Steel Manufacturing Cost Analysis: Strength Built on Numbers
_11zon.webp)
What is Steel?
Steel is an alloy that consists of iron and carbon in addition to trace amounts of other elements like manganese, silicon, chromium, and nickel. The amount of carbon in steel is usually less than two percent and is an important factor in determining the strength, hardness, and ductility of steel. Steel is made by refining iron in a way that removes impurities and adjusts the composition of the alloy. The ability of steel to be cast, rolled, forged, and welded in addition to its high strength and durability makes it one of the most versatile materials used in industry.
Key Applications Across Industries:
Steel is a basic material in various industries because of its strength, malleability, and economic viability. In the construction industry, steel is widely used in the form of structural steel, beams, columns, reinforcement rods, bridges, and other infrastructure projects. The high strength and ability to withstand heavy loads make steel an essential material in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.
In the transport sector, steel is a key material in the automotive, railway, shipbuilding, and aircraft industries. Automakers use different types of steel in the manufacture of bodies, chassis, engines, and safety systems, striking a balance between strength and weight reduction. The railway industry uses steel for track laying, manufacturing train coaches, and signaling systems, while the shipbuilding industry uses specialized steel sheets for constructing ships and offshore platforms.
Steel is also used extensively in manufacturing and machinery. Industrial equipment, machinery, pipelines, pressure vessels, and heavy machinery rely on the mechanical properties and abrasion resistance of steel. In the energy industry, steel is used in power plants, oil and gas pipelines, wind turbine towers, and transmission lines.
Another significant application area is consumer products and appliances. Steel is utilized in domestic appliances, packaging (such as cans), furniture, and electrical enclosures. Its lengthy service life and recyclable nature add to its allure. Steel's wide range of applications demonstrates its flexibility in meeting a variety of structural, functional, and financial needs.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global steel market reached a value of USD 1,004.9 Billion in 2025. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 1,308.7 Billion by 2034, at a projected CAGR of 2.98% during 2026-2034.
The steel market is influenced by a set of macroeconomic, industrial, and structural drivers. Among the most important factors is the process of urbanization and infrastructure development, especially in the emerging markets. Urbanization and infrastructure development create a continuous demand for construction-grade steel.
Industrialization and growth in manufacturing activities also create a demand for steel. As countries industrialize, there is a growing demand for machinery, equipment, and industrial facilities that consume a lot of steel. The automotive and transportation sectors remain important demand drivers, especially as the production of vehicles moves towards increased safety and advanced steel grades.
Energy transition and the development of power infrastructure are becoming increasingly important demand drivers. Steel is a critical material for renewable energy projects like wind farms and solar panel mounting structures. Steel is also a critical component in traditional power infrastructure projects like power generation, transmission, and energy storage. Oil and gas infrastructure, although in transition, remains an important source of baseline demand.
Another major factor is the recyclability and use of steel in circular economy systems. Steel can be recycled again and again without any degradation in performance. This is a major factor in markets where resource efficiency and sustainability are emphasized.
Supply chain factors include technological advancements in steel production, including more efficient furnaces and better process control. This improves productivity and quality. Along with the growing global population and economic development, these factors cumulatively drive the global steel manufacturing market.
Case Study on Cost Model of Steel Manufacturing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale steel manufacturing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed steel manufacturing plant in India. This plant is designed to manufacture 500,000 tons of steel annually.
Manufacturing Process: The steel production process involves the treatment of iron-bearing materials to produce refined steel of specific chemical and mechanical composition. The steel production process starts with the iron-making process, where iron ore is reduced to obtain molten iron or solid metallic iron. In the blast furnace process, iron ore, coke, and limestone, a flux, are fed into a blast furnace, where high temperatures and reducing gases from the blast remove oxygen from the iron ore to obtain hot metal. Iron can also be produced in direct reduction processes, where sponge iron is produced and used in electric furnaces.
The second step in steel production is steel making, where impurities such as carbon, sulfur, and phosphorus are removed, and alloying elements are adjusted. In the basic oxygen furnace (BOF) process, molten iron is refined by blowing oxygen into the iron, oxidizing impurities such as excess carbon. In the electric arc furnace (EAF) process, steel scrap and/or direct reduced iron are melted with electrical energy.
After steel production, the molten steel is subjected to secondary refining, also referred to as ladle metallurgy. Various processes such as deoxidation, desulfurization, vacuum treatment, and alloying are performed as required.
The refined steel is then cast into semi-finished products using continuous casting machines, which yield slabs, blooms, or billets. These semi-finished products are then hot rolled or cold rolled to produce finished steel products such as plates, sheets, bars, and rods. Final processing may involve heat treatment, surface treatment, and inspection, depending on the requirements of the final product.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
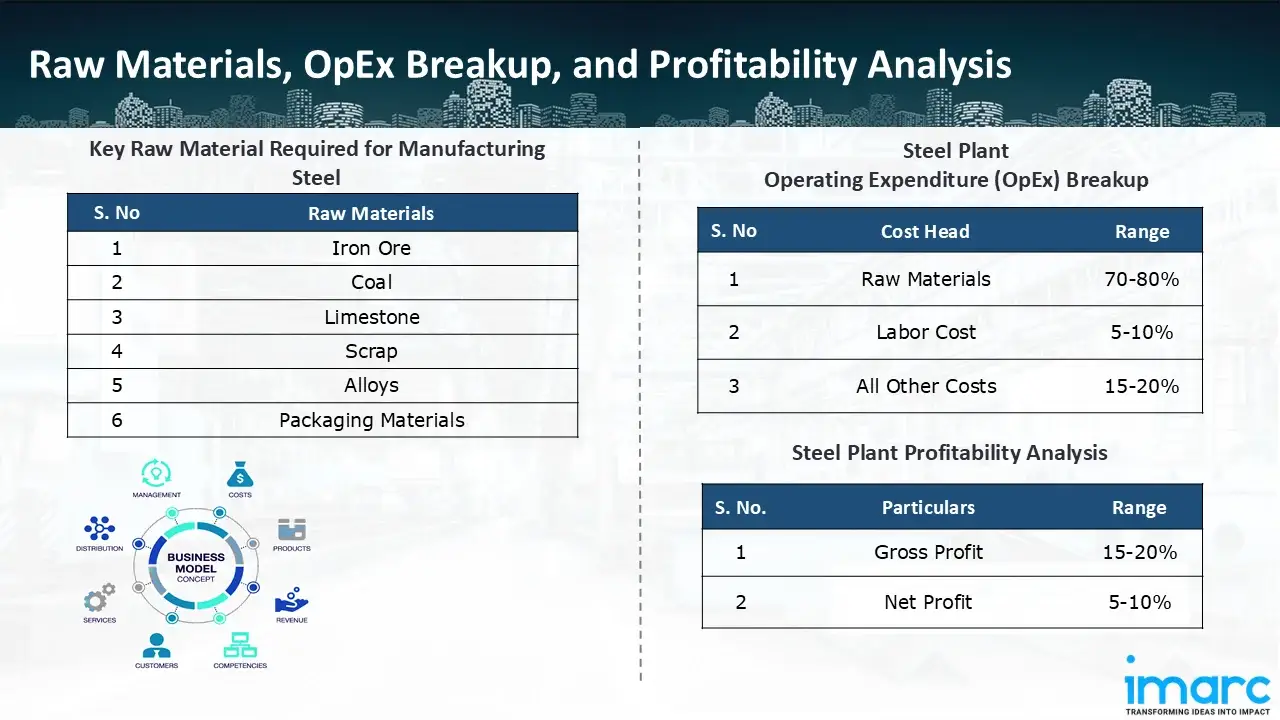
Raw Material Required:
The basic raw materials required for steel manufacturing include:
- Iron Ore
- Coal
- Limestone
- Scrap
- Alloys
- Packaging Materials
Machine Section or Lines Required:
- Blast Furnace
- Basic Oxygen Furnace
- Continuous Caster
- Rolling Mill
- Packing
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. OpEx in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in steel manufacturing plant ranges between 70-80%, labor cost ranges between 5% to 10%, and all other costs ranges between 15-20% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 15-20%, and net profit lie between the range of 5-10% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the steel manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of manufacturing 500,000 tons of steel annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In January 2026, SMS group has marked a crucial stride in its global expansion strategy with the official launch of its new manufacturing facility in Sanand, near Ahmedabad.
- In October 2025, Indian steel manufacturer Jindal Steel announced the commissioning of a new basic oxygen furnace (BOF) capable of producing three million tonnes annually at its Anguli factory in Odisha. As a result, the business is expanding the steel mill's annual capacity from 6 million tonnes to 9 million tonnes.
- In September 2024, Tata Steel announced the commissioning of the biggest blast furnace in India in Kalinganagar, Odisha. The Phase II extension at Kalinganagar will increase the site's capacity from 3 million tonnes per annum (MTPA) to 8 MTPA with a total expenditure of Rs 27,000 crore.
Why Choose IMARC?
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104










