Pectin Manufacturing Cost Analysis: Gelling the Margins

What is Pectin?
Pectin represents a naturally occurring polysaccharide mainly extracted from cell walls of fruits (mainly from citrus peel and apple pomace). It is a soluble dietary fiber and a hydrocolloid with gelling, thickening, and stabilizing properties. It is mostly composed of galacturonic acid units. Chemical classification can be done by the degree of esterification, which affects functional performance in various formulations. Given its plant origin, biodegradability, and functional versatility, pectin finds numerous applications as a food ingredient and functional additive in foods, pharmaceuticals, and personal care.
Key Applications Across Industries:
Pectin is an industrially important carbohydrate with a wide range of applications in foods, pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and cosmetics. In the food industry, pectin is mostly known as a gelling agent in jams, jellies, marmalades, and fruit preserves, improving their texture and consistency. It has also found applications as a stabilizer/thickener in a host of dairy products, namely yogurt, drinking yogurt, and flavored milks, to name a few, by inhibiting whey separation and improving the mouthfeel of these products. In beverages, it can stabilize fruit pulp suspensions and increase viscosity without adding unwanted flavor.
In bakery and confectionery products, pectin is used in applications like fruit fillings, glazing, gummies, and soft candies, which offer structure with a controlled gel strength. Low-sugar and reduced-calorie food formulations increasingly rely on the application of pectin, since it can work effectively in low-sugar or sugar-free systems. Pectin contributes to the texture of sauces, dressings, and ready-to-eat meals by enhancing their water retention capacity.
Beyond food, pectin finds its applications in pharmaceuticals as an excipient in tablets and capsules, as a binder, or as a release modifier. Its biocompatibility and dietary fiber properties support digestive health applications in nutraceuticals. Pectin could be functionally used in personal care and cosmetic formulations for creams, lotions, and gels as a natural thickener and stabilizer agent. Besides this, pectin has applications in developing edible films and coatings used in food packaging for shelf-life extension by providing barrier protection and helping achieve packaging sustainability.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers:
The global pectin market reached a value of USD 1,142.5 Million in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 2,107.4 Million by 2033, at a projected CAGR of 7.0% during 2025-2033. The global drive for natural, plant-based, and clean-label ingredients across applications continues to propel the demand for pectin in various industries. Currently, one of the major drivers of this trend is the oncoming global demand for clean label food ingredients, where consumers are gravitating towards recognizable, minimally processed ingredients with natural origins. Pectin fits this bill due to its fruit origin and label-friendliness, making it increasingly popular compared to synthetic hydrocolloids.
Growth in the consumption of processed and convenience foods also drives demand for pectin. As new product developments with enhanced texture and stability unfold for jams, beverages, dairy, and ready-to-consume foods, pectin becomes an important player in formulation efficiency. Growing demand for low-sugar and low-calorie foods accelerates adoption further as pectin enables gelling and stabilization in low sugar-containing formulations.
Another huge driver is the trends in health and wellness. Pectin, being a soluble dietary fiber, helps in digestive health and cholesterol management. This consumption of pectin for food functionality in foods and nutraceuticals arises accordingly. Furthermore, aging populations and growing awareness of preventive healthcare drive demand for fiber-enriched products, which indirectly supports the consumption of pectin.
Sustainability considerations also drive the market. Production of pectin is done by fruit-processing by-products, like peels of citrus and apple pomace, in support of circular economy principles and waste valorization. This enhances appeal to environmentally responsible manufacturers.
Advances in extraction and modification technologies have enhanced pectin functionality, consistency, and range of application, making customization for specific end-uses possible. Moreover, food-processing industries growth in emerging economies and the rise in export volumes of processed foods are urging demand in the global marketplace. Altogether, clean-label preference, health trends, sustainability, and food industries growth is forming the basis of a stable growth in the global pectin market.
Case Study on Cost Model of Pectin Manufacturing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale pectin manufacturing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed pectin manufacturing plant in India. This plant is designed to manufacture 250 tons of pectin annually.
Manufacturing Process: Pectin manufacturing is the controlled extraction and purification process of pectic substances from such fruit-based raw materials as citrus peels and apple pomace, by-products of juice and food-processing industries. Manufacturing proper starts with raw-material preparation, in which citrus peels or apple pomace are washed to eliminate sugars, oils, and other impurities and then dried or partly dehydrated to stabilize the material. Cleaning of feedstock by milling increases the surface area and thereby ensures efficient extraction. Extraction is done by hot, dilute acidic treatment-commonly minerals or food-grade organic acids-under conditions of carefully controlled temperature and pH. This treatment dissolves pectin from the plant cell walls into the liquid extract. The slurry obtained is filtered to separate the insoluble solids from the pectin-rich solution. The extract then goes through clarification to remove fine particulates in order for purity and consistent quality to be ensured. Alcohol precipitation of the dissolved pectin, normally by addition of ethanol or isopropyl alcohol, precipitates as a solid mass. The resulting precipitate is washed several times to remove residual acids, sugars, and salts. After washing, the material is dried either in belt dryers or vacuum dryers to the desired level of moisture to preserve functionality. The dried pectin is then milled into a fine powder and blended in a way that the gel strength, degree of esterification, and viscosity are standardized. If the need arises, pectin may be chemically or enzymatically modified to produce high-methoxyl or low-methoxyl grades. Final tests on quality confirm purity, gel performance, particle size, and food-safety standards before packaging for either food, pharmaceutical, or industrial use.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
Raw Material Required:
The basic raw materials required for pectin manufacturing include:
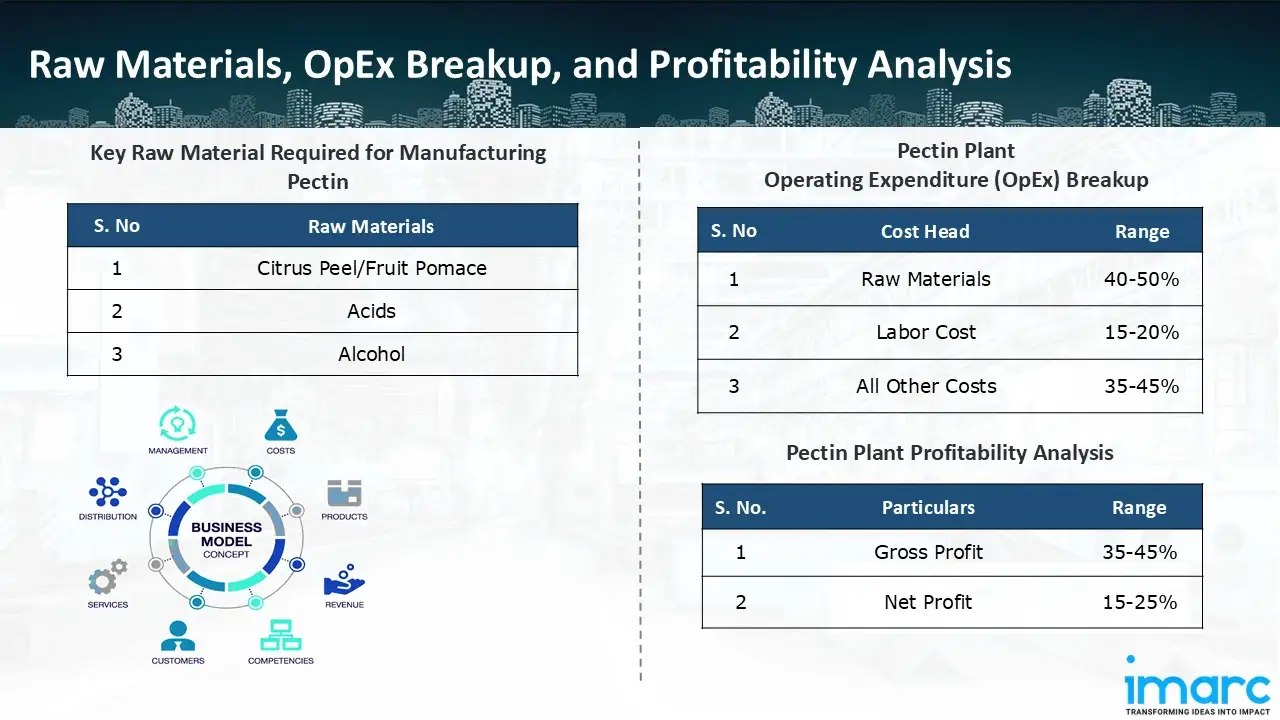
- Citrus Peel/Fruit Pomace
- Acids
- Alcohol
Machine Section or Lines Required:
- Extraction
- Filtration
- Precipitation
- Drying
- Milling
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. OpEx in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in pectin manufacturing plant ranges between 40-50%, labor cost ranges between 15% to 20%, and all other costs ranges between 35-45% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 35-45%, and net profit lie between the range of 15-25% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the pectin manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of manufacturing 250 tons of pectin annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In November 2024, Tate & Lyle declared that it had successfully acquired from J.M. Huber Corporation all of the issued share capital of (i) CP Kelco U.S.; (ii) CP Kelco China; and (iii) CP Kelco ApS, along with each of their respective subsidiaries, a major supplier of pectin, speciality gums, and other natural ingredients.
- In September 2023, Cargill announced the introduction of a new line of LM conventional (LMC) pectins that are suitable for products marketed with "organic" claims and have been developed using proprietary technology to give innovative texture.
Why Choose IMARC?
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104










