How the 3D Printing Market is Shaping the Global Manufacturing Industry: Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities

Introduction:
The 3D printing industry is currently experiencing a revolutionary growth that has had a radical change on the manufacturing operations within the industries of the world. The technology is also referred to as additive manufacturing (AM), and it is the way to create three-dimensional objects by adding layers to the digital model, thereby providing unprecedented flexibility in both design and production. The 3D printing sector of the world has become a pivotal source of innovation enabler, efficiency, supply chain resilience, and competitive edges to organizations as small-and-medium-sized as small businesses to Fortune 500 organizations.
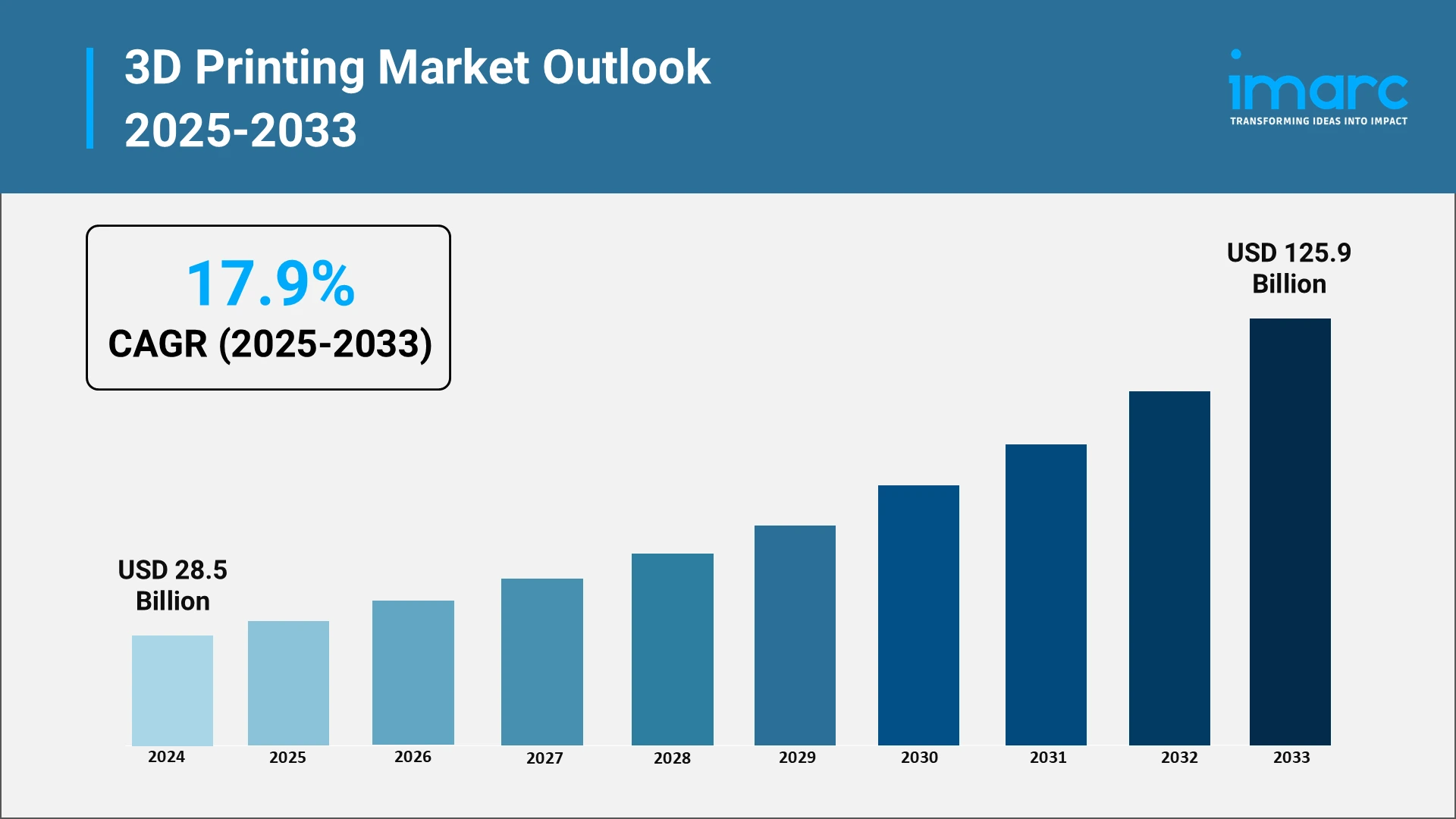
Recent market intelligence will signify exquisite growth paths of the sector. In 2024, the world 3D printing market will reach USD 28.5 Billion. This market will reach USD 125.9 Billion by 2033 with a CAGR of 17.9% in the 2025- 2033 period. This speed is an indication of how the technology is changing into a prototyping tool and a manufacturing solution that is ready to produce and deliver tailored, complicated parts at a reasonable cost.
The strategic significance of the 3D printing market is not restricted to the economic factors. The technology helps manufacturers to overcome the major challenges that include the vulnerabilities in the supply chain, the need to be sustainable, and the increasing pressure on mass customization. Additive manufacturing is a way forward to a more resilient, responsive, and responsible production system as organizations find their way in an increasingly complex global environment with geopolitical tensions, environmental regulations, and rapid technological change.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
The Role, Impact, and Benefits of 3D Printing in the Manufacturing Industry:
3D printing has fundamentally altered traditional manufacturing paradigms by offering capabilities that were previously impossible or economically prohibitive. Unlike conventional subtractive manufacturing methods that remove material from solid blocks, additive manufacturing builds objects layer by layer, enabling the creation of complex geometries with minimal waste. This approach delivers substantial operational and strategic advantages that are driving adoption across diverse industrial sectors.
Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction
The technology delivers significant cost savings through multiple mechanisms. Organizations can reduce material waste by up to 90% compared to traditional machining processes, as additive manufacturing only uses the exact amount of material required for each part. Lead times for prototyping and production shrink dramatically, enabling faster product development cycles and time-to-market acceleration. According to a global survey by Protolabs on market growth in 2024, 70% of businesses printed more parts in 2023 than in 2022, while 80% of respondents reported that 3D printing enabled them to save substantial costs.
Organizations in various industries are using them as a competitive edge. Manufacturers in the aerospace industry apply 3D printing to manufacture lightweight parts that are fuel-efficient and emit less carbon. The technology is used in the automotive industry to perform rapid prototyping, tooling, and more often in producing parts used in the final product. It is noteworthy that most of the respondents (47 percent) in the Protolabs survey expressed that they would choose 3D printing rather than any other manufacturing technique.
Design Freedom and Innovation Enablement
Additive manufacturing opens new design opportunities never before possible due to the restrictions of traditional manufacturing. This allows engineers to make parts that have internal lattice structures, complex cooling channels, and organic geometries optimized by computational design and topology optimization algorithms. This freedom of design allows it to perform better than the traditional techniques, including the consolidated assemblies that minimize the number of parts, weight, and failure points.
Healthcare is one of the areas that has demonstrated these transformational capabilities. Medical practitioners have been using 3D printing to make patient-specific surgical guides, custom implants, and anatomy models to use in pre-surgical planning. Approximately 77 percent of the respondents feel that the medical industry will be the most affected using 3D printing. Dental uses, such as the custom aligners, crowns, and bridges, are the fast-growing market segments where personalization is directly proportional to improved patient results.
Supply Chain Resilience and Localized Production
The COVID-19 pandemic brought unprecedented focus to supply chain weaknesses, spurring interest in additive manufacturing as a supply chain resilience strategy. With digital inventories instead of physical components, organizations can produce on-demand near end-use points, creating a distributed manufacturing paradigm that eliminates inventory carrying costs, obsolescence exposure, and transportation emissions while enhancing responsiveness to demand variability.
In January 2025, 3D Systems and Daimler Truck AG partnered to enable certified additive manufacturing partners to 3D print nearly 40,000 bus spare parts on demand, cutting delivery times by up to 75%. This collaboration demonstrates how 3D printing enables decentralized production networks that enhance supply chain agility and reduce service downtime in critical applications.
Key Growth Drivers in the Global 3D Printing Market:
Multiple converging factors are propelling the 3D printing market toward sustained double-digit growth through the end of the decade. Understanding these drivers provides insight into where opportunities and investments will concentrate in the coming years.
Technological Advancements and Material Innovation
Continuous improvements in printing technologies are expanding the performance envelope and application scope of additive manufacturing. The integration of hybrid manufacturing and the MELD process is revolutionizing production efficiency and expanding the application scope of 3D printing. Multi-laser systems now achieve deposition rates exceeding 150 cc/hour for high-performance alloys, addressing historical speed limitations that constrained industrial adoption.
Material science breakthroughs are equally critical to market expansion. Metals and alloys are expected to witness rapid expansion driven by their widening applications across aerospace, medical, and automotive sectors, supported by declining powder prices and advancements in multi-laser printing technologies. The availability of certified materials for regulated industries removes adoption barriers and enables qualification for flight-critical aerospace components and medical implants.
Industry 4.0 Integration and Digital Transformation
The convergence of additive manufacturing with broader Industry 4.0 technologies amplifies its strategic value. Cloud-based platforms enable collaborative design and distributed manufacturing networks. Artificial intelligence optimizes build parameters, predicts failures, and accelerates qualification processes. Real-time process monitoring through embedded sensors ensures quality assurance and enables closed-loop control systems.
These digital integrations transform 3D printing from a standalone technology into a fully networked manufacturing capability. Organizations can now implement lights-out production facilities where automated systems handle part removal, post-processing, and quality inspection with minimal human intervention. This automation drives down labor costs while improving consistency and traceability.
Rising Demand for Customization and Rapid Prototyping
Consumer expectations for personalized products are driving demand for manufacturing technologies capable of economic customization at scale. The 3D printing market benefits when OEMs bundle subscription-based machine leasing with remote monitoring, lowering financial barriers and expanding the user base. This shift toward servitization makes advanced manufacturing capabilities accessible to organizations that cannot justify large capital expenditures on equipment.
The prototyping market remains robust as companies seek to accelerate innovation cycles. However, the transition toward production applications is accelerating, with functional parts manufacturing expected to grow at the highest CAGR through 2030 as technologies mature and costs decline.
Regulatory Framework and Policy Landscape in the 3D Printing Industry:
Standardization and regulatory frameworks are evolving to address the unique challenges posed by additive manufacturing while enabling broader industrial adoption. International standards bodies and regulatory agencies are developing comprehensive guidelines that balance innovation with safety, quality, and intellectual property protection.
International Standards Development
The collaboration between ASTM International and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has produced a comprehensive framework for additive manufacturing standards. These organizations established a partnership to jointly develop and publish standards that harmonize requirements globally, reducing compliance complexity for multinational manufacturers.
Key standards address fundamental aspects of the technology. ISO/ASTM 52900:2021 defines Additive Manufacturing General Principles, Fundamentals And Vocabulary, establishing uniform terminology that reduces ambiguity across industries. Additional standards specify requirements for materials characterization, machine qualification, operator certification, and part acceptance testing.
The ISO/ASTM 52941-20 standard addresses Additive Manufacturing System Performance and Reliability for Laser Beam Powder Bed Fusion Machine Acceptance Testing for Aerospace Metallic Materials. This specification enables qualification of 3D prints for use in civil, commercial, and military aircraft, addressing one of the most demanding regulatory environments in manufacturing.
Industry-Specific Regulatory Developments
Regulated industries including aerospace, medical devices, and automotive have developed sector-specific qualification pathways. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has published roadmaps for certifying additively manufactured aircraft components, while medical device regulators require extensive biocompatibility and performance testing for implantable parts.
In June 2025, ASTM International launched a new manufacturer certification program to improve process control across the entire AM chain, featuring over 25 end users including Siemens Energy, Ford, Lockheed Martin, Boeing, and Medtronic. This certification validates activities specific to additive manufacturing that traditional quality management systems do not address, closing critical gaps in qualifying manufacturers for high-performance applications.
Intellectual Property and Data Security Considerations
The digital nature of additive manufacturing raises novel intellectual property challenges. Design files can be easily copied and distributed, creating enforcement difficulties for patent holders. Organizations must balance the need for secure file management with the collaborative opportunities enabled by digital manufacturing networks.
Regulatory frameworks are beginning to address these concerns through enhanced traceability requirements and digital rights management solutions. However, the pace of technological change continues to outstrip regulatory development, requiring organizations to implement robust internal controls and contractual protections.
Government Support and Initiatives for the 3D Printing Market:
Government programs worldwide recognize additive manufacturing as strategically important for economic competitiveness, national security, and technological leadership. Public sector investments are accelerating technology development, workforce training, and commercial adoption through multiple mechanisms.
United States Government Programs
The United States has established comprehensive programs to advance domestic additive manufacturing capabilities. America Makes, founded in 2012 as the Department of Defense's National Manufacturing Innovation Institute for AM and the first of the Manufacturing USA network, is based in Youngstown, Ohio, and managed by the National Center for Defense Manufacturing and Machining. This public-private partnership accelerates technology adoption and builds workforce capabilities through collaborative research projects.
In 2025, America Makes issued a new open project call worth $4.5 million, funded by the Office of the Under Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering, titled "Improvements in Manufacturing Productivity via Additive Capabilities and Techno-Economic Analysis 3.0" (IMPACT 3.0). The initiative focuses on demonstrating improvements in lead time, productivity, and yield for casting and forging operations using additive manufacturing technologies.
The AM Forward initiative represents another major federal effort. Supported by the Applied Science & Technology Research Organization (ASTRO), the federal government is working with GE Aviation, Honeywell, Lockheed Martin, Raytheon, and Siemens Energy to drive AM adoption among small-and-medium sized enterprises through financing, technical assistance, and procurement commitments.
International Government Initiatives
Beyond the United States, governments worldwide are implementing supportive policies. Under China's "Made in China 2025" strategy, 3D printing has been identified as a key development area, with government support primarily focused on research and development (R&D) over commercialization, prioritizing aviation and metal printing. Between 2014 and 2016, the Ministry of Science and Technology launched 51 research and development (R&D) projects on 3D printing, with over 400 million CNY pledged for multi-year research initiatives.
Defense and National Security Applications
Military organizations represent significant drivers of additive manufacturing adoption and funding. The Department of Defense has invested heavily in research and development since launching a 2014 initiative to explore 3D printing for military applications, with many initiatives transitioning into operational use. The Marine Corps has used 3D printing to produce replacement parts for ground vehicles, while the Navy has used it to make components for aircraft.
In January 2025, America Makes awarded USD 2.1 Million to projects focused on in-situ metrology, sustainable powder recycling, and low-cost aluminum parameter sets. These investments address technical barriers to scaling production while reducing costs and environmental impacts.
Top 3D Printing Companies Worldwide:
The 3D printing market features a competitive landscape with established industry leaders, innovative challengers, and specialized players serving specific technology segments or applications. Understanding the capabilities and strategies of leading companies provides insight into competitive dynamics and future market evolution.
Market Leadership and Competitive Positioning
The 3D printing market remains highly fragmented, with the top five players, Stratasys (US), EOS GmbH (Germany), HP Development Company, L.P. (US), 3D Systems, Inc. (US), and General Electric Company (US), collectively accounting for just 15–18% of the total market share as of 2024. This fragmentation reflects the diversity of technologies, materials, and applications within additive manufacturing, with different companies excelling in specific niches.
Stratasys maintains leadership in polymer 3D printing through its diverse technology portfolio, including FDM and PolyJet systems. For the full year 2024, Stratasys revenue came in at $572.5 Million, with the company posting an adjusted net income of $4.2 Million, reflecting the impact of cost-cutting measures and strategic changes. The company maintained a strong cash position, ending the year with $150.7 Million in cash and equivalents, with no debt on its balance sheet.
In March 2025, Stratasys unveiled the Neo800+, a large-format SLA 3D printer at the AMUG conference, which integrates ScanControl+ to boost print speeds by up to 50%, while maintaining high accuracy. The company's focus on large-scale printing and industrial customers positions it to capture growth in production applications.
Technology Innovators and Specialists
EOS GmbH has established dominance in industrial metal printing through its direct metal laser sintering technology. In June 2024, EOS launched the EOS M 290-2, featuring dual 400W lasers and a 250×250×325mm build volume, with enhanced productivity through optimized gas flow and active cooling. Nearly 2,000 M 290 systems are already installed worldwide. This installed base provides recurring revenue through materials and services while establishing de facto industry standards.
HP Inc. entered the additive manufacturing market with its Multi Jet Fusion technology and has rapidly gained share in polymer powder bed fusion. In March 2024, HP and DyeMansion partnered to integrate HP's 3D printing technology with DyeMansion's postprocessing workflows, offering a complete solution for large-scale, high-quality part production. HP's emphasis on production-grade systems and ecosystem integration aligns with market shifts toward serial production.
Emerging Competitors and Market Consolidation
The market continues to see entry from specialized players and consolidation as companies seek scale and complementary capabilities. Following the earnings release, a major development is the pending $120 Million investment from Fortissimo Capital, which will give the Israeli private equity firm a 14% stake in Stratasys and a seat on its board, providing additional cash for potential acquisitions.
The competitive landscape is also being reshaped by Asian manufacturers expanding into Western markets with cost-competitive offerings. In July 2025, India's first 3D-printed flexible toy brand, Vinglits, was launched by WOL3D, demonstrating how additive manufacturing is enabling new product categories and business models in emerging markets.
Opportunities and Challenges in the Global 3D Printing Market:
The 3D printing market presents substantial growth opportunities alongside significant challenges that organizations must navigate to capture value from this transformative technology. Understanding both sides of this equation is essential for strategic planning and investment decisions.
Market Opportunities
- Production Scale Applications: The transition from prototyping to production represents the largest opportunity in additive manufacturing. Industrial platforms dominate market spending as the automotive, energy, and aerospace sectors shift from prototype tooling toward large-scale, serial production, reflecting accelerating adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies. Technologies now achieve speeds and costs approaching conventional manufacturing for specific applications, opening addressable markets worth billions of dollars.
- Services and Distributed Manufacturing: Contract manufacturers such as Stratasys Direct Manufacturing, Materialize, and Protolabs leverage multi-site networks to distribute load, allowing customers to prototype and receive production ISO-13485 parts within ten days. This services boom lowers financial barriers and expands the user base by enabling access to capabilities without capital expenditure.
- Sustainability and Circular Economy: Additive manufacturing inherently supports sustainability objectives through material efficiency, localized production that reduces transportation emissions, and the ability to use recycled materials. Organizations pursuing ESG objectives can leverage 3D printing to demonstrate tangible environmental improvements.
Market Challenges
- High Capital Investment Requirements: Despite declining equipment costs for desktop systems, industrial-grade 3D printing systems require substantial capital outlays. Advanced metal printers can cost hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars, while supporting infrastructure, including powder handling, post-processing equipment, and quality inspection systems, adds significant expenses. This investment threshold limits adoption among small and medium enterprises without access to financing or government support programs.
- Material Limitations and Certification: While material options continue expanding, many industries require specialized materials that lack established supply chains or regulatory approvals. Qualification processes for new materials in regulated industries can require extensive testing spanning months to years, delaying commercialization of innovative material formulations. Material costs remain significantly higher than conventional manufacturing feedstocks, constraining economic viability for price-sensitive applications.
- Skilled Workforce Shortage: The interdisciplinary nature of additive manufacturing demands expertise spanning materials science, mechanical engineering, software development, and quality assurance. However, translating academic exposure into industry-ready capabilities requires sustained workforce development investments that many organizations struggle to justify.
- Macroeconomic Headwinds: Interest rate changes had a downstream effect that discouraged purchases of 3D printing equipment in 2024, while generally poor macroeconomic conditions, especially in Europe, impacted the 3D printing industry's growth. Economic uncertainty causes organizations to defer capital investments and technology transitions, creating cyclical challenges for equipment manufacturers and service providers.
- Quality Assurance and Process Control: Ensuring consistent part quality remains challenging due to the complex interplay of process parameters, material properties, and equipment capabilities. Real-time process monitoring and in-situ quality inspection technologies are advancing, but not yet universally deployed. Industries with stringent quality requirements demand extensive validation that increases time-to-qualification and costs.
Conclusion:
The 3D printing market stands at a pivotal juncture in its evolution from emerging technology to mainstream manufacturing solution. Market fundamentals remain strong, supported by rapid technological progress, broader material innovations, and rising adoption across a wide range of industrial applications. The technology has proven its value proposition through countless applications spanning aerospace, automotive, healthcare, consumer goods, and beyond.
Government support through initiatives like America Makes and AM Forward provides crucial backing for continued innovation and commercialization. International standards development by ASTM and ISO removes adoption barriers while ensuring quality and safety. Leading companies, including Stratasys, 3D Systems, EOS, and HP continue investing in next-generation capabilities that push performance boundaries and expand addressable markets.
However, realizing the full potential of additive manufacturing requires addressing persistent challenges. Organizations must justify capital investments in uncertain economic environments, develop skilled workforces capable of leveraging advanced technologies, and navigate complex regulatory landscapes. The transition from prototyping to production-scale applications demands sustained focus on quality assurance, process control, and total cost of ownership optimization.
For corporate strategy teams, investors, and business development professionals, the 3D printing market represents both opportunity and imperative. Companies that successfully integrate additive manufacturing into their operations will gain competitive advantages through faster innovation cycles, more resilient supply chains, and superior customization capabilities. Those that delay risk being disrupted by more agile competitors who leverage these capabilities to deliver better products faster and at lower costs.
The future of manufacturing is undoubtedly additive. The question is not whether organizations will adopt 3D printing, but when and how effectively they will do so.
Partner with IMARC Group for Strategic 3D Printing Market Intelligence:
Choose IMARC Group as your trusted partner in navigating the rapidly evolving 3D printing market and unlocking opportunities within the global manufacturing landscape.
- Data-Driven Market Research: Gain comprehensive insights into market dynamics, technology trends, and competitive positioning through our in-depth research reports covering additive manufacturing adoption across aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and industrial sectors.
- Strategic Growth Forecasting: Anticipate emerging trends in 3D printing technologies—from metal powder bed fusion and binder jetting to advanced polymer systems and hybrid manufacturing—segmented by geography, application, and end-user industry.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Analyze the strategies of leading 3D printing companies, evaluate technology portfolios, and monitor innovations in materials science, software platforms, and production workflows that are reshaping manufacturing competitiveness.
- Policy and Infrastructure Advisory: Stay ahead of regulatory developments, government funding programs, and standardization initiatives affecting additive manufacturing adoption, qualification processes, and supply chain integration.
- Custom Reports and Consulting: Access tailored market intelligence aligned with your strategic objectives—whether expanding into new geographic markets, evaluating technology investments, assessing acquisition targets, or developing go-to-market strategies for 3D printing solutions.
At IMARC Group, we empower manufacturing leaders, investors, and policymakers with the clarity and intelligence required to make confident decisions in the transformative 3D printing market. Connect with us to accelerate your organization's journey toward advanced manufacturing excellence—because innovation demands insight.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










