How Government Policies Are Driving the India Vaccines Industry
.webp)
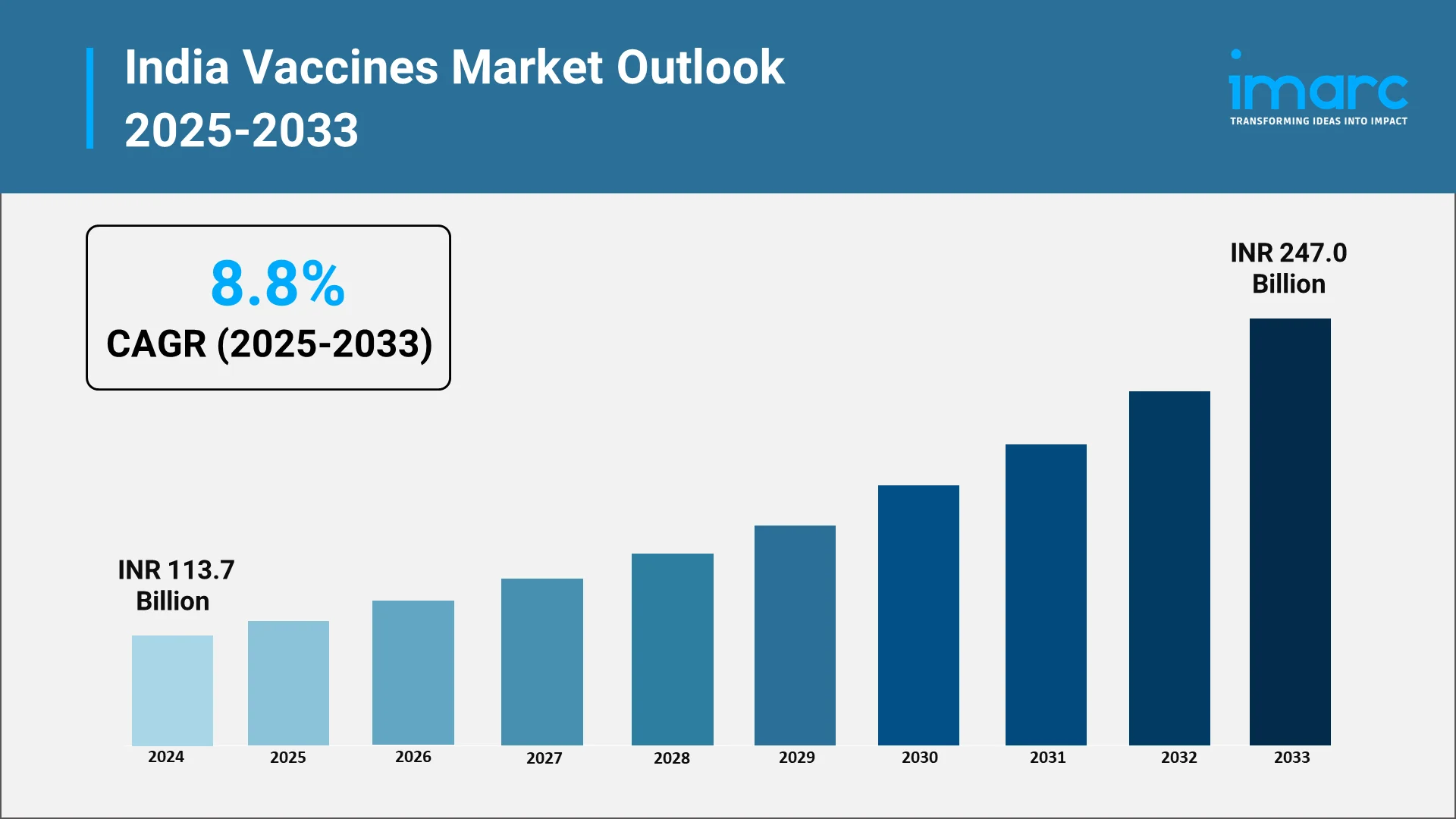
The Indian vaccines industry holds an unparalleled position globally, often celebrated as the pharmacy of the world due and its massive production scale and capabilities. It reached INR 113.7 Billion in 2024 according to IMARC Group and it is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.8% from 2025-2033. This status is not a matter of chance, but the result of decades of strategic planning, significant public-sector investment, and most importantly, proactive and comprehensive Government policies. These policies have effectively engineered a virtuous cycle, helping create a vast, reliable domestic market while simultaneously fostering an enabling environment for innovation, quality manufacturing, and global competitiveness.
The Government of India’s role extends beyond mere regulation; it acts as the single largest purchaser, a primary funding source for R&D, and a strategic facilitator for international collaboration, ensuring the sector’s continuous, robust growth.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
Large-Scale Immunization Programs: The Bedrock of Routine Vaccination Demand
The engine room of the Indian vaccines market is the guaranteed, continuous, and vast demand generated by the nation's public health commitments. Government-led immunization programs are the single most powerful driver, ensuring high routine vaccination coverage for both children and, increasingly, adults. This predictable demand volume is the foundation upon which the industry builds its capacity.
The Universal Immunization Programme (UIP)
The Universal Immunization Programme (UIP) is among the largest and most extensive public health campaigns globally. By committing to provide essential vaccines free of cost to millions of pregnant women and newborns every year, the UIP ensures a foundational, large, and non-volatile procurement market for domestic manufacturers. This guaranteed volume allows companies to confidently make long-term capital investments in scaling up production and adhering to international quality standards.
The Government's strategic expansion of the UIP—incorporating newer, often more complex and expensive vaccines like the Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) and the Rotavirus Vaccine—not only addresses crucial public health needs but also systematically broadens the market opportunity for sophisticated, next-generation vaccine manufacturers within the country.
Strategic Outreach and Demand Generation
To ensure equitable access and coverage, the Government launches focused, time-bound initiatives designed to reach the last mile. Campaigns such as Mission Indradhanush specifically target unvaccinated and partially vaccinated children and pregnant women in hard-to-reach areas. As of December 2024, Mission Indradhanush has achieved remarkable results, vaccinating a cumulative total of 5.46 crore children and 1.32 crore pregnant women across all phases.
By relentlessly chasing high coverage goals, the Government systematically converts potential public health need into realized vaccine uptake. These campaigns also enforce rigorous supply chain management, logistics, and cold chain maintenance, thereby strengthening the entire distribution infrastructure that the industry relies upon for domestic success and, critically for demonstrating capability to international buyers.
The digital health infrastructure, significantly boosted by the successful model of the CoWIN platform, is now being repurposed for routine immunization and broader health management through platforms like U-WIN. By December 2024, over 711 million Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA) had been created, enabling seamless integration of digital health records. This digitalization brings efficiency, accountability, and better inventory management, further stabilizing the demand signal for manufacturers.
Market Size & Growth Opportunity: Catalyzing India’s Global Leadership
Government policies have been instrumental in transforming India from a recipient nation into a global manufacturing hub for vaccines, earning its reputation as a global leader in both volume and affordability.
Policy Support for Global Manufacturing Prowess
India's early commitment to self-reliance and indigenous manufacturing through deliberate policy choices has led to its current strength. Indian manufacturers now supply a substantial majority of the global vaccine needs procured by major international health bodies, including UNICEF, the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), and Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance. This global penetration is facilitated by the Government's support in achieving pre-qualification by the World Health Organization (WHO), a gold standard that opens international markets.
Financial Incentives and Investment Promotion
Policies like the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme are specifically designed to catalyze growth in the pharmaceutical and biotech sectors, with a significant positive spillover effect on vaccine manufacturing. By offering financial incentives based on incremental production and sales, particularly for high-value and new-generation biological products, the PLI scheme encourages both domestic and foreign companies to make substantial investments in setting up or expanding high-tech manufacturing facilities within India. This directly promotes scale, reduces manufacturing costs, and enhances the nation's competitive edge globally.
Furthermore, supportive policies related to Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and easing business operations make India an attractive destination for global vaccine companies seeking to establish manufacturing or research bases in the region.
Fueling Innovation: New Vaccine Formulations Emerging
The future competitiveness of the Indian vaccines industry rests on its ability to transition from being primarily a volume producer of traditional vaccines to a leader in developing cutting-edge formulations. Government support, particularly in funding and regulatory streamlining, is accelerating the emergence of new generation vaccines for diseases such as influenza, dengue, Human Papillomavirus (HPV), and those utilizing novel platforms like mRNA and viral vectors.
Directed R&D and Academic Collaboration
Key Government bodies, notably the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) and the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), play a pivotal role in channeling research grants and public funding into critical areas of vaccine science. This includes supporting translational research, product development consortia, and establishing Centers of Excellence in vaccinology. By de-risking the early stages of R&D, the Government encourages private sector participation in high-risk, high-reward projects.
Regulatory Streamlining and Crisis Acceleration
The experience gained during recent public health crises demonstrated the Government’s capacity to create accelerated and adaptive regulatory pathways for rapid vaccine development, testing, and approval. This flexibility, when applied judiciously, encourages manufacturers to fast-track their novel formulations. Furthermore, the commitment to indigenization pushes companies to develop domestic solutions for public health needs, leading to significant advances in vaccines that are thermally stable and adapted for tropical climates.
Improving Export Quality and Domestic Adoption
The success in developing new formulations directly translates to improved exports by providing high-value products to developed and emerging markets, further enhancing India’s global reputation. Domestically, the integration of these sophisticated, new vaccines into the national health system, even if phased, ensures that the domestic population benefits from the latest advancements, creating a sophisticated and continuously evolving market.
Growth in Private Vaccination Clinics and Pharmacy Tie-ups:
While Government procurement dominates, robust regulatory and infrastructural support is simultaneously enabling the growth of a sophisticated private market catering to non-UIP and adult vaccination needs, especially in urban and semi-urban areas.
Expanding Access to Adult and Travel Vaccines
The private sector, comprising dedicated vaccination clinics, large hospital chains, and increasingly, strategic pharmacy tie-ups, provides faster access to specialized vaccines such as seasonal influenza shots, travel vaccines, zoster, and adult-specific pneumococcal vaccines. This growth is facilitated by clear regulatory guidelines regarding vaccine storage, prescription, and administration protocols for private providers.
Formalizing Private Healthcare Integration
Government policies that acknowledge and integrate the private sector into the broader vaccination strategy—particularly for non-UIP vaccines and during booster campaigns—are key. The digital backbone established during large-scale campaigns is a foundational asset that helps the private sector manage inventory, track beneficiaries, and adhere to standardized clinical and reporting procedures. This formality increases consumer trust and facilitates faster uptake of adult and optional vaccines. The rising awareness among urban populations about preventive healthcare, coupled with Government health communication campaigns, also fuels this segment’s growth.
Top Companies in India Vaccines Market: Policy Beneficiaries and Drivers
The policy environment has nurtured a set of globally competitive domestic companies that form the core of India’s vaccine production capability. These firms are both the beneficiaries of the supportive Government policies and the primary drivers of the sector's growth.
These key players leverage large-scale, cost-efficient manufacturing, strong R&D capabilities, and deep market access knowledge:
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Sanofi Aventis
- Serum Institute of India
- Panacea Biotec
- Pfizer
- Novartis
- VHB Lifesciences
- Zydus Cadila
- MSD
The success of these companies is intrinsically linked to policies that provide a large domestic purchase guarantee, facilitate global quality certifications (WHO pre-qualification), and offer financial incentives for capacity expansion. Their ability to deliver high-quality, high-volume, and affordable vaccines is what truly secures India’s position as a global vaccine leader.
Conclusion:
The evolution of the India vaccines industry is a compelling case study in policy-driven industrial and public health success. The Government has strategically engineered demand through its massive immunization programs, minimized risk for manufacturers through guaranteed procurement, and incentivized future growth through R&D funding and schemes like the PLI. This proactive approach has not only met the critical public health needs of its own vast population but has also cemented India’s strategic importance as a reliable, high-volume supplier to the world. As the industry matures, the focus will continue to shift towards high-end innovation, ensuring India’s sustained leadership in the global fight against infectious diseases.
Choose IMARC Group for Unmatched Expertise and Strategic Guidance in the India Vaccines Industry:
Leverage IMARC Group’s deep domain knowledge for strategic direction in the evolving Indian vaccines sector.
- Market Insights: In-depth analysis of domestic and global vaccine demand, covering UIP procurement, private market growth, exports, product types, technologies (mRNA, viral vector), and logistics.
- Growth Forecasting: Intelligence on pediatric and adult immunization, R&D pipelines (Dengue, HPV), and opportunities from global health initiatives.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Assessment of major players like Serum Institute and Bharat Biotech, focusing on capacity, pipelines, and partnerships.
- Policy & Regulation: Guidance on incentives (PLI), regulatory pathways, and government policies shaping market access.
- Consulting Solutions: Tailored support for scale-up, market entry, tenders, and distribution optimization.
- Trusted Partner: IMARC empowers pharma firms, investors, and health agencies with actionable insights to reinforce India’s global vaccine leadership.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










