How Big Will the Japan Industrial Automation Components Market Be by 2033?
.webp)
Introduction to Japan's Industrial Automation Components Market:
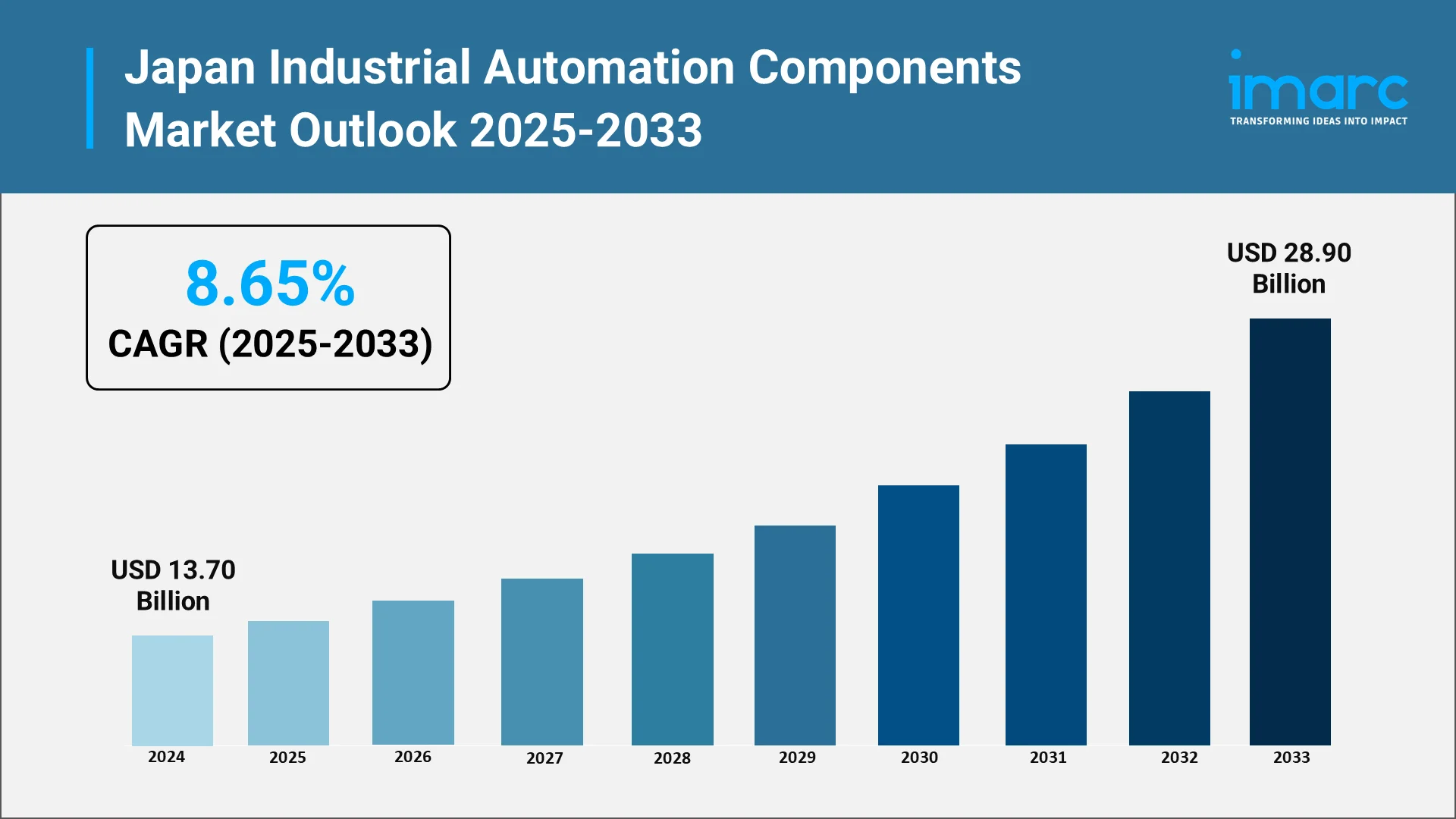
Japan's industrial automation components market stands at a pivotal juncture as the nation continues its transformation toward advanced manufacturing excellence. The market reached USD 13.70 Billion in 2024 as per IMARC Group. As one of the world's leading industrial powerhouses, Japan has long been recognized for its commitment to technological innovation and manufacturing precision. The industry for industrial automation components—encompassing sensors, controllers, actuators, drives, robotics, and human-machine interfaces—represents the backbone of modern manufacturing infrastructure.
There is increasing pressure on the Japanese manufacturing sector to tackle multiple pressing issues at once. Unprecedented investment in automation technology is being driven by labor shortages resulting from demographic shifts, the need for increased productivity, and the necessity to maintain global competitiveness. All around the archipelago, manufacturing facilities are undergoing extensive digital revolutions, substituting sophisticated, networked technologies for outdated systems.
Industrial automation components serve as the foundational building blocks that enable factories to operate with minimal human intervention while maximizing efficiency, quality, and flexibility. These technologies facilitate seamless communication between machines, enable predictive maintenance, optimize energy consumption, and support real-time decision-making. Japan's historical expertise in precision engineering and electronics manufacturing positions the nation uniquely to both develop and implement cutting-edge automation solutions.
The trajectory toward comprehensive factory automation reflects broader economic imperatives. Japanese manufacturers recognize that survival in an increasingly competitive global marketplace demands continuous innovation and operational excellence. Smart manufacturing initiatives are no longer optional enhancements but essential strategies for maintaining relevance and profitability.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
Growing Demand for Smart and Connected Manufacturing Systems:
The transition toward smart and connected manufacturing systems represents a fundamental paradigm shift in how Japanese factories operate. Traditional manufacturing models characterized by isolated machines and linear production processes are giving way to integrated ecosystems where every component communicates and collaborates seamlessly. This transformation is creating substantial demand for sophisticated automation components capable of supporting complex, data-driven operations.
Industry 4.0 principles are being embraced across Japanese manufacturing sectors with remarkable enthusiasm. Factory floors are being reimagined as intelligent environments where physical assets and digital systems merge to create unprecedented levels of operational visibility and control. Manufacturers are investing heavily in sensor technologies that provide granular insights into equipment performance, environmental conditions, and product quality throughout the production cycle.
The concept of the connected factory extends beyond mere machine-to-machine communication. It encompasses comprehensive integration of enterprise resource planning systems, supply chain management platforms, quality assurance protocols, and customer relationship management tools. Automation components must now support bidirectional data flows, enabling information to move seamlessly between the shop floor and executive decision-makers.
Japanese manufacturers are particularly focused on achieving mass customization capabilities—the ability to produce highly personalized products at scale without sacrificing efficiency. This requirement demands flexible automation systems that can rapidly reconfigure production lines, adjust process parameters, and accommodate diverse product specifications. Modular automation components that support quick changeovers and adaptive manufacturing processes are experiencing heightened demand.
Predictive maintenance capabilities enabled by smart automation components are revolutionizing equipment management strategies. By continuously monitoring machine health through embedded sensors and advanced analytics, manufacturers can anticipate failures before they occur, schedule maintenance during optimal windows, and extend asset lifespans. This shift from reactive to proactive maintenance approaches delivers substantial cost savings and operational reliability improvements.
Integration of IoT, AI, and Robotics in Industrial Operations:
The convergence of Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and robotics technologies is reshaping the landscape of industrial automation in Japan. These complementary technologies work synergistically to create manufacturing environments that are more intelligent, responsive, and capable than ever before. By 2025, Mitsubishi Electric aims to unite IoT and robotics to forge intelligent manufacturing systems that redefine efficiency. Moreover, generative AI improves manufacturing by enabling natural language-controlled robotics and automating complex design tasks, especially in the automotive and electronics sectors. The Japanese government continues to bolster its AI development strategy through targeted investments and strategic policy frameworks. Sophisticated automation components created especially to enable computationally complicated, data-intensive procedures are needed to integrate these advanced capabilities.
IoT connectivity transforms industrial equipment into data-generating assets that provide continuous streams of operational information. Sensors embedded throughout production facilities capture temperature readings, vibration patterns, pressure levels, positional data, and countless other parameters. This wealth of information flows through industrial networks to centralized platforms where it can be analyzed, visualized, and acted upon. Automation components must now support robust communication protocols, edge computing capabilities, and secure data transmission.
Artificial intelligence applications in manufacturing extend across numerous use cases. Machine learning algorithms optimize production scheduling by considering variables like material availability, equipment capacity, energy costs, and delivery deadlines. Computer vision systems powered by AI perform quality inspections with superhuman accuracy, detecting defects that might escape human observers. AI-driven process optimization continuously adjusts manufacturing parameters to maximize yield, minimize waste, and ensure consistent quality.
Collaborative robotics represents one of the most visible manifestations of automation advancement in Japanese factories. Unlike traditional industrial robots confined to safety cages, collaborative robots work alongside human operators, combining robotic precision and endurance with human judgment and adaptability. These systems require sophisticated sensors, force-limiting mechanisms, and intuitive programming interfaces—all specialized automation components designed to enable safe human-robot collaboration.
Digital twin technology is gaining traction as manufacturers seek to model, simulate, and optimize operations before implementing changes on actual production lines. Creating and maintaining accurate digital twins requires automation components capable of providing real-time data feeds that keep virtual models synchronized with physical reality. This technology enables manufacturers to test new processes, predict outcomes, and troubleshoot issues in risk-free virtual environments.
The integration of these advanced technologies creates new requirements for cybersecurity in industrial environments. As factories become increasingly connected and data-driven, protecting critical infrastructure from cyber threats becomes paramount. Automation components must incorporate robust security features, including encrypted communications, authentication protocols, and intrusion detection capabilities.
Key Industries Driving the Demand for Automation Components:
Multiple sectors within Japan's diverse industrial ecosystem are contributing to the expanding demand for automation components, each driven by unique operational requirements and competitive pressures. Understanding these industry-specific dynamics provides insight into the market's evolution and future trajectory.
The automotive manufacturing sector remains one of the most significant consumers of industrial automation components in Japan. As vehicle production becomes increasingly complex—incorporating advanced electronics, alternative powertrains, and autonomous driving technologies—assembly processes require unprecedented precision and flexibility. Automotive manufacturers are implementing sophisticated automation solutions throughout their operations, from stamping and welding to final assembly and quality verification.
Electronics and semiconductor manufacturing facilities demand extremely high levels of precision and cleanliness that can only be achieved through extensive automation. The production of integrated circuits, displays, batteries, and consumer electronics involves intricate processes where contamination or dimensional variations measured in nanometers can result in product failures. Cleanroom environments staffed primarily by robots and automated handling systems are becoming standard across this sector.
The pharmaceutical and healthcare industries are embracing automation to meet stringent regulatory requirements, ensure product safety, and respond to demographic trends driving increased healthcare demand. In 2025, Omron Corporation's robotics division expanded to feature AI-powered surgical robots and automated pharmaceutical packaging systems, reflecting the industry's accelerating shift toward intelligent automation. Automated systems handle everything from drug formulation and sterile filling to packaging and serialization. At Keio University Hospital, robots scan prescriptions, prepare medicines, and then deliver them smoothly across floors using sensor-enabled elevators—a system that is currently being built, tested, and implemented. Traceability requirements mandate comprehensive data capture throughout production processes, creating demand for intelligent automation components with robust data management capabilities.
Food and beverage processing operations are modernizing rapidly as manufacturers seek to address labor shortages while meeting evolving consumer preferences for variety, quality, and transparency. Automation enables flexible production lines capable of handling multiple product formats, ensures consistent quality and food safety compliance, and provides the traceability information increasingly demanded by consumers and regulators.
The metals and materials processing sectors utilize automation to optimize energy-intensive operations, improve worker safety in hazardous environments, and maintain consistent quality in commodity production. Automated systems monitor and control furnaces, rolling mills, chemical reactors, and material handling equipment with precision impossible for human operators to achieve manually.
Logistics and warehousing operations supporting e-commerce and just-in-time manufacturing are being transformed by automation technologies. Automated storage and retrieval systems, autonomous mobile robots, and intelligent conveyor systems require sophisticated control components to orchestrate complex material movements efficiently and accurately.
Government Initiatives Supporting Industrial Digitalization:
With over JPY196.9 billion set aside for AI-related initiatives in fiscal year 2025, the Japanese government is continuing to bolster its AI development strategy through focused investments and strategic policy frameworks. The authority has demonstrated strong commitment to advancing industrial digitalization through comprehensive policy frameworks, funding programs, and collaborative initiatives designed to accelerate technology adoption across the manufacturing sector. These public sector efforts create favorable conditions for sustained investment in automation components and systems.
Industrial policy frameworks specifically target manufacturing competitiveness and digital transformation as national priorities. Recognizing that Japan's economic prosperity depends heavily on maintaining leadership in advanced manufacturing, government agencies have established strategic programs promoting the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, smart factory concepts, and cyber-physical production systems.
Financial incentives and support mechanisms help manufacturers—particularly small and medium-sized enterprises—overcome financial barriers to automation investment. Subsidy programs, low-interest financing, tax incentives, and grants reduce the capital requirements associated with modernizing production facilities. These programs recognize that comprehensive factory automation requires substantial upfront investment that can be challenging for smaller manufacturers to justify or finance.
Research and development partnerships between government laboratories, academic institutions, and industrial participants accelerate innovation in automation technologies. Public funding supports fundamental research into areas like advanced robotics, AI applications, sensor technologies, and industrial communication standards. These collaborations help ensure that Japanese industry maintains access to cutting-edge technologies while contributing to the global knowledge base.
Skills development programs address the critical need for workforce capabilities aligned with automated manufacturing environments. Government-sponsored training initiatives help workers transition from manual operations to roles involving robot programming, data analysis, system maintenance, and digital process management. Ensuring that human capital keeps pace with technological advancement is essential for realizing the full benefits of automation investment.
Regulatory modernization efforts aim to eliminate outdated rules that might impede technology adoption while establishing appropriate frameworks for emerging capabilities. Standards development for industrial networks, data security, robot safety, and AI ethics provide clarity that encourages investment and facilitates interoperability across different manufacturers' equipment.
International collaboration initiatives promote technology exchange, standardization efforts, and market access for Japanese automation technologies. Government agencies facilitate participation in global forums addressing industrial digitalization, helping ensure that Japanese perspectives influence international standards and that domestic manufacturers remain connected to global innovation trends.
Future Outlook: Market Size and Growth Prospects by 2033
According to IMARC Group, the Japan industrial automation components market is expected to reach USD 28.90 Billion by 2033 at a CAGR of 8.65% during 2025-2033. The future trajectory of Japan's industrial automation components market reflects the convergence of technological advancement, economic imperatives, and demographic realities that will continue shaping the manufacturing landscape for years to come. Understanding the forces that will influence market evolution provides valuable context for strategic decision-making by industry participants, investors, and policymakers.
Demographic pressures will intensify as Japan's working-age population continues declining, creating labor shortages that cannot be addressed through conventional recruitment strategies. Manufacturers will have no choice but to embrace comprehensive automation to maintain production capacity. This demographic inevitability ensures sustained demand for automation components regardless of cyclical economic fluctuations.
Technological maturation of AI, robotics, and IoT platforms will make automation solutions more capable, accessible, and cost-effective. As technologies mature, implementation becomes less complex, integration challenges diminish, and total cost of ownership decreases. These trends will accelerate adoption rates, particularly among smaller manufacturers that previously found advanced automation prohibitively complex or expensive.
Sustainability imperatives will drive additional automation investment as manufacturers seek to optimize energy consumption, minimize waste, and reduce environmental footprints. Automated systems enable precise control over resource utilization, support circular economy principles through improved recycling and remanufacturing processes, and provide the data transparency required to document environmental performance.
Supply chain resilience considerations emerging from recent global disruptions will motivate manufacturers to enhance production flexibility and reduce dependencies on complex international networks. Automation enables more economical domestic production of components previously sourced from lower-cost locations, supports rapid production reconfiguration in response to supply disruptions, and facilitates nearshoring strategies.
Competitive dynamics in global markets will continue pressuring Japanese manufacturers to differentiate through quality, innovation, and responsiveness rather than cost alone. Automation provides the operational excellence necessary to compete effectively against rivals with lower labor costs while enabling the rapid product development cycles and customization capabilities that sophisticated customers increasingly demand.
Technology convergence will create entirely new categories of automation components and systems. The blending of operational technology and information technology, the emergence of quantum computing applications, advances in materials science enabling new sensor capabilities, and breakthroughs in energy storage and power electronics will expand the functional possibilities of automated manufacturing systems.
Looking toward the future, Japan's industrial automation components market appears positioned for sustained expansion driven by fundamental structural forces rather than temporary cyclical trends. The combination of demographic necessity, technological opportunity, policy support, and competitive imperatives creates compelling conditions for continued investment in advanced manufacturing capabilities.
Choose IMARC Group for Unparalleled Market Intelligence and Strategic Guidance:
- Navigating Japan's industrial automation landscape requires authoritative research and strategic perspectives. As the manufacturing sector undergoes profound transformation, decision-makers need partners who understand both technological intricacies and business implications.
- Data-driven market research services provide comprehensive insights into automation technologies, supplier landscapes, and adoption trends across manufacturing sectors, exploring advanced robotics, AI-powered quality systems, IoT sensor networks, and cyber-physical production platforms.
- Strategic growth forecasting helps organizations anticipate trends from intelligent machine tools and collaborative robots to edge computing and digital twin platforms, while regional analysis identifies opportunities and regulatory developments across Japan and Asia-Pacific.
- Competitive benchmarking analyzes market forces, technology roadmaps, and breakthrough innovations in precision control and industrial communication, informing partnership and investment decisions.
- Policy advisory capabilities track regulatory frameworks, government programs, and infrastructure initiatives affecting automation adoption and market access.
- Custom research delivers tailored insights for introducing automation products, investing in manufacturing ventures, or developing industrial infrastructure.
At IMARC Group, we empower manufacturing leaders, technology providers, and investors to navigate Japan's dynamic automation market—supporting a more productive, sustainable, and competitive manufacturing future.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










