How Government Policies Are Driving the India Electric Rickshaw Industry

Introduction:
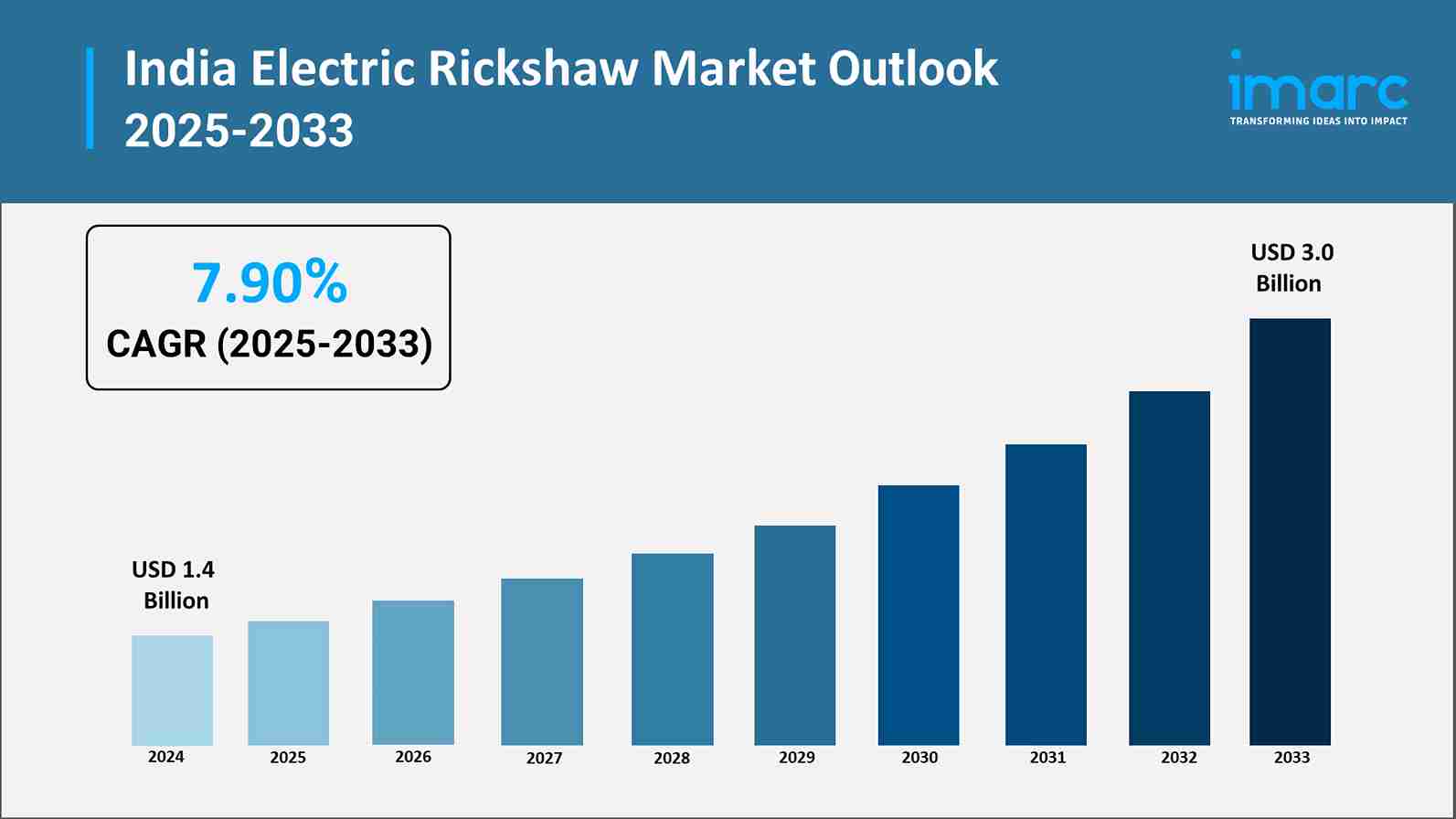
The electric rickshaw sector in India has experienced a significant upheaval in recent years and is now a vital part of the country's sustainable transportation network. Strategic government policies aimed at hastening the adoption of clean mobility solutions have played a major role in orchestrating this evolution. India's larger vision of sustainable urbanization is in line with the electric rickshaw industry, which combines social development objectives, economic opportunities, and environmental imperatives. The India electric rickshaw market size reached USD 1.4 Billion in 2024. The market is projected to reach USD 3.0 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 7.90% during 2025-2033.
 Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
Government interventions across multiple levels have created a favorable ecosystem for electric vehicle adoption in the last-mile connectivity segment. From regulatory frameworks to financial incentives, policymakers have recognized electric rickshaws as instrumental in addressing urban pollution, providing affordable transportation, and creating livelihood opportunities for millions of drivers. The comprehensive policy approach encompasses manufacturing incentives, operational subsidies, charging infrastructure development, and regulatory reforms that collectively shape market dynamics.
This analysis explores the multifaceted government initiatives that are propelling the India electric rickshaw market forward, examining how policy interventions influence manufacturing capabilities, consumer adoption patterns, and the competitive landscape of this rapidly evolving sector.
Regulatory Framework and Vehicle Standards:
The foundation of India's electric rickshaw expansion rests on robust regulatory frameworks established by central and state authorities. The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has implemented comprehensive vehicle standards specifically designed for battery-operated rickshaws, creating clarity for manufacturers and operators. These regulations address critical aspects including vehicle dimensions, motor specifications, battery requirements, and safety features that ensure passenger protection while maintaining operational efficiency.
Type approval processes have been streamlined to facilitate faster market entry for compliant vehicles. Manufacturers must obtain certification from designated testing agencies that verify adherence to prescribed technical standards. This regulatory rigor ensures that only vehicles meeting minimum safety and performance criteria operate on public roads, protecting both passengers and pedestrians.
Compared to traditional automobiles, registration processes have been greatly streamlined. In order to reduce the bureaucratic hurdles that previously impeded market growth, several state transport agencies have set up specific counters for the registration of electric rickshaws. Small business owners now have easier access to car ownership thanks to lower costs and the removal of some documentation requirements.
To strike a balance between practical utility and safety concerns, speed limits and operational rules have been legislated. Although operators initially opposed these restrictions, they have helped establish electric rickshaws as acceptable modes of transportation as opposed to uncontrolled vehicles existing in legal limbo.
Financial Incentives and Subsidy Programs:
The FAME scheme (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles) represents the cornerstone of India's electric mobility push. This comprehensive program provides demand incentives that directly reduce vehicle acquisition costs for buyers, making electric rickshaws economically competitive with their fossil fuel counterparts. The subsidy structure is designed to promote vehicles with advanced battery technology and longer operational range.
State governments have added region-specific incentive packages that are adapted to local market conditions to support central initiatives. The cumulative benefit structure produced by these extra subsidies has the potential to significantly lower the effective purchase price. Recognizing the importance of finance accessibility for small companies, some states give purchase refunds, while others offer interest subsidies on auto loans.
Goods and Services Tax concessions on electric vehicles and components have improved affordability across the value chain. Reduced GST rates on electric rickshaws compared to conventional vehicles create a price differential that influences purchasing decisions. Similarly, concessional tax treatment for batteries and electric drivetrains has helped manufacturers optimize production costs.
Electric rickshaws are encouraged to replace diesel and gasoline-powered ones by eliminating incentives for outdated, polluting vehicles. These schemes, which accelerate fleet modernization while addressing environmental goals, usually provide financial compensation to owners who voluntarily retire their conventional vehicles and switch to electric models.
Manufacturing Support and Production Linked Incentives:
The Production Linked Incentive scheme for automotive and auto components has catalyzed domestic manufacturing capabilities in the electric vehicle segment. This program provides performance-based incentives to manufacturers achieving specified production and sales thresholds, encouraging investment in manufacturing capacity, technology upgradation, and quality improvement initiatives.
Make in India policies have created a favorable environment for both domestic and international manufacturers to establish production facilities. Localization requirements ensure that a significant portion of vehicle components are manufactured domestically, creating employment opportunities and developing supplier ecosystems. This approach reduces import dependence while building indigenous technological capabilities.
Additional advantages provided by Special Economic Zones and designated manufacturing clusters include infrastructure support, expedited permits, and land at concessional rates. The manufacturing base has expanded beyond conventional automotive centers thanks to these industrial policy measures, which have drawn investment from both major automotive manufacturers and cutting-edge mobility businesses.
Favorable foreign direct investment rules have promoted technology transfer agreements and partnerships with foreign partners. In an effort to improve product quality and competitiveness, the government has enabled collaborations that bring cutting-edge battery technology, motor design know-how, and manufacturing best practices to Indian facilities.
Charging Infrastructure Development Initiatives:
Recognizing that charging infrastructure availability is critical for electric vehicle adoption, governments have implemented programs specifically targeting battery swapping and charging station deployment. Public-private partnership models have been promoted to accelerate infrastructure rollout while managing capital requirements efficiently.
State electrical boards are required to supply charging stations with dedicated power connections at uniform rates. Early concerns about the cost and availability of power that would have hampered the construction of infrastructure are addressed by this regulatory action. Infrastructure investors now have less ambiguity due to clear criteria on connection procedures and timing promises.
Policies pertaining to the distribution of land for charging stations give preference to sites close to important transit routes, marketplaces, and residential areas where electric rickshaws are frequently used. Municipal authorities have the authority to set aside particular areas for infrastructure related to charging, frequently including these facilities with already-existing public amenities.
Battery swapping standards are being developed to create interoperability across different vehicle models and service providers. Standardization efforts aim to prevent market fragmentation while enabling economies of scale in battery production and swapping station operations. This approach could significantly reduce operational downtime and improve fleet utilization for commercial operators.
Environmental Regulations and Emission Standards:
Stringent pollution control measures in major urban centers have created strong regulatory drivers for electric rickshaw adoption. Cities facing severe air quality challenges have implemented restrictions on conventional vehicle operations, creating dedicated opportunities for zero-emission alternatives. These environmental regulations effectively create protected market segments for electric vehicles.
Progressive tightening of emission standards for internal combustion engine vehicles has increased compliance costs for conventional rickshaw manufacturers. The regulatory trajectory clearly signals that electric mobility represents the sustainable path forward, influencing long-term planning by manufacturers and fleet operators.
Green zone designations in city centers and sensitive areas restrict entry of polluting vehicles while allowing electric rickshaws unrestricted access. This preferential treatment provides operational advantages that translate into revenue benefits for electric vehicle operators, creating economic incentives aligned with environmental objectives.
Noise pollution norms also favor electric rickshaws, which operate significantly quieter than conventional vehicles. In residential areas and near schools or hospitals where noise restrictions apply, electric vehicles enjoy operational freedom that conventional rickshaws lack, opening additional market opportunities.
State-Level Policy Variations and Regional Strategies:
Different states have adopted customized approaches reflecting local priorities and market conditions. Some states focus heavily on manufacturing incentives to establish automotive clusters, while others prioritize operational subsidies to accelerate consumer adoption. This policy diversity creates a dynamic landscape where best practices emerge through experimentation and competition.
Urban local bodies have significant autonomy in implementing transportation policies within their jurisdictions. Metropolitan cities have been particularly proactive in promoting electric rickshaws as solutions for last-mile connectivity, often integrating them with public transit systems. Dedicated pickup and drop zones, preferential permits, and integration with digital payment platforms enhance their utility.
Rural electrification programs have expanded the potential market for electric rickshaws beyond urban centers. As reliable electricity access reaches smaller towns and villages, the operational feasibility of electric vehicles improves, supported by government schemes targeting rural transportation needs.
Some states have mandated minimum percentages of electric vehicles in commercial fleets, creating assured demand that provides visibility for manufacturers and operators. These fleet electrification targets apply to various categories including last-mile delivery, tourist transport, and government department vehicles.
Financing Support and Credit Facilitation
Priority sector lending guidelines have been modified to include electric vehicle financing, encouraging banks and financial institutions to extend credit on favorable terms. Lower interest rates and extended repayment periods make electric rickshaw ownership accessible to operators with limited capital resources.
Credit guarantee schemes reduce lender risk when financing small operators without substantial collateral. Government-backed guarantees enable financial institutions to serve first-time buyers and entrepreneurs from economically weaker sections who represent the primary operator demographic for electric rickshaws.
Non-banking financial companies have entered the electric vehicle financing space, supported by regulatory clarity and refinancing facilities from development financial institutions. This competitive financing ecosystem offers diverse products tailored to different customer segments, from individual operators to fleet aggregators.
Digital lending platforms leveraging alternative credit assessment methods have improved financing accessibility. These technology-enabled approaches evaluate creditworthiness using operational data and alternative metrics, expanding financial inclusion for operators who lack traditional banking relationships.
Skills Development and Livelihood Programs:
Government initiatives recognize that the transition to electric mobility requires workforce development across multiple skill levels. Training programs for mechanics and technicians address the knowledge gap in electric vehicle maintenance and repair, ensuring that after-sales service infrastructure develops alongside vehicle adoption.
Initiatives for driver training facilitate the switch to electric vehicles for traditional rickshaw operators. These courses educate drivers about the features of electric vehicles, battery management, charging techniques, and best practices for extending vehicle life and efficiency.
Aspiring electric rickshaw drivers are the focus of entrepreneurship support programs, which offer both technical and business training. These interventions acknowledge that in order to ensure sustainable livelihoods, a successful transition necessitates both operational skills and fundamental business management abilities.
Electric rickshaw operations have also been marketed as a feasible source of income by women's empowerment programs. Women entrepreneurs are assisted in entering this industry through special financing terms, training programs, and operational support, which addresses the goals of economic inclusion and mobility.
Future Policy Directions and Industry Evolution:
The policy landscape continues evolving as governments refine approaches based on implementation experience and changing market dynamics. Increased focus on battery recycling and end-of-life management reflects growing awareness of circular economy principles and environmental stewardship responsibilities.
Integration with smart city initiatives positions electric rickshaws as components of intelligent transportation systems. Digital connectivity requirements, data-sharing protocols, and integration with mobility-as-a-service platforms represent emerging policy frontiers that will shape the industry's next phase.
International partnerships and technology collaborations are being actively pursued to access cutting-edge innovations in battery chemistry, motor efficiency, and vehicle design. Policy support for research and development aims to position India as a global hub for electric vehicle innovation rather than merely a manufacturing destination.
Conclusion:
India's electric rickshaw industry has undergone a significant transformation from an unorganized sector to a regulated and expanding market niche as a result of government policies. Conditions for long-term growth have been established by the comprehensive policy framework that addresses adoption, manufacturing, infrastructure, and financing. In order to show how integrated policy approaches can propel industrial transformation, strategic interventions have struck a balance between environmental goals, economic opportunities, and social development objectives.
India's electric rickshaw industry is poised for exponential growth owing to the ongoing development of policies that are supportive, technological advancements, and rising environmental consciousness. Maintaining momentum requires policymakers to commit to long-term goals for electric mobility, implement them consistently, and refine them adaptively. The effectiveness of government programs in this area provides important insights for the wider adoption of electric vehicles in other transportation categories.
Choose IMARC Group for Comprehensive Electric Mobility Intelligence:
IMARC Group delivers authoritative market research and strategic insights that empower stakeholders across the electric vehicle ecosystem. Our specialized services include detailed policy impact analysis, comprehensive manufacturing landscape assessment, and competitive intelligence covering the rapidly evolving electric rickshaw sector. We provide in-depth regional market dynamics evaluation, infrastructure development tracking, and comprehensive consumer adoption pattern studies that inform strategic investment decisions effectively.
Our custom consulting services address specific organizational needs whether you're entering the electric mobility market, evaluating manufacturing opportunities, or assessing policy implications for existing operations. We combine rigorous quantitative data analysis with qualitative insights from industry stakeholders, regulatory bodies, and leading technology providers. Partner with IMARC Group to navigate India's dynamic electric vehicle transformation with confidence and strategic clarity.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










