How Government Policies Are Driving the India Fintech Industry

UPI Making Digital Payments Mainstream Across Cities and Villages:
India’s fintech revolution is being driven by strong policy initiatives and a robust digital public infrastructure that has made financial services more accessible than ever before. At the center of this transformation is the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) a flagship innovation by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) that has redefined digital payments in both urban and rural markets. In October 2025, the Indian government announced its plans to enhance the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) by introducing fingerprint and facial recognition for transactions, eliminating the need for PINs. Users will have a daily transaction limit of INR 5,000, while enhanced security measures will verify payments through robust checks.
Interoperability across banks and mobile applications has enabled millions of Indians to make instant, low-cost transactions through UPI. This has been driven at the mass level by the zero MDR policy for small merchants, given that businesses can receive digital payments without any extra charge. Real-time, 24x7 payment capability and a QR code-based ecosystem have contributed to bridging formal banking with informal commerce, fostering inclusion at the grassroots.
From local kirana stores to large e-commerce platforms, UPI has emerged as the preferred mode of payment due to its simplicity, speed, and security. The integration of UPI with Aadhaar and mobile number verification has ensured seamless onboarding and fraud reduction. Moreover, innovations such as UPI Lite for offline transactions and UPI AutoPay for recurring payments have expanded its utility across diverse user segments.
As India continues to scale its digital financial ecosystem, UPI serves as a foundational enabler of the broader fintech landscape. It has not only accelerated digital payment adoption but also paved the way for growth in adjacent fintech domains such as lending, insurance, and wealth management by creating a reliable and inclusive digital payment infrastructure.
Market Size and Growth Opportunity:
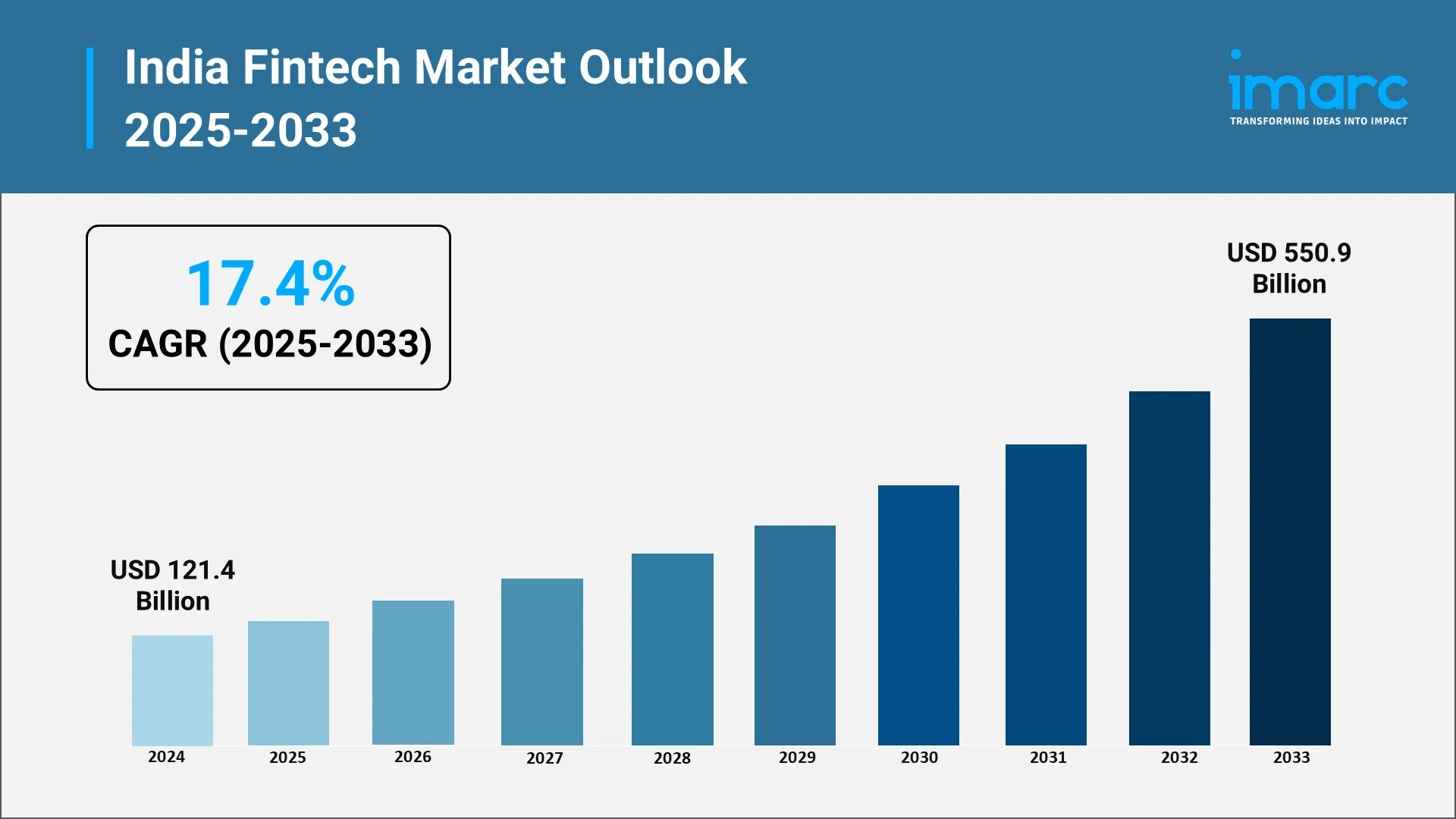
The India fintech market has grown exponentially over the past decade, supported by policy reforms, digital adoption, and an expanding user base. The market was valued at USD 121.4 Billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 550.9 Billion by 2033, growing at a robust CAGR of 17.4% during 2025–2033. This growth trajectory highlights India’s emergence as one of the fastest-growing fintech ecosystems globally.
While digital payments continue to dominate the sector, digital lending platforms are rapidly gaining traction by addressing credit gaps in underserved populations, particularly MSMEs and self-employed individuals. Embedded finance models, Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) solutions, and AI-driven credit scoring systems are making lending faster, more transparent, and more inclusive.
The digital wallets and neobanking segments are also witnessing strong growth as consumers increasingly prefer app-based, paperless financial management tools. The wealthtech segment, driven by investment platforms and robo-advisory solutions, is democratizing access to financial planning and stock market participation for young and first-time investors. Similarly, insurtech companies are simplifying insurance distribution through AI chatbots, digital underwriting, and micro-insurance offerings.
Government-backed infrastructure such as India Stack which integrates Aadhaar, e-KYC, and UPI continues to serve as the backbone of this rapid expansion. It enables fintech players to innovate within a trusted, interoperable, and compliant framework.
As India’s fintech ecosystem matures, the opportunity lies in bridging financial access gaps across Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities, where digital adoption is rising but formal financial penetration remains limited. The combination of policy support, innovation, and rising consumer awareness is expected to sustain this high growth momentum through the next decade.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
RBI Regulations Supporting Secure and Compliant Fintech Growth:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has played a pivotal role in shaping the fintech ecosystem by establishing clear, forward-looking regulations that balance innovation with consumer protection. As fintech activity accelerated, the central bank introduced guidelines to ensure transparency, data security, and systemic stability, which in turn have enhanced investor and customer confidence. In October 2025, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) introduced a retail sandbox for its central bank digital currency (CBDC), enabling fintechs to develop and test solutions. This follows the e-rupee pilot launch which has attracted around 7 million users across the country.
Key regulatory measures include KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) norms that prevent financial fraud and identity misuse. The RBI has also introduced frameworks for digital lending platforms, ensuring responsible credit practices and preventing predatory lending. This includes mandating direct loan disbursement between lenders and borrowers without intermediary accounts a step that has strengthened accountability across digital lending ecosystems.
Data privacy remains a core regulatory focus. The RBI and the Indian government are increasingly emphasizing compliance with data localization norms and secure data handling practices. These measures are aligned with the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 (DPDPA), ensuring that user information remains confidential and processed only with consent.
In the payments space, RBI initiatives such as tokenization and two-factor authentication (2FA) have fortified transaction security for digital consumers. The regulator’s continued push for Payment Aggregator (PA) and Payment Gateway (PG) licensing frameworks has introduced greater oversight and standardization in digital transaction ecosystems.
Beyond compliance, the RBI’s regulatory sandbox programs have fostered innovation by allowing fintech startups to test new products in a controlled environment. This initiative encourages experimentation while safeguarding user interests, promoting a responsible innovation culture in India’s fintech sector.
By maintaining a balance between innovation and regulation, the RBI has ensured that India’s fintech growth remains sustainable, inclusive, and globally competitive.
Government Initiatives Accelerating Digital Financial Inclusion:
Government policies have been central to democratizing financial access and building trust in India’s digital financial ecosystem. Initiatives such as Jan Dhan Yojana, Aadhaar, and UPI have laid the foundation for large-scale digital financial inclusion, enabling millions of unbanked citizens to enter the formal economy.
The Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) has created a robust foundation for direct benefit transfers, savings mobilization, and digital payments. Integration with Aadhaar authentication has simplified customer verification and reduced onboarding friction, while the Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AePS) allows biometric-based transactions in remote areas.
The FASTag initiative has automated toll payments and exemplifies the government’s push toward a cashless economy. Similarly, QR-based merchant payments supported by initiatives like BharatQR and UPI QR codes have empowered small businesses to accept digital transactions easily, contributing to formalization and transparency in commerce.
The Digital India mission continues to play a transformative role by promoting digital literacy, expanding internet connectivity, and driving adoption of online financial services across rural and semi-urban India. The government’s partnership with NPCI and RBI to introduce initiatives like e-RUPI a voucher-based payment system demonstrates its commitment to promoting targeted and secure digital transactions.
Moreover, programs like Startup India and Invest India have encouraged entrepreneurship in the fintech sector by simplifying regulatory processes, offering funding support, and fostering collaboration between financial institutions and technology startups.
As a result of these combined efforts, India has become a global benchmark for scalable, inclusive, and interoperable digital finance. The policy-led fintech ecosystem has not only enhanced convenience for consumers but also strengthened transparency, financial literacy, and trust vital pillars for long-term economic growth.
Top Companies in the India Fintech Market:
India’s fintech ecosystem is led by a dynamic mix of established corporations and high-growth startups that are reshaping financial services delivery through technology-driven innovation. These companies cater to diverse segments including payments, lending, wealth management, and insurance.
- Paytm: In November 2025, Paytm launched a revamped app featuring a cleaner interface and AI-driven innovations, enhancing everyday payments. Notable features include smart expense categorization, privacy controls, and a unique reward system offering Gold Coins on every transaction. The app aims to simplify money management while delivering a user-friendly experience for Indian consumers.
- PhonePe: In June 2025, PhonePe acquired the GSPay IP to develop a UPI payment app for feature phones in India, aiming to serve the millions of underserved users. The app will support peer-to-peer transfers, offline QR payments, and receiving money via mobile numbers, set to launch in the coming quarters.
- Google Pay: In February 2025, Google Pay announced its plans to launch an AI-powered voice payment feature in India, enabling UPI transactions through voice commands in users' preferred languages. This initiative, developed with the Bhashini AI project, aims to enhance digital payment accessibility and security while simplifying transactions for millions, particularly those with limited literacy.
Some of the other major key players include Razorpay, PolicyBazaar, etc.
How IMARC Group Empowers Fintech Innovation in India:
IMARC Group provides in-depth market intelligence and consulting services that help stakeholders navigate the fast-evolving fintech ecosystem. Our expertise covers payments, lending, wealthtech, insurtech, and blockchain applications, offering clients actionable insights for sustainable growth.
- Comprehensive Market Insights: Our research captures the full spectrum of India’s fintech landscape, analyzing emerging trends, evolving business models, and policy impacts across segments. From digital payments to AI-driven lending, our studies identify key opportunities shaping the future of fintech.
- Strategic Forecasting: Through proprietary forecasting models, IMARC provides accurate market projections, helping clients assess growth potential and plan long-term strategies. Our detailed analysis of policy developments, investment trends, and consumer adoption patterns enables data-driven decision-making.
- Regulatory and Policy Analysis: IMARC tracks India’s evolving fintech regulations, including RBI guidelines, data privacy frameworks, and financial inclusion policies. We assess their implications for market participants, helping companies align their compliance and innovation strategies effectively.
- Customized Consulting Solutions: We offer tailored consulting services that address specific business challenges from product positioning and market entry to partnership assessment and regional expansion. Our consultants collaborate closely with clients to identify growth drivers and mitigate operational risks.
As India’s fintech market continues to grow under the strong influence of government policy, technological innovation, and consumer demand, IMARC Group remains committed to equipping businesses with the insights and strategies needed to thrive in this dynamic landscape. For detailed insights, data-driven forecasts, and strategic advice, see the complete report here: https://www.imarcgroup.com/india-fintech-market
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










