Tractor Manufacturing Cost Analysis: From Engine Block to Farmland

What is Tractor?
A tractor is a self-propelled, torque-requiring vehicle intended primarily for pulling power at low speeds for agricultural, industrial, and utility purposes. It functions as a mobile power source that can be used for towing, pushing, lifting, or driving a variety of agricultural implements through mechanical, hydraulic, or power take-off systems. Tractors are designed with powerful propulsion systems, sturdy frames, and versatile coupling systems for use on different terrains and under heavy loads. Modern tractors also feature sophisticated hydraulic systems, electronic controls, and comfortable operator interfaces to enhance efficiency, safety, and operational accuracy in different environments.
Key Applications Across Industries:
Tractors are mainly used in agricultural settings where they function as the main source of power for a variety of agricultural tasks. They are used for land preparation tasks such as plowing, tillage, harrowing, and leveling, which are essential for soil preparation before planting. During the crop growing season, tractors are used for powering or pulling various implements such as seeders, fertilizers, sprayers, and irrigation equipment. During the harvesting season, tractors are used for hauling agricultural produce, powering harvest support equipment, and managing post-harvest activities.
Apart from agriculture, tractors are also crucial in the construction industry. They can be employed in earthmoving, handling materials, site preparation, and towing construction equipment when equipped with accessories like loaders, backhoes, or trailers. In rural and semi-urban settings, tractors can be employed as means of transporting goods, construction materials, water tanks, and farm inputs.
Tractors can also be applied in forestry, landscaping, and municipal applications. They can be employed in land preparation, maintenance of green spaces, roadside maintenance, snow removal in sub-zero environments, and waste management. Tractors are employed in industrial settings for transporting goods within the factory or towing other equipment. The versatility of tractors is in their capacity to support a variety of interchangeable attachments, which enables different tasks to be accomplished using the same equipment.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global tractor market reached a value of USD 95.03 Billion in 2025. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 130.20 Billion by 2034, at a projected CAGR of 3.6% during 2026-2034.
The global tractor market is fueled by the changes in the agricultural sector, the development of infrastructure, and the growing mechanization of economies. The first and foremost driver for the global tractor market is the need to increase agricultural productivity in the face of growing populations and food requirements. Tractors assist farmers in carrying out time-sensitive tasks in an efficient manner, minimizing crop losses, and maximizing yield potential, making them an integral part of the modern agricultural sector.
The labor force is another major driver for the global tractor market. In many countries, the lack of labor in rural areas and the increasing cost of labor are pushing the agricultural sector from manual to mechanized farming. Tractors assist in overcoming this issue by minimizing the need for human labor while maximizing efficiency.
Government policies and support play a crucial role in the adoption of tractors. Subsidies, credit schemes, and rural development programs minimize the cost of tractors for farmers and promote the use of agricultural machinery. Government investment in irrigation, roads, and rural infrastructure further increases the use of tractors beyond the agricultural sector.
Also, the growth in the construction and infrastructure development sectors helps support demand, as tractors are increasingly being used for non-agricultural purposes. Moreover, technological innovations such as better engine efficiency, emission norms, remote monitoring, and comfort features make modern tractors more desirable and economical compared to their entire life cycle.
Replacement demand remains a constant contributor to developed markets, as old tractors are being replaced by new ones to comply with tougher environmental and safety regulations.
Case Study on Cost Model of Tractor Manufacturing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale tractor manufacturing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed tractor manufacturing plant in India. This plant is designed to manufacture 10,000 units of tractor annually.
Manufacturing Process: The production process of tractors is an intricate and multi-step industrial process that encompasses the assembly of mechanical fabrication, powertrain, hydraulics, and electronics. The process begins with design and engineering, where tractor models are designed based on horsepower, usage, emission standards, and attachment suitability. After the design criteria have been determined, the production process commences with the production of components. The major components of tractors, including engines, transmissions, axles, chassis, and hydraulic systems, are either produced internally or outsourced from dedicated suppliers.
The chassis and other components are produced through cutting, bending, machining, and welding operations to produce a strong chassis that can support heavy loads and torque. The components are then subjected to surface treatment operations such as shot blasting, phosphating, and painting to make them corrosion-resistant. Simultaneously, engines and transmissions are assembled and tested for integration.
During the main assembly process, the tractor chassis is moved along a conveyor line where the powertrain, axles, wheels, fuel system, cooling system, and hydraulic system are mounted one after the other. Electrical wiring harnesses, control units, and instrument panels are also mounted to facilitate monitoring and control. The operator interface, comprising the cab or platform, steering system, operator seat, and controls, is also assembled to ensure operator comfort.
Finally, the assembled tractors are subjected to fluid filling and calibration, followed by functional testing of engine power, braking, steering, hydraulic, and transmission systems. Quality inspections and test drives are also conducted on each unit to ensure reliability and adherence to safety and environmental regulations. Finally, the accepted tractors are cleaned, packaged, and shipped for distribution.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
Raw Material Required:
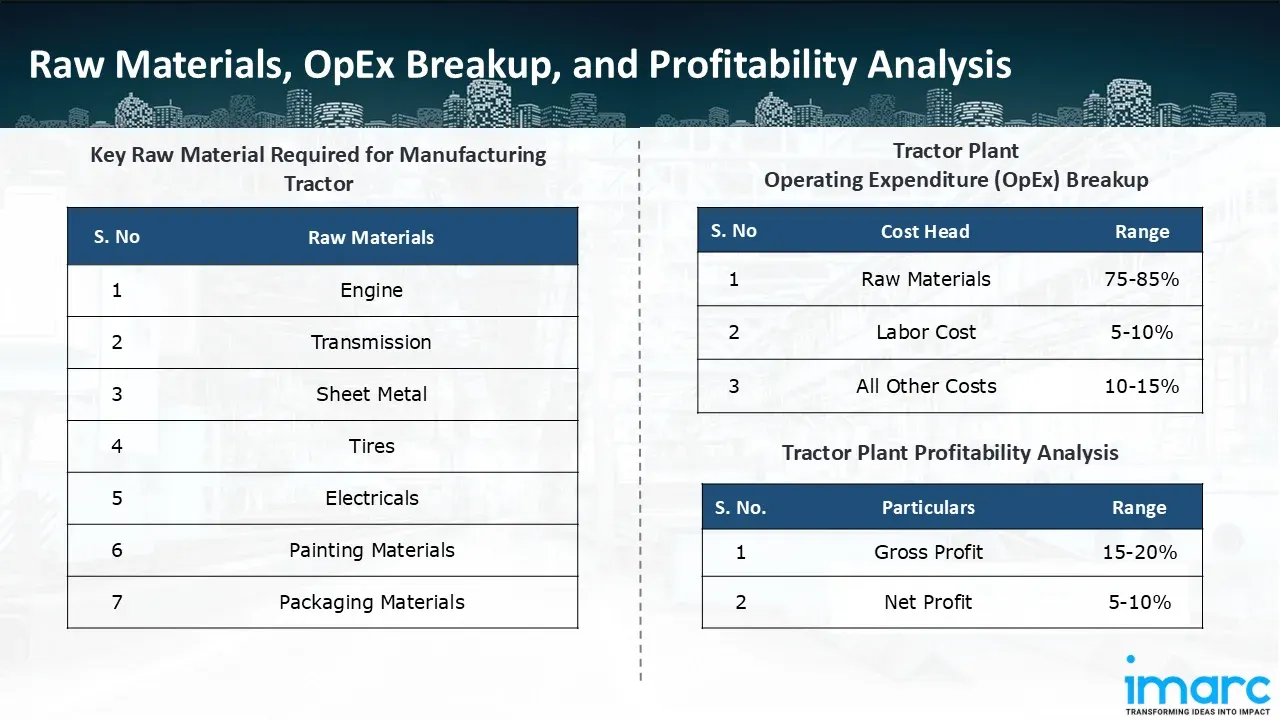
The basic raw materials required for tractor manufacturing include:
- Engine
- Transmission
- Sheet Metal
- Tires
- Electricals
- Painting Materials
- Packaging Materials
Machine Section or Lines Required:
- Stamping
- Welding
- Painting
- Assembly
- Testing
- Packing
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. OpEx in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in tractor manufacturing plant ranges between 75-85%, labor cost ranges between 5% to 10%, and all other costs ranges between 10-15% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 15-20%, and net profit lie between the range of 5-10% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the Tractor manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of manufacturing 10,000 units of tractor annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In September 2025, CNH Industrial's New Holland brand announced its plans to build its second tractor production plant in India. The new New Holland plant is expected to be bigger than CNH’s existing facility in Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh. The Greater Noida plant is spread across 60 acres and has the capacity to produce 60,000 tractors a year, which can be increased to 70,000.
- In February 2025, Cooper Corporation, a maker of engines and parts, opened its first tractor production plant in Satara, Maharashtra. Additionally, the company unveiled its NDC Series tractors, which were created in partnership with foreign companies like Ricardo UK, Magna Steyr, Carraro, and Mita.
Why Choose IMARC?
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104










