How the United States Shrimp Market is Shaping the Global Seafood Industry: Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities

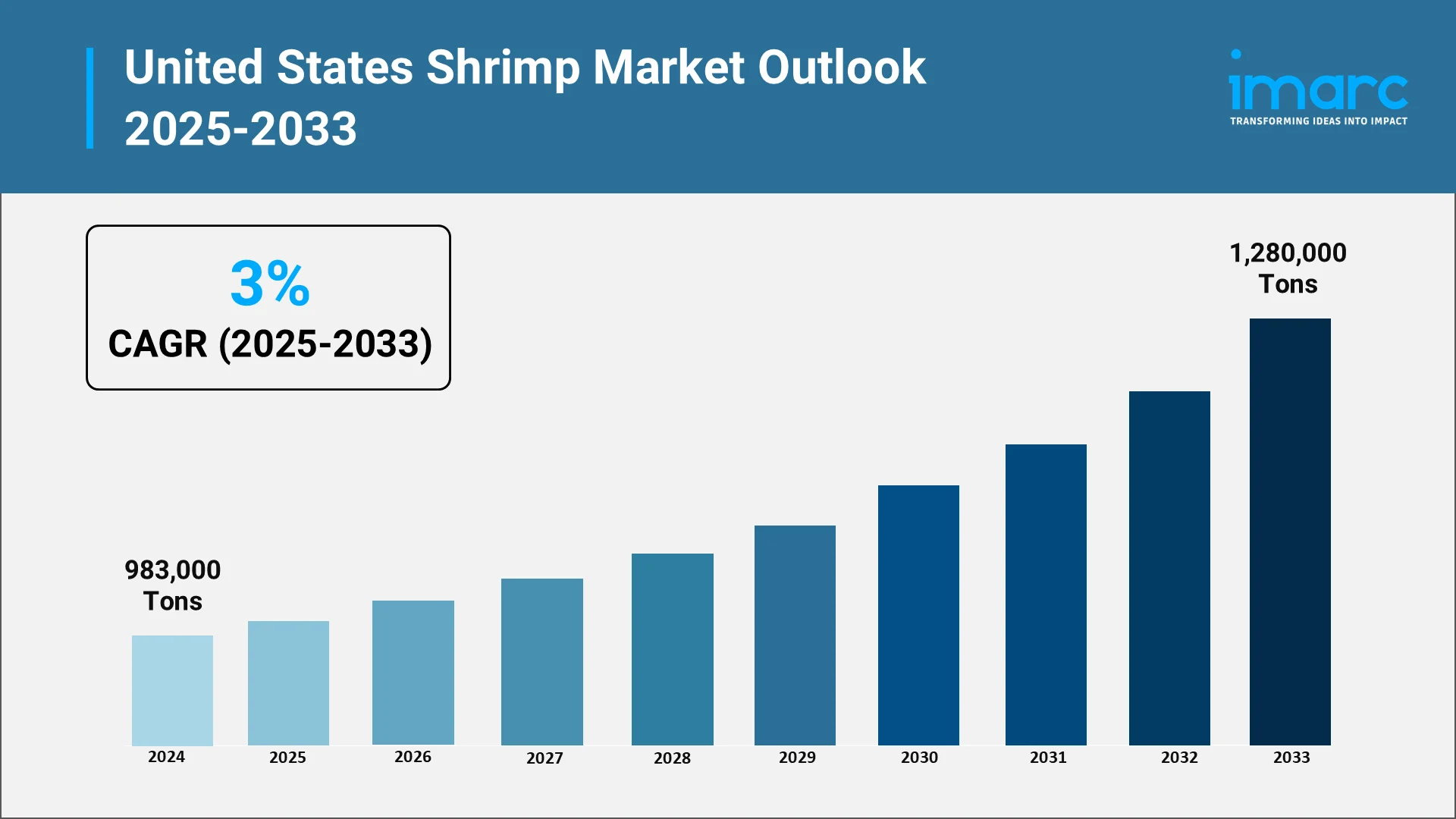
The United States shrimp market stands as one of the most dynamic segments within the global seafood industry. It reached 983,000 Tons in 2024 as per IMARC Group and is projected to reach 1,280,000 Tons by 2033 at a growth rate of 3% from 2025 to 2033. As consumer preferences shift toward healthier protein sources and sustainable options, shrimp has emerged as a cornerstone of American dietary habits. The market reflects transformations in consumer behavior, international trade dynamics, and technological innovation within aquaculture and seafood processing.
Shrimp consumption maintains its position as the most popular seafood choice among American consumers. This preference stems from versatility in culinary applications, health benefits, and widespread availability across retail and foodservice channels. The US shrimp industry encompasses domestic producers, international suppliers, distributors, processors, and retailers collaborating to meet escalating demand.
The market's significance extends beyond domestic consumption. According to the Shrimp Insights website, US shrimp imports ended the first half of 2025 on a good note, with June volumes of 72,763 Metric Tons, up 36% year over year. Additionally, the value of imports rose dramatically, increasing by 47% to USD 613 Million. American import requirements and quality standards influence production practices worldwide, particularly in major exporting nations throughout Asia and Latin America. This positions the United States as a pivotal player in shaping global aquaculture development and sustainability initiatives.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
The Role, Impact, and Benefits of Shrimp in the U.S. Seafood Industry:
Shrimp occupies a distinctive position within the American seafood landscape, serving as both a dietary staple and an economic driver. The product's widespread appeal transcends demographic boundaries, finding favor among diverse consumer segments. This universal acceptance has cemented shrimp's status as an anchor product for grocery retailers and restaurant operators nationwide.
From a nutritional perspective, shrimp delivers exceptional value through high-quality protein content and beneficial omega-3 fatty acids. Low calorie density combined with essential vitamins and minerals makes shrimp attractive for consumers pursuing balanced diets. These attributes align perfectly with contemporary wellness trends emphasizing lean proteins and functional foods supporting overall health objectives.
The economic impact resonates throughout coastal communities and inland distribution hubs. Domestic shrimp harvesting operations support thousands of families along the Gulf Coast and Southeastern Atlantic regions, preserving cultural traditions while contributing to regional economic stability. The industry generates substantial downstream opportunities in processing facilities, cold storage operations, logistics networks, and retail environments.
Shrimp's culinary versatility further amplifies its market significance. The product integrates seamlessly into countless cuisines and cooking methods, from traditional Southern preparations to contemporary fusion dishes. This adaptability enables food service operators to feature shrimp across diverse menu categories while retailers offer multiple product formats addressing various consumer preferences.
Key Growth Drivers in the United States Shrimp Market:
Multiple interconnected factors propel ongoing expansion within the US shrimp industry. Health consciousness represents a primary catalyst, as consumers increasingly prioritize protein sources offering nutritional benefits without excessive calories. Shrimp's favorable nutritional profile positions it advantageously against traditional protein options, attracting consumers seeking healthier alternatives.
Convenience has emerged as another critical growth driver. Busy lifestyles drive demand for value-added shrimp products requiring minimal preparation. Pre-cooked options, breaded varieties, and ready-to-eat formats address consumer needs for quick meal solutions. This convenience-oriented product development expands consumption occasions beyond traditional dinner preparations into snacking and lunch applications.
Sustainability considerations increasingly influence purchasing decisions as environmental awareness permeates mainstream consciousness. The aquaculture industry's response through improved farming practices, certification programs, and traceability systems addresses consumer concerns while supporting market growth. Retailers and foodservice operators emphasize sustainable sourcing as a differentiating factor.
Innovation in aquaculture technology continues advancing production efficiency and product quality. Recirculating aquaculture systems, improved feed formulations, and disease management protocols enhance domestic production capabilities while reducing environmental footprints. These technological improvements support supply chain resilience.
The expanding Hispanic population within the United States contributes significantly to consumption growth. Cultural preferences favoring seafood and traditional recipes featuring shrimp drive above-average consumption rates. As Hispanic communities grow and exert increasing influence on mainstream food culture, their preferences help normalize higher shrimp consumption across broader population segments.
Regulatory Framework and Policy Landscape in the Shrimp Industry:
The United States shrimp market operates within a comprehensive regulatory environment ensuring food safety, environmental protection, and fair trade practices. The Food and Drug Administration maintains primary oversight regarding seafood safety standards, establishing requirements for pathogen control, chemical residue limits, and proper handling procedures. These regulations apply equally to domestic production and imported products.
The National Marine Fisheries Service manages wild-caught shrimp fisheries through science-based conservation measures. Regulations establish harvest seasons, gear restrictions, and catch limits designed to maintain sustainable population levels. Turtle Excluder Device requirements exemplify regulatory approaches balancing commercial interests with environmental protection mandates.
Import regulations significantly impact market dynamics. To protect American customers against contaminated shrimp and other food imports, for example, Representatives Clay Higgins (R-LA) and Troy A. Carter (D-LA) reintroduced the Destruction of Hazardous Imports Act of 2025. This bipartisan bill, supported by the Southern Shrimp Alliance, closes a critical legal gap by enabling the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to destroy imported food goods that represent a major public health risk and removing the possibility to re-export hazardous products. Moreover, the Seafood Import Monitoring Program requires detailed traceability information for imported shrimp, helping combat illegal fishing and fraudulent practices. These requirements enhance supply chain transparency while protecting consumers and legitimate industry participants.
Trade policies and tariff structures periodically shift based on international relations. Anti-dumping investigations and countervailing duties targeting specific exporting nations reflect efforts to protect American producers. These policy interventions create market fluctuations affecting pricing structures and sourcing strategies.
Environmental regulations governing aquaculture operations continue evolving. Permitting requirements for new facilities, effluent discharge standards, and habitat protection measures influence domestic production expansion. These frameworks attempt reconciling industry growth with public concerns regarding environmental degradation.
Government Support and Initiatives for the U.S. Shrimp Market:
Federal and state government programs provide multifaceted support strengthening the US shrimp industry. Marketing assistance programs help domestic producers compete against lower-cost international suppliers by funding promotional activities highlighting American-caught shrimp advantages. These initiatives emphasize quality, sustainability, and support for domestic fishing communities.
Research funding through agricultural and marine science programs advances technological innovation benefiting the industry. Government-supported research addresses disease prevention in aquaculture, sustainable fishing gear development, and improved processing techniques. This publicly funded research generates knowledge spillovers benefiting commercial operators.
Disaster assistance programs provide crucial support for coastal producers facing hurricane damage, oil spills, or catastrophic events. These emergency interventions help maintain industry continuity, preventing permanent capacity losses. Recovery assistance enables fishing communities to rebuild infrastructure and resume operations following devastating natural disasters.
Trade promotion programs facilitate market access for American shrimp products internationally, supporting export development that provides alternative revenue streams. While the United States remains predominantly a net importer, export opportunities in premium markets help showcase American product quality standards.
Workforce development initiatives address skilled labor shortages affecting processing facilities and vessel operations. Training programs and safety education improve operational efficiency while reducing workplace injuries. These human capital investments strengthen industry competitiveness and support long-term sustainability.
Top Shrimp Producers and Suppliers in the United States:
The United States shrimp market features diverse producers and suppliers operating across different segments and geographic regions. Gulf Coast operations represent the heart of domestic wild-caught production, with Louisiana, Texas, Alabama, Mississippi, and Florida harboring significant fishing fleets. These operations maintain traditional harvesting methods while incorporating modern technology.
Large-scale aquaculture facilities, though representing a smaller portion of domestic production, continue expanding their footprint. Indoor recirculating systems and coastal pond operations demonstrate varying approaches to controlled farming. These facilities target premium market segments emphasizing freshness, traceability, and domestic origin.
International suppliers dominate overall market supply, with major exporting nations playing indispensable roles in meeting consumption demand. Asian and Latin American producers have developed sophisticated farming operations and processing capabilities tailored to American market requirements. These operations range from small family farms to massive integrated operations.
Distribution companies and importers serve as critical intermediaries connecting international production with American consumers. These organizations manage complex logistics involving multiple transportation modes, cold chain maintenance, and customs clearance. Leading distributors have developed extensive networks enabling rapid product movement.
Major retail chains and foodservice operators increasingly influence production practices through purchasing specifications. These large buyers leverage market power to demand specific production methods, certification standards, and traceability documentation. Their requirements effectively set industry standards that suppliers must meet for market access.
Opportunities and Challenges in the United States Shrimp Market:
The US shrimp industry faces an evolving landscape presenting both promising opportunities and formidable challenges. Domestic aquaculture expansion represents a significant opportunity for reducing import dependence while meeting growing demand. Advanced farming technologies and increased investment capital flowing into indoor facilities could substantially increase domestic production capacity.
Premium product development targeting health-conscious and environmentally aware consumers offers lucrative market segments willing to pay price premiums. Organic certification, specific pathogen-free designations, and documented sustainable practices create competitive advantages. These value-added approaches enable producers to escape commodity pricing dynamics through quality differentiation.
Technology adoption throughout the supply chain presents opportunities for efficiency improvements and enhanced traceability. Blockchain applications, IoT sensors, and advanced data analytics can optimize cold chain management, reduce waste, and provide consumers with unprecedented transparency. Early adopters may secure lasting competitive advantages.
However, significant challenges temper this outlook. Price competition from low-cost international suppliers continues pressuring domestic producers. Production cost disadvantages stemming from higher labor rates and stricter environmental regulations make competing on price virtually impossible. This dynamic forces domestic producers into premium niches rather than mass market segments.
Climate change impacts increasingly threaten both wild harvest and aquaculture operations. Ocean warming, acidification, and extreme weather events disrupt traditional fishing patterns while threatening coastal infrastructure. Aquaculture facilities face heightened disease pressures as environmental conditions shift beyond historical norms.
Labor shortages affect all industry segments. The physically demanding nature of work combined with relatively modest compensation struggles to attract adequate workforces. Immigration policy uncertainties compound these challenges as many processing facilities historically relied on foreign-born workers.
Consumer education represents an ongoing challenge as marketplace complexities create confusion regarding product origins and sustainability claims. Competing certification schemes and inconsistent labeling make informed purchasing difficult. Industry-wide standardization efforts face obstacles from diverse stakeholder interests.
Conclusion:
The United States shrimp market continues demonstrating remarkable resilience amid evolving consumer preferences, regulatory requirements, and competitive pressures. As the dominant seafood choice for American consumers, shrimp occupies a unique position bridging international trade relationships, domestic production traditions, and emerging sustainability imperatives.
Future success requires collaborative approaches addressing shared challenges while capitalizing on emerging opportunities. Domestic producers must leverage quality advantages to differentiate themselves within competitive marketplaces. International suppliers need continued investment in production systems meeting increasingly stringent American requirements. Retailers and foodservice operators must effectively communicate value propositions justifying premium pricing.
The intersection of technological innovation, sustainability commitments, and consumer engagement will determine industry winners. Organizations demonstrating genuine environmental stewardship while delivering consistent quality will earn consumer loyalty in saturated markets. The US shrimp industry stands poised for continued growth provided stakeholders successfully navigate complex challenges while maintaining focus on delivering products meeting evolving consumer expectations.
Choose IMARC Group As We Offer Unmatched Expertise and Core Services:
- Market Research: Gain insights into U.S. shrimp market trends, RAS technology, sustainable farming, biofloc systems, value-added innovations, import-export dynamics, and blockchain traceability.
- Growth Forecasting: Track expansion in domestic aquaculture, ready-to-cook products, e-commerce channels, certification programs, and evolving trade and regulatory frameworks.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Evaluate producer strategies, supplier positioning, distribution efficiency, partnerships, biosecure farming, disease control, and automated processing advancements.
- Policy & Advisory: Monitor FDA seafood safety, USDA aquaculture programs, import duties, NOAA fisheries policies, and trade agreements shaping production and imports.
- Custom Consulting: Access tailored guidance on land-based farming, sourcing strategies, sustainable product development, traceability, certification, and U.S. market entry.
IMARC Group helps seafood businesses convert intelligence into competitive advantage and sustainable growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










