Top Petrochemical Segments Driving Global Market Growth

Market Overview: The State of Petrochemicals in 2025
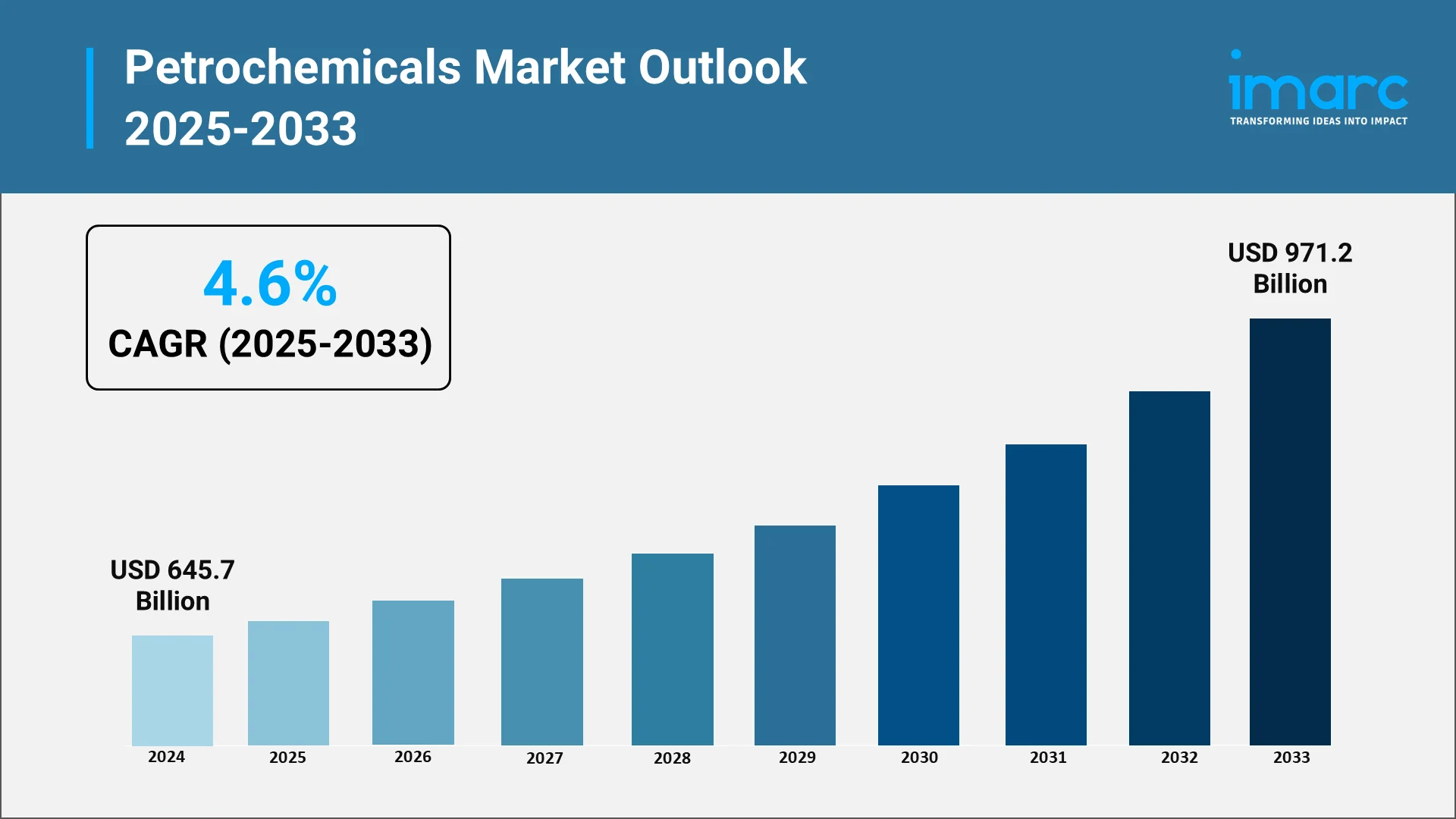
The global petrochemicals market is witnessing steady growth, supported by rising end-user consumption, industrial diversification, and infrastructure development across both developed and emerging economies. As industries increasingly adopt lighter and high-performance materials, demand for synthetic polymers, specialty chemicals, and plastics derived from petrochemicals continues to expand. As per IMARC projections, the global petrochemicals market reached USD 645.7 Billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 971.2 Billion by 2033, reflecting a CAGR of 4.6% during 2025-2033.
In parallel, governments and manufacturers are investing in domestic production to reduce import dependency and enhance export capabilities. Regulatory mandates on emissions and plastic waste are accelerating the transition toward cleaner technologies and bio-based feedstocks. This article provides a detailed examination of the top segments driving growth in the petrochemical industry.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
Top Growth-Driving Segments:
The petrochemical market in 2025 is shaped by rising demand across several key product categories, each playing a central role in industrial supply chains. Among these, ethylene, propylene, aromatics, methanol, and bio-based derivatives continue to demonstrate significant growth due to their diverse applications and alignment with global industrial and sustainability goals.
1. Ethylene and Its Derivatives
Ethylene remains a fundamental building block in the petrochemical industry. Its primary derivative, polyethylene (PE), is the most widely used plastic globally, applied in sectors such as food packaging, medical disposables, industrial films, and household products. In 2025, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) are witnessing strong demand.
Ethylene oxide is widely used in producing surfactants, detergents, and antifreeze solutions. In November 2024, Argus launched a global weekly Ethylene Oxide and Derivatives service, providing price assessments, capacity analysis, and trade insights to support strategic decisions across the ethylene value chain. Capacity expansions in China, India, the United States, and the Middle East are underway to meet global demand. These new facilities are increasingly integrating energy-efficient technologies and carbon capture systems to align with environmental compliance expectations.
2. Propylene and Polypropylene
Propylene is the second-most significant olefin in the global petrochemical market. Its major derivative, polypropylene (PP), is essential in automotive components, medical tools, consumer goods, and textile fibers. In March 2025, LyondellBasell approved a propylene expansion project at its Channelview Complex in Houston, adding 400,000 Metric Tons of annual capacity, with operations expected to begin by late 2028. Polypropylene’s lightweight, durability, and thermal resistance make it a preferred alternative to traditional materials such as metals in structural and packaging applications.
Beyond polypropylene, propylene is used in the production of acrylonitrile (for ABS plastics), propylene oxide (used in foams and coatings), and cumene (a precursor for phenol and acetone). Ongoing innovation and material substitution trends continue to drive the expansion of propylene-based products.
3. Aromatics: Benzene, Toluene, and Xylene (BTX)
Aromatic compounds, including benzene, toluene, and xylene (collectively referred to as BTX), are essential for producing a range of downstream products such as resins, nylon, and synthetic fibers. Benzene remains highly utilized for producing styrene and phenol, key ingredients in engineering plastics and adhesives. In March 2025, Lotte Chemical announced the startup of its USD 3.9 Billion Cilegon facility in Indonesia, which will manufacture key BTX products to support regional and global petrochemical demand.
Toluene is processed into toluene diisocyanate (TDI), used in flexible foams for furniture and automotive seating. Xylene, particularly para-xylene, is in demand for manufacturing purified terephthalic acid (PTA), a precursor to polyester and PET bottles. As transport fuels undergo decarbonization, producers are investing in integrated refining-petrochemical complexes to optimize BTX production.
4. Methanol and Its Derivatives
Methanol is gaining importance due to its role in producing formaldehyde, acetic acid, and MTBE, as well as in methanol-to-olefins (MTO) technologies. Additionally, methanol is being adopted as an alternative fuel source in marine, industrial, and transportation applications. Latin America and Southeast Asia are seeing significant investments in green methanol projects using biomass and carbon capture-based hydrogen. For example, in October 2024, HIF Global launched its first Brazilian project to produce 800,000 tons of e-methanol annually from green hydrogen, utilizing 1.6 GW of electrolyzers and captured CO2.
5. Bio-Based and Sustainable Petrochemicals
Sustainability trends are accelerating the development of bio-based petrochemicals such as bio-ethylene, bio-PET, and green methanol. In July 2025, Chevron Lummus Global and INA successfully produced sustainable aviation fuel and renewable diesel from biogenic feedstocks at Croatia’s Rijeka Refinery, demonstrating scalable bio-based fuel integration in existing infrastructure.
Derived from renewable feedstocks like sugarcane and agricultural waste, these products support compliance with environmental regulations and consumer demand for lower-emission materials. Further, bio-based derivatives are projected to expand within specialty chemicals, driven by advancing technologies and public-private collaboration supporting commercial-scale adoption.
Regional Trends and Demand Centers:
North America
North America holds a strategic position in the petrochemical industry, underpinned by abundant natural gas liquids and advanced infrastructure. The region’s cost-effective feedstock and policy-driven sustainability measures enable stable expansion across ethylene, methanol, and polymer production, supporting both domestic growth and export competitiveness.
Key Trends:
- Significant investments in ethane-based ethylene production in the US Gulf Coast states
- Widespread adoption of chemical recycling and carbon capture technologies
- Increasing use of digital monitoring systems in process optimization
In February 2025, TCL USA announced a USD 200 Million investment in a West Virginia plant to produce maleic anhydride and specialty chemicals, with operations expected to begin in Q4 2025. Moreover, petrochemical demand in North America is driven by the packaging, construction, and automotive sectors. Continued growth is also supported by downstream chemical exports, proximity to end-markets, and the development of integrated refining and petrochemical hubs across the US.
Europe
Europe is transitioning toward climate-aligned petrochemical production, driven by regulatory frameworks under the EU Green Deal. Investments in low-emission feedstocks, specialty chemicals, and closed-loop systems are accelerating as producers adapt operations to remain compliant, competitive, and aligned with circular economy mandates and carbon reduction targets.
Key Trends:
- Expansion of hydrogen-based and electrified production systems
- Strong emphasis on ESG-compliant operations and traceability
- Shift toward high-margin, specialty petrochemical derivatives
- Adoption of chemical recycling and advanced recovery technologies
In May 2025, the Kassø e-methanol facility in Denmark was officially inaugurated, becoming the world’s first commercial-scale plant producing e-methanol using renewable power and carbon capture technologies. Moreover, demand stems from high-performance applications in automotive, pharmaceuticals, electronics, and food packaging. End-users prioritize traceability and low environmental impact, prompting the industry to develop value-added, sustainable solutions.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is a key center for petrochemical manufacturing and end-use growth, with countries expanding local production to enhance industrial resilience. In May 2023, BPCL announced a USD 5.95 Billion ethylene cracker project at its Bina refinery in India, targeting expanded production of ethylene, propylene, polyethylene, and polypropylene by FY 2027–28. Governments across the region support backward integration in polymers and chemicals, prioritizing feedstock diversification and infrastructure development.
Key Trends:
- Ongoing expansion of domestic ethylene, polypropylene, and aromatics capacity
- Development of automation-enabled petrochemical complexes
- Rising implementation of plastic waste regulations and circular policies
Demand across Asia-Pacific is broad-based, spanning construction, textiles, packaging, automotive, and electronics. Population growth, rising incomes, and urbanization continue to increase per capita consumption, while regulatory reforms and foreign investments are reshaping the structure of downstream petrochemical markets regionally.
Middle East and Africa
The Middle East is strengthening its position in value-added petrochemical manufacturing through integrated complexes and feedstock optimization. Africa is advancing selectively, focusing on refinery-linked chemical zones to support local industrialization and enhance access to fertilizers, plastics, and construction inputs for regional development.
Key Trends:
- Deployment of crude-to-chemicals and derivative park projects
- Expansion into methanol, ammonia, and urea production
- Exploration of green hydrogen and blue ammonia technologies
- Public-private partnerships in African countries for infrastructure upgrades
In June 2025, Algeria announced petrochemical and refining projects worth USD 7 Billion, aiming to raise hydrocarbon conversion rates to 50% by 2029, including new refineries and cracking units.
Also, regional demand centers include fertilizer chemicals in agriculture, building materials for infrastructure, and consumer goods packaging. Middle Eastern producers target export markets, while African countries are focused on meeting domestic demand growth.
Latin America
Latin America is strengthening its petrochemical production base through targeted investments in bio-based chemicals, ethylene, and gas-fed methanol. Key economies are aligning with sustainability goals by leveraging biomass, shale gas, and regional integration to reduce dependency on imports and increase value-added production capacity.
Key Trends:
- Expansion of bio-polymer production in Brazil using renewable feedstock
- Capacity upgrades in Mexico supported by USMCA trade incentives
- Infrastructure development near Vaca Muerta shale in Argentina
Demand is led by agriculture (fertilizers and films), consumer packaging, and construction materials. Increasing regional consumption and trade integration are encouraging localized production, enabling Latin America to serve domestic needs and selected export markets efficiently.
Sector Innovations and Technology Drivers:
- Process Automation and Digital Twins
Digital twins, virtual replicas of plants, are being used to simulate, predict, and optimize production performance in real-time. Operators gain insights into equipment wear and energy consumption, leading to significant cost savings.
- AI and Predictive Maintenance
AI-powered analytics support yield optimization, maintenance scheduling, and logistics planning. Advanced algorithms detect early signs of asset fatigue and recommend interventions before costly failures occur.
- Advanced Catalysis
Catalyst innovation is enhancing reaction selectivity, reducing by-products, and enabling lower-temperature operations. Companies are also using nanotechnology to develop next-generation catalytic converters for cleaner emissions.
- Carbon Capture and Utilization
CCU solutions are being deployed at scale in integrated petrochemical plants, particularly in the US and Europe. Captured CO2 is converted into polymers, synthetic fuels, or building materials, turning waste into value.
- Recycling and Circular Economy
Technologies such as pyrolysis, depolymerization, and solvent-based extraction allow for chemical recycling of mixed plastic waste. These processes deliver virgin-quality polymers, meeting growing demand for recycled content in consumer products.
Market Challenges and Risks:
- Feedstock and Price Volatility: Crude oil and natural gas prices continue to fluctuate due to geopolitical tensions, OPEC+ decisions, and speculative trading. This affects raw material costs, profit margins, and investment predictability for petrochemical plants.
- Capital Intensity and Long Payback Periods: The development of large-scale petrochemical plants involves significant capital expenditure and extended project timelines.
- Environmental and Regulatory Pressures: The industry is subject to stringent environmental regulations, requiring continuous upgrades and investments to ensure compliance with emissions, resource usage, and sustainability reporting standards.
- Workforce and Talent Constraints: There is a noticeable shortage of skilled professionals in process engineering, automation, and compliance, necessitating strategic efforts in workforce development, retention, and specialized skill enhancement.
- Global Supply Chain Disruptions: Port congestion, shipping container shortages, and geopolitical instability (e.g., Middle East tensions, trade restrictions) are impacting raw material flow and delivery schedules.
Strategic Insights for Stakeholders:
- Integrate Production Facilities: Combine refining and petrochemical operations to maximize feedstock flexibility and margin control.
- Invest in Net-Zero Tech: Adopt renewable energy sources, CCS systems, and green hydrogen inputs to future-proof operations.
- Localize Sourcing: Develop regional supply chains to reduce risk exposure and improve resilience.
- Leverage Data: Use AI, IoT, and cloud platforms to streamline supply chains, sales forecasting, and quality control.
- Differentiate Through ESG: Build brand equity and attract investors by aligning with ESG benchmarks and transparent reporting.
Conclusion:
- The petrochemical industry in 2025 is shaped by rising demand, innovation in key segments, and pressure to align with sustainability and digitalization goals. Key segments such as ethylene, polypropylene, aromatics, and methanol continue to expand, supported by infrastructure growth and regional diversification. Regional shifts and operational challenges require precise, forward-looking strategies.
- IMARC delivers actionable intelligence and tailored advisory to help companies navigate complexity, optimize performance, and achieve long-term growth in a competitive global landscape.
How IMARC Can Help:
IMARC Group offers data-driven insights and strategic support to businesses navigating the evolving petrochemical market. Our services help companies gain clarity on emerging trends, competitor activity, and investment feasibility.
Our capabilities include:
- Segment-specific market size forecasts
- Investment feasibility studies and ROI modeling
- Industry benchmarking and SWOT analysis
- Location-based opportunity mapping
- Go-to-market and regulatory strategy support
- Support for technology assessment and partner selection
Whether you are entering a new market, expanding capacity, or digitizing operations, IMARC helps you minimize risk and maximize growth potential.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
-(1)_11zon.webp)










