track workforce capabilities and align learning with strategic goals.
- Expanding Markets and Demographic Shifts: Younger generations, remote work, and emerging economies are reshaping soft skills needs. Companies are focusing on digital communication, cross-generational collaboration, and workforce upskilling. Developing regions investing in education present significant market opportunities for adaptable training providers.
- Emphasis on Mental Health and Wellbeing: Workplace wellbeing is now central to learning agendas. Training in emotional resilience and stress management boosts retention and engagement. Integrating soft skills programs with wellness initiatives broadens impact and funding potential.
IMARC Group: Strategic Intelligence for Soft Skills Training Market Success
As the global soft skills training market undergoes rapid transformation—driven by technological innovation, evolving workforce dynamics, and shifting organizational priorities—IMARC Group stands as a trusted partner for enterprises, training providers, technology vendors, and investors seeking comprehensive market intelligence and strategic guidance.
- Market Research and Analysis: IMARC Group provides detailed insights into the soft skills training market, covering segments, delivery modes, industries, and regions to support strategic decision-making.
- Technology and Innovation Tracking: The firm analyzes technology adoption trends, identifies early signs of mainstream acceptance, and evaluates vendor competitiveness.
- Regional Intelligence: With global reach and local expertise, IMARC Group tracks adoption patterns and highlights region-specific opportunities and challenges across all major markets.
- Competitive and Strategic Insights: The firm supports established players in refining strategies, guides new entrants toward untapped segments, and assists investors with due diligence and integration analysis.
- ROI and Business Case Support: Consultants develop measurable frameworks and financial models that demonstrate clear value to decision-makers.
- Custom Research and Advisory: Tailored studies address market entry feasibility, benchmarking, and technology evaluation aligned with client goals.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










