How Big will the Japan Warehouse Robotics Market be by 2033

Introduction to the Japan Warehouse Robotics Market:
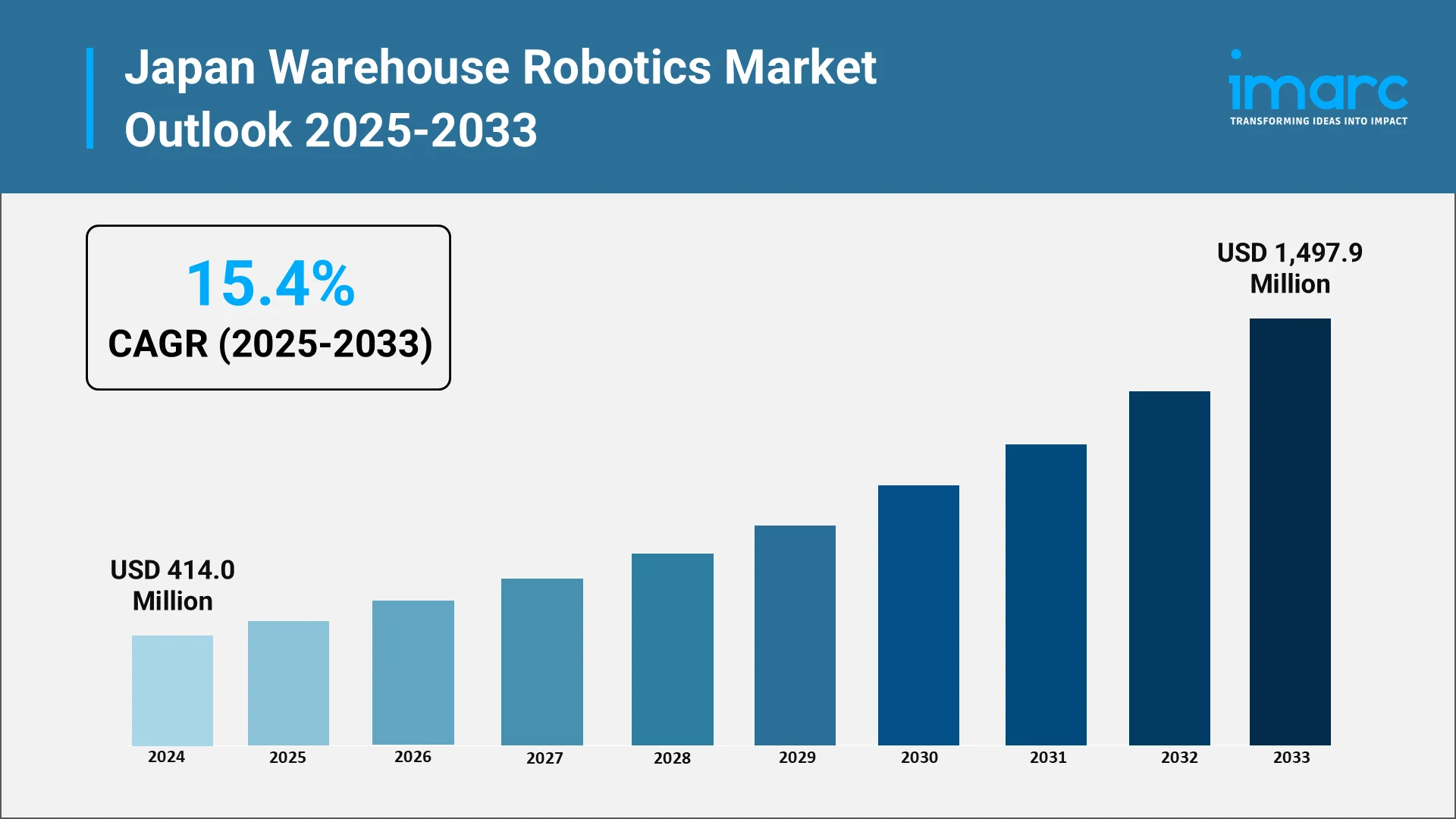
The Japan warehouse robotics market is a highly dynamic and rapidly expanding segment of the global automation industry. The market, valued at USD 414.0 Million in 2024, is on a sharp growth trajectory. Its growth is fueled by critical domestic factors, including a severe labor shortage, the rapid expansion of e-commerce, and Japan's strategic position as a world-leading robotics manufacturer. This exceptional growth is underpinned by Japan's unique demographic challenge: an aging population (over 28% of the total population is over 65) and a declining workforce. This creates an urgent need for automation across all sectors, especially logistics. Simultaneously, Japan e-commerce market is booming, valued at USD 258.0 Billion in 2024 and projected to grow to USD 692.8 Billion by 2033 (a CAGR of 11.02%). This digital shift demands the precision and speed that only advanced robotic solutions can provide.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
Japan is exceptionally positioned to capitalize on this demand, as it is the world's leading robot manufacturing country, producing 46% of industrial robots globally. This confluence of technological strength, a pressing need for operational efficiency, and strong government backing positions the Japan warehouse robotics market as a critical component of the nation's economic future.
Current Market Landscape and Adoption Trends:
The current Japanese warehouse robotics landscape is defined by technological innovation, diverse solutions, and accelerating adoption across sectors. The market utilizes a comprehensive range of systems, including automated guided vehicles (AGVs), autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), robotic arms, and specialized picking and sorting systems—all designed to replace manual labor and enhance operational efficiency.
The competitive landscape is robust, featuring both global powerhouses and domestic leaders. Japanese heavyweights include Fanuc and Yaskawa, two of the Big 4 industrial robot manufacturers worldwide. They compete alongside major international players like ABB Ltd., KUKA AG, and Omron Corporation, alongside Japanese firms such as Daifuku Co. Ltd. and Kawasaki Heavy Industries, which drives continuous innovation.
Adoption trends show strong momentum led by e-commerce and third-party logistics providers, but also by the automotive, electronics, and pharmaceutical sectors. The cold chain logistics segment is an increasingly high-value application, as robotic systems address the difficulties of operating in temperature-controlled environments, reducing human exposure to harsh conditions.
Recent market activity highlights accelerating innovation and strategic partnerships. For example, in July 2024, Sumitomo Corporation and Dexterity Inc. formed a new joint venture, Dexterity-SC Japan, focusing on AI-powered intelligent robotic solutions for logistics. Furthermore, the e-commerce drive is evident with Ocado Group and AEON's plan to construct a third Customer Fulfilment Centre (CFC) in Saitama Prefecture by 2027, following earlier launches in Chiba and Hachioji. These expansions demonstrate a commitment to using advanced automation to meet fast-delivery consumer expectations.
Market segmentation shows that while AGVs remain dominant for structured material handling, AMRs are rapidly gaining traction due to their flexibility and adaptability in dynamic warehouse environments. This adoption is being driven by the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities, enabling sophisticated autonomous navigation and real-time operational monitoring.
Key Factors Driving Growth in Warehouse Robotics:
The market's significant growth is propelled by powerful, mutually reinforcing economic and structural factors:
- E-Commerce Expansion and Fulfilment Demands
The massive growth of Japan's e-commerce sector creates complex fulfilment challenges. The need to process vast numbers of small, diverse orders with high speed and accuracy is pushing demand for intelligent robots capable of item recognition, real-time sorting, and autonomous movement. This demand is further intensified by the shift toward mobile commerce, which accounts for over 50% of all e-commerce transactions.
- Demographic Challenges and Workforce Transformation
Japan's aging population reduces the available workforce while simultaneously increasing labor costs, strengthening the economic case for automation. Robotics solutions allow companies to maintain operational efficiency and competitiveness despite the demographic constraints and the difficulty in finding skilled staff for logistics roles.
- Industry 4.0 Integration and Technological Advancement
The adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, including AI, machine learning, and advanced sensor and vision systems, has dramatically improved the capabilities and cost-effectiveness of warehouse robotics. These innovations enable robots to perform more complex tasks and integrate seamlessly with existing warehouse management systems (WMS).
- Cold Chain and Temperature-Sensitive Logistics
The increasing demand for temperature-sensitive products, such as pharmaceuticals and fresh food, has created a specialized need for highly efficient robotic systems in cold storage. Automation is often a more viable solution than human labor in these demanding, freezing environments, delivering both operational and safety benefits.
- Cost Efficiency and Return on Investment
The economic value proposition is strengthening as robotics technology costs decline while labor costs rise. Robotic systems enable warehouse operations to be more flexible, require less space per volume of goods, reduce product damage, and lower long-term operating expenses, ensuring a strong Return on Investment (ROI).
Government Support and Technological Advancements:
Japan's technological advantage is strongly supported by comprehensive government policy and a world-class R&D infrastructure.
- Government Policies and Strategic Initiatives
The Japanese government actively promotes robotics adoption through strategic programs. The "New Robot Strategy" (2016-2020) and the Robotics for Social Transformation Promotion Plan (2019) aim to use robot technology to solve social issues—specifically the labor crisis—and achieve a sustainable economy. These initiatives position robotics as a core technology for the government's Society 5.0 vision, which seeks a technology-enabled social transformation.
- Financial Support and Investment Programs
Substantial public funds are committed to robotics R&D and deployment. Key investments include hundreds of millions of dollars appropriated for robotics-related projects across manufacturing, nursing, and infrastructure. Furthermore, the government focuses support on creating a "robot-friendly" environment in key sectors like logistics warehouses, offering various national and local support systems to reduce barriers to adoption.
- Technological Innovation and Breakthroughs
Japan's leadership in robotics is driving continuous innovation. Advancements in articulated arms, AMRs, and AGVs for heavy tasks are increasing demand. The integration of advanced sensors, machine learning, and AI has fundamentally improved robot performance, enabling greater precision and reliability. Furthermore, new business models like Robot-as-a-Service (RaaS) are gaining traction, allowing businesses to reduce capital costs and increase accessibility to advanced automation.
- Regulatory Framework and Standards Development
Japan maintains a progressive regulatory environment. A New International Standard for the Safe Operation of Service Robots, originating from a Japanese proposal, was issued in November 2023, and automated delivery robots began operating on public roads in April 2023. This proactive stance on establishing global standards for robotics ensures rapid deployment and commercialization.
Market Size Forecast and Projections to 2033:
The Japan warehouse robotics market is set for exceptional, sustainable growth, driven by deep structural factors and continuous technological advancement.
- Market Size and Growth Trajectory
Projections indicate the Japan warehouse robotics market is anticipated to reflect a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.4% during the forecast period (2025-2033). This strong momentum is projected to continue, with the market reaching will reach USD 1,497.9 Million in fiscal year 2033. This strong consensus among independent market analyses reinforces the long-term confidence in the market's expansion.
- Segment-Specific Growth Projections
Growth is not uniform across all technologies:
- The autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) segment is a key growth driver, holding a significant market share in 2024. Their flexibility and AI-based navigation make them ideal for dynamic, high-speed e-commerce fulfilment environments.
- Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) also show substantial growth globally, reflecting their continued importance in high-volume, fixed-route material handling in large-scale warehouses and manufacturing facilities.
- Integration with Broader Logistics Automation
Warehouse robotics growth is part of a larger, systemic change in Japan's logistics sector. The overall logistics automation market size in Japan was USD 5 Billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 17.6 Billion by 2033 (15.1% growth rate). This comprehensive automation encompasses robotics, WMS, and supply chain integration platforms, working together to deliver end-to-end operational improvements.
Future Opportunities and Strategic Outlook:
The long-term outlook for the Japan warehouse robotics market is highly positive, driven by several key future opportunities:
- Emerging Technology Integration Opportunities
The ongoing integration of AI and machine learning will drive the next wave of innovation, enabling sophisticated automation capabilities like adaptive task allocation and predictive maintenance. This advancement will be further enhanced by the widespread use of collaborative robots (cobots) for precision tasks alongside human workers.
- Business Model Innovation and Service Delivery
The increased adoption of the robot-as-a-service (RaaS) model is a critical opportunity. By reducing significant upfront capital costs, RaaS increases accessibility for small and medium-sized enterprises, substantially expanding the addressable market and accelerating overall adoption rates.
- Cold Chain and Specialized Logistics Expansion
The temperature-controlled logistics segment, particularly for pharmaceuticals and fresh food, will be a high-growth area. The stringent requirements for precision, traceability, and reliability in these segments align perfectly with advanced robotics capabilities, creating a high-value, defensible market niche.
- E-Commerce Fulfilment Center Transformation
The continuous construction and technological upgrades of large-scale automated fulfilment centers, such as those planned by AEON and Ocado, will serve as powerful demonstration effects, validating the economic and operational benefits of robotics and accelerating broader market adoption across the entire logistics sector.
- Sustainability and Environmental Performance
Warehouse robotics contributes to corporate sustainability goals. Robotic warehouses use less space per volume of goods, reduce energy consumption, and limit product damage. This alignment with environmental performance targets provides an additional, compelling value proposition for investment.
The long-term outlook remains exceptionally positive. The convergence of demographic imperatives, e-commerce growth, and sustained government support creates a multi-decade opportunity. The transformation of Japanese logistics through warehouse robotics is not just a technological change; it is a fundamental reimagining of the supply chain, positioning the country as a global exemplar for advanced automation.
Choose IMARC Group to Automate Your Success in the Japan Warehouse Robotics Market—We Offer Unmatched Expertise and Core Services:
- Data-Driven Market Research: Deepen your knowledge of the market size, growth drivers (e-commerce surge, aging workforce), and technological adoption across key segments like Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs), Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), and Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS).
- Strategic Growth Forecasting: Predict emerging trends in logistics automation, from the proliferation of 'Robot-as-a-Service (RaaS)' and AI-driven picking systems to the integration of robotics within cold chain logistics and cross-border fulfilment centers.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Analyze the competitive landscape, review the product pipelines of local giants (Fanuc, Yaskawa, Daifuku), and monitor breakthroughs in human-robot collaboration (Cobots) and vision-guided robotics tailored for high-mix, low-volume Japanese operations.
- Policy and Infrastructure Advisory: Stay one step ahead of government incentives (Industry 4.0/Society 5.0), local regulatory paradigms, and the required capital expenditure for next-generation warehouse build-outs and retrofitting existing facilities.
- Custom Reports and Consulting: Get tailored insights geared to your organizational objectives—be it market entry strategy, identifying potential M&A targets among domestic technology providers, or optimizing your supply chain's response to Japan's relentless fulfillment speed expectations.
For more details, click: https://www.imarcgroup.com/japan-power-electronics-market
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










