Does the Tobacco Market still have the Power to Shape Modern Infrastructure?

Introduction:
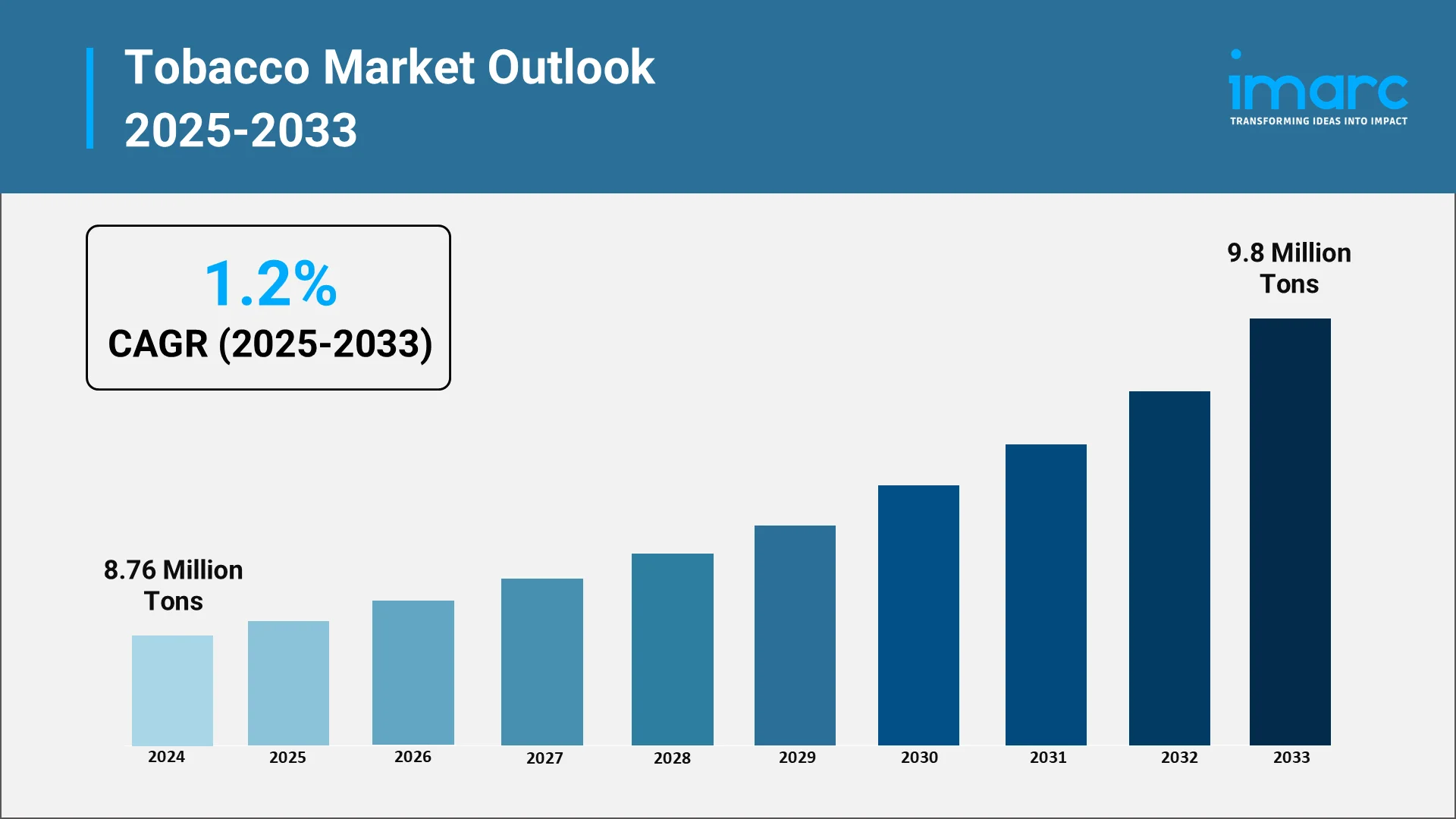
The tobacco industry has long been a cornerstone in world trade and consumer culture, shaping the courses of economies, employment landscapes, and industrial practices for centuries. Even in today's world, with growing awareness regarding health and sustainability, tobacco remains an imposing force in global commerce. The global tobacco market size reached a volume of 8.76 Million Tons in 2024, and the market is expected to reach 9.8 Million Tons by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 1.2% during 2025–2033. This sustained growth underscores the sector’s enduring significance despite intensifying regulatory scrutiny and health-driven shifts in consumption. Tobacco continues to influence agricultural practices, logistics, and manufacturing systems extending well beyond the ambit of consumer goods. Such a long, interlinked value chain from cultivation right to packaging reflects the resilience and adaptability of this sector in view of changing regulations and consumer preferences. Whether the Tobacco Market is still powerful in setting up modern infrastructure is not only a matter of consumption patterns but also its embedded role in global systems that sustain trade, technology, and employment.
Its influence is long-lived through incorporation into vast supply chains, agricultural innovation, and financial networks. Modern infrastructure has, in many ways, evolved alongside the trade in tobacco, which through history has required advances in logistics, technologies of processing, and systems of distribution. Today, its visibility has been diminished in developed markets through regulation and public health campaigns, but in developing economies, the presence remains significantly structural. It supports millions of livelihoods, financing government revenues and sustaining crucial parts of the industrial and agricultural frameworks.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
The Role, Impact, and Benefits of Tobacco in the Consumer Goods Industry:
Tobacco has long been more than a consumer product, it has functioned as a driver of economic and industrial development. The modern consumer goods industry, heavily reliant on brand loyalty, efficiency in distribution, and product differentiation, owes part of its evolution to tobacco companies. Their pioneering efforts at branding, packaging design, and consumer engagement helped lay the foundation for modern marketing. In a recent example, major tobacco companies have begun using digital tools such as NFTs, online gaming, and virtual avatars to promote products and engage younger audiences, highlighting how the industry continues to influence modern advertising strategies. Before tobacco products became regulated commodities themselves, they were among the first to adopt large-scale advertising, celebrity endorsements, and emotional marketing strategies, tools now standard across the consumer goods sector.
From a manufacturing perspective, tobacco processing introduced techniques focusing on precision, consistency, and scalability, which afterward found applications in food, beverage, and pharmaceutical production. Packaging innovations stemming from the tobacco industry, such as vacuum sealing and foil lining, set standards for product preservation and presentation. Even today, several global packaging companies trace their technological advancements back to innovations developed initially for tobacco products.
The economic benefits go well beyond the consumer himself. Tobacco farming forms the basis of extensive agricultural networks, providing a source of employment for farmers, laborers, and distributors. The industry supports other industries linked to fertilizers, paper, logistics, and advertising, to name a few. In many developing countries, the tobacco trade continues to provide a source of assured income for smallholder farmers who depend on the commercial value of the crop. Its high export potential has traditionally stabilized foreign exchange earnings and national revenues in countries with limited industrial diversification.
Key Growth Drivers in the Global Tobacco Market:
The global tobacco industry continues to evolve through innovation and diversification, adapting to changing consumer preferences and regulatory challenges. Product innovation remains central, with companies expanding their portfolios to include smokeless tobacco, e-cigarettes, and heat-not-burn devices. In 2025, Japan Tobacco International (JTI) announced the expansion of its Ploom X Advanced device across multiple European markets, emphasizing its commitment to smoke-free innovation and aligning with growing demand for reduced-risk products. These alternatives cater to modern consumers seeking convenience, reduced odor, and perceived lower health risks. Strong brand loyalty further sustains the market, as decades of trust and familiarity help leading brands retain dominance. Additionally, digital marketing and consumer engagement strategies have become vital tools for maintaining brand presence in a highly regulated advertising environment.
Emerging markets in Asia, Africa, and Latin America serve as major growth engines, supported by urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and shifting lifestyle trends. In many of these regions, tobacco consumption retains social and cultural significance, ensuring steady demand despite health awareness campaigns and stricter policies. Technological advancements also play a crucial role—automation, data analytics, and enhanced quality control systems have streamlined production and reduced costs. This continuous focus on efficiency and adaptability enables the industry to maintain profitability and global reach, even amid mounting regulatory and societal pressures.
Regulatory Framework and Policy Landscape in the Tobacco Industry:
Stringent regulations on tobacco promotion, tobacco packaging, and taxation have reshaped the industry's operating environment. Advertising bans and plain packaging laws have limited traditional marketing channels, pushing companies to innovate and diversify. In 2025, Australia tightened its tobacco control laws further by introducing the world’s first standardized packaging for e-cigarettes and vaping products, reinforcing its commitment to reduce nicotine appeal among youth and setting a new global benchmark for regulatory enforcement. As a result, major tobacco players are focusing on reduced-risk products (RRPs) like e-cigarettes and heat-not-burn devices, alongside sustainability and corporate social responsibility initiatives. Enhanced traceability and environmental compliance have also become central, with companies strengthening supply chain transparency and adopting ethical sourcing practices to meet global standards.
In addition, agricultural sustainability programs are increasingly influencing tobacco cultivation. Governments and manufacturers are collaborating on soil conservation, crop rotation, and reduced pesticide use to align with international agricultural frameworks. Such initiatives not only support environmental goals but also contribute to rural development by improving farming infrastructure and providing training to growers. While regulatory compliance remains complex, it has driven the industry toward stronger governance, operational efficiency, and technological integration. These transformations have modernized the tobacco sector, making it more resilient and better equipped to meet evolving market and environmental demands.
Government Support / Initiatives for the Tobacco Market:
Despite the global momentum towards tobacco control, many governments continue to support aspects of the industry due to its economic importance. Tobacco is a major contributor to tax revenues, employment, and export earnings and thus forms an important part of the national budgets of many countries. Therefore, public policies most often balance carefully between public health objectives and economic dependencies.
In some developing countries, governments improve infrastructure by constructing irrigation systems, rural roads, and processing facilities in the areas that grow tobacco. This facilitates local economic growth, efficiency in logistics, and a better export capacity. Whereas global health organizations are calling for reduced dependence on tobacco, national policies in some regions still integrate the crop into a broad agricultural and industrial development plan.
Top Tobacco Companies of the World:
The world’s leading tobacco companies have evolved from traditional cigarette manufacturers into diversified global conglomerates with far-reaching influence. Their enduring success stems from their ability to anticipate regulatory and consumer shifts, invest in product innovation, and sustain vast global supply and distribution networks. In August 2024, Philip Morris International announced a US $232 million investment to expand production of its “ZYN” nicotine pouches at its Kentucky facility, underscoring the industry's pivot toward next-generation nicotine products and reduced-risk alternatives. Operating across multiple continents, these corporations employ millions while engaging with intricate ecosystems of suppliers, retailers, and logistics partners. Beyond tobacco sales, their strategic vision has expanded to include next-generation nicotine delivery systems, sustainable farming practices, and energy-efficient production processes, positioning them as pioneers in industrial modernization and responsible manufacturing.
Driven by intense competition, the industry has seen a wave of consolidation and strategic partnerships aimed at achieving economies of scale and greater market adaptability. Mergers have enabled tobacco companies to optimize operations, enter new geographies, and strengthen resilience amid shifting global demand. Their large-scale resources allow for deep investments in R&D, digital transformation, and sustainability initiatives, further embedding them in the broader narrative of industrial innovation. Meanwhile, strong brand management and consumer engagement strategies emphasizing quality, packaging innovation, and product diversification have helped these companies maintain brand equity despite strict advertising restrictions. In doing so, they have influenced global marketing practices and set new benchmarks across the fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) landscape.
Opportunities and Challenges in the Global Tobacco Market:
The modern tobacco industry operates within a landscape shaped by both opportunity and constraint. Shifting consumer preferences and rapid technological advancement are creating new avenues for growth, even as regulatory scrutiny and public health concerns continue to intensify. Innovation and diversification remain central to industry strategy. The rise of alternative products such as heated tobacco, e-cigarettes, and other nicotine delivery systems marks a significant shift toward reduced-risk consumption. According to reports, the World Health Organization recently warned that the industry is targeting youth with these products via flavours and digital marketing as it pivots away from conventional cigarettes. These innovations not only meet evolving consumer expectations but also utilize the sector’s well-established production and distribution networks. Furthermore, the digital transformation of global commerce has opened new pathways for engagement through data analytics, personalized marketing, and integrated e-commerce platforms, allowing companies to maintain relevance in a changing marketplace.
However, the challenges confronting the industry are deeply interlinked. The declining social acceptance of smoking, coupled with tightening health regulations, compels firms to strike a delicate balance between profitability, ethics, and public image. Climate change and labor issues further complicate agricultural sustainability, urging diversification to reduce economic dependence on tobacco farming. As the industry transitions from conventional manufacturing toward research-driven product innovation, it is poised to influence wider industrial practices in technology, logistics, and production efficiency. The tobacco sector’s impact extends beyond consumption—it remains embedded in the global framework of trade, agriculture, and manufacturing. Despite mounting ethical and policy pressures, its historical adaptability and commitment to innovation ensure it continues to shape modern industrial and commercial systems.
Empower Your Decisions with IMARC’s Global Tobacco Market Insights:
For comprehensive, data-driven intelligence into the evolving tobacco industry, IMARC Group stands as a trusted partner, delivering actionable insights that support innovation, regulatory compliance, and strategic decision-making across traditional and next-generation product segments.
- Extensive Market Coverage: IMARC’s research spans the entire tobacco value chain, from raw leaf production and manufacturing processes to emerging categories such as heated tobacco, e-cigarettes, and nicotine pouches, offering clients a 360° perspective on market transformation and diversification trends.
- Reliable Forecasting and Strategic Outlook: Leveraging advanced forecasting models and real-time analytics, IMARC integrates global regulatory shifts, public health initiatives, and consumer behavior dynamics to provide accurate projections that guide product development and market entry strategies.
- In-Depth Competitive Landscape: Our reports deliver detailed assessments of leading industry players including Philip Morris International, British American Tobacco, Japan Tobacco, and Imperial Brands, analyzing their innovation pipelines, product portfolios, sustainability goals, and strategic partnerships to help stakeholders benchmark performance and identify competitive advantages.
- Regional and Sectoral Insights: IMARC’s granular analysis covers consumption patterns and policy environments across regions, from traditional tobacco markets in Asia-Pacific and Africa to rapidly evolving alternative product segments in Europe and North America, enabling clients to pinpoint growth opportunities and risk factors.
- Policy and Innovation Intelligence: We continuously monitor international tobacco regulations, harm-reduction policies, and R&D advancements shaping the future of nicotine delivery systems, offering clarity on how the industry is adapting to sustainability and public health objectives.
- Trusted Global Expertise: With deep analytical capabilities and a commitment to delivering precision-driven intelligence, IMARC empowers clients to navigate the global tobacco landscape with confidence, transforming data into strategic advantage in an era of rapid industry evolution.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










